- Department of Neurosurgery, Lenox Hill Hospital, Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
- Department of Pathology, Lenox Hill Hospital, Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
- Department of Radiology, Lenox Hill Hospital, Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
- Department of Otolaryngology, Lenox Hill Hospital, Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
Correspondence Address:
John A. Boockvar
Department of Neurosurgery, Lenox Hill Hospital, Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
DOI:10.4103/sni.sni_229_17
Copyright: © 2017 Surgical Neurology International This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Kay O. Kulason, Julia R. Schneider, Ralph Rahme, Fanni Ratzon, Todd A. Anderson, Deborah R. Shatzkes, Christopher G. Filippi, Peter D. Costantino, David J. Langer, John A. Boockvar. Suprasellar and third ventricular cavernous malformation: Lessons learned in differential diagnosis and surgical planning. 13-Oct-2017;8:251
How to cite this URL: Kay O. Kulason, Julia R. Schneider, Ralph Rahme, Fanni Ratzon, Todd A. Anderson, Deborah R. Shatzkes, Christopher G. Filippi, Peter D. Costantino, David J. Langer, John A. Boockvar. Suprasellar and third ventricular cavernous malformation: Lessons learned in differential diagnosis and surgical planning. 13-Oct-2017;8:251. Available from: http://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/suprasellar-and-third-ventricular-cavernous-malformation-lessons-learned-in-differential-diagnosis-and-surgical-planning/
Abstract
Background:While craniopharyngiomas (CPs) are the most common cystic suprasellar lesions in adults, cavernous malformations (CMs) only exceptionally occur in this location and are seldom considered in the differential diagnosis of such lesions. However, unlike CPs, suprasellar CMs are not typically approached via an endoscopic endonasal approach.
Case Description:We present a unique clinical case of suprasellar and third ventricular CM mimicking a CP, posing a major decision-making dilemma at the levels of both preoperative diagnosis and surgical planning.
Conclusion:This case highlights the importance of carefully considering all the differential diagnoses of sellar pathology to select the most appropriate management strategy and surgical approach.
Keywords: Cavernous malformation, craniopharyngioma, endoscopic endonasal surgery, interhemispheric transcallosal approach, third ventricle
INTRODUCTION
The sellar region is anatomically complex and a common site of neoplastic, infectious, inflammatory, developmental, and vascular pathologies.[
In contrast to other cystic lesions, cavernous malformations (CMs) rarely occur in the sellar region and/or third ventricle, and thus are not typically considered in the differential diagnosis of cystic sellar lesions.[
