- Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, Florida, United States.
Correspondence Address:
Ashia M. Hackett, Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, Florida, United States.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_701_2022
Copyright: © 2022 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Ashia M. Hackett, Evan M. Luther, Ariel P. Walker, Joshua Burks, Victor M. Lu, Michael A. Silva, Robert M. Starke. Telescoping pipeline vantage embolization devices with shield technology for the treatment of a giant, symptomatic dolichoectatic basilar trunk aneurysm. 23-Sep-2022;13:434
How to cite this URL: Ashia M. Hackett, Evan M. Luther, Ariel P. Walker, Joshua Burks, Victor M. Lu, Michael A. Silva, Robert M. Starke. Telescoping pipeline vantage embolization devices with shield technology for the treatment of a giant, symptomatic dolichoectatic basilar trunk aneurysm. 23-Sep-2022;13:434. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/11884/
Abstract
Background: Dolichoectatic basilar trunk aneurysms are exceedingly rare and carry a poor prognosis. Treatment strategies are often reserved for patients with severe and progressive symptoms.
Case Description: A patient in their 40s with a dolichoectatic basilar trunk aneurysm developed significant progression of the lesion and neurologic decline, necessitating treatment. He underwent flow diversion utilizing multiple telescoping Pipeline Vantage Embolization Devices with Shield Technology for treatment. At 1-year follow-up, the aneurysm was stable in size and the patient remained at his neurologic baseline.
Conclusion: This case illustrates the need for continued development of next-generation endovascular devices as these aneurysms have limited management options.
Keywords: Aneurysm, Case report, Flow diverter, Intervention, Technique
INTRODUCTION
Dolichoectatic basilar trunk aneurysms are exceedingly rare and carry a poor prognosis with nearly half experiencing aneurysmal progression within 5 years of diagnosis.[
CASE DESCRIPTION
In 2013, a patient in their 30s presented with transient right-sided weakness and was found to have a small left pontine stroke as well as a dolichoectatic basilar trunk aneurysm without evidence of mass effect on the brainstem or intraluminal thrombi [
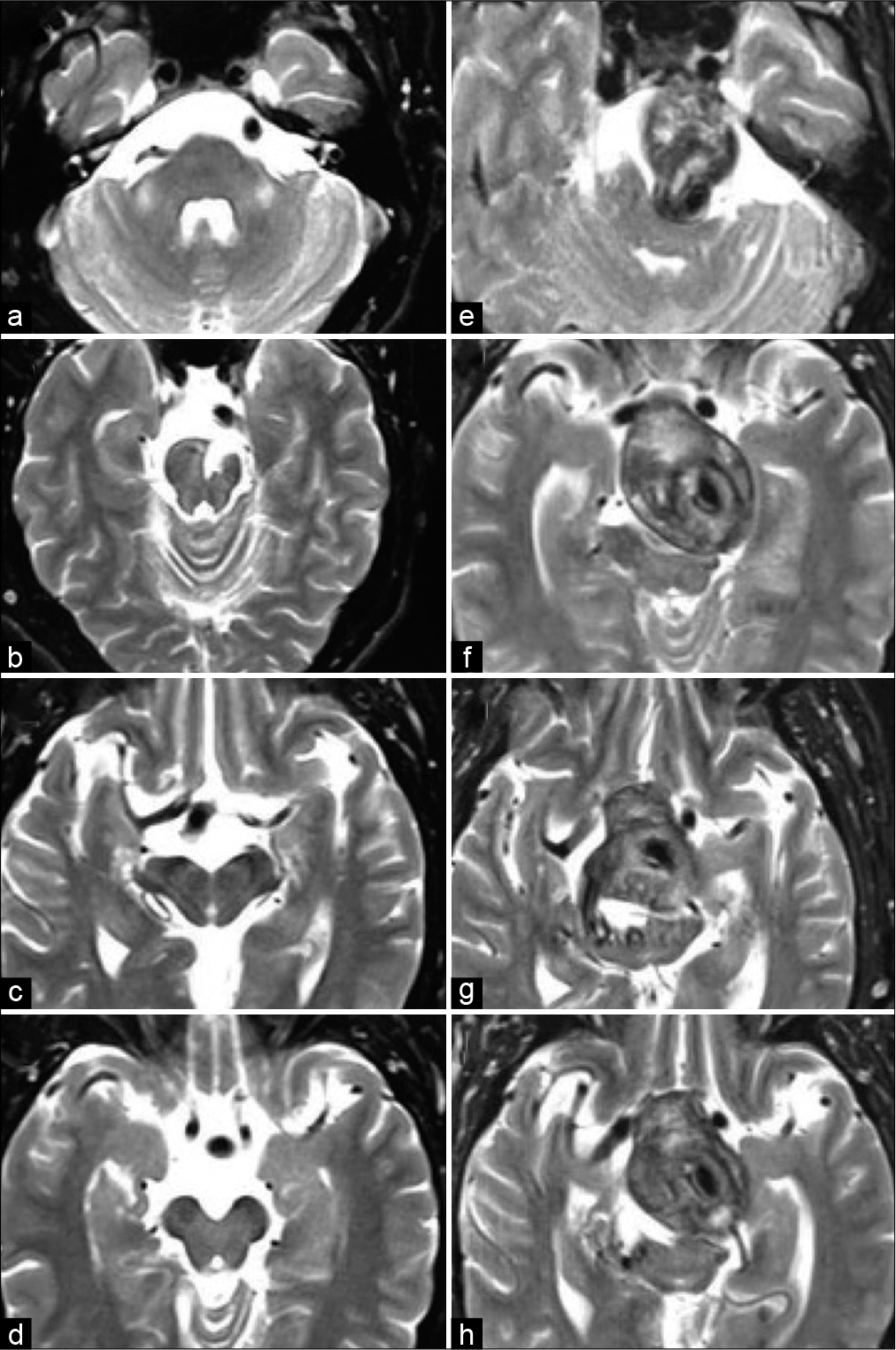
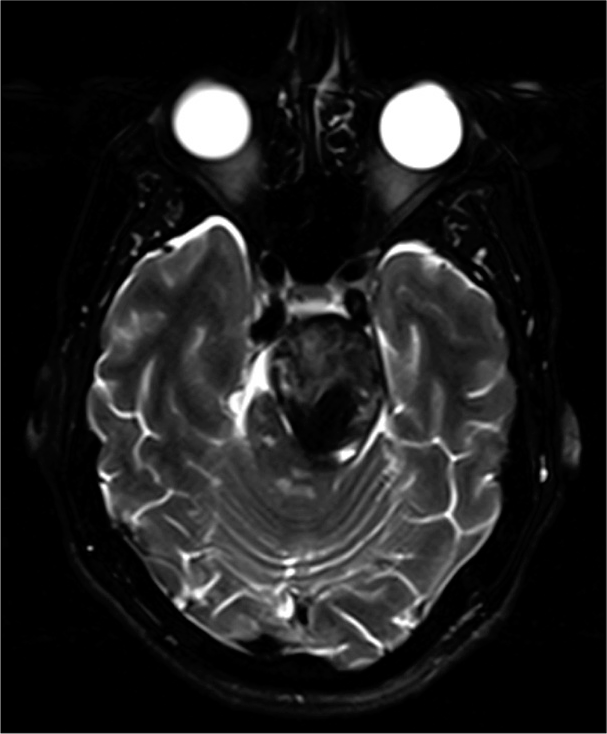
Figure 1:
(a-d) T2-weighted axial magnetic resonance image (MRI) from 2013 showing chronic left pontine stroke and a dolichoectatic basilar trunk. (e-h) T2-weighted axial MRI from 2020 showing significant interval enlargement of the dolichoectatic basilar trunk now with periluminal thrombus and brainstem compression.
