- Department of Neurosurgery, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan
- Department of Neurosurgery, Uchikado Neuro-Spine Clinic, Fukuoka, Japan.
- Department of Neurosurgery, Saiseikai Fukuoka General Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan.
- Department of Neurosurgery, Ichinomiya Neurosurgical Hospital, Hita Oita, Japan.
Correspondence Address:
Jin Kikuchi, Department of Neurosurgery, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_624_2022
Copyright: © 2022 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Jin Kikuchi1, Hisaaki Uchikado2, Gohsuke Hattori1, Satoshi Nagase1, Yukihiko Nakamura3, Tomoya Miyagi4, Akira Okura3, Motohiro Morioka1. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt for normal pressure hydrocephalus patient exacerbates cord symptoms due to spinal tumor. 12-Aug-2022;13:352
How to cite this URL: Jin Kikuchi1, Hisaaki Uchikado2, Gohsuke Hattori1, Satoshi Nagase1, Yukihiko Nakamura3, Tomoya Miyagi4, Akira Okura3, Motohiro Morioka1. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt for normal pressure hydrocephalus patient exacerbates cord symptoms due to spinal tumor. 12-Aug-2022;13:352. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/11794/
Abstract
Background: Normal-pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) and spinal intradural extramedullary benign tumors rarely exist together. Here, a 72-year-old female who presented with NPH symptoms (i.e., gait disturbance and dementia) newly developed symptoms of spinal cord compression attributed to a previously undiagnosed schwannoma.
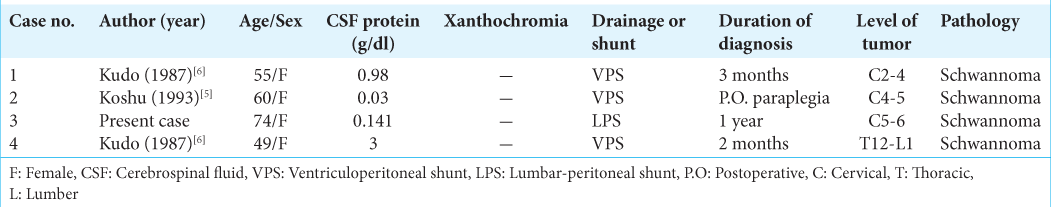
Case Description: A 72-year-old female was diagnosed with NPH without disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus. The lumbar puncture revealed an elevated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) protein level of 0.141 g/dl, but with normal pressure. The patient’s NPH symptoms improved after lumbar-peritoneal shunt placement. However, a year later, she subacutely developed a progressive Brown-Sequard syndrome. On the cervical magnetic resonance (MR), an intradural extramedullary lesion was found at the C5-C6 level which at surgery, proved to be a schwannoma. A review of this patient and three others with NPH and intradural extramedullary benign tumors revealed that 4.3 months following CSF shunting for NPH, they developed rapidly progressive cord deficits, attributed to their benign spinal tumors.
Conclusion: Before the placement of shunts for NPH, patients should undergo holospinal MR imaging studies to rule out attendant spinal intradural extramedullary tumors.
