- Department of Neurosurgery, Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University School of Medicine, Detroit, Michigan,
- Seattle Science Foundation, Seattle, Washington, USA.
Correspondence Address:
Shiwei Huang
Department of Neurosurgery, Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University School of Medicine, Detroit, Michigan,
Seattle Science Foundation, Seattle, Washington, USA.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_240_2019
Copyright: © 2019 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Shiwei Huang, Ari D. Kappel, Catherine Peterson, Parthasarathi Chamiraju, Gary B. Rajah, Marc D. Moisi. Cervical spondylodiscitis caused by Candida albicans in a non-immunocompromised patient: A case report and review of literature. 02-Aug-2019;10:151
How to cite this URL: Shiwei Huang, Ari D. Kappel, Catherine Peterson, Parthasarathi Chamiraju, Gary B. Rajah, Marc D. Moisi. Cervical spondylodiscitis caused by Candida albicans in a non-immunocompromised patient: A case report and review of literature. 02-Aug-2019;10:151. Available from: http://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/9557/
Abstract
Background: Fungal cervical spondylodiscitis is rare and accounts for less than 1% of all cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebral osteomyelitis and discitis.
Case Description: A 32-year-old non-immunocompromised male presented with persistent neck pain and paresthesias. The magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine demonstrated a contrast-enhancing erosive lesion involving the cervical C6 and C7 vertebral bodies accompanied by epidural phlegmon. Blood culture was negative. The patient underwent a C6 and C7 anterior corpectomy with instrumented fusion (e.g., expandable cage C5 to T1). Intraoperatively, frank pus was noted within the C6-C7 disc space and was accompanied by thick prevertebral and epidural phlegmon extending from C5 to T1. Intraoperative cultures grew Candida albicans. Three days later, a C6-C7 laminectomy with C4-T2 posterior instrumented fusion was performed; the cultures again grew C. albicans. The patient was treated with intravenous micafungin for 14 days followed by 6–12 months of 400 mg oral fluconazole daily.
Conclusion: There are few cases in literature where non-immunocompromised patients developed fungal cervical spondylodiscitis. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate management are critical to effectively treat these patients. Surgical intervention may warrant corpectomy, discectomy, and operative debridement followed by long-term targeted antifungal therapy.
Keywords: Candida albicans, Cervical spine, Discitis, Osteomyelitis, Spondylodiscitis
INTRODUCTION
Osteomyelitis of the spine accounts for 2%–7% of all bony infections. Only 10% of spondylodiscitis cases involve the cervical spine.[
CASE DESCRIPTION
History and physical examination
A 32-year-old male with a history of intravenous drug use and hepatitis B and C presented with a 2-month history of progressive limited cervical range of motion, neck pain, bilateral upper extremity weakness, and paresthesias. His examination revealed mild 4/5 bilateral upper extremity weakness, right greater than left, with mild bilateral hyperreflexia, and significant kyphosis.
Diagnostic workup
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance studies
The computed tomography (CT) scan demonstrated severe bony erosion of the C6-C7 vertebral bodies with kyphosis and retropulsion of bone into the central canal, resulting in marked cord/root compression [
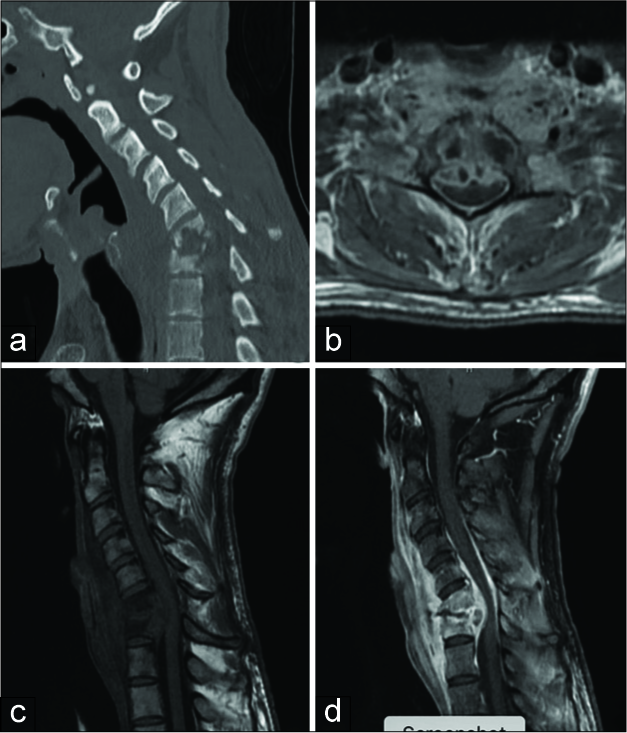
Figure 1:
Sagittal (a) computed tomography without contrast, axial T1 magnetic resonance imaging w/contrast (b) and sagittal T1 magnetic resonance imaging without (c) and with (d) contrast demonstrate an enhancing erosive lesion involving the C6 and C7 vertebral bodies with peripherally enhancing fluid collection within the intervertebral disc space and a large fluid collection along the posterior aspect of the vertebral bodies with compression of the ventral spinal cord at C6-C7. There is also extensive prevertebral swelling with anterior and posterior epidural enhancement extending from C4 to T1.