Seven years later, he presented with progressive headaches, dysphonia, swallowing dysfunction, and dysarthria. On physical examination, the patient had a dense right temporal hemianopsia and redemonstrated dysphonia, swallowing dysfunction, and dysarthria. Repeat imaging demonstrated interval enlargement of the aneurysm with significant periluminal thrombosis causing mass effect on the optic chiasm, brainstem, and cerebral aqueduct resulting in obstructive hydrocephalus [
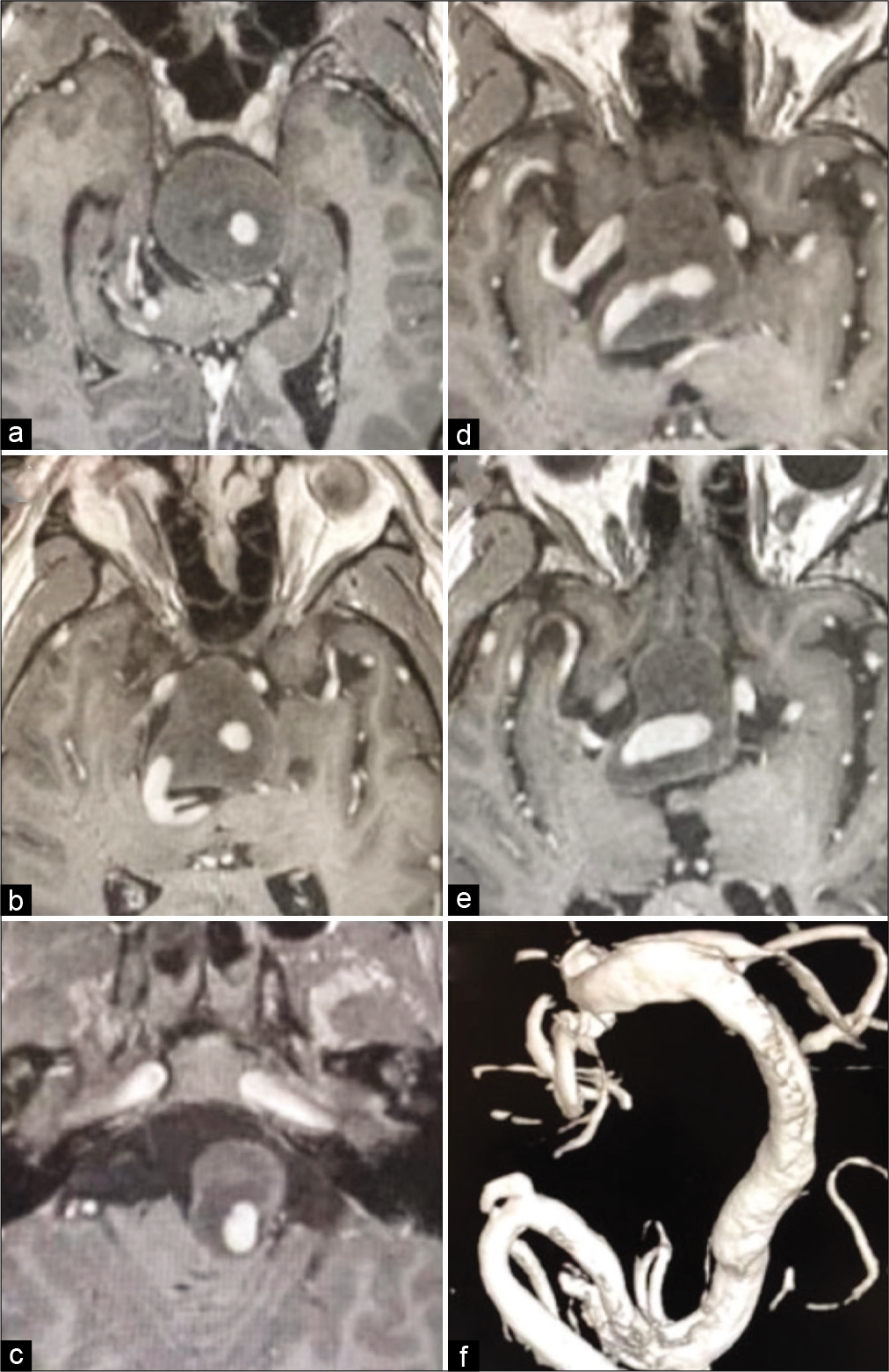
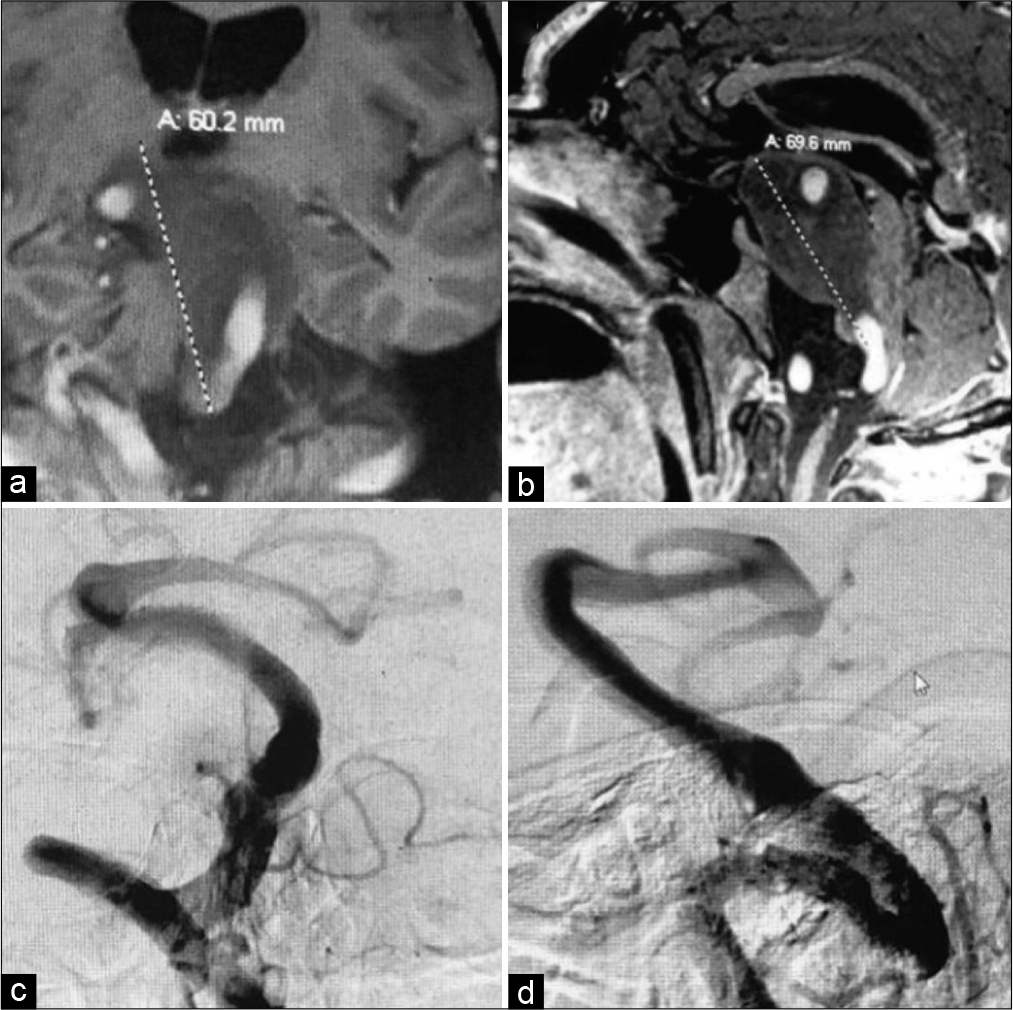
Figure 3:
(a) Coronal and (b) sagittal T1-weighted magnetic resonance image showing massive partially thrombosed enlargement of the aneurysm, marked by the dashed lines, with hydrocephalus and brainstem/optic chiasm compression. (c) AP and (d) lateral left vertebral angiogram demonstrating mildly increased caliber of the patent portion of the aneurysm when compared to 2013.
