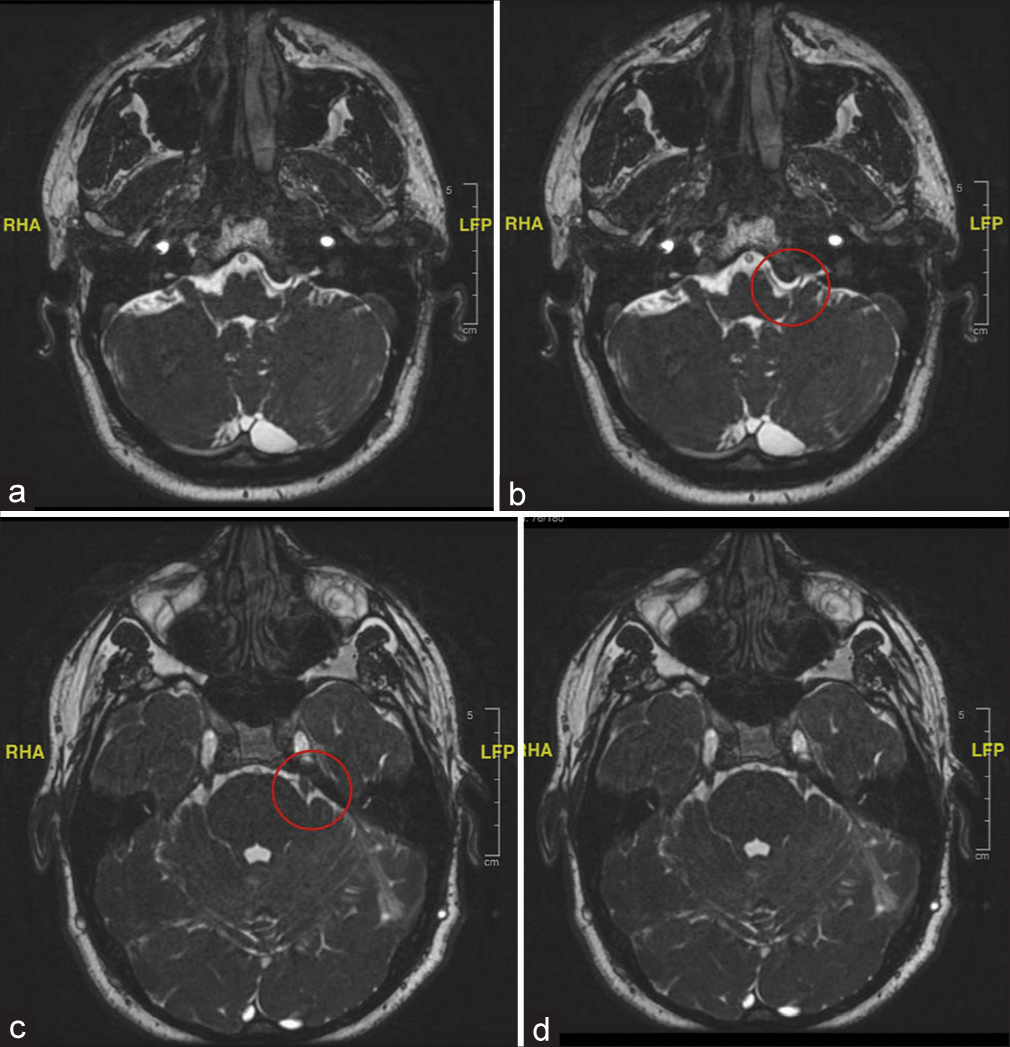
Endoscopic transsphenoidal resection of parasellar abducens nerve schwannoma: A video demonstration
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
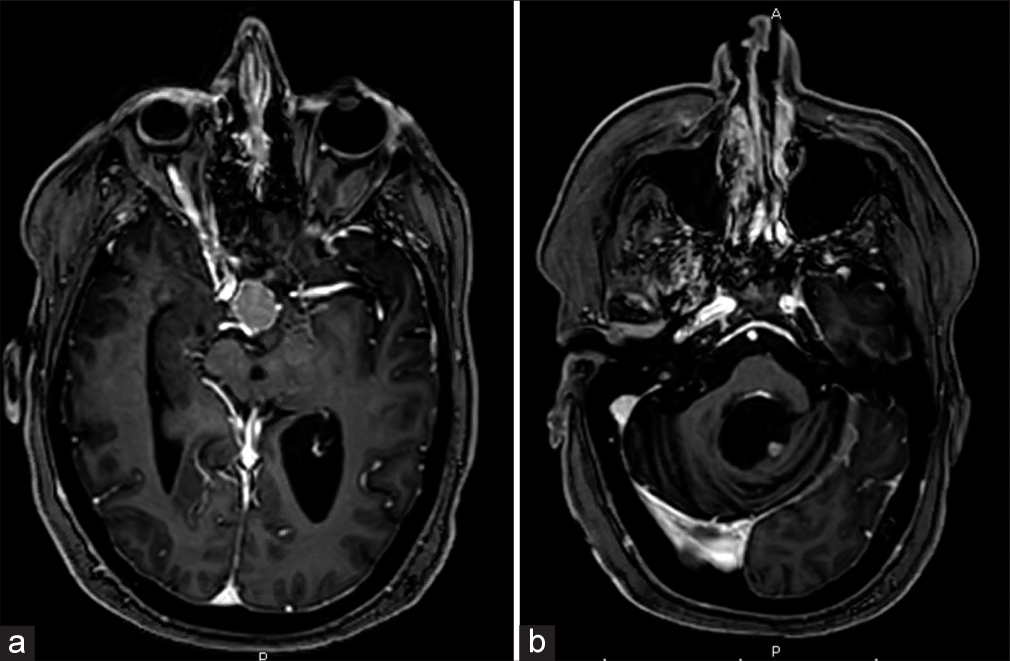
Background: The abducens nerve schwannoma (ANS) in the sellar and parasellar region are extremely rare. Only around two dozen of ANS have been described in the world literature. These cases were, however, operated through the transcranial approach. We demonstrate, with the help of an edited video, that ANS located in the sellar and parasellar region can be safely and effectively operated through a transsphenoidal approach under endoscopic visualization.
Concurrent glossopharyngeal neuralgia and oromandibular dystonia resolved after microvascular decompression of the trigeminal and glossopharyngeal nerve: A rare presentation
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: This type of pain syndrome occurs suddenly and briefly, beginning unilaterally from one side of the face. Modestly stimulating speech can provoke it, affecting the ear, tongue, throat, and jaw angle. Interestingly, it is the sensory distribution of the auricular and the pharyngeal branches of the cranial nerves IX and X. People have not had a confirmed case of glossopharyngeal neuralgia (GPN), along with oromandibular dystonia (OMD). Nevertheless, usually in the medical literature, this case report supplies information about a patient who has concurrent GPN and OMD.
Parasagittal meningeal hemangiopericytoma/solitary fibrous tumor: Two case reports and a literature review
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: Solitary fibrous tumor/meningeal hemangiopericytoma (SFT/M-HPC) is a rare neoplasm which accounts for around 1% of the intracranial masses. This pathology has a high risk for recurrence and metastasis to distant locations such as the liver, lungs, and bones. Precise diagnosis necessitates detailed histopathological examination.
Do we need a neurosurgical frailty index?
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: An increasing number of elderly patients now require neurosurgical intervention, and it is sometimes unclear if the benefits of surgery outweigh the risks, especially considering the confounding factor of numerous comorbidities and often poor functional states. Historically, many patients were denied surgery on the basis of age alone. This paper examines the current selection criteria being used to determine which patients get offered neurosurgical management and attempts to show if these patients have a good outcome. Particular focus is given to the increasing insight into the need to develop a neurosurgical frailty index.