Laboratory studies
Laboratory studies demonstrated nonspecific markers of inflammation (e.g., erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR] of 24 mm/h, and C-reactive protein [CRP] of 23.1 mg/L). Blood cultures before antibiotic or antifungal therapy were negative. The patient tested negative for human immunodeficiency virus and tuberculosis.
Hospital course
The patient underwent a C6 and C7 anterior corpectomy with instrumented fusion (e.g., placement of an expandable cervical cage and C5 to thoracic [T] 1 anteriorly). Intraoperatively, frank pus was noted within the C6-C7 disc space and was accompanied by thick prevertebral and epidural phlegmon extending from C5 to T1. Three days later, a C6-C7 laminectomy with C4-T2 posterior instrumented fusion was performed [
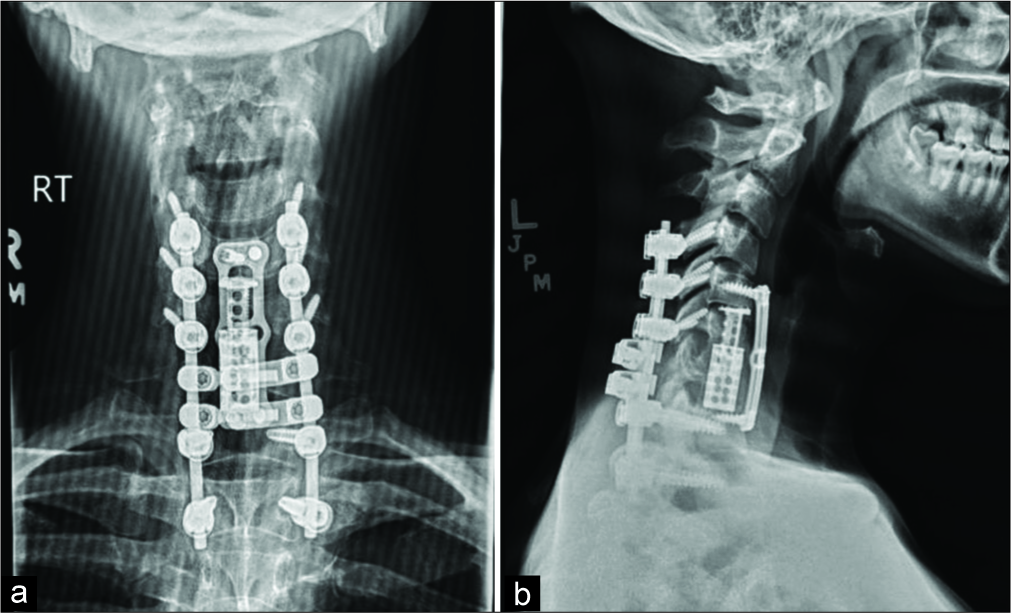
Figure 2:
Postoperative cervical X-rays anterior-posterior (a) and lateral (b) show placement of C6-C7 expandable cervical cage and C5 to T1 anterior discectomy with instrumentation and fusion, as well as posterior C4 to T2 instrumentation and fusion with C6 and C7 laminectomy. There is restoration of normal anatomic height with interval improvement in alignment of the cervical spine and reduction of the preoperative kyphotic deformity.
