- Pars Advanced and Minimally Invasive Medical Manners Research Center, Pars Hospital, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_663_2020
Copyright: © 2020 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Abolfazl Rahimizadeh, Walter Williamson, Shaghayegh Rahimizadeh, Mahan Amirzadeh. Painful torticollis due to tubercular atlantoaxial rotatory fixation: A case report. 16-Dec-2020;11:440
How to cite this URL: Abolfazl Rahimizadeh, Walter Williamson, Shaghayegh Rahimizadeh, Mahan Amirzadeh. Painful torticollis due to tubercular atlantoaxial rotatory fixation: A case report. 16-Dec-2020;11:440. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/10461/
Abstract
Background: Tubercular atlantoaxial, rotary dislocation warranting fixation (AARF) is an extremely rare event.
Case Description: AARF was suspected in a 23-year-old female with painful torticollis. When diagnostic studies documented unilateral destruction of the left lateral mass of the atlas, she underwent removal of the lateral mass, reduction of the deformity, and C1-C2 fusion/reconstruction utilizing an iliac bone graft. Laboratory tests and the pathologic surveys were all consistent with the diagnosis of underlying tuberculosis.
Conclusion: We present a case of tubercular atlantoaxial, rotary dislocation (AARF) in a patient who warranted C1-C2 decompression, reduction, and fusion.
Keywords: Atlantoaxial dislocation, Atlantoaxial rotatory fixation, Atlas, Craniovertebral junction, Tuberculosis, Upper cervical
INTRODUCTION
Tuberculosis (TB) involving the atlantoaxial complex is rare, accounting for approximately 0.1% of all spinal tubercular infections.[
CASE REPORT
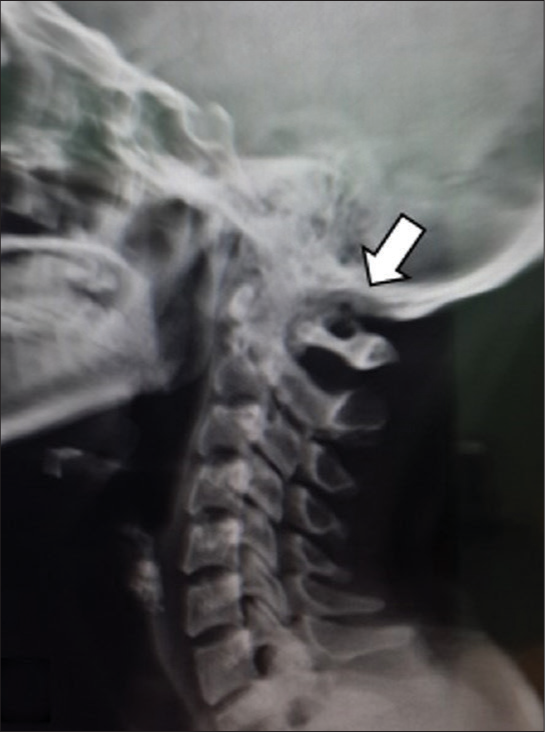
