- Department of Neurosurgery, Vardhman Mahavir Medical College and Safdarjung Hospital, New Delhi, Delhi, India
- Department of Neuroscience, Dr. B.L Kapur-Max Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi, Delhi, India.
Correspondence Address:
Amit Kumar Sharma, Department of Neurosurgery, Vardhman Mahavir Medical College and Safdarjung Hospital, New Delhi, Delhi, India.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_51_2024
Copyright: © 2024 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Amit Kumar Sharma1, Ruhi Mamualiya2, Atul Agrawal1. Analysis of the impact of intraventricular hemorrhage on the functional outcome of ruptured anterior cerebral artery aneurysm after clipping. 29-Mar-2024;15:105
How to cite this URL: Amit Kumar Sharma1, Ruhi Mamualiya2, Atul Agrawal1. Analysis of the impact of intraventricular hemorrhage on the functional outcome of ruptured anterior cerebral artery aneurysm after clipping. 29-Mar-2024;15:105. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/12834/
Abstract
Background: Various clinical symptoms and variables have been suggested as potential indicators of outcomes in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) resulting from ruptured intracranial aneurysms. The detailed discussion of the consequences of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), frequently reported in cases of anterior communicating artery (ACoA) aneurysms, is still pending. The study aimed to assess the results of aneurysm surgery performed early versus delayed in patients with SAH, specifically focusing on the occurrence of IVH.
Methods: This study involved patients with ACoA aneurysms who experienced SAH and underwent microsurgical clipping of the aneurysm. A retrospective review was conducted on the patients’ medical records. The modified Rankin score was compared between two groups of patients based on the presence or absence of IVH.
Results: Ninety-one participants (52 males and 39 females) were included in the study. The initial computed tomography scan showed that 20 patients (with a mean age of 51 ± 13.7 years) had IVH, while 71 patients (with a mean age of 45.8 ± 11.7 years) did not have any signs of IVH. The proportion of patients with poor functional outcomes after six months was 55% in the presence of IVH, compared to 25.4% in patients without IVH, indicating a significant difference in outcome between the two groups (P
Conclusion: Patients with SAH having aneurysms located in the ACoA associated with the intraventricular hemorrhage had a poor functional outcome.
Keywords: Aneurysm, Anterior communicating artery, Intraventricular hemorrhage, Lamina terminalis, Outcome
INTRODUCTION
A ruptured intracranial aneurysm stands as the primary cause of non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).[
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective study was done on the management of a ruptured anterior cerebral artery aneurysm presenting with SAH, focusing on the use of clipping. A total of 91 patients were included in the study. All information, such as clinical and radiological data, SAH grade based on the Hunt and Hess scale, WFNS score, and modified Fischer grade, were recorded. To compare, two groups were formed based on whether or not intra-ventricular hemorrhage was observed on the non-contrast computed tomography (CT) brain scan during the presentation. The at-discharge and 6-month follow-ups were recorded. The result was evaluated using the modified Ranking scale. The data were analyzed utilizing Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software version 23.0. The data for quantitative variables were given as the mean ± standard deviation, whereas frequencies and percentages were used to describe the qualitative factors. The comparison of two qualitative variables was conducted utilizing either the Chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests. The changes were deemed significant when P-values were below 0.05.