DISCUSSION
The most common pathogen involved in spondylodiscitis is Staphylococcus aureus. With the current increase of broad-spectrum antibiotics and central venous catheter use, the incidence of fungal spondylodiscitis is on the rise. The involvement of Candida species is rare and only occurs in 0.3%–2% cases of spondylodiscitis.[
Risk factors
Risk factors for C. albicans spondylodiscitis include long courses of broad-spectrum antibiotics, central venous catheter use, intravenous drug use, poorly controlled diabetes, immunosuppressive therapies, and spinal surgeries.[
Laboratory studies for Candida spondylodiscitis
Candida spondylodiscitis can occur either as a result of a contiguous infection, direct inoculation (through lumbar puncture, spinal anesthesia, or spinal surgery), or hematogenous spread after prolonged candidemia. The classical time interval between the initial candidemia and onset of spondylodiscitis is several months.[
XR, magnetic resonance, and computed tomography of Candida spondylodiscitis
MRI is the best imaging modality for spondylodiscitis; it delineates early erosive bony changes consisting of hypointensities in the vertebral bodies on T1-weighted images, the absence of disc hyperintensity, and preservation of the intranuclear cleft in the disc on T2-weighted images.[
Treatment of Candida spondylodiscitis
Candida osteomyelitis can be treated nonoperatively with a prolonged course of fluconazole or a lipid formulation of amphotericin B. Where applicable, optimizing risk factors such as tight glycemic control (e.g., in diabetics) or prompt removal of central venous catheters are often advocated. Surgical intervention may be necessary, particularly where nonsurgical measures fail. Critically, any evidence of new/progressive neurological deficits or radiological findings of significant spinal cord compression/instability may warrant surgical decompression with/without fusion.[
CONCLUSION
Cervical spondylodiscitis caused by C. albicans is rare, especially in non-immunocompromised patients. For those who present with progressive neurological deterioration, MR followed by CT findings of compressive/erosive/ osteomyelitis pathology warrants surgical intervention to avoid long-term sequelae.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient has given his consent for his images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
Dr. Moisi is a consultant for Synpative Medical.
Acknowledgment
We thank Drs. Emre Yilmaz and Ronen Blecher from Swedish Neuroscience Institute whose comments and suggestions have improved our manuscript.
References
1. Blecher R, Yilmaz E, Moisi M, Oskouian RJ, Chapman J. Extreme lateral interbody fusion complicated by fungal osteomyelitis: Case report and quick review of the literature. Cureus. 2018. 10: e2719-
2. Cottle L, Riordan T. Infectious spondylodiscitis. J Infect. 2008. 56: 401-12
3. Gamaletsou MN, Kontoyiannis DP, Sipsas NV, Moriyama B, Alexander E, Roilides E. Candida osteomyelitis: Analysis of 207 pediatric and adult cases (1970-2011). Clin Infect Dis. 2012. 55: 1338-51
4. Hendrickx L, Van Wijngaerden E, Samson I, Peetermans WE. Candidal vertebral osteomyelitis: Report of 6 patients, and a review. Clin Infect Dis. 2001. 32: 527-33
5. Kulcheski ÁL, Graells XS, Benato ML, Santoro PG, Sebben AL. Fungal spondylodiscitis due to Candida albicans An atypical case and review of the literature. Rev Bras Ortop. 2015. 50: 739-42
6. Richaud C, De Lastours V, Panhard X, Petrover D, Bruno F, Lefort A. Candida vertebral osteomyelitis (CVO) 28 cases from a 10-year retrospective study in france. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. 96: e7525-
7. Sans N, Faruch M, Lapègue F, Ponsot A, Chiavassa H, Railhac JJ. Infections of the spinal column spondylodiscitis. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2012. 93: 520-9
8. Tali ET. Spinal infections. Eur J Radiol. 2004. 50: 120-33