- Department of Medicine, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia,
- Department of Medicine, Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine, Erie,
- Department of Neurosurgery, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, United States.
Correspondence Address:
Brandon C. Rogowski, Department of Medicine, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, United States.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_1148_2022
Copyright: © 2023 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Brandon C. Rogowski1, Rosh Bharthi2, Peter G. Zaki1, Michael Moran1, Coby J. Cunningham3, Nathan Esplin3, Dorian Mateusz Kusyk3, Nestor D. Tomycz3. Spinal cord stimulation: A novel approach to pain management in Dercum’s disease. 17-Mar-2023;14:93
How to cite this URL: Brandon C. Rogowski1, Rosh Bharthi2, Peter G. Zaki1, Michael Moran1, Coby J. Cunningham3, Nathan Esplin3, Dorian Mateusz Kusyk3, Nestor D. Tomycz3. Spinal cord stimulation: A novel approach to pain management in Dercum’s disease. 17-Mar-2023;14:93. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/12194/
Abstract
Background: Dercum’s Disease (DD) is a rare chronic pain syndrome in which patients experience extreme burning pain associated with subcutaneous lipomatous tissue deposits. These patients may also present with; weakness, psychiatric symptoms, metabolic derangements, sleep disturbance, impaired memory, and easy bruising. Common risk factors for DD include: obesity, Caucasian race, and female sex. The etiology of DD remains under debate while it has proven highly resistant to treatment (i.e., requiring high doses of opioids for adequate pain management).
Case Description: A 48-year-old female with DD and a prior spinal cord stimulator (SCS) placed for chronic back pain, presented with recurrent back pain, and increased falling. Surgery to replace her SCS resulted in improvement in her back pain and a decreased incidence of falls. Furthermore, she noticed significant improvement in the burning pain attributed to her subcutaneous nodules; this most markedly occurred at and below the level of stimulator placement.
Conclusion: A 48-year-old female with the extremely rare condition, DD experienced dramatic reduction in her pain following the successful revision of her SCS.
Keywords: Adiposis dolorosa, Ander syndrome, Chronic pain, Dercum’s Disease, Spinal cord stimulation
INTRODUCTION
Dercum’s disease (DD), also known as Adiposis Dolorosa, is a rare condition in which patients experience chronic burning or searing pain. Their pain is typically attributed to subcutaneous lipomatous tissue deposits that are often multiple, diffuse, symmetric, and varying in size.[
The most controversial factor for managing DD is how to best manage the pain. Treatments are primarily based on anecdotal evidence and widely vary. They have included weight loss, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, low dose d-amphetamines, lidocaine, ketamine, methotrexate, infliximab, interferon alpha-2b, corticosteroids, pregabalin, calcium channel modulators, rapid cycling hypobaric pressure, and short-term transcutaneous electrical stimulation.[