CASE DESCRIPTION
A 52-year-old woman presented with several months of progressive anterograde amnesia noticed by her colleagues at work. Neurologic exam was otherwise unremarkable. Noncontrast head computed tomography (CT) revealed a hyperdense, suprasellar, and third ventricular lesion, consistent with either intralesional microcalcifications or hemorrhage [
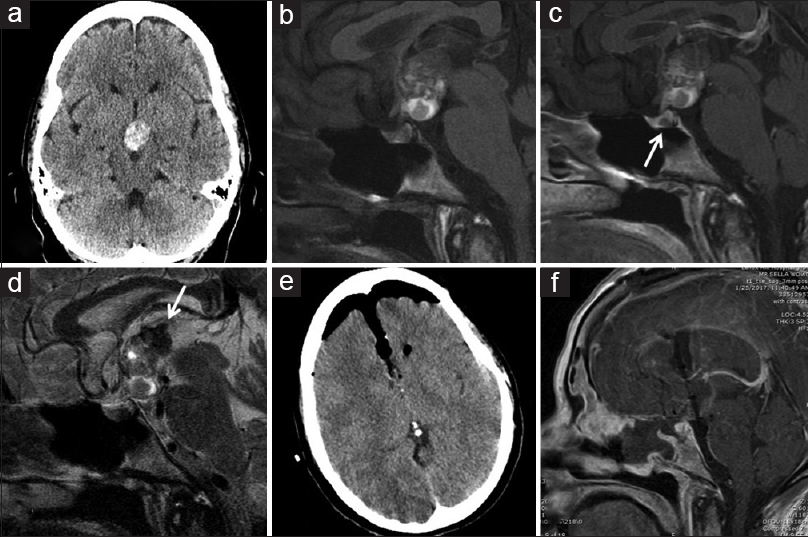
Figure 1
(a) Noncontrast head CT shows a heterogeneously hyperdense mass in the suprasellar cistern. (b) Sagittal T1-weighted brain MRI shows a large, partially cystic lesion without contrast, and (c) no enhancement with contrast. A small cystic lesion is seen in the pituitary gland (arrow). (d) Sagittal T2-weighted brain MRI demonstrates heterogenous signal in the lesion. Areas of low signal superiorly (arrow) are consistent with susceptibility effects suggesting hemorrhagic products. (e, f) Postoperative noncontrast head CT (e) and brain MRI (f) demonstrate gross total resection of the lesion
Following lumbar drain placement, a standard endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach was undertaken using intraoperative neuronavigation (Stryker, Kalamazoo, MI, USA). After opening the sellar dura, the small lesion in the posterior portion of the pituitary gland was easily identified and excised. Intraoperative frozen section examination was suggestive of CP. However, this intrasellar portion did not appear to be in direct continuity with the suprasellar lesion. An attempt to access the suprasellar space was then made. Unfortunately, however, a surgical corridor could not be safely developed. Anteriorly, the optic chiasm and anterior communicating artery complex completely obstructed the line of sight. Posteriorly, the neurohypophysis and dorsum sellae impeded access to the suprasellar compartment. Thus, a decision was made to abort the endoscopic procedure and plan a transcranial approach. Pathologic examination of the permanent intrasellar specimen showed a cystic lesion with clusters of simple squamoid epithelium and a rare strip of nonciliated columnar epithelium and proteinaceous contents. This was most consistent with the diagnosis of RCC, although a colloid or pars intermedia cyst or even a CP could not be ruled out [
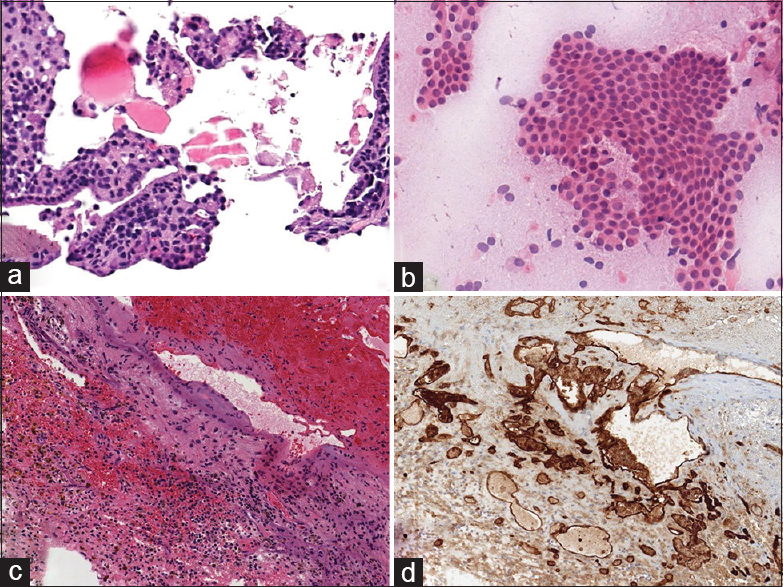
Figure 2
(a) Microphotograph of sellar lesion shows fibrotic adenohypophyseal tissue with scant strip of benign nonciliated columnar epithelium (hematoxylin-eosin, ×130). (b) Intraoperative smear of specimen shows numerous cohesive clusters of benign squamoid epithelium with macrophages (hematoxylin-eosin, ×120). (c) Microphotograph demonstrates hemorrhage and fibrin with hemosiderin-laden macrophages and fragments of benign tissue (hematoxylin-eosin, ×50). (d) Immunohistochemical staining highlights abnormal vascular channels, consistent with a vascular malformation (CD31 stain, ×50)
