- Department of Plastic Surgery, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin, United States.
- Department of Vascular Surgery, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin, United States.
- Department of Neurosurgery, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin, United States.
Correspondence Address:
Amgad Hanna, Department of Neurosurgery, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin, United States.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_665_2023
Copyright: © 2024 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Pradeep Attaluri1, Shady Elmaraghi1, Claudia Vilela Casaretto1, Brian Gander1, Courtney Morgan2, Amgad Hanna3. Compressive median neuropathy caused by brachial artery pseudoaneurysm. 12-Jan-2024;15:11
How to cite this URL: Pradeep Attaluri1, Shady Elmaraghi1, Claudia Vilela Casaretto1, Brian Gander1, Courtney Morgan2, Amgad Hanna3. Compressive median neuropathy caused by brachial artery pseudoaneurysm. 12-Jan-2024;15:11. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/12703/
Abstract
Background: Brachial artery pseudoaneurysms (PSAs) are a rare complication of trauma and medical intervention, estimated to constitute 0.3–0.7% of all PSAs. Although neurologic symptoms are common in patients undergoing hemodialysis, direct nerve compression by large PSAs is rare.
Case Description: We report a case of median nerve compression by a brachial artery PSA treated by PSA resection and distal nerve transfer of the extensor carpi radialis brevis nerve to the anterior interosseous nerve.
Conclusion: This case illustrates the successful use of distal nerve transfers for the treatment of median neuropathy secondary to brachial PSA. In addition, this case highlights the importance of imaging before any exploratory nerve surgery in the setting of a mass and/or prior vascular procedure. Embarking on a nerve release/ repair surgery in the absence of a vascular surgeon would be disastrous.
Keywords: Brachial artery pseudoaneurysm, Nerve compression, Nerve transfer
INTRODUCTION
Brachial artery pseudoaneurysms (PSAs) are a rare complication of trauma and medical intervention, estimated to constitute 0.3–0.7% of all PSAs.[
CASE PRESENTATION
A 69-year-old male presented to our multidisciplinary brachial plexus clinic with severe proximal median neuropathy causing paresthesia in the median nerve distribution, benediction hand [
Figure 1:
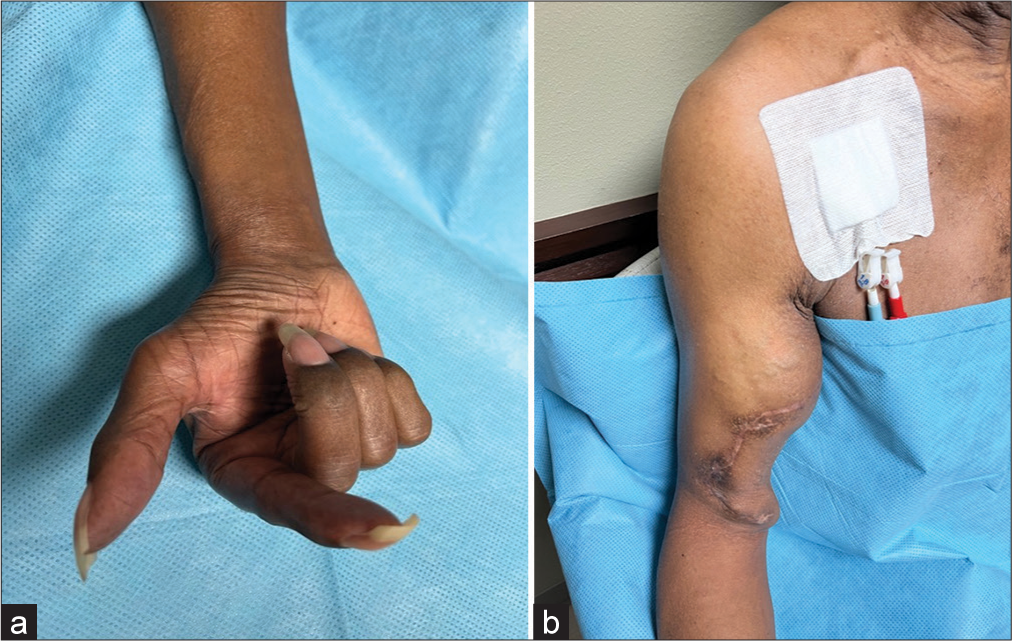
(a) Preoperative presentation of the patient showing physical examination consistent with benediction hand. (b) Preoperative photograph showing compressible swelling in the upper arm. A positive Tinel’s sign over the expected course of the median nerve in the upper arm was also noted to be present.
