- Department of Anesthesia and Pain Management, John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL, USA
Correspondence Address:
Azzam M. Alkhudari
Department of Anesthesia and Pain Management, John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL, USA
DOI:10.4103/2152-7806.181906
Copyright: © 2016 Surgical Neurology International This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Alkhudari AM, Malk CS, Rahman A, Penmetcha T, Torres M. Epidural hematoma after routine epidural steroid injection. Surg Neurol Int 06-May-2016;7:55
How to cite this URL: Alkhudari AM, Malk CS, Rahman A, Penmetcha T, Torres M. Epidural hematoma after routine epidural steroid injection. Surg Neurol Int 06-May-2016;7:55. Available from: http://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint_articles/epidural-hematoma-after-routine-epidural-steroid-injection/
Abstract
Background:There are few reported cases of an epidural spinal hematoma following interventional pain procedures.
Case Description:We report a case of a spinal epidural hematoma in a patient with no known risk factors (e.g. coagulopathy), who underwent an epidural steroid injection (ESI) in the same anatomic location as two previously successful ESI procedures.
Conclusion:Early detection was the key to our case, and avoiding sedation allowed the patient to recognize the onset of a new neurological deficit, and lead to prompt diagnosis as well as surgical decompression of the resultant hematoma.
Keywords: Epidural hematoma, epidural steroid injection, increased risk of neurological deficit, no long-term efficacy, paraparesis
INTRODUCTION
There is no documented long-term efficacy of epidural steroid injections (ESI) documented in the literature. Furthermore, they are not always safe as documented in this case of an ESI leading to an epidural spinal hematoma requiring emergency evacuation.
CASE REPORT
A 48-year-old-female with lumbar radiculopathy had previously undergone an L5 discectomy. Following an L5 hemilaminectomy, she presented with increased left lower extremity radiculopathy. As the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) did not show any significant epidural scar, she underwent two sets of interlaminar lumbar ESIs under fluoroscopic guidance. Both provided >50% pain relief lasting 2 months each. While undergoing a third ESI, in the same interlaminar space, she reported severe worsening of her lower low back pain after injection of 0.5 ml of radiographic contrast dye; the procedure was immediately aborted.
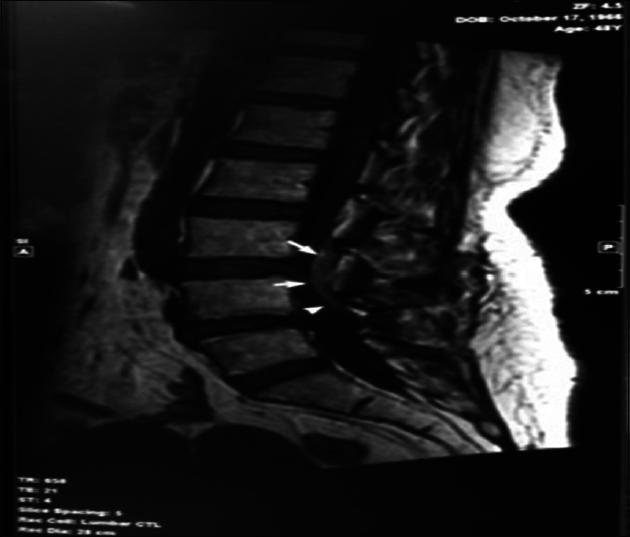
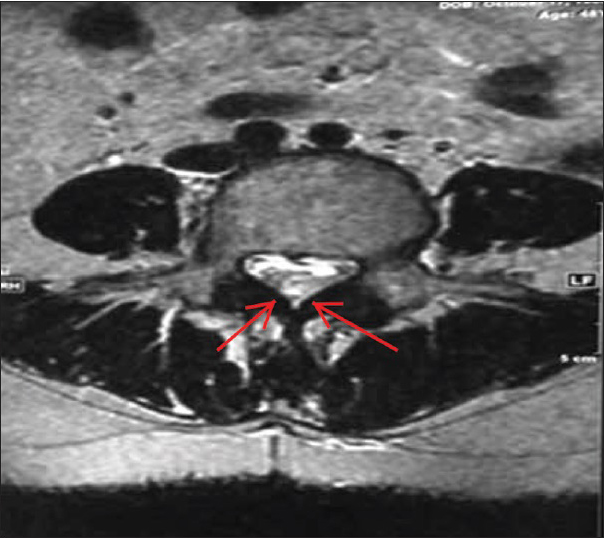
In the postoperative anesthesia care unit, she not only continued to have severe low back and left leg pain, but newly demonstrated increased an acute left-sided foot drop. She immediately underwent both computed tomography scan and MRI evaluations [Figures
DISCUSSION
Complication of epidural steroid injection
ESIs are the most commonly performed pain procedures in the United States. However, in the literature,[
Complications of epidural spinal anesthesia
Although the incidence and prevalence of epidural hematoma after steroid injections are not well known, the overall incidence of hematoma formation after epidural anesthesia ranges from 1/15,000 to 1/220,000.[
While such hematomas constitute rare complication, when they development, they can result in acute spinal cord compression characterized by severe back pain, motor deficits, bowel or bladder dysfunction, and paraplegia.[
Case presentation
In the case presented, the patient had no known risk factors for the development of an epidural hematoma. While we acknowledge that such a severe complication occurred after a routine ESI procedure, the anesthetic management in this particular case (e.g. only local anesthetic) that helped lead to a rapid diagnosis of an evolving hematoma and definitive surgical intervention.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Benzon .editors. Essentials of Pain Medicine. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011. p. 311-12
2. Horlocker TT. Regional anaesthesia in the patient receiving antithrombotic and antiplatelet therapy. Br J Anaesth. 2011. 107: i96-106
3. Kreppel D, Antoniadis G, Seeling W. Spinal hematoma: A literature survey with meta-analysis of 613 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2003. 26: 1-49
4. Meikle J, Bird S, Nightingale JJ, White N. Detection and management of epidural haematomas related to anaesthesia in the UK: A national survey of current practice. Br J Anaesth. 2008. 101: 400-4
5. Neal JM, Bernards CM, Hadzic A, Hebl JR, Hogan QH, Horlocker TT. ASRA practice advisory on neurologic complications in regional anesthesia and pain medicine. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2008. 33: 404-15