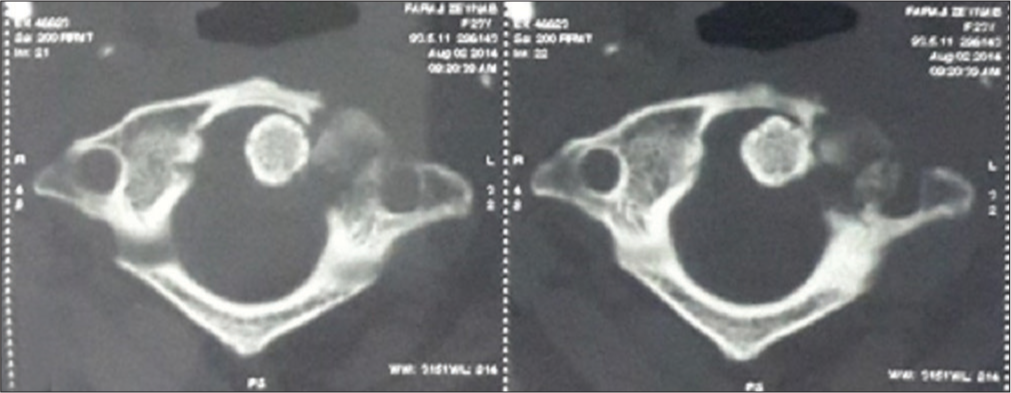
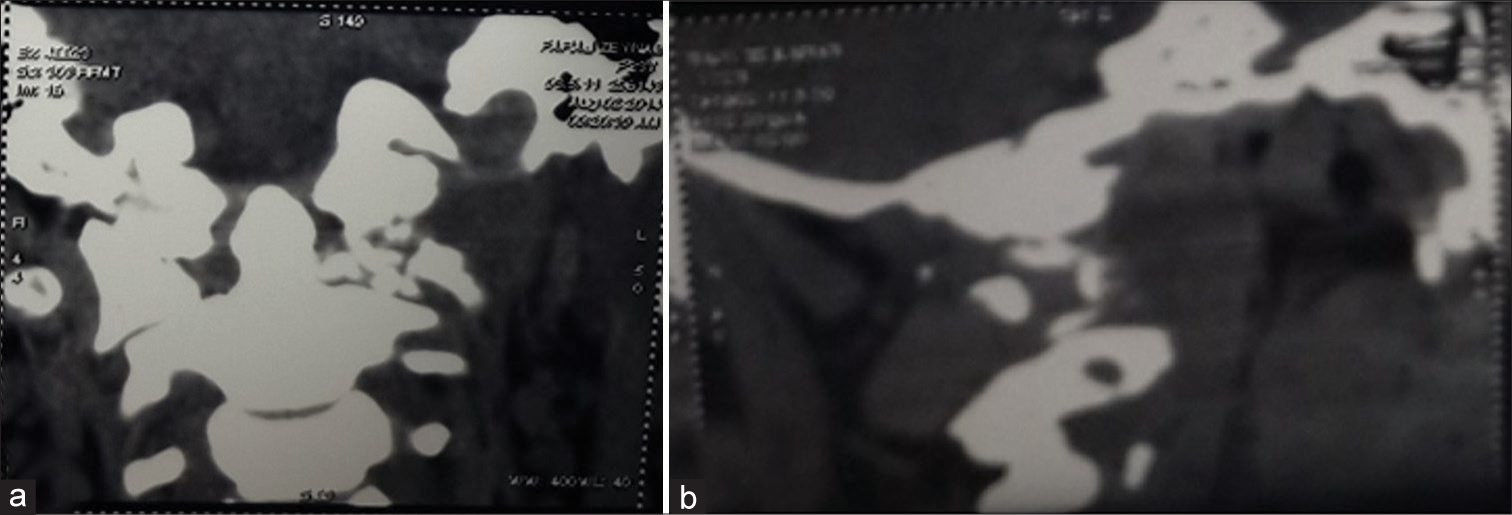
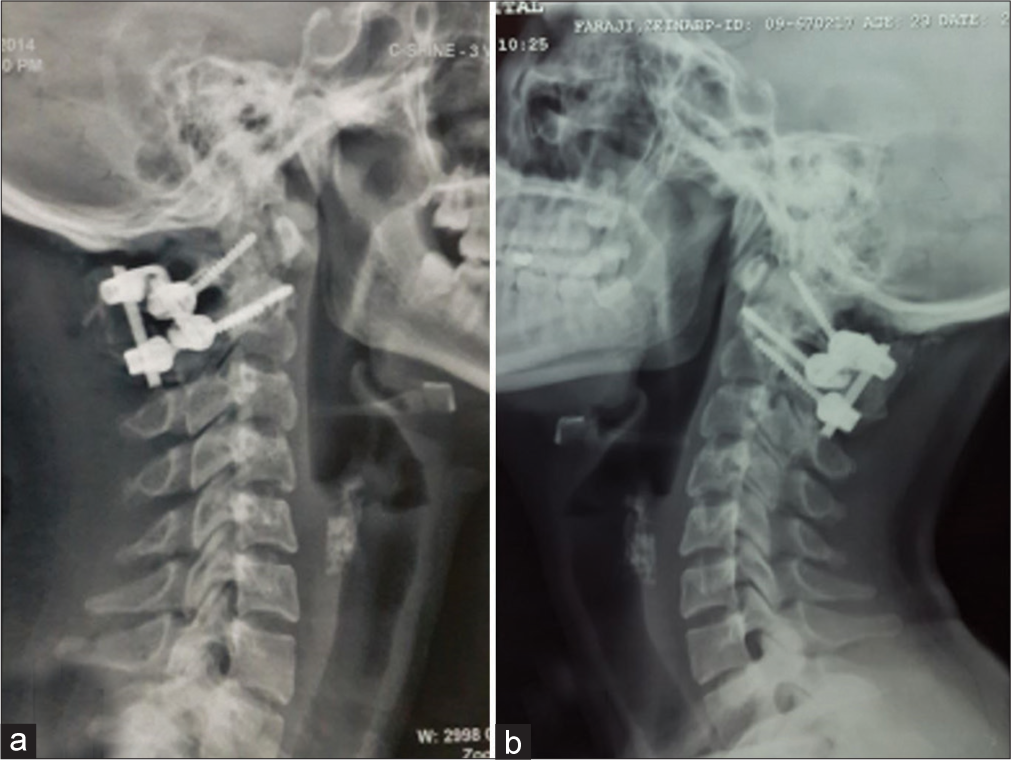
A 23-year-old female presented with a 4-week history of severe neck pain (VAS:10) and torticollis with a classic “Cock Robin” deformity. Laboratory studies demonstrated an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 42. The lateral cervical plain radiographs and computed tomography (CT) axial, 2D, and 3D reconstructed images showed C1–C2 AARF with destruction of the left lateral mass of the atlas [
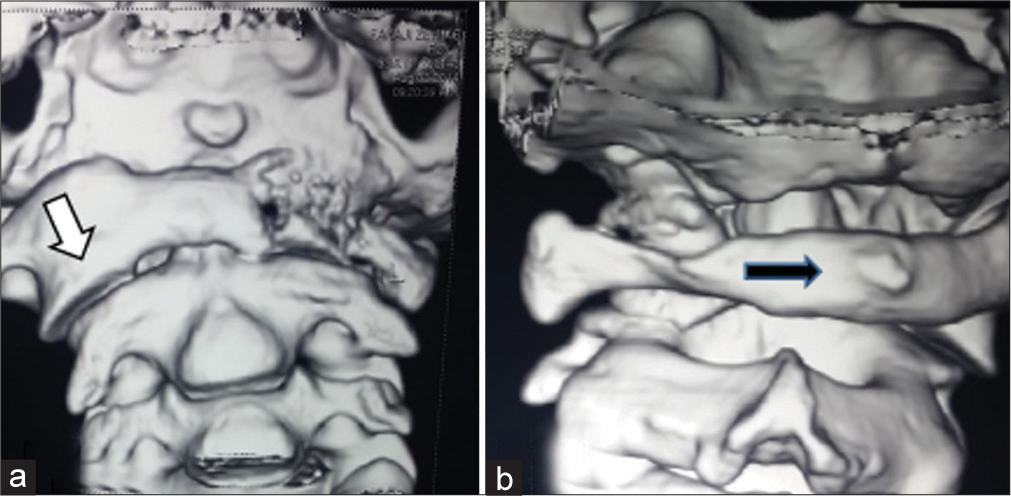
Figure 4:
3D computed tomography scan of the atlantoaxial complex (a) frontal view showing destruction of the left lateral mass and a part of anterior ring of atlas, note forward displacement of the right C1 lateral mass. (b) Occipital view demonstrates rotation of the posterior ring of atlas to the right.