On initial physical examination, he demonstrated Medical Research Council (MRC) Grade 4/5 pronator teres (PT) strength, 0/5 FPL, 0/5 abductor pollicis brevis (APB), 0/5 flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS), 0/5 FDP to index finger, and 4/5 FDP to the remaining fingers. Sensory examination was significant for diminished sensation to light touch in the palmar cutaneous branch distribution and 10–14 mm static two-point discrimination in the median nerve distribution of the fingers. In addition, he had a positive Tinel sign and sensory collapse test over the carpal tunnel and PT. He was noted to have compressible swelling over the medial upper arm [
Electrodiagnostic studies were obtained and confirmed severe median neuropathy proximal to the takeoff of the PT. These electrodiagnostic findings suggested a severe median neuropathy localizing proximal to the elbow. In addition, low compound muscle action potentials (CMAPs) and absent sensory nerve conduction suggested some degree of axonal injury.
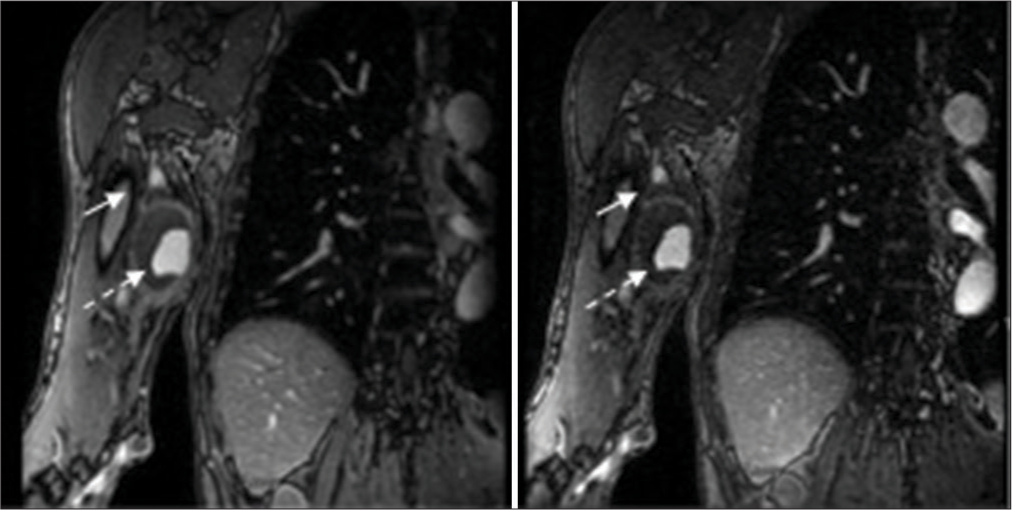
Magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance angiography were also obtained and showed a 4.6 cm × 4.2 cm × 6.7 cm mass, likely a PSA within the brachial artery, compressing the median nerve [
Figure 2:
A 4.2 × 5.2 × 6.7 cm mass located at the level of the mid humeral shaft abutting the medial aspect of the brachial artery (dashed arrow). The median nerve (solid arrow) demonstrates thickening, edema, and abnormal enhancement at the level of the mass through the distal humerus. The median nerve is compressed as it contours the anterior margin of the mass.