Keywords: Cerebrospinal fluid protein, Disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus, Normal-pressure hydrocephalus, Shunt surgery, Spinal schwannoma
INTRODUCTION
The concurrence of normal-pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) and spinal intradural extramedullary tumors has rarely been reported.[
CASE REPORT
A 72-year-old female presented with increased dementia (Mini-Mental State Examination [MMSE] score = 11) and gait disturbance. The brain computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MR) studies confirmed enlarged ventricles without a brain tumor; she was diagnosed with non disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus (DESH: a form of NPH[
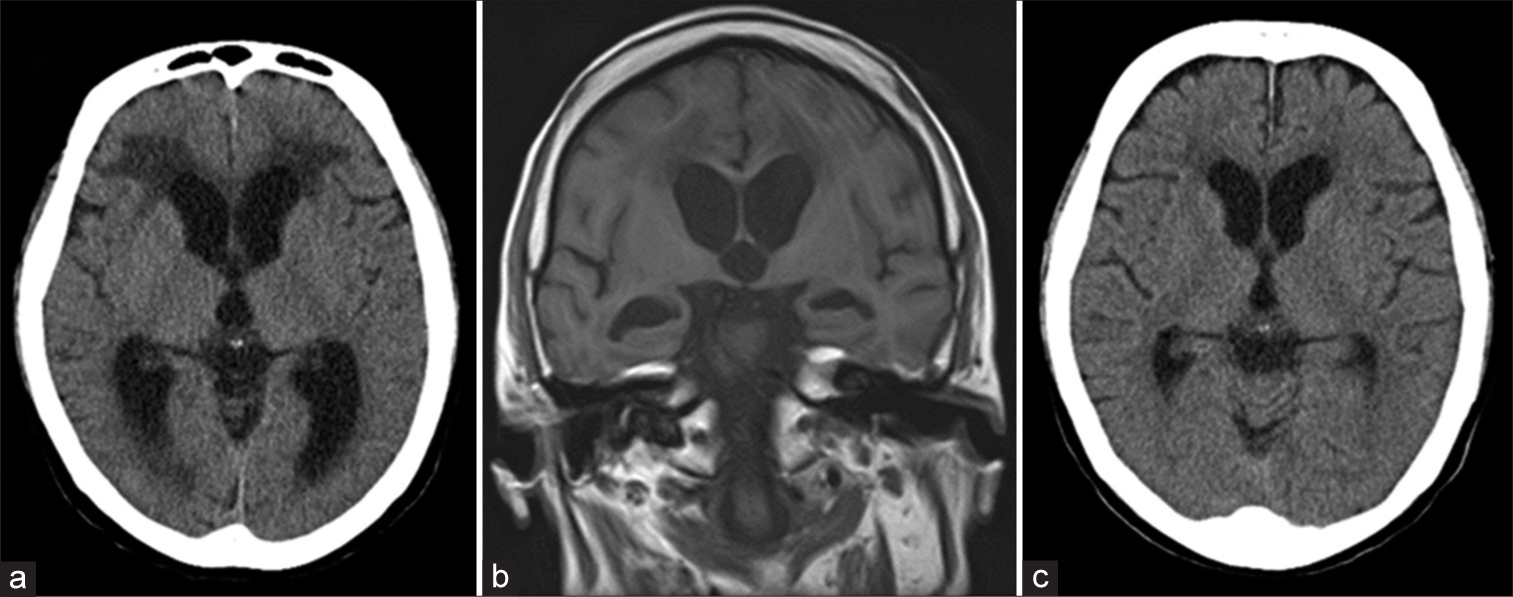
Figure 1:
Head computed tomography (CT) scan (a) and head magnetic resonance imaging (MRI; b) at onset showing enlargement of the ventricles. No typical disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus findings can be seen. There is no evidence of exacerbation of the hydrocephalus, such as enlargement of the ventricle, or over drainage on the head CT scan (c) when symptoms worsened.
One-year follow-up
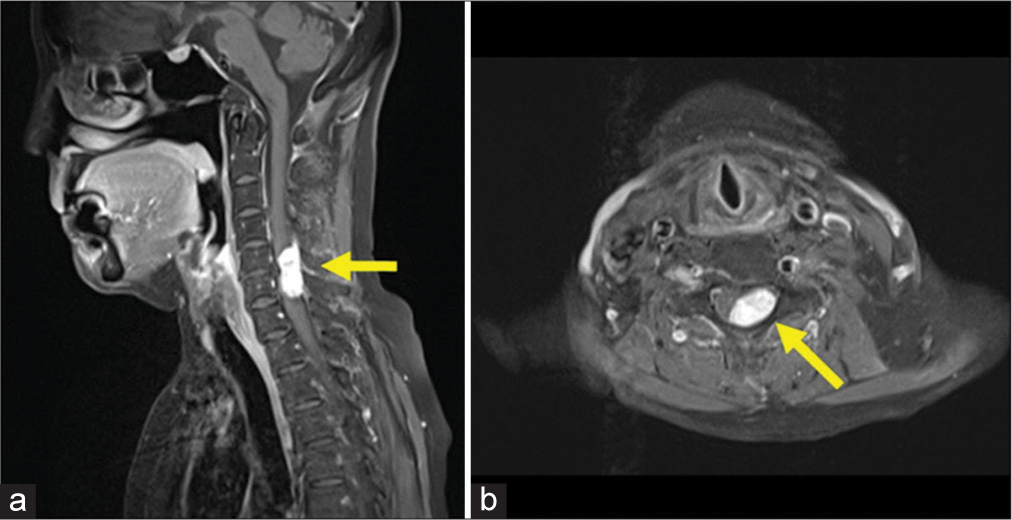
A year later, she presented with “abnormal sensations in the left hand and both lower extremities.” Within 1 month, findings extended to the right hand and she developed a progressive myelopathy (i.e., weakness in the left upper and both lower extremities 2/5 motor level) with diffuse hyperreflexia and abnormal sensory findings. The brain CT confirmed the ventricular size remained unchanged [
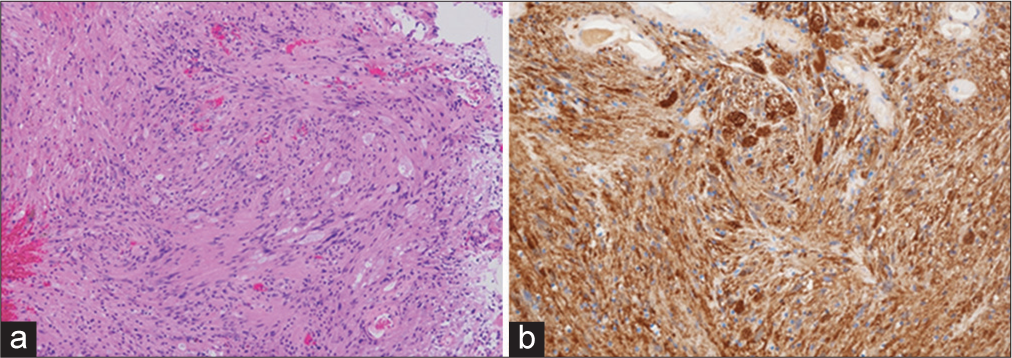
Figure 3:
Histopathological examination of an intradural extramedullary tumor. (a) Photomicrograph showing a bundle of spindle-shaped cells, some of which have a shelf-like arrangement of nuclei. Hematoxylin and eosin staining, ×100. (b) Immunohistochemical staining for S-100 protein showing strong and diffuse positive staining of the tumor cells. ×400.
DISCUSSION
Notably, in this patient with a diagnosis of NPH, the CSF cell protein elevation reflected the presence of an accompanying spinal tumor (i.e., range 0.03–4.073 g/dl).[
Cause of NPH with spinal tumors