Surgery
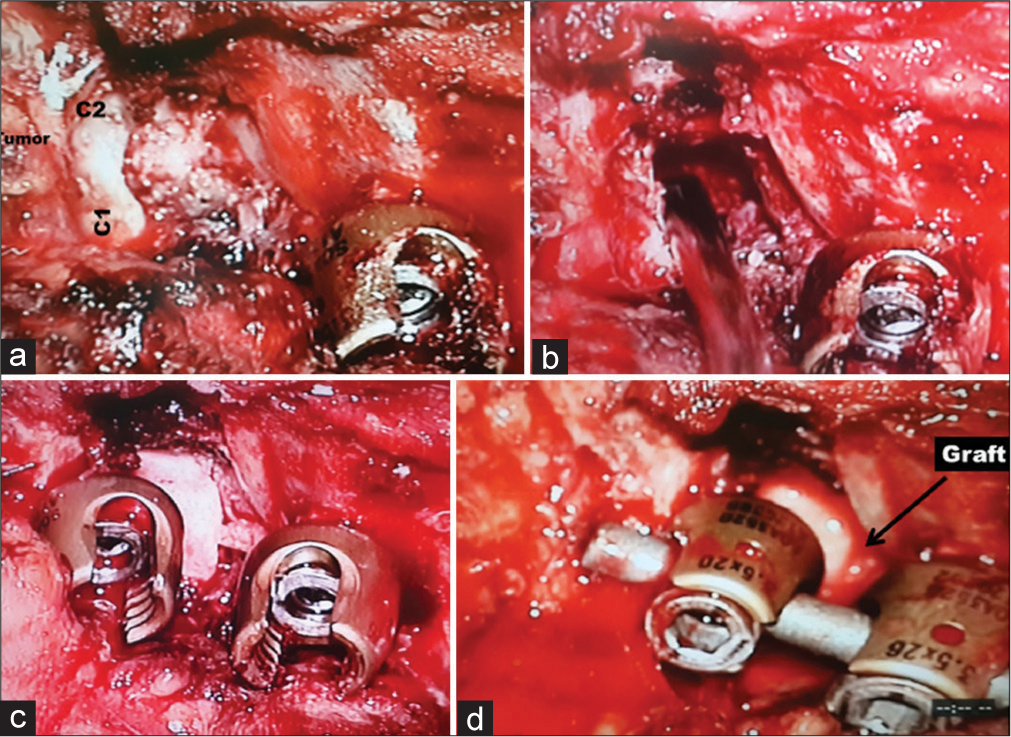
As cervical traction failed to reduce the deformity, surgical intervention was warranted. Surgery required; the initial insertion of bilateral C2 pedicle screws, isolation of the V3 segment of the vertebral artery, removal of the destroyed left C1 lateral mass in a piecemeal fashion, and fusion (e.g., utilizing a tricortical iliac bone graft secured with left C1 laminar hook-C2 pedicle screw, and an additional right C1 lateral mass-C2 pedicle screw rod construct) [
Bacteriology and pathology
The operative specimens demonstrated: a positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for TB, and the pathology was compatible with a granulomatous infection.
Tubercular treatment
Four-drug therapy was warranted for TB; isoniazid (5 mg/kg), rifampicin (10 mg/kg), ethambutol (15 mg/kg), and pyrazinamide (25 mg/kg). They were administered as a first-line of treatment for 4 months. This was followed by an additional 12 months of rifampicin and isoniazid.
DISCUSSION
Spinal TB, presenting as AARF with painful torticollis, is extremely rare.
