- Department of Neurosurgery, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY, United States.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_16_2020
Copyright: © 2020 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Zaid Aljuboori, Kimberly Meyer, Mayur Sharma, Tyler Ball, Haring Nauta. Cost comparison among punctate midline myelotomy, intrathecal pain pump, and spinal cord epidural stimulator. 18-Feb-2020;11:25
How to cite this URL: Zaid Aljuboori, Kimberly Meyer, Mayur Sharma, Tyler Ball, Haring Nauta. Cost comparison among punctate midline myelotomy, intrathecal pain pump, and spinal cord epidural stimulator. 18-Feb-2020;11:25. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/9873/
Abstract
Background:Invasive pain procedures can be valuable tools to manage chronic pain. Here, we compared the costs of three procedures used to address chronic pain; punctate midline myelotomy (PMM), placement of a spinal cord stimulator (SCS), or placement of an intrathecal pain pump (ITPP).
Case Description:This retrospective chart review yielded 9 patients with chronic pain syndromes; 3 had PMM, 3 had SCS, and 3 had ITPP procedures. Variables studied included; pain type, the procedures performed, and the cost of each procedure. The Wilcoxon rank-sum and one-way analysis of variance were used to compare the three groups (P
Conclusion:For the three pain procedures discussed in this report, PMM is the most cost-effective as it obviates the need for efficacy trials, and there are: no implant device costs, no medication refills, no maintenance costs, and no complication management costs.
Keywords: Cost, Intrathecal, Myelotomy, Pain, Pump, Refractory, Stimulator
INTRODUCTION
Several reports have shown that three invasive pain procedures, punctate midline myelotomy (PMM), spinal cord stimulation (SCS), and intrathecal drug delivery, can be beneficial to treat chronic pain syndromes and reduce consumption of opioids;[
METHODS
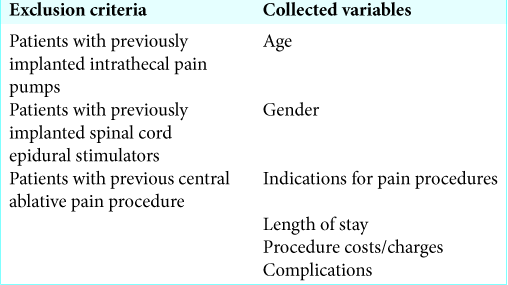
We performed a retrospective chart review for 9 patients with chronic pain syndromes who underwent PMM (3 patients), SCS (3 patients), and ITPP (3 patients) procedures at our institution. Patients had to be >18 years of age with chronic pain resistant to conventional pain protocols [
RESULTS
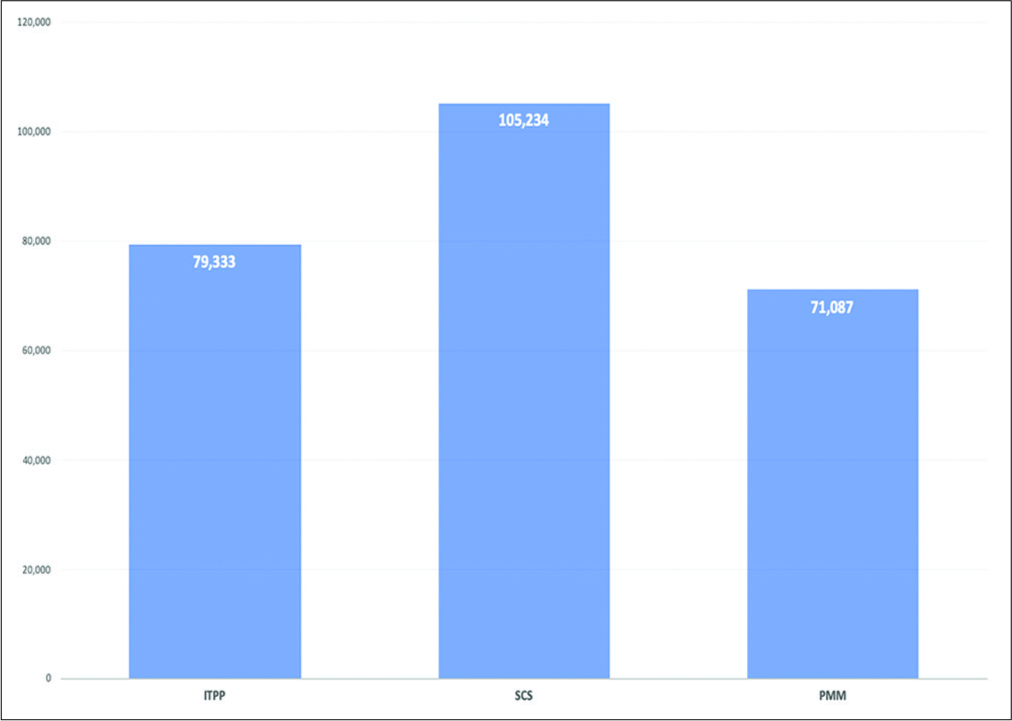
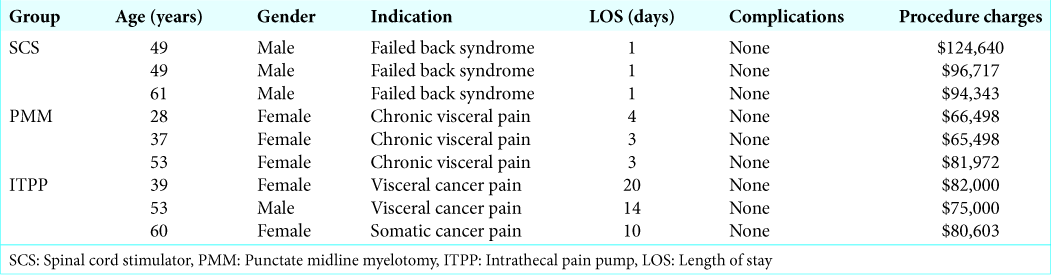
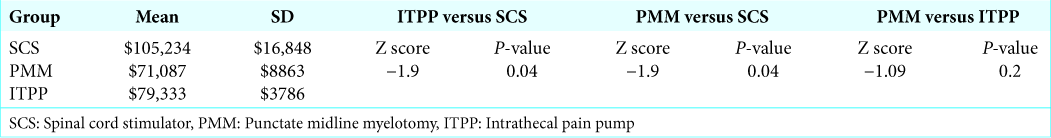
In the SCS, PMM, and ITPP group patients, respectively, averaged 53, 39.3, and 50.7 years of age. The indications for these chronic pain procedures included: SCS for failed back syndrome, PMM for non-malignant visceral pain, and ITPP; two for chronic visceral cancer pain and one for chronic somatic cancer pain. There were no complications in any of the three groups. For SCS, PMM, and ITPP, SCS had the shortest LOS and ITPP the longest: 1, 3.6 ± 0.6 and 15 ± 5.6 days, respectively. Notably, SCS was significantly more expensive ($105,234) than PMM ($71,087) and ITPP ($79,333): the latter two had comparable average costs [