RESULTS
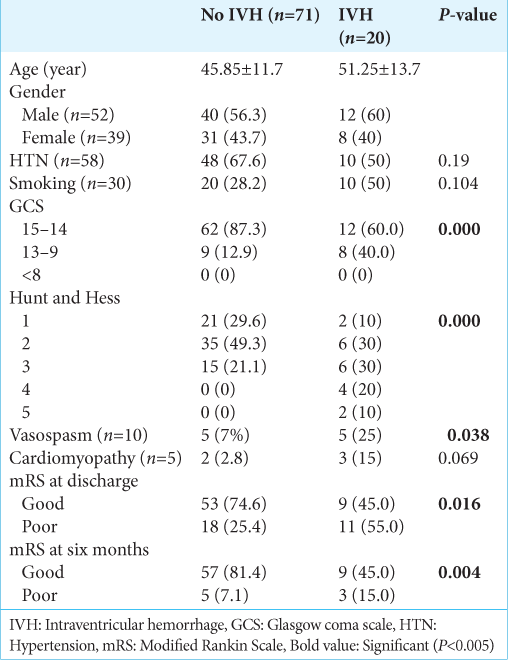
Ninety-one patients were analyzed in the study. the clinical-demographic profile is described in
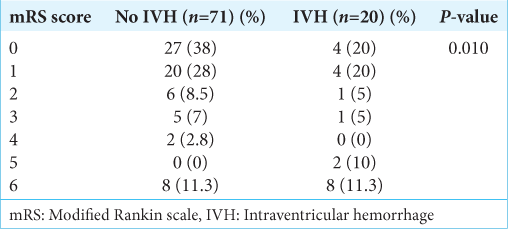
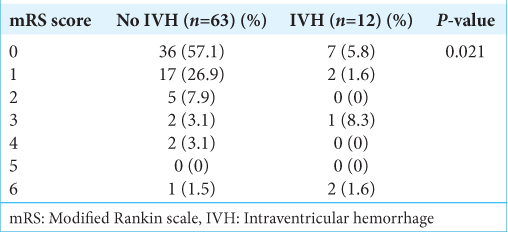
The extension to the ventricles, especially the third ventricle, was due to the blood passing from the subarachnoid cisterns and LT. Fifty-eight (63.7%) patients had a history of hypertension, and 30 (33%) had a history of smoking for variable durations. The most frequent Glasgow coma scale (GCS) at presentation was 15 in 62 (68.1%) patients, followed by 14 in 12 (13.2%) and 13 in 10 (11.0%) patients. The poor Hunt and Hess grade was found in 26 (28.6%), and poor WFNS was found in 11 (12.1%) patients. The patient was followed up for six months. It was found that the patients with IVH (20/91) had moderate GCS (13–8) at presentation in 9 (40%) patients, and it was found to be significant (P = 0.000). Similarly, poor Hunt and Hess (3–5) were found in 12 (60%) patients with intraventricular hemorrhage, which were statistically significant (P = 0.000). Ten (11%) patients had clinical vasospasm requiring intensive medical management. The difference between the IVH and no IVH groups was statistically significant (P = 0.038). However, no statistically significant correlation was found between cardiomyopathy and IVH (P = 0.06). The overall survival rate was 82.4%, with in-hospital mortality seen in 16 (17.6%). The functional outcome was assessed with a modified Rankin scale (mRS). Poor outcomes at discharge (mRS 3–6) were seen in 23 (25.3%) patients. The comparison of functional outcome at discharge is shown in
DISCUSSION
There is still ongoing debate and uncertainty surrounding various aspects of aneurysm surgery, such as the optimal timing for the procedure and the factors that can help predict the outcome.[
CONCLUSION
The occurrence of IVH can be a strong indicator of adverse outcomes in cases involving microsurgical treatment of ruptured ACoA aneurysms. Patients with ruptured ACoA aneurysms who had IVH on their initial CT scans experienced generally poor surgical outcomes in comparison to those without IVH.
Ethical approval
The Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent are not required as there are no patients in this study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Publication of this article was made possible by the James I. and Carolyn R. Ausman Educational Foundation.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Journal or its management. The information contained in this article should not be considered to be medical advice; patients should consult their own physicians for advice as to their specific medical needs.
