- Department of Surgery, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan.
- Medical College, Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan.
Correspondence Address:
Shahzad M. Shamim
Department of Surgery, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_907_2020
Copyright: © 2021 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Rida Mitha1, Syed Faisal Nadeem2, Syed Sarmad Bukhari1, Shahzad M. Shamim1. Management of symptomatic disc herniation in pregnancy: A case report and literature review. 10-May-2021;12:215
How to cite this URL: Rida Mitha1, Syed Faisal Nadeem2, Syed Sarmad Bukhari1, Shahzad M. Shamim1. Management of symptomatic disc herniation in pregnancy: A case report and literature review. 10-May-2021;12:215. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/10798/
Abstract
Background: Lower back pain with radiculopathy due to a disc herniation occurs in about 0.01% of pregnant females. Surgical intervention is seldom required unless there is intractable pain, and for a significant neurological deficit. Further, the use of intraoperative ionizing radiation may adversely affect the developing fetus.
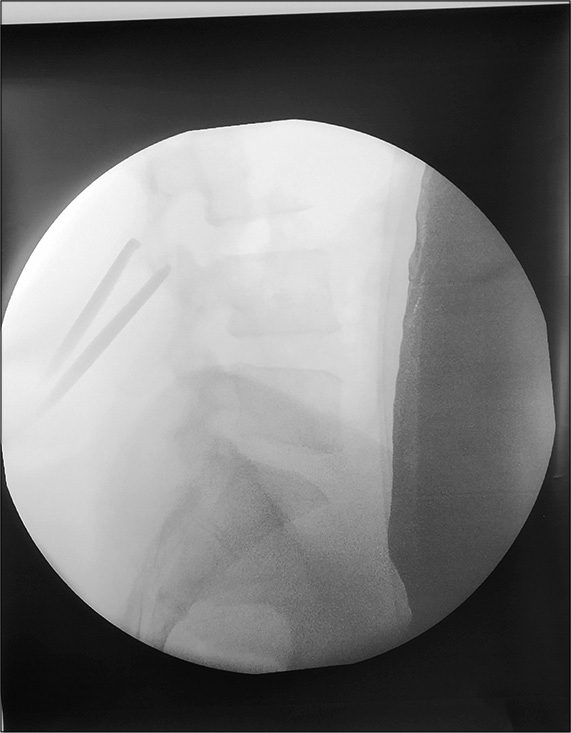
Case Description: A 25-year-old female, 17-weeks pregnant, presented with right lower extremity sciatica due to a L4-5 unilateral disc herniation. She underwent a microdiscectomy that required just one intraoperative C-arm fluoroscopic image. Postoperatively, her leg pain resolved, and she delivered a healthy baby at term.
Conclusion: Using single-image C-arm fluoroscopy in a pregnant female undergoing an emergent lumbar discectomy, employing as low as reasonably achievable/shielding, did not adversely impact the developing fetus.
Keywords: Ionizing radiation, Microdiscectomy, Pregnancy
INTRODUCTION
Lower back pain with radiculopathy due to a disc herniation occurs in 0.01% of pregnant females, with just 15% of those patients going on to develop significant neurological deficits warranting surgical intervention.[
CASE REPORT
A 25-year-old, 17 week pregnant female, presented with severe lower back pain radiating posterolaterally into her right lower extremity of 3 months duration. When she failed conservative therapy, an MRI was performed that showed a right-sided L4-L5 disc herniation with severe canal stenosis. As she exhibited significant unilateral deficits (motor 4/5 quadriceps/extensor hallucis longus/dorsiflexor), she underwent a right-sided L4-L5 microdiscectomy. This was performed in the prone position and utilized a single lateral C-arm fluoroscopic image (e.g., using as low as reasonably achievable [ALARA]/shielding for the fetus-lead aprons over her abdomen) to confirm the correct vertebral level [
DISCUSSION
The incidence of LBP associated with true radiculopathy from disc herniations has been estimated to occur in approximately 1 in 10,000 pregnant women.[
Performing X-rays in pregnant women has long been known to carry risks. In 1929, Goldstein and Murphy found a 34% incidence of congenital malformations in the progeny of 74 women who had undergone radiation treatment for uterine cancer during pregnancy.[
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends postponing procedures until after delivery or at least until well into the second trimester although it recognized that surgery cannot be delayed in certain cases.[
At present, it is considered safe to perform MRI and ultrasonography in pregnant patients.[
CONCLUSION
Here, we utilized ALARA precautions to limit the ionizing radiation employed to confirm intraoperatively the correct level of a disc herniation in a 25-year-old female who was 17-months pregnant. Following the right-sided L45 disc removal, the patient delivered a healthy baby girl 22 weeks later.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patients identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. . ACOG committee opinion No. 474: Nonobstetric surgery during pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2011. 117: 420-1
2. Ardaillon H, Laviv Y, Arle JE, Kasper EM. Lumbar disk herniation during pregnancy: A review on general management and timing of surgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2018. 160: 1361-70
3. Fager CA. Observations on spontaneous recovery from intervertebral disc herniation. Surg Neurol. 1994. 42: 282-6
4. Goldstein L, Murphy DP. Etiology of ill-health in children born after maternal pelvic irradiation. II. Defective children born after postconception pelvic irradiation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1929. 22: 322-1
5. Harel R, Knoller N. Intraoperative spine ultrasound: Application and benefits. Eur Spine J. 2016. 25: 865-9
6. LaBan MM, Perrin JC, Latimer FR. Pregnancy and the herniated lumbar disc. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1983. 64: 319-21
7. Nguyen CP, Goodman LH.editors. Fetal risk in diagnostic radiology. Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI. United States: WB Saunders; 2012. 33: 4-10