DISCUSSION
All three pain procedures (SCS, PMM, and ITPP) achieve good pain control and reduced the consumption of opioids.[
Relative cost analysis
For PMM, the mean cost was the lowest ($71,087) with the lowest LOS of 1 day, e.g. it does not require a preimplantation trial or annual maintenance cost. Although ITPP initially cost $79,333 with the longest mean LOS was 15 days, it had many other drawbacks both treatment and financial; a preimplantation trial, needed intermittent refills, had initial (median of 1.1 year), and late failures (median 5.9 years) required monthly costs of medication (about $486) and the cost of 1st year – $18,00–30,000 versus later complications ($1000–32,000).[
CONCLUSION
Three invasive pain procedures SCS, PMM, and ITPP help patients with chronic pain refractory to conventional regimens and may be performed safely and effectively. Here, we found: SCS had the shortest LOS (1 day) and ITPP the longest (15 ± 5.6 days), respectively, but SCS was significantly more expensive ($105,234) than PMM ($71,087) or ITPP ($79,333).
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patient’s identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Bell GK, Kidd D, North RB. Cost-effectiveness analysis of spinal cord stimulation in treatment of failed back surgery syndrome. J Pain Symptom Manage. 1997. 13: 286-95
2. Bhatia G, Lau ME, Koury KM, Gulur P. Intrathecal drug delivery (ITDD) systems for cancer pain. F1000Res. 2013. 2: 96-
3. Brogan SE, Winter NB, Abiodun A, Safarpour R. A cost utilization analysis of intrathecal therapy for refractory cancer pain: Identifying factors associated with cost benefit. Pain Med. 2013. 14: 478-86
4. Burchiel KJ, Raslan AM. Contemporary concepts of pain surgery. J Neurosurg. 2019. 130: 1039-49
5. Jeon YH. Spinal cord stimulation in pain management: A review. Korean J Pain. 2012. 25: 143-50
6. Kumar K, Bishop S. Financial impact of spinal cord stimulation on the healthcare budget: A comparative analysis of costs in Canada and the United States. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009. 10: 564-73
7. Meyer R, Patel AM, Rattana SK, Quock TP, Mody SH. Prescription opioid abuse: A literature review of the clinical and economic burden in the United States. Popul Health Manag. 2014. 17: 372-87
8. Nauta HJ, Soukup VM, Fabian RH, Lin JT, Grady JJ, Williams CG. Punctate midline myelotomy for the relief of visceral cancer pain. J Neurosurg. 2000. 92: 125-30