References
1. Daniere F, Gascou G, Menjot de Champfleur N, Machi P, Leboucq N, Riquelme C. Complications and follow up of subarachnoid hemorrhages. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015. 96: 677-86
2. Davis KR, New PF, Ojemann RG, Crowell RM, Morawetz RB, Roberson GH. Computed tomographic evaluation of hemorrhage secondary to intracranial aneurysm. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976. 127: 143-53
3. De Gans K, Nieuwkamp DJ, Rinkel GJ, Algra A. Timing of aneurysm surgery in subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2002. 50: 336-40 discussion 340-2
4. Dorhout Mees SM, Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Algra A, Rinkel GJ. Timing of aneurysm treatment after subarachnoid hemorrhage: Relationship with delayed cerebral ischemia and poor outcome. Stroke. 2012. 43: 2126-9
5. Haley EC, Kassell NF, Torner JC. The international cooperative study on the timing of aneurysm surgery. The North American experience. Stroke. 1992. 23: 205-14
6. Inagawa T. Risk factors for cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A review of the literature. World Neurosurg. 2016. 85: 56-76
7. Jackson A, Fitzgerald JB, Hartley RW, Leonard A, Yates J. CT appearances of haematomas in the corpus callosum in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage. Neuroradiology. 1993. 35: 420-3
8. Ji Y, Meng QH, Xu Z, Zhang QL, Wang ZG. Correlation of surgical timing and prognosis for ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012. 92: 924-6 [Chinese]
9. Kassell NF, Torner JC, Haley EC, Jane JA, Adams HP, Kongable GL. The international cooperative study on the timing of aneurysm surgery. Part 1: Overall management results. J Neurosurg. 1990. 73: 18-36
10. Kitkhuandee A, Thammaroj J, Munkong W, Duangthongpon P, Thanapaisal C. Cerebral angiographic findings in patients with non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012. 95: S121-9
11. Nieuwkamp DJ, de Gans K, Algra A, Albrecht KW, Boomstra S, Brouwers PJ. Timing of aneurysm surgery in subarachnoid haemorrhage--an observational study in The Netherlands. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005. 147: 815-21
12. Ohman J, Heiskanen O. Timing of operation for ruptured supratentorial aneurysms: A prospective randomized study. J Neurosurg. 1989. 70: 55-60
13. Ozdemir G, Torun S, Bradshaw JR. Effect of circulating pattern and complicating factors on outcome for ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysms. Neurol Res. 1992. 14: 197-200
14. Pegoli M, Mandrekar J, Rabinstein AA, Lanzino G. Predictors of excellent functional outcome in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 2015. 122: 414-8
15. Risselada R, de Vries LM, Dippel DW, van Kooten F, van der Lugt A, Niessen WJ. Incidence, treatment, and case-fatality of non-traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage in the Netherlands. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2011. 113: 483-7
16. Roganovic Z, Pavlicevic G. Factors influencing the outcome after the operative treatment of cerebral aneurysms of anterior circulation. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2002. 59: 463-71
17. Ross N, Hutchinson PJ, Seeley H, Kirkpatrick PJ. Timing of surgery for supratentorial aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: Report of a prospective study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002. 72: 480-4
18. Solis OJ, Davis KR, New PF, Roberson GH. Evaluation of intracranial aneurysms by computed tomography. Rev Interam Radiol. 1976. 1: 1-8
19. Stoeter P, Reulen HJ, Groeger U. CT-findings in haemorrhages from aneurysms of the anterior communicating artery: Correlation with angiography and clinical course. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1987. 87: 22-30
20. Sviri GE, Feinsod M, Soustiel JF. Brain natriuretic peptide and cerebral vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Clinical and TCD correlations. Stroke. 2000. 31: 118-22
21. Sviri GE, Shik V, Raz B, Soustiel JF. Role of brain natriuretic peptide in cerebral vasospasm. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2003. 145: 851-60 discussion 860
22. Van Gijn J, Rinkel GJ. Subarachnoid haemorrhage: Diagnosis, causes and management. Brain. 2001. 124: 249-78
23. Weisberg LA. Ruptured aneurysms of anterior cerebral or anterior communicating arteries: CT patterns. Neurology. 1985. 35: 1562-6
24. Wong GK, Boet R, Ng SC, Chan M, Gin T, Zee B. Ultra-early (within 24 hours) aneurysm treatment after subarachnoid hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2012. 77: 311-5
25. Zhou GS, Song LJ. Influence of different surgical timing on outcome of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage and the surgical techniques during early surgery for ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Turk Neurosurg. 2014. 24: 202-7