- Department of Neurosurgery, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
- Department of Neuroradiology, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
- Department of Neuropathology, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Correspondence Address:
Amey R. Savardekar
Department of Neurosurgery, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
DOI:10.4103/2152-7806.179849
Copyright: © Surgical Neurology International This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Savardekar AR, Verma A, Narayan V, Mahadevan A, Rao MB. Pathological correlation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging features in a classical case of lipomatous meningioma. Surg Neurol Int 07-Apr-2016;7:32
How to cite this URL: Savardekar AR, Verma A, Narayan V, Mahadevan A, Rao MB. Pathological correlation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging features in a classical case of lipomatous meningioma. Surg Neurol Int 07-Apr-2016;7:32. Available from: http://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint_articles/pathological-correlation-of-magnetic-resonance-imaging-features-in-a-classical-case-of-lipomatous-meningioma/
Meningiomas are common tumors, constituting about 20% of all primary brain tumors.[
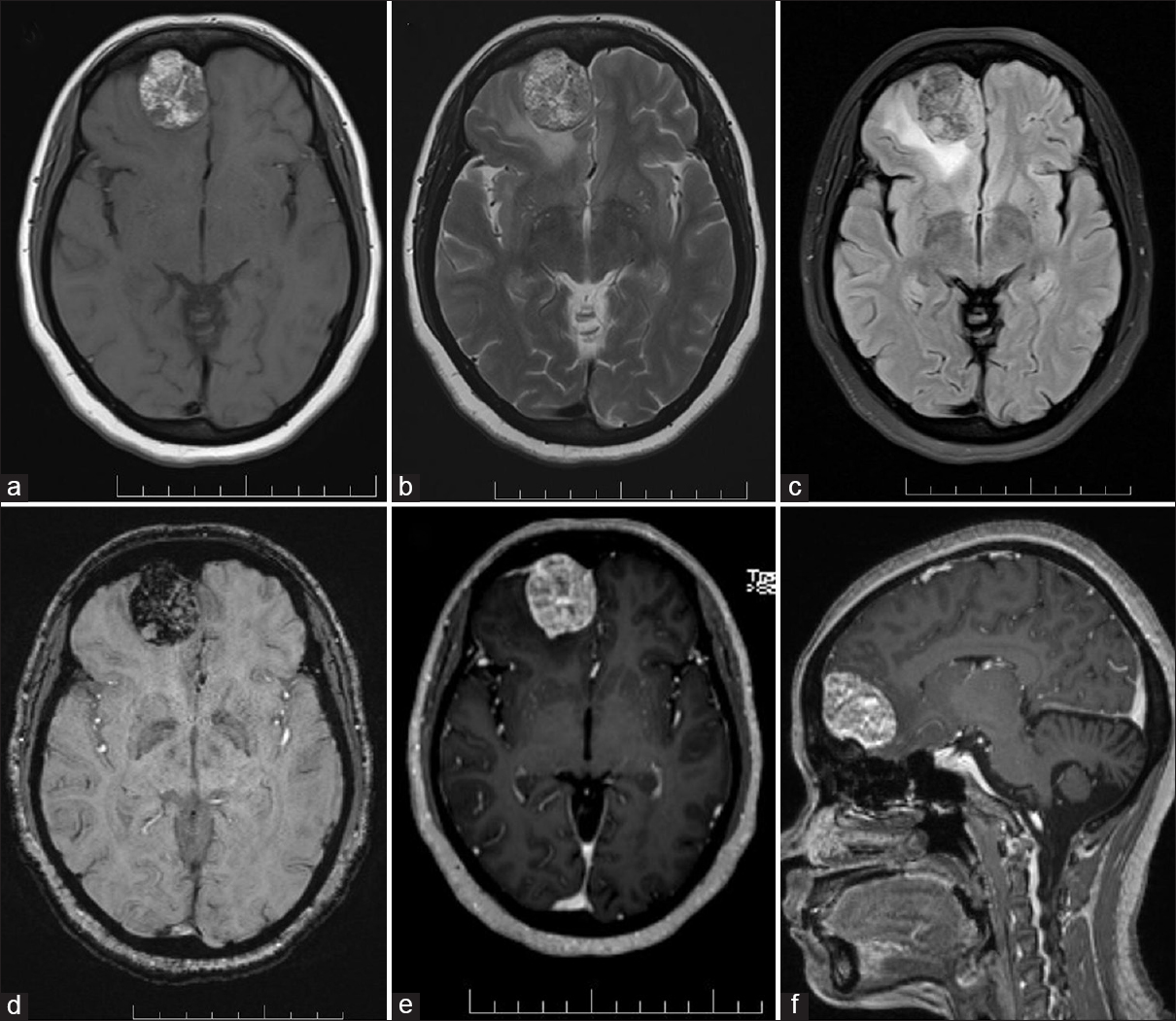
A 44-year-old female presented with history of long-standing generalized tonic-clonic seizures of 9 years duration on antiepileptic medications. MRI of the brain revealed a well-demarcated, extra-axial, dural-based, right anterior one-third, parasagittal lesion with predominant areas of intrinsic T1- and T2-weighted hyperintensity [Figure
Figure 1
Magnetic resonance imaging findings in a classical case of lipomatous meningioma. (a) T1-axial, (b) T2-axial, (c) fluid attenuation inversion recovery-axial, (d) susceptibility weighted imaging-axial, (e) T1 magnetization prepared rapid gradient-echo-axial, and (f) T1 magnetization prepared rapid gradient-echo sagittal. The areas of hyperintensity on T1- and T2-weighted images are hypointense on fluid attenuation inversion recovery images, indicating the fat content of the tumor
