- Department of Neurosurgery, American University of Beirut Medical Center, Beirut, Lebanon.
Correspondence Address:
Dr. Ibrahim Omeis, Department of Neurosurgery, American University of Beirut Medical Center, Beirut, Lebanon.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_755_2021
Copyright: © 2021 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Sarah Kawtharani, Shadi Abdelatif Bsat, Mohamad El Houshiemy, Charbel Moussalem, Adham Halaoui, Ibrahim Omeis. Retained foreign needle in the thoracic spinal canal in a child: Case report. 30-Sep-2021;12:484
How to cite this URL: Sarah Kawtharani, Shadi Abdelatif Bsat, Mohamad El Houshiemy, Charbel Moussalem, Adham Halaoui, Ibrahim Omeis. Retained foreign needle in the thoracic spinal canal in a child: Case report. 30-Sep-2021;12:484. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/11144/
Abstract
Background: The presence of retained foreign bodies in the spinal canal has been reported in the literature. They are attributed to retained pieces of medical equipment after surgery, or, following trauma, to residual bullets, glass fragments, or knife blades. Although some retained materials do not cause any neurological deficits in the short run, others may become symptomatic months later.
Case Description: A 2-year-old male presented with a history of intermittent fever and mild lower extremity weakness. Notably, the original infectious workup was negative. However, a noncontrast CT scan later documented a needle-shaped foreign body in the spinal canal at the T10 level. During the T10 laminectomy, a needle (i.e. from a medical syringe) was removed, the patient remained neurologically intact. The foreign body turned out to be a medical syringe needle tip.
Conclusion: A 2-year-old male presented with fevers and mild lower extremity weakness attributed to an intraspinal needle tip found utilizing CT at the T10 level. T10 laminectomy allowed for removal of a small needle tip. This shows the importance of removing retained spinal foreign bodies to avoid further/future neurological injury, and/or the potential risks/complications of foreign body migration/sequestration.
Keywords: Spinal needle, Retained foreign body, CT myelography, CT spine, Pediatric
INTRODUCTION
The presence of retained foreign bodies in the spinal canal has been reported in the literature. They have been attributed to retained pieces of medical equipment after surgery, or after trauma, to retained bullets, glass fragments, or knife blades. Some of the retained material did not cause any neurological deficits in the short run, while others may contribute to new deficits months later.
CASE PRESENTATION
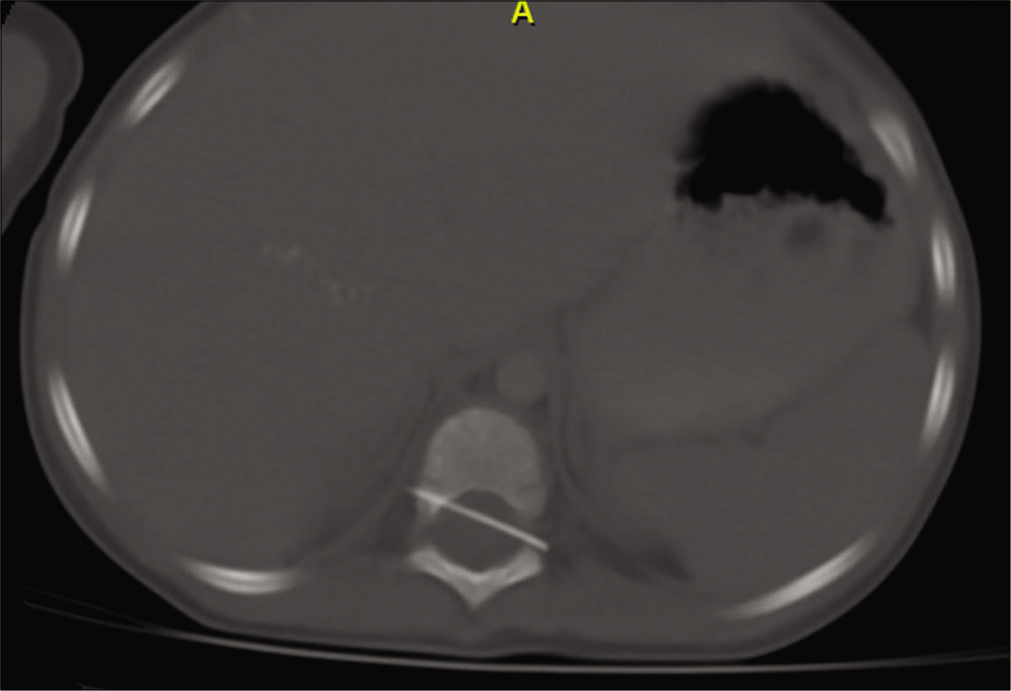
A 2-year-old male presented with fevers, leukocytosis (studies were only positive for leukocytosis with WBC of 179,000/cu.mm), and mild lower extremity weakness. The thoracic CT scan showed a needle-shaped foreign body in the spinal canal at the level of T10 level [
CT myelography documented the presence of a linear radiopaque foreign body (likely a pin/ needle) in the spinal canal at the T10 level traversing from the right pedicle to the left neural foramen; it appeared to be traversing the anterolateral aspect of the cord with no clear contrast separating it from the cord.