Five days later, the patient underwent bifrontal craniotomy and gross total resection of the suprasellar and third ventricular lesion via an interhemispheric transcallosal interforniceal approach [Figure
On the second postoperative day, the patient suffered sudden acute deterioration of her level of consciousness with right nonreactive mydriasis. Head CT revealed a new right hemispheric subdural fluid collection with mass effect and midline shift to the left [Figure
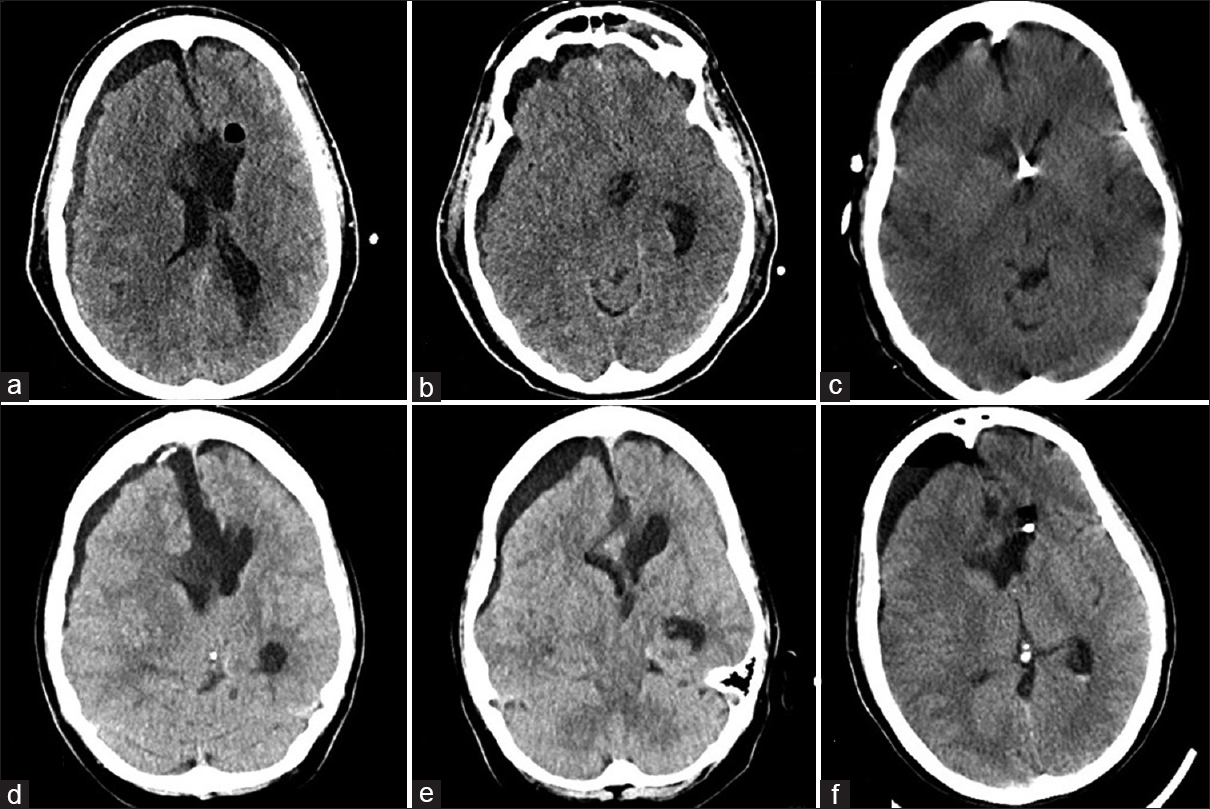
Figure 3
(a and b) Noncontrast head CT following postoperative neurological worsening shows a right hemispheric subdural fluid collection with mass effect and midline shift. (c) Noncontrast head CT after evacuation of the subdural collection and right frontal EVD placement shows improvement in mass effect and midline shift. (d and e) Non-contrast head CT, 3 weeks later, shows recurrence of the right subdural hygroma with concomitant ventriculomegaly, consistent with external hydrocephalus. (f) Non-contrast head CT after permanent CSF diversion shows reduction in subdural collection size and mass effect
Three weeks later, the patient exhibited worsening mental status and increasing lethargy. Head CT demonstrated external hydrocephalus [Figure
DISCUSSION
This case report illustrates the importance of carefully studying the differential diagnosis of lesions arising from the suprasellar space given the significant impact of histopathologic diagnosis on the overall management strategy and surgical approach. In fact, suprasellar and third ventricular lesions can be approached through a wide variety of endoscopic transfacial and open transcranial approaches. The decision-making process is often complex and depends on multiple factors, ranging from the nature, size, and extent of the lesion to the local anatomy, surgeon experience, and patient preference.[
First, the differential diagnosis of suprasellar and third ventricular lesions is broad and all possibilities should be considered. The fact that this lesion was hyperdense on CT, suggesting possible microcalcifications, partially cystic and minimally enhancing on MRI, made us overly confident of the diagnosis of CP. This was further compounded by the fact that CP is, by far, the most common suprasellar cystic lesion in adults.[
Second, the indication for surgery and the choice of approach largely depend on the suspected histopathologic diagnosis. There is general consensus that CMs involving the third ventricle should be aggressively surgically managed, given that these lesions tend to grow more rapidly and cause more mass effect than CMs arising in other locations.[
CONCLUSIONS
