- Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle WA, USA
- Department of Neurosurgery, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, USA
Correspondence Address:
Gerald A. Grant
Department of Neurosurgery, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, USA
DOI:10.4103/sni.sni_376_17
Copyright: © 2019 Surgical Neurology International This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: James Pan, Allen L. Ho, Arjun V. Pendharkar, Eric S. Sussman, May Casazza, Samuel H. Cheshier, Gerald A. Grant. Brain abscess caused by Trueperella bernardiae in a child. 29-Mar-2019;10:35
How to cite this URL: James Pan, Allen L. Ho, Arjun V. Pendharkar, Eric S. Sussman, May Casazza, Samuel H. Cheshier, Gerald A. Grant. Brain abscess caused by Trueperella bernardiae in a child. 29-Mar-2019;10:35. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/9258/
Abstract
Background:Recurrent intracranial abscesses secondary to refractory otitis media present a challenge which demands multidisciplinary collaboration.
Case Description:We present the first known case of pediatric brain abscess caused by a polymicrobial infection of Trueperella bernardiae, Actinomyces europaeus, and mixed anaerobic species resulting from acute-on-chronic suppurative left otitis media. This patient required two separate stereotactic abscess drainages and a complex course of antibiotics for successful management.
Conclusion:Surgery is essential in the management of cerebral abscess both in agent identification and therapeutic drainage. Management of abscesses secondary to unusual and polymicrobial organisms often requires consultation from other medical and surgical specialties.
Keywords: Brain abscess, neurology, neurosurgery, pediatrics, polymicrobial
INTRODUCTION
Intracranial cerebral abscesses are life threatening conditions that require immediate medical and neurosurgical attention. If left untreated, permanent neurological damage and result from damage to the brain parenchyma, or resulting inflammation from ventricular dissemination can prove to be fatal. Identification of the etiology and organisms associated with the abscess is crucial to selecting an appropriate antibiotic regimen. Surgery plays an important role in initial biopsy for identification of organisms, and resection can be considered for residual disease. We review an unusual case of pediatric brain abscess caused by Trueperella bernardiae and review both medical and surgical management strategies.
CASE REPORT
The patient is a 5-year-old male with a history of acute-on-chronic suppurative left otitis media status post bilateral percutaneous tympanostomy tube placement and multiple courses of antibiotics. He initially presented to his local emergency department with left-sided otalgia, lethargy, emesis, and decreased oral intake. As per the family, he did not have any focal neurological deficits or headaches at that time. He was diagnosed with suppurative acuteotitis externa and prescribed ciprofloxacin ear drops.
Five days later, he returned to his local emergency department with a tactile fever and seizures. Upon arrival, his temperature was 38.4°C and he was found to have tonic-clonic movements. A febrile seizure was suspected, successfully aborted with acetaminophen and lorazepam, and he was loaded on levetiracetam. A computed tomography (CT) scan demonstrated a low-density temporal lesion with left to right midline shift. There was increased density of the external auditory meatus, middle ear, and inner ear. Laboratory studies were notable for a white blood count (WBC) of 33.9 (82.3% neutrophils, 11% bands). He was given one dose of ceftriaxone and piperacillin/tazobactam, intubated, started on a midazolam infusion, and was transferred to our institution for further evaluation.
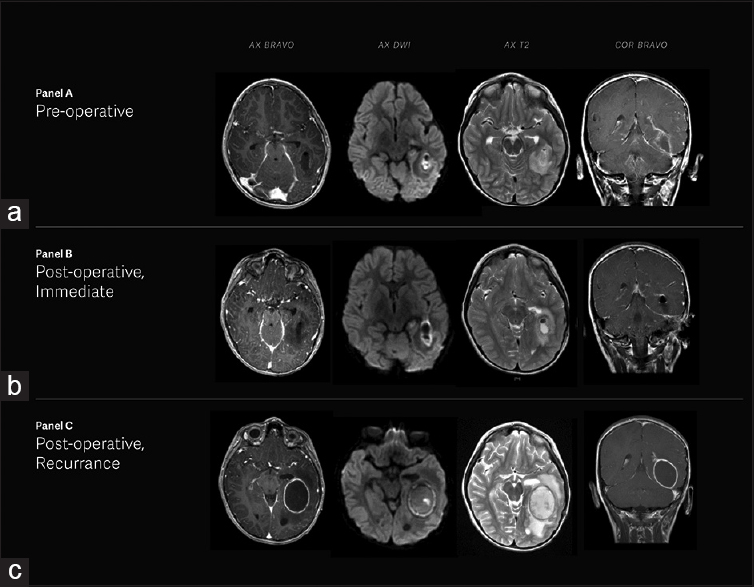
He was stabilized in our pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) with a non-focal neurologic examination. Vancomycin, cefepime, and metronidazole were started for empiric coverage. On hospital day 2, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrated left tympanomastoiditis with a 3.0 × 1.7 × 2.5 cm left temporal lobe brain abscess. Stereotactic burr hole aspiration yielded 3 mL of foul-smelling yellow-gray fluid, which was sent for cultures [
Figure 1
(a) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain illustrating left temporal brain abscess, pachymeningitis, leptomeningitis, ependymitis, and left tympanomastoiditis. (b) Post-surgical changes showing interval drainage of left temporal lobe abscess with decreased amounts of perihilar material in the resection cavity. (c) Interval increase in size of left temporal lobe abscess with small satellite abscesses seen extending to the ependymal surface of the left lateral ventricle
The patient tolerated the procedure well and was extubated without any complication. Post-operative MRI demonstrated interval drainage of the left temporal lobe abscess [
After returning home, the patient was doing well until he presented to his ED the next day with persistent emesis and left ear pain with intermittent purulent drainage. An MRI obtained at this time demonstrated an interval increase in size of the left temporal lobe abscess with small satellite abscesses extending to the ependymal surface of the left lateral ventricle [
Cultures of the repeat aspiration remained sterile. Our infectious disease colleagues recommended continuation of triple therapy of vancomycin, cefepime, and metronidazole for 6 weeks and he was discharged on hospital day 14 at his neurologic baseline. Susceptibility testing later revealed that this particular strain of Actinomyces was sensitive to the penicillin class; therefore, after he completed a 6-week course of triple therapy, and he was transitioned to oral amoxicillin monotherapy for 6 additional months.