CASE REPORT
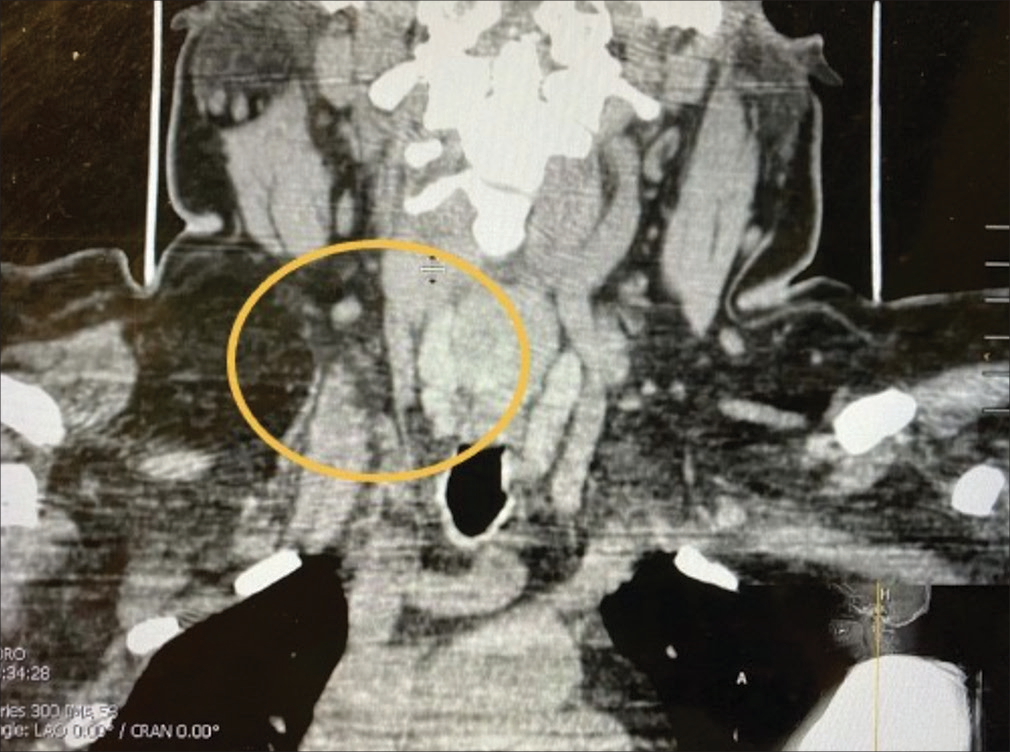
A 48-year-old morbidly obese female (Body mass index 44.2) with DD presented with chronic back pain and increased falls. She had previously received a SCS in 2013 that provided satisfactory relief until 2015. From 2017 to 2018, she noticed the new onset of painful (i.e., 10/10 burning pain) subcutaneous nodules; these first appeared on her abdomen and then occurred diffusely [
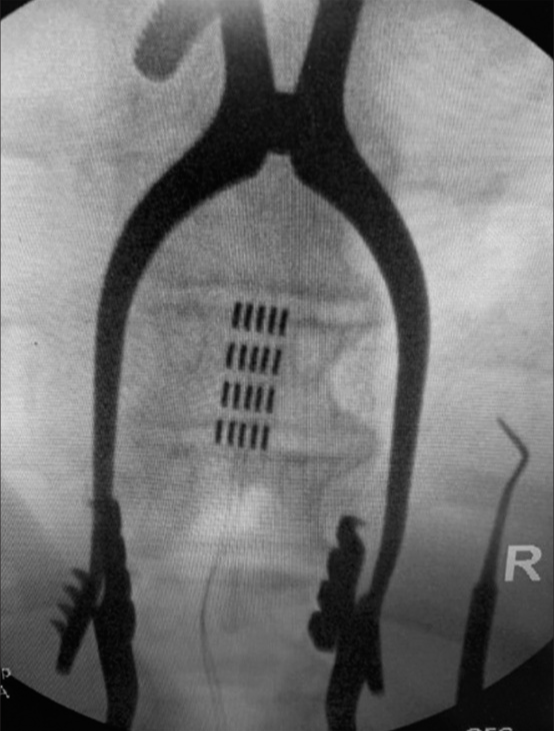
She underwent successful replacement of her SCS; the paddle lead was placed at the T8 level along with a non-rechargeable generator placed in the buttock [
DISCUSSION
A possible etiology of chronic pain in DD is chronic inflammation from subcutaneous nodules. Notably, chronic compression from these subcutaneous nodules may elicit a cascade of inflammatory factors that may then contribute to the development of peripheral nerve sensitization, ectopic neuronal activity and resultant severe pain.[
CONCLUSION
When a 48-year-old morbidly obese female underwent revision of her previously placed but non-functioning “burst” SCS, she experienced marked improvement in pain (i.e., 90%) without significant morbidity.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Journal or its management. The information contained in this article should not be considered to be medical advice; patients should consult their own physicians for advice as to their specific medical needs.
References
1. Amtmann D, Cook KF, Jensen MP, Chen WH, Choi S, Revicki D. Development of a PROMIS item bank to measure pain interference. Pain. 2010. 150: 173-82
2. Attal N, Bouhassira D. Mechanisms of pain in peripheral neuropathy. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1999. 173: 12-24 discussion 48-52
3. Cook JC, Gross GP, editors. Adiposis dolorosa. StatPearls. Florida: StatPearls Publishing; 2021. p. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507867 [Last accessed on 2021 Jul 21]
4. Ghazala S, Bilal J, Ross E, Riaz IB, Kalb B, Herbst KL. Low-dose d-amphetamine induced regression of liver fat deposits in dercum disease. Am J Med. 2018. 131: 705-8
5. Hansson E, Svensson H, Brorson H. Review of Dercum’s disease and proposal of diagnostic criteria, diagnostic methods, classification and management. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012. 7: 23
6. Kucharz EJ, Kopeć-Mędrek M, Kramza J, Chrzanowska M, Kotyla P. Dercum’s disease (adiposis dolorosa): A review of clinical presentation and management. Reumatologia. 2019. 57: 281-7
7. Martinenghi S, Caretto A, Losio C, Scavini M, Bosi E. Successful treatment of Dercum’s disease by transcutaneous electrical stimulation: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. 94: e950
8. Sdrulla AD, Guan Y, Raja SN. Spinal cord stimulation: Clinical efficacy and potential mechanisms. Pain Pract. 2018. 18: 1048-67
9. Thacker MA, Clark AK, Marchand F, McMahon SB. Pathophysiology of peripheral neuropathic pain: Immune cells and molecules. Anesth Analg. 2007. 105: 838-47