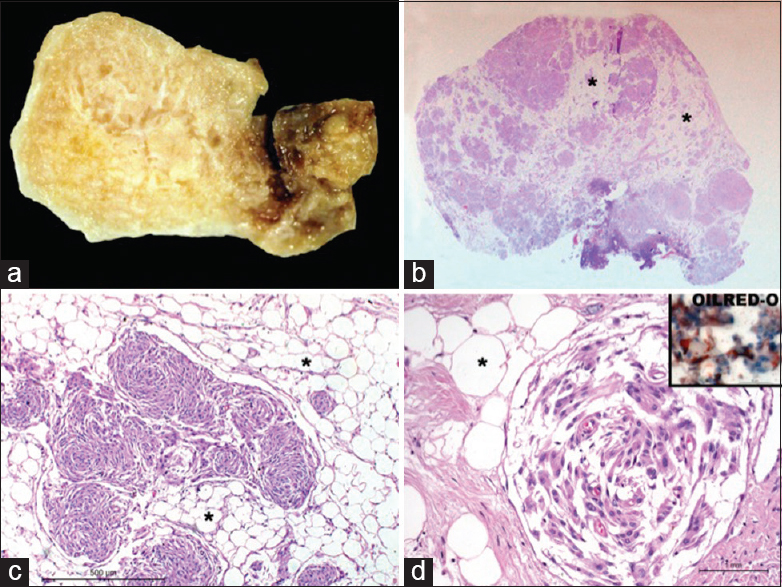
Figure 2
(a) Gross appearance of the tumor that is bright yellow and greasy; (b) scanner view of tumor reveals large lucent areas (*) separating islands of tumor cells; (c) microscopy reveals lobules of mature adipose tissue (*) separating whorls of meningothelial cells; (d) fine intracellular vacuolation seen within meningothelial cells that have intracytoplasmic Oil red O positive neutral lipid droplets (inset)
Lipomatous meningioma is a subtype of metaplastic meningioma, which was first described by Bailey and Bucy in 1931.[
The preoperative differential diagnoses considered, in our case, were lipoma, dermoid cyst, teratoma, or xanthomatous meningioma. The classical “dural tail” sign, intense contrast enhancement of the lesion, and hyperostosis of the overlying calvarium were highly suggestive of meningioma; the suppression of T1-weighted hyperintense areas on FLAIR imaging indicated the lipomatous nature of the meningioma. Our report highlights the distinct MRI findings correlating with characteristic histopathological findings in a “classical case” of lipomatous meningioma.
Financial Support and Sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Fitt GJ, Kalnins R, Mitchell LA. Lipomatous meningioma: Characteristic computed tomographic appearance. Australas Radiol. 1996. 40: 84-7
2. Jaiswal AK, Mehrotra A, Kumar B, Jaiswal S, Vij M, Behari S. Lipomatous meningioma: A study of five cases with brief review of literature. Neurol India. 2011. 59: 87-91
3. LeRoux P, Hope A, Lofton S, Harris AB. Lipomatous meningioma – An uncommon tumor with distinct radiographic findings. Surg Neurol. 1989. 32: 360-5
4. Ohba S, Yoshida K, Akiyama T, Ikeda E, Kawase T. Lipomatous meningioma. J Clin Neurosci. 2007. 14: 1003-6
5. Withers T, Klevansky A, Weinstein SR. Lipomeningioma: Case report and review of the literature. J Clin Neurosci. 2003. 10: 712-4