Due to the progressive nature of the lesion and his worsening symptoms, the decision was made to proceed with intervention. However, given the extent of thrombosis within the aneurysm and the involvement of the basilar apex, it was believed that bypassing with flow reversal and vertebral artery sacrifice carried too much risk of periprocedural mortality and would not result in any further meaningful reduction in the size and resultant mass effect of the thrombosed portion of the aneurysm.[
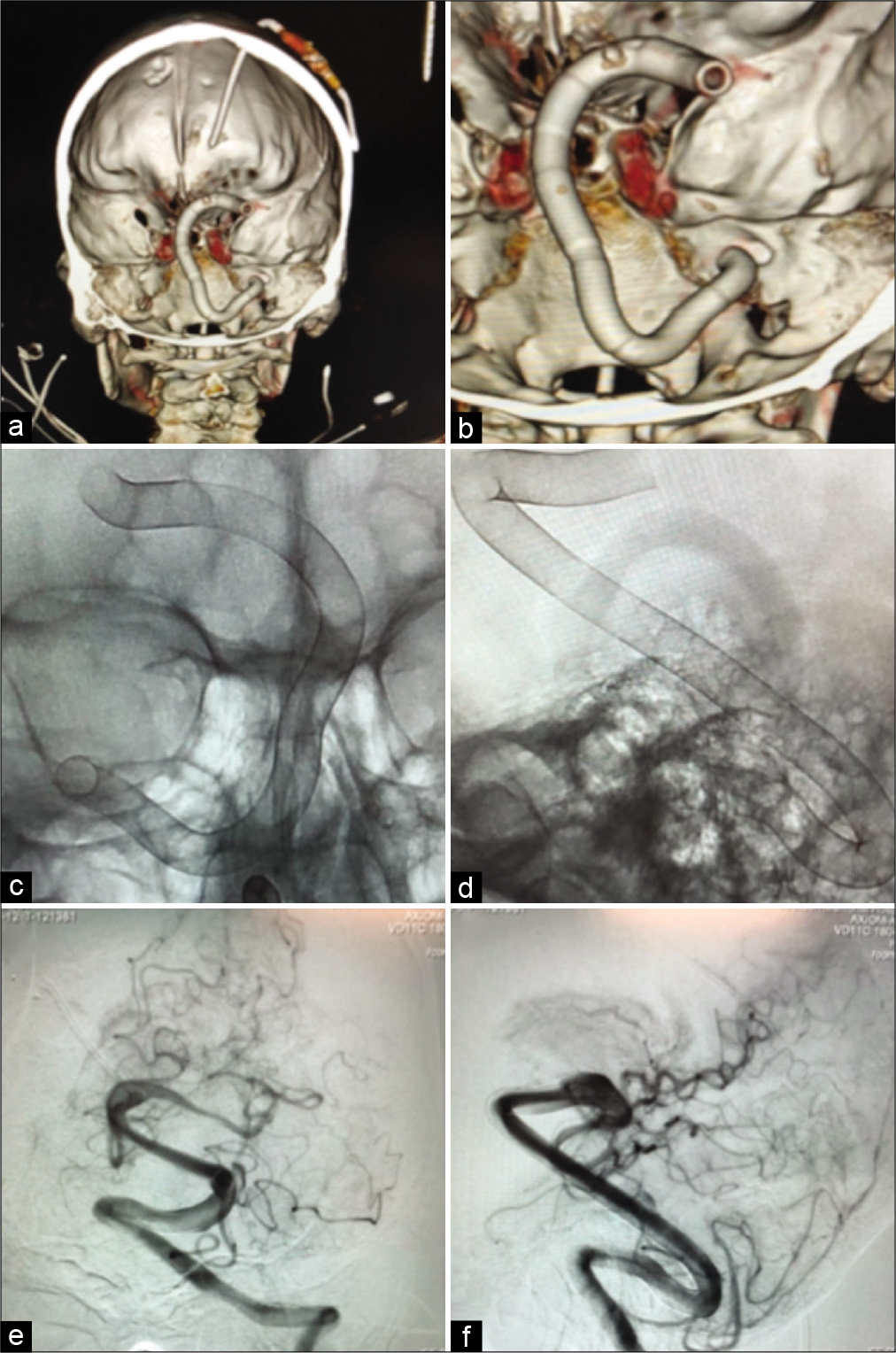
Figure 4:
(a and b) 3D computed tomography reconstructions of the telescoping stent construct. (c) AP and (d), lateral plane X-rays demonstrating placement of the stents within the aneurysm. (e) AP and (f) lateral left vertebral artery angiograms demonstrating patency of the stents without distal emboli after deployment.
The patient tolerated the procedure well and was discharged at his neurologic baseline. At nearly 1-year follow-up, the aneurysm was relatively stable in size and the patient remained at his neurologic baseline [
DISCUSSION
Dolichoectatic basilar trunk aneurysms remain some of the most difficult to treat with significant morbidity and mortality associated with any intervention.[
CONCLUSION
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report deploying multiple Pipeline Vantage Embolization Devices telescopically to treat a symptomatic partially thrombosed giant, dolichoectatic basilar trunk aneurysm. Our case illustrates the need for continued development of next generation flow diverters as there still remains aneurysms with very limited and potentially high risk, management options.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Anson JA, Lawton MT, Spetzler RF. Characteristics and surgical treatment of dolichoectatic and fusiform aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1996. 84: 185-93