There are several considerations regarding the cause of NPH with spinal tumors.[
Avoiding NPH shunt placement before spinal tumor removal to avoid precipitous neurological deterioration
Wajima et al., 13 patients with both NPH and intradural extramedullary spinal lesions underwent tumor removal before shunting with nine subsequently improving and not requiring shunt placement.[
CONCLUSION
A 72-year-old female with NPH became symptomatic 1 year later from a C5-C6 spinal intradural extramedullary schwannoma. This study demonstrates that before shunting for NPH, patients should undergo holospinal MRI studies to rule out accompanying spinal lesions that may be contributing to/responsible for NPH-like symptoms/signs due to their production of high-protein levels with resultant interference with CSF flow dynamics.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Di Russo P, Fava A, Vandenbulcke A, Miyakoshi A, Kohno M, Evins AI. Characteristics and management of hydrocephalus associated with vestibular schwannomas: A systematic review. Neurosurg Rev. 2021. 44: 687-98
2. Feldmann E, Bromfield E, Navia B, Pasternak GW, Posner JB. Hydrocephalic dementia and spinal cord tumor: Report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Neurol. 1986. 43: 714-8
3. Hashimoto M, Ishikawa M, Mori E, Kuwana N. Diagnosis of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus is supported by MRI-based scheme: A prospective cohort study. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res. 2010. 7: 18
4. Khoulali M, Haouas MY, Mortada J, Srour R. Tumors of the conus medullaris and of the cauda equina associated with chronic hydrocephalus: About 2 cases. Pan Afr Med J. 2018. 29: 206
5. Koshu K, Tominaga T, Fujii Y, Yoshimoto T. Quadraparesis after a shunting procedure in a case of cervical spinal neurinoma associated with hydrocephalus: Case report. Neurosurgery. 1993. 32: 669-71
6. Kudo H, Tamaki N, Kim S, Shirataki K, Matsumoto S. Intraspinal tumors associated with hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 1987. 21: 726-31
7. Wajima D, Ida Y, Inui T, Nakase H. Normal pressure hydrocephalus caused by a spinal neurinoma at the cauda equina level: A case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014. 54: 423-7