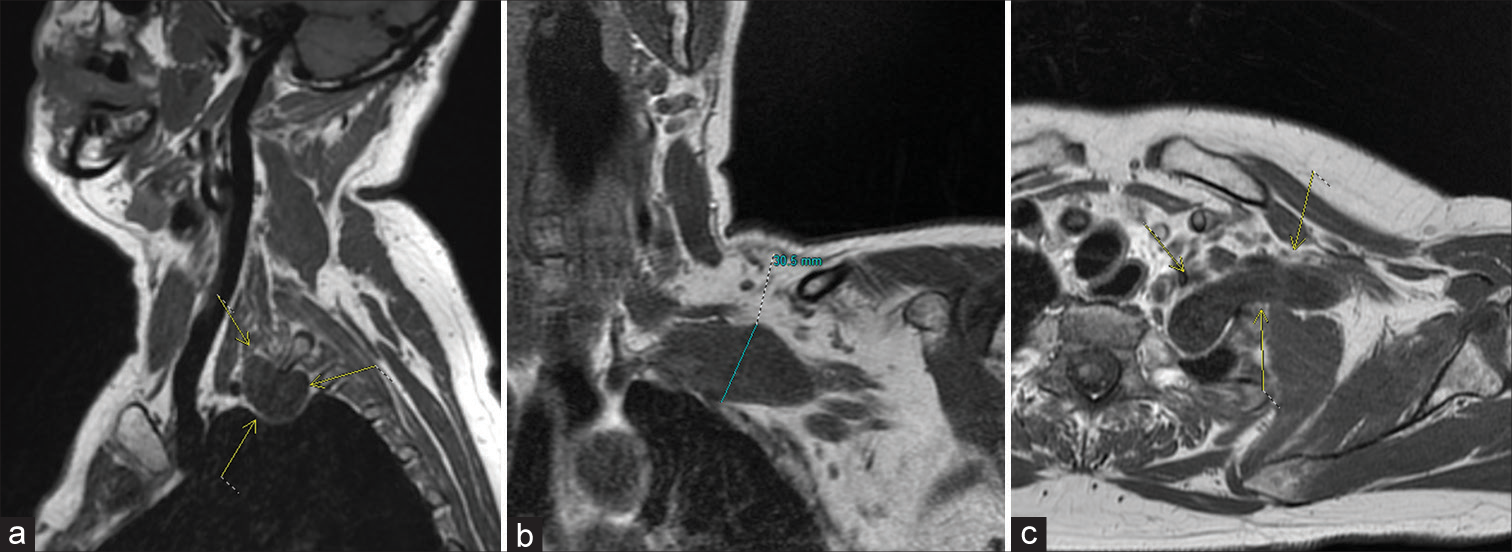
Clavicular window for brachial plexus schwannoma removal
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: Schwannomas are benign nerve sheath tumors that can either be sporadic or part of neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). Tumors of the brachial plexus (BP) with both supra- and infraclavicular components are uncommon and represent a challenge to complete surgical resection. There are few reports on single clavicular osteotomies for BP exposure; however, there are currently no reports of utilization of a clavicular window for a large schwannoma resection.