DISCUSSION
The development of recurrent intracranial abscesses secondary to refractory otitis media presents a clinical challenge in terms of neurosurgical and antimicrobial treatment. Bacterial cerebral abscess formation can result from direct or hematogenous spread. The direct spread of bacterial agents from a contiguous site is responsible for 20%–60% of cases.[
Brain abscesses due to spread from parameningeal foci are often complex. A systematic review and meta-analysis identified Streptococcus as the most common agent from the middle ears, mastoids, and sinuses leading to brain abscess formation.[
Antibiotic therapy should be started immediately when there is a clinical suspicion for brain abscess. A retrospective study examining factors associated with mortality from brain abscesses identified that a delay in initiating antibiotics resulted in an increased odds ratio of 1.5 per day of delay for in-hospital death.[
Surgery is essential for identification of the causative organism since the abscess can be polymicrobrial and to reduce the size of the abscess when there is mass effect. Needle aspiration and surgical resection are both methods which can aid in diagnosis, and treatment even if performed after antibiotic treatment has been initiated. If the brain abscess is suspected to be secondary to hematogenous spread, antibiotics can initially be selected based on blood cultures. If neuroimaging does not show a central cavity in the abscess, stereotactic biopsy of the area of presumed cerebritis and administering empirical antibiotics with follow-up imaging should be considered.[
Stereotactic needle aspiration is generally preferred over surgical resection due to a lower complication rate and adverse neurological sequelae. With modern neurosurgical techniques, almost any abscess that measures at least 1 cm in diameter, regardless of location, is amenable to stereotactic aspiration.[
Surgical resection is a much more invasive approach and is now infrequently performed as first-line therapy. However, excision can be considered in cases where the abscess is superficial and not located in or near eloquent structures, and particularly when there is suspicion of fungal or tuberculous infection or of branching bacteria (e.g., Actinomyces or Nocardia spp.).[
This rare case of a cerebral abscess due to Trueperella bernardiae clearly benefited from multidisciplinary collaboration among infectious disease specialists, otolaryngologists, and neurosurgeons to achieve the best possible outcome in this child with a life-threatening condition.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Brouwer MC, Coutinho JM, van de Beek D. Clinical characteristics and outcome of brain abscess: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology. 2014. 82: 806-13
2. Brouwer MC, Tunkel AR, McKhann GM, van de Beek D. Brain abscess. N Engl JMed. 2014. 371: 447-56
3. Chun CH, Johnson JD, Hofstetter M, Raff MJ. Brain abscess: A study of 45 consecutive cases. Medicine. 1986. 65: 415-
4. Gilarranz R, Chamizo F, Horcajada I, Bordes-Benítez A. Prosthetic joint infection caused by Trueperella bernardiae. J Infect Chemother. 2016. 22: 642-4
5. Gutiérrez-Cuadra M, Ballesteros MA, Vallejo A, Miñambres E, Fariñas-Alvarez C, García-Palomo JD. Brain abscess in a third-level hospital: Epidemiology and prognostic factors related to mortality. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2009. 22: 201-6
6. Kangsanarak J, Fooanant S, Ruckphaopunt K, Navacharoen N, Teotrakul S. Extracranial and intracranial complications of suppurative otitis media.Report of 102 cases. J Laryngol Otol. 1993. 107: 999-1004
7. Masalma Al M, Lonjon M, Richet H, Dufour H, Roche PH, Drancourt M. Metagenomic analysis of brain abscesses identifies specific bacterial associations. Clin Infect Dis. 2012. 54: 202-10
8. Parha E, Alalade A, David K, Kaddour H, Degun P, Namnyak S. Brain abscess due to Trueperella bernardiae. Br J Neurosurg. 2015. 29: 728-9
9. Ratnaike TE, Das S, Gregson BA, Mendelow AD. A review of brain abscess surgical treatment-78 years: Aspiration versus excision. World Neurosurg. 2011. 76: 431-6
10. Rattes ALR, Araujo MR, Federico MP, Magnoni CD, Neto PAM, Furtado GH. Trueperella bernardiae: First report of wound infection post laparoscopic surgery. Clin Case Rep. 2016. 4: 812-5
11. Yassin AF, Hupfer H, Siering C, Schumann P. Comparative chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic studies on the genus Arcanobacterium Collins et al. 1982 emend. Lehnen et al. 2006: Proposal for Trueperella gen. nov. and emended description of the genus Arcanobacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2011. 61: 1265-74
12. Yen PT, Chan ST, Huang TS. Brain abscess: With special reference to otolaryngologic sources of infection. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995. 113: 15-22