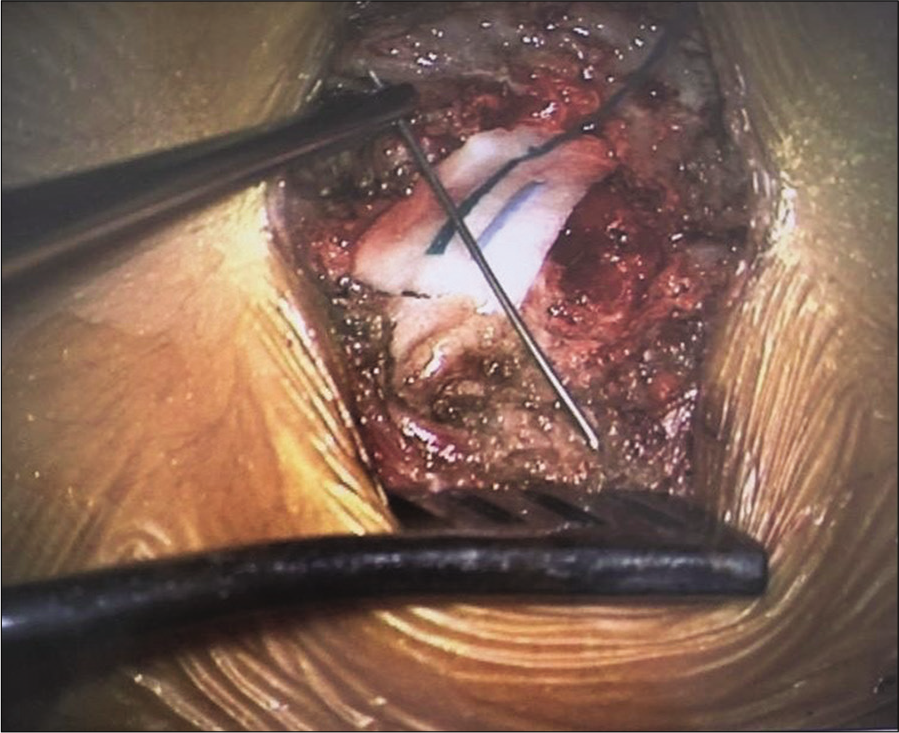
The patient underwent a T10 laminectomy for removal of the foreign body that proved to be a medical syringe needle tip [
DISCUSSION
It has been reported that foreign bodies as needles or wires can migrate into the spinal canal over time and cause nerve injuries.[
According to most of the reported case reports in the literature, it was opted to remove foreign bodies surgically to avoid any future damage to the cord or neural elements.
Here, we chose surgical intervention after documenting the presence of the foreign body on imaging studies (i.e. CT scan and CT myelogram).
CONCLUSION
A 2-year-old male presented with fever, leukocytosis, and mild lower extremity weakness. Although the infectious workup was negative, the noncontrast CT documented a metallic foreign body at the T10 level that was removed; it proved to be an entrapped spinal medical needle tip. Here, we highlight the importance of removing retained spinal foreign bodies to avoid future long-term neurological injury or foreign body migration.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patients identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Publication of this article was made possible by the James I. and Carolyn R. Ausman Educational Foundation.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patients identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Publication of this article was made possible by the James I. and Carolyn R. Ausman Educational Foundation.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Li H, Lou J, Liu H. Migration of titanium cable into spinal cord and spontaneous C2 and C3 fusion: Case report of possible causes of fatigue failure after posterior atlantoaxial fixation. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. 95: e5744
2. Lv X, Lu X, Wang Y. Entrapment of a metal foreign body in the cervical spinal canal during surgical procedure: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. 97: e0548
3. Reddy N, Fata P, Balzer A, Diaz-Marchan P, Lincoln CM. Thorn in my spine: A case of a retained intradural extramedullary foreign body. Clin Imaging. 2017. 45: 118-21
4. Wu WQ. Delayed effects from retained foreign bodies in the spine and spinal cord. Surg Neurol. 1986. 25: 214-8
5. Yoshioka K, Kawahara N, Murakami H, Demura S, Matsuda M, Tomita K. A glass foreign body migrating into the lumbar spinal canal: A case report. Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2012. 20: 257-9