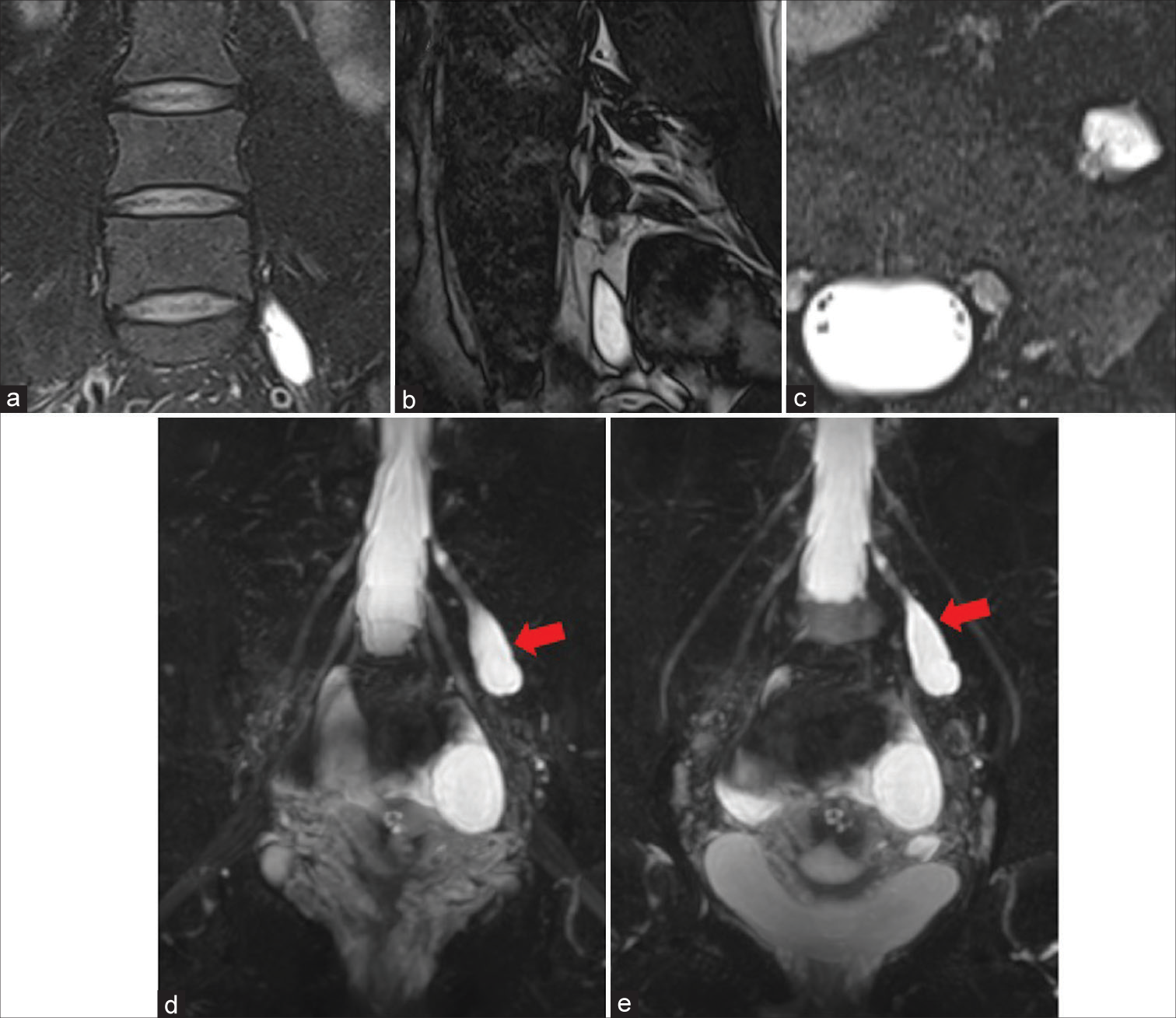
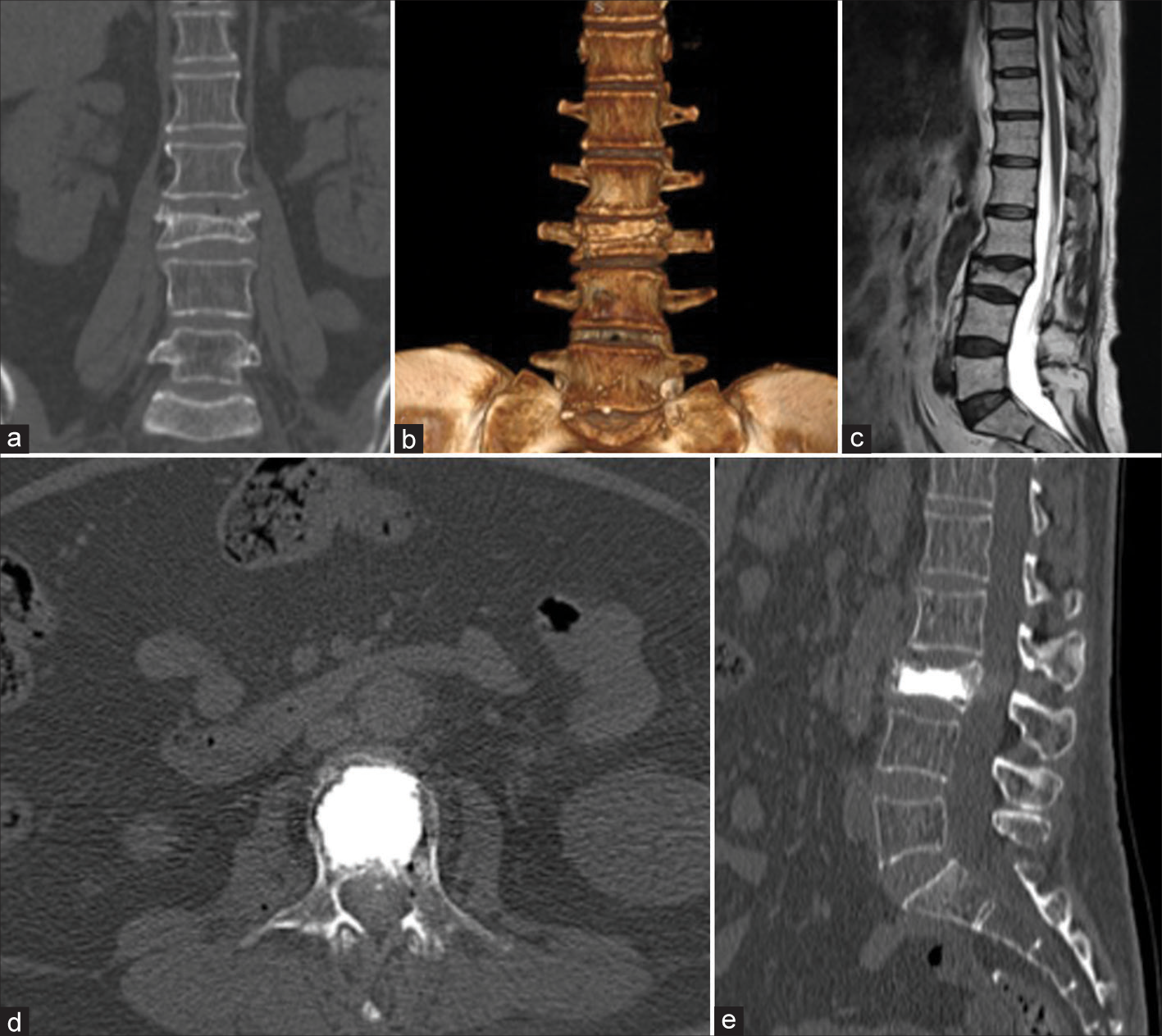
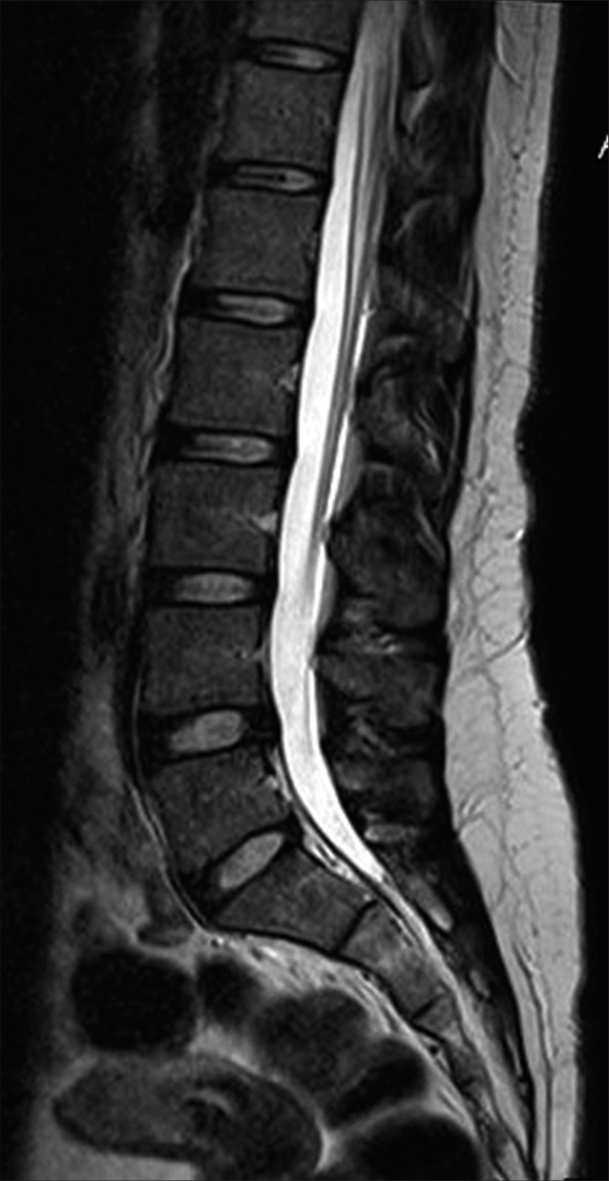
Symptomatic lumbar Tarlov cyst resolution after computed tomography-guided percutaneous trans-sacral fibrin glue intracystic injection: A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: Perineural Tarlov cysts are extrathecal cerebrospinal fluid-filled cavities in the perineural recesses around dorsal spinal nerve roots. They are mostly asymptomatic but may occasionally cause back pain, radiculopathy, neurological deficits, and idiopathic intracranial hypotension.
Three cases of kyphoplasty performed in the lateral position due to significant comorbidities
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: More than 700,000 people suffer from vertebral compression fractures attributed to osteoporosis, metastatic disease, or trauma each year in the United States, and undergo kyphoplasty. They are typical. These often undergo kyphoplasty to treat resultant pain or new neurological deficits. Here, we present three patients who, due to significant comorbidities, underwent kyphoplasty performed in the lateral decubitus rather than the prone position.
Local compression of the sciatic nerve by a vascular malformation as a rare cause of sciatica: A case report and review of literature
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: Sciatica is typically caused by disc herniations or spinal stenosis. Extraspinal compression of the sciatic nerve is less frequent.