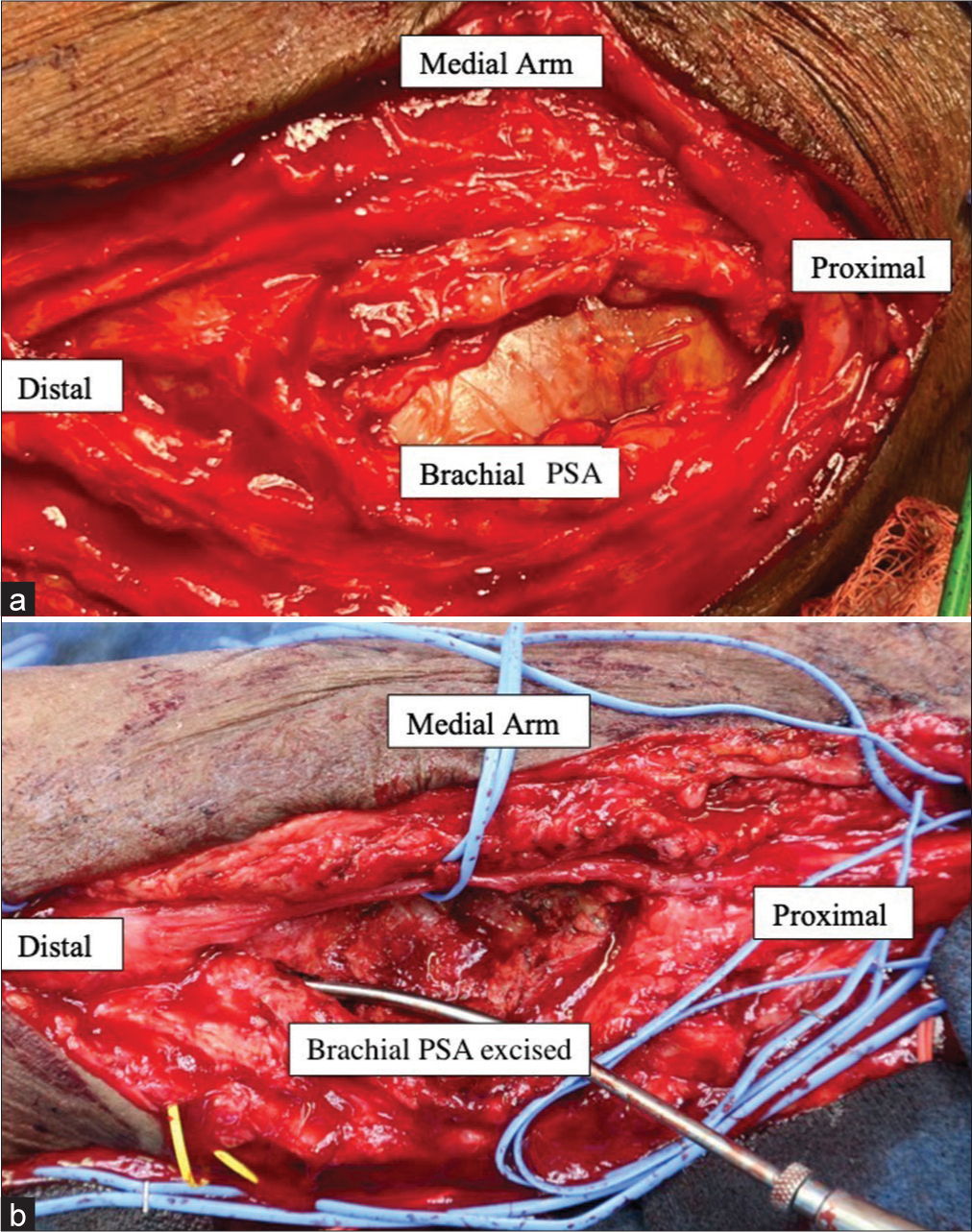
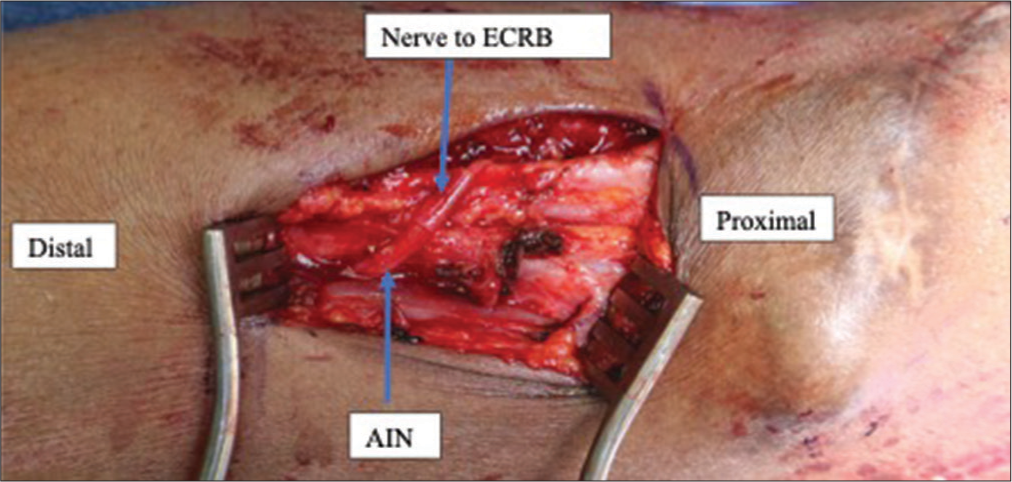
In conjunction with vascular surgery who planned to resect and repair the brachial artery PSA, we decided to proceed with decompression of the median nerve in the upper arm, forearm, and carpal tunnel, along with distal extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) to anterior interosseous nerve (AIN) transfer to restore pinch. Intraoperatively, we were able to successfully resect and reconstruct the brachial artery PSA [
At 1-year follow-up, the patient has regained some function of the median nerve. On physical examination, he was found to have MRC grade 2/5 FPL strength, FDS 2/5, FDP to the index 2/5, and APB 0/5. On transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation examination, he notes sensation in the palmar cutaneous branch distribution to be 60% of the contralateral side and sensation in the fingers in the median nerve distribution around 40% of the contralateral side. He is currently planning to undergo opponensplasty to restore thumb opposition.