Neurosurgeons should keep an open mind when considering the differential diagnosis of sellar pathology because the optimal management strategy and surgical approach may vary considerably depending on the suspected underlying histopathologic diagnosis. Specifically, a CM should be routinely considered, along with CP, in the differential diagnosis of suprasellar and/or third ventricular, cystic-appearing lesions. While the endoscopic endonasal approach is often a good choice for suprasellar CPs, it is less so for CMs which are best approached transcranially.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Barber SM, Rangel-Castilla L, Baskin D. Neuroendoscopic Resection of Intraventricular Tumors: A Systematic Outcomes Analysis. Minim Invasive Surg 2013. 2013. p. 898753-
2. Bernstein M. Neuro-oncology, the essentials. Thieme. 2007. p.
3. Blitstein MK, Tung GA. MRI of cerebral microhemorrhages. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007. 189: 720-5
4. Cavallo LM, Prevedello D, Esposito F, Laws ER, Dusick JR, Messina A. The role of the endoscope in the transsphenoidal management of cystic lesions of the sellar region. Neurosurg Rev. 2008. 31: 55-64
5. Eldevik OP, Blaivas M, Gabrielsen TO, Hald JK, Chandler WF. Craniopharyngioma: Radiologic and histologic findings and recurrence.AJNR. Am J Neuroradiol. 1996. 17: 1427-39
6. Giannetti AV. Purely neuroendoscopic resection of an intraventricular cavernous angioma: Case report. J Neurol Surg. 2013. 74: 47-50
7. Ginat DT, Meyers SP. Intracranial lesions with high signal intensity on T1-weighted MR images: Differential diagnosis. Radiographics. 2012. 32: 499-516
8. Katayama Y, Tsubokawa T, Maeda T, Yamamoto T. Surgical management of cavernous malformations of the third ventricle. J Neurosurg. 1994. 80: 64-72
9. Laws ER. Endoscopic surgery for cystic lesions of the pituitary region. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2008. 4: 662-3
10. Patibandla MR, Thotakura AK, Panigrahi MK. Third ventricular cavernous malformation: An unusual lesion. Br J Neurosurg. 2014. 28: 110-2
11. Rennert J, Doerfler A. Imaging of sellar and parasellar lesions. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2007. 109: 111-24
12. Shirvani M, Hajimirzabeigi A. Intraventricular Cavernous Malformation: Review of the Literature and Report of Three Cases with Neuroendoscopic Resection. J Neurol Surg. 2017. p.
13. Thapar K.editorsDiagnosis and management of pituitary tumors. Humana Pr Inc; 2001. p.
14. Wannemuehler TJ, Rubel KE, Hendricks BK, Ting JY, Payner TD, Shah MV. Outcomes in transcranial microsurgery versus extended endoscopic endonasal approach for primary resection of adult craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. 41: E6-
15. Zada G, Lin N, Ojerholm E, Ramkissoon S, Laws ER. Craniopharyngioma and other cystic epithelial lesions of the sellar region: A review of clinical, imaging, and histopathological relationships. Neurosurg Focus. 2010. 28: E4-