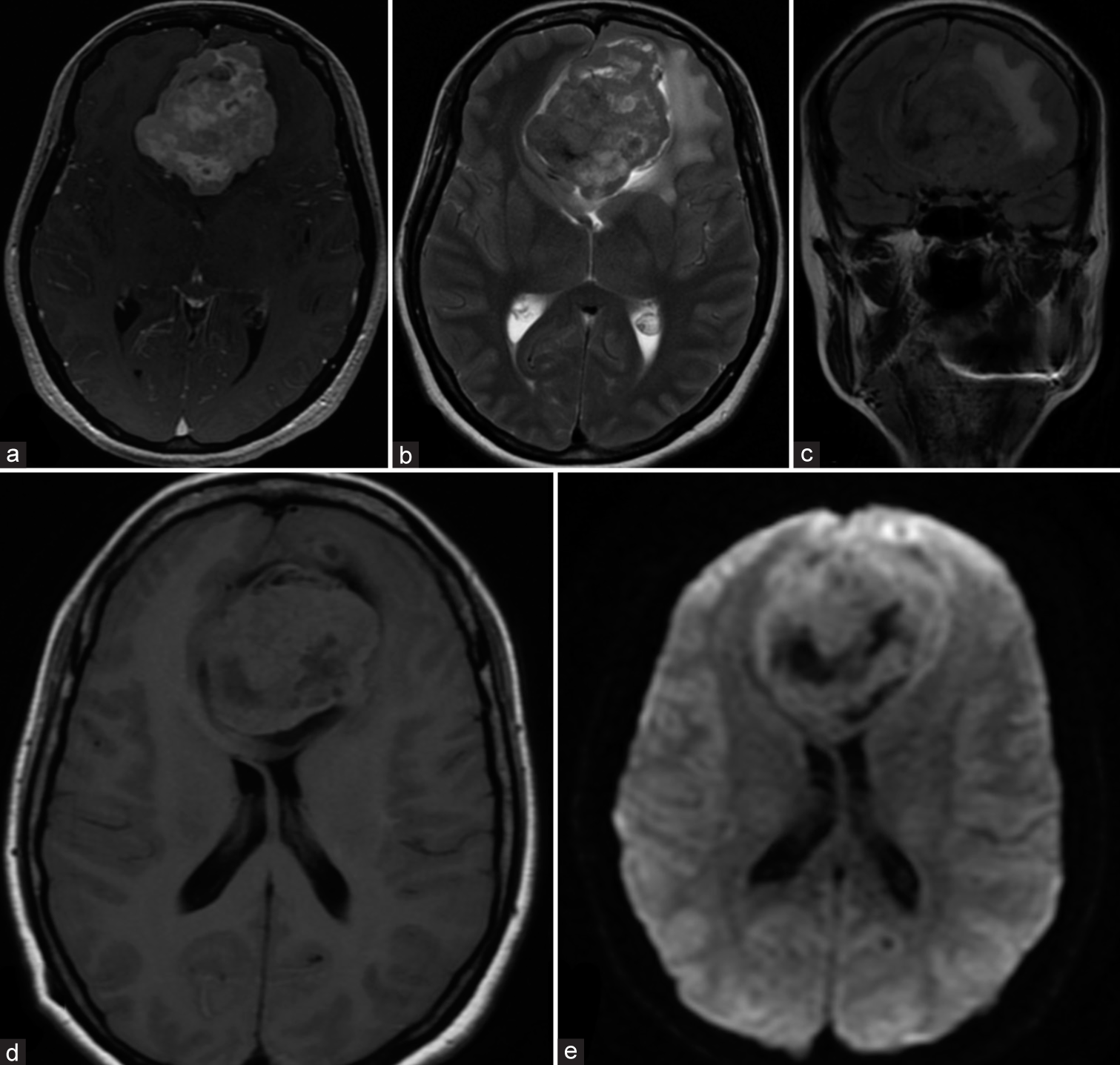
Metastatic choroid plexus papilloma presenting as a sellar mass: A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: Choroid plexus papillomas (CPPs) are rare neoplasms arising from choroid plexus epithelium representing <1% of all intracranial tumors. Symptoms vary based on location and regional mass effect; however, hydrocephalus is common due to cerebrospinal fluid flow obstruction and/or overproduction. Distant site metastasis or de novo formation in extraventricular sites is rare.