DISCUSSION
Previous studies reporting on the treatment of arterial PSA causing nerve compression have focused on decompression by surgical management of the PSA. Papadopoulos et al. reported two cases of median neuropathy associated with a brachial artery aneurysm in which neurological symptoms completely resolved after resection of the compressive PSA.[
We report a case of delayed presentation of severe proximal median neuropathy with evidence of axonal loss on electrodiagnostic studies. In this case, it is unclear whether axonal loss was induced by prolonged unrecognized compression or by direct injury during dialysis access. However, we elected to perform distal nerve transfers due to the low likelihood of spontaneous motor recovery after this prolonged period of denervation and the distance from the level of injury to the target. This is further supported by the lack of recovery of the median innervated hand intrinsics one year after PSA resection and median nerve release.
CONCLUSION
To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of the successful use of distal nerve transfers for the treatment of median neuropathy secondary to brachial PSA. In addition, this case illustrates the importance of imaging before any exploratory nerve surgery in the setting of a mass and/or prior vascular procedure. Embarking on a nerve release/ repair surgery in the absence of a vascular surgeon would have been a disaster in this case.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Journal or its management. The information contained in this article should not be considered to be medical advice; patients should consult their own physicians for advice as to their specific medical needs.
References
1. Borghese O, Pisani A, DiCenta Isabelle. Treatment of iatrogenic pseudoaneurysm of the brachial artery: Case report and literature review. Vascu Dis Manag. 2019. 16: E87-91
2. Chemla E, Nortley M, Morsy M. Brachial artery aneurysms associated with arteriovenous access for hemodialysis. Semin Dial. 2010. 23: 440-4
3. Ergungor MF, Kars HZ, Yalin R. Median neuralgia caused by brachial pseudoaneurysm. Neurosurgery. 1989. 24: 924-5
4. Hatano M, Kitajima I, Yamamoto S, Nakamura M, Isawa K, Suwabe T. Dialysis-related carpal tunnel syndrome in the past 40 years. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2022. 26: 68-74
5. Lijftogt N, Cancrinus E, Hoogervorst EL, Mortel RH, Vries JP. Median nerve neuropraxia by a large false brachial artery aneurysm. Vascular. 2014. 22: 378-80
6. Lobo J, Ferreira MC, Ramos PN. Pseudoaneurysm of brachial artery: A rare cause of median nerve compression. Trauma Case Rep. 2018. 14: 8-10
7. Papadopoulos SM, McGillicuddy JE, Messina LM. Pseudoaneurysm of the inferior gluteal artery presenting as sciatic nerve compression. Neurosurgery. 1989. 24: 926-8
8. Rahimizadeh A, Davaee M, Shariati M, Rahimizadeh S. Posterior tibial neuropathy secondary to pseudoaneurysm of the proximal segment of the anterior tibial artery with delayed onset. J Brachial Plexus Peripher Nerve Inj. 2018. 13: e15-9
9. Santiago FR, Villares PJ, Fernández JM, Parra FM. Median nerve compression by an iatrogenic pseudoaneurysm of brachial artery. Eur J Radiol Extra. 2004. 50: 75-6
10. Villanueva AG, de Oña IR, de Oya AS. Median nerve compression caused by brachial pseudoaneurysm: Report of two cases and review of the literature. J Hand Microsurg. 2016. 8: 109-10