Pathogenesis
Severe painful torticollis may be the only clinical indication that AARP is present. Patients may exhibit unilateral destruction of the lateral mass of the atlas with/ without infiltration/disruption of the alar ligaments. The ESRs are typically increased, and the Mantoux test is typically positive.[
Imaging
AARF is the best documented utilizing axial reconstructed 2D and 3D CT images and CTA.[
The following findings are classical for TB; an osteolytic, fragmented lesion involving the C1 lateral mass, deviation of the odontoid to the affected lateral mass side, and forward displacement of the contralateral lateral mass of atlas.[
Magnetic resonance imaging also may help to establish the diagnosis of tuberculous involvement of the C1 lateral mass, by demonstrating heterogeneous intensity on the T1, and hyperintensity on the T2-weighted and fat-suppressed images.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnoses for painful torticollis with unilateral involvement of the C1 lateral mass include TB tumors, rheumatoid arthritis, and other types of pyogenic spondylitis.[
Management
In classic tubercular atlantoaxial dislocation, management strategies range from purely conservative treatment to radical operations.[
CONCLUSION
Here, we presented an extremely rare cause of painful torticollis due to tubercular AARF involving a unilateral C1 lateral mass requiring decompression, reduction, and fixation.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Allali F, Benomar A, El Yahyaoui M, Chkili T, HajjajHassouni N. Atlantoaxial tuberculosis: Three cases. Joint Bone Spine. 2000. 67: 481-4
2. Behari S, Nayak SR, Bhargava V, Banerji D, Chhabra DK, Jain VK. Craniocervical tuberculosis: Protocol of surgical management. Neurosurgery. 2003. 52: 72-81
3. Chaudhary K, Potdar P, Bapat M, Rathod A, Laheri V. Structural odontoid lesions in craniovertebral tuberculosis: A review of 15 cases. Spine. 2012. 37: E836-43
4. Dhaon BK, Jaiswal A, Nigam V, Jain V. Atlantoaxial rotatory fixation secondary to tuberculosis of occiput: A case report. Spine. 2003. 28: E203-5
5. Gupta SK, Mohindra S, Sharma BS, Gupta R, Chhabra R, Mukherjee KK. Tuberculosis of the craniovertebral junction: Is surgery necessary?. Neurosurgery. 2006. 58: 1144-50
6. Halla JT, Bliznak J, Hardin JG, Finn S. Septic arthritis of the C1-C2 lateral facet joint and torticollis: Pseudo-grisel’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1991. 34: 84-8
7. Halla JT, Fallahi S, Hardin JG. Nonreducible rotational head tilt and lateral mass collapse. A prospective study of frequency, radiographic findings and clinical features in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982. 25: 1316-24
8. Jain R, Sawhney S, Berry M. Computed tomography of vertebral tuberculosis: Patterns of bone destruction. Clin Radiol. 1993. 47: 196-9
9. Lal AP, Rajshekhar V, Chandy MJ. Management strategies in tuberculous atlanto-axial dislocation. Br J Neurosurg. 1992. 6: 529-35
10. Ngu BB, Khanna AJ, Pak SS, McCarthy EF, Sponseller PD. Eosinophilic granuloma of the atlas presenting as torticollis in a child. Spine. 2004. 29: E98-100
11. Pandya SK. Tuberculous atlanto-axial dislocation (with remarks on the mechanism of dislocation). Neurol India. 1971. 19: 116-21
12. Rahimizadeh A, Williamson W, Rahimizadeh S. Traumatic chronic irreducible atlantoaxial rotatory fixation in adults: Review of the literature, with two new examples. Int J Spine Surg. 2019. 13: 350-60
13. Simsek S, Yigitkanli K, Kazanci A, Belen D, Bavbek M. Medically treated paravertebral Brucella abscess presenting with acute torticollis: Case report. Surg Neurol. 2007. 67: 207-10
14. Sinha S, Singh AK, Gupta V, Singh D, Takayasu M, Yoshida J. Surgical management and outcome of tuberculous atlantoaxial dislocation: A 15-year experience. Neurosurgery. 2003. 52: 331-9
15. White GM, Healy WL. Tumor-associated atlanto-axial rotatory fixation: A case report. Spine. 1987. 12: 406-8