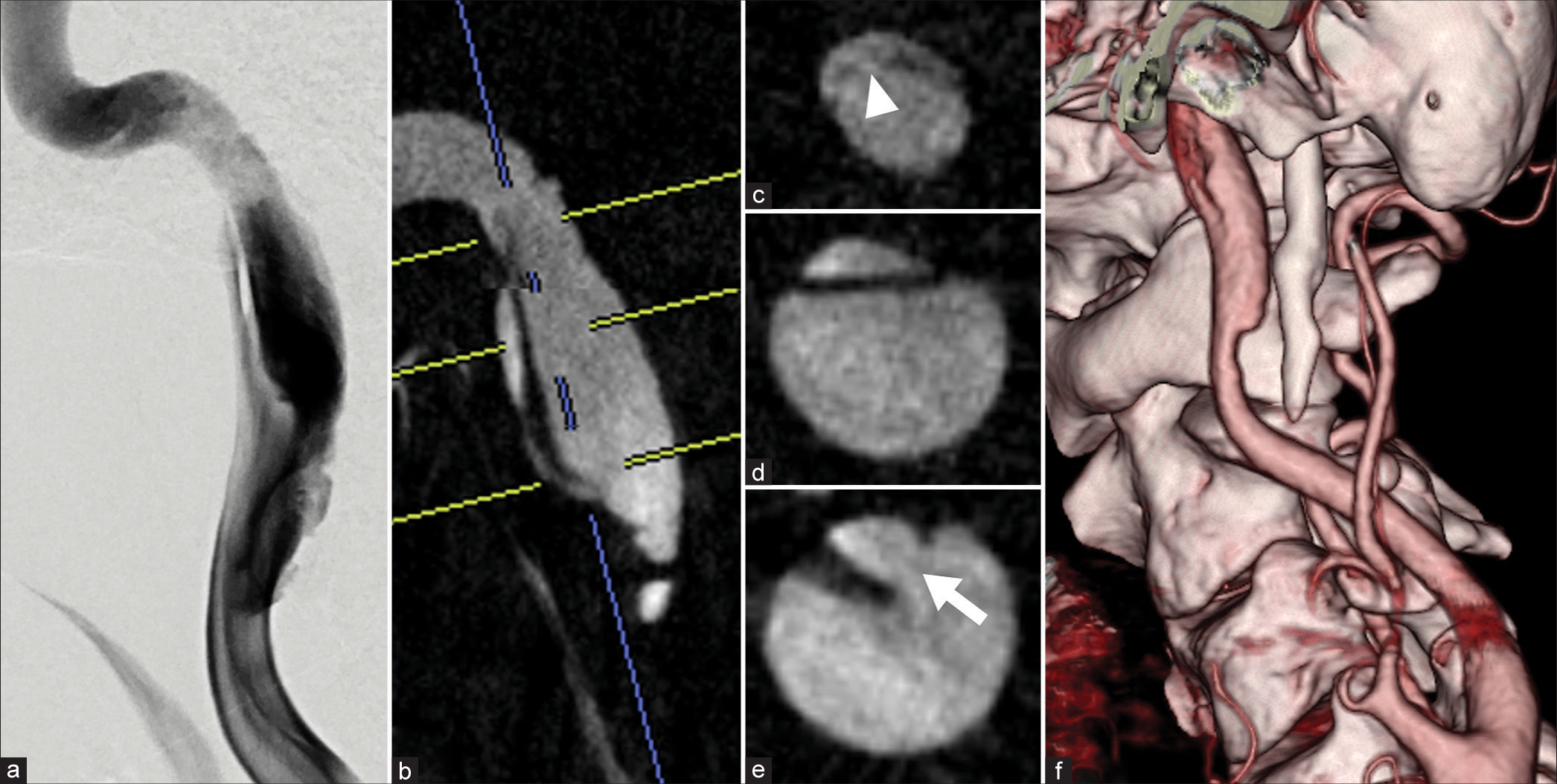
Extracranial internal carotid artery-dissecting aneurysm having a re-entry tear and causing lower cranial nerve palsies treated with flow-diverting stent: A case report
Date of publication: 12-Apr-2024
Background: Extracranial internal carotid artery (ICA)-dissecting aneurysms (DAs) rarely cause re-entry tears and lower cranial nerve palsies. The therapeutic strategies for these pathologies are not well established. This report presents a case of an extracranial ICA -DA with a re-entry tear that caused lower cranial nerve palsy.