2. Awad AJ, Mascitelli JR, Haroun RR, De Leacy RA, Fifi JT, Mocco J. Endovascular management of fusiform aneurysms in the posterior circulation: The era of flow diversion. Neurosurg Focus. 2017. 42: E14
3. Faught RW, Satti SR, Hurst RW, Pukenas BA, Smith MJ. Heterogeneous practice patterns regarding antiplatelet medications for neuroendovascular stenting in the USA: A multicenter survey. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014. 6: 774-9
4. Fiorella D, Lylyk P, Szikora I, Kelly M, Albuquerque F, McDougall C. Curative cerebrovascular reconstruction with the pipeline embolization device: The emergence of definitive endovascular therapy for intracranial aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. 2009. 1: 56-65
5. Lawton MT, Abla AA, Rutledge WC, Benet A, Zador Z, Rayz VL. Bypass surgery for the treatment of dolichoectatic basilar trunk aneurysms: A work in progress. Neurosurgery. 2016. 79: 83-99
6. Miyachi S, Hiramatsu R, Ohnishi H, Yagi R, Kuroiwa T. Usefulness of the pipeline embolic device for large and giant carotid cavernous aneurysms. Neurointervention. 2017. 12: 83-90
7. Starke RM, Thompson J, Pagani A, Choubey A, Wainwright JM, Wolf MF. Preclinical safety and efficacy evaluation of the pipeline vantage embolization device with shield technology. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020. 12: 981-6
8. Xu DS, Levitt MR, Kalani MY, Rangel-Castilla L, Mulholland CB, Abecassis IJ. Dolichoectatic aneurysms of the vertebrobasilar system: Clinical and radiographic factors that predict poor outcomes. J Neurosurg. 2018. 128: 560-6