- Department of Radiological Technology, Tohoku University Hospital, Tohoku University, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan,
- Department of Neurosurgery, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Tohoku University, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan,
- Department of Neurosurgical Engineering and Translational Neuroscience, Graduate School of Biomedical Engineering, Tohoku University, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan,
- Department of Neurosurgical Engineering and Translational Neuroscience, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan.
Correspondence Address:
Akira Ito, Neurosurgery, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_1190_2021
Copyright: © 2022 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Shingo Kayano1, Akira Ito2, Toshiki Endo2, Hitoshi Nemoto1, Kazuki Shimada1, Kuniyasu Niizuma2,3,4, Teiji Tominaga2. Efficacy of ultra-high-resolution computed tomographic angiography for postoperative evaluation of intracranial aneurysm after clipping surgery: A case report. 11-Mar-2022;13:85
How to cite this URL: Shingo Kayano1, Akira Ito2, Toshiki Endo2, Hitoshi Nemoto1, Kazuki Shimada1, Kuniyasu Niizuma2,3,4, Teiji Tominaga2. Efficacy of ultra-high-resolution computed tomographic angiography for postoperative evaluation of intracranial aneurysm after clipping surgery: A case report. 11-Mar-2022;13:85. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/11437/
Abstract
Background: Following clipping surgery for intracranial aneurysm, computed tomography angiography (CTA) is often used to confirm complete aneurysm obliteration. However, artifacts from the titanium clips usually degrade the images around them. The ultra-high-resolution computed tomography (UHR-CT) system recently became available in clinical practice. Here, we report a case in which CTA using the UHR-CT system successfully pointed out a small aneurysmal remnant after the clipping surgery, which was validated by digital subtraction angiography.
Case Description: A patient underwent clipping surgery for an unruptured aneurysm using two titanium alloy clips. CTA using the UHR-CT system demonstrated a small remnant aneurysm. Digital subtraction angiography confirmed the minor remnant. The UHR-CTA images were comparable to three-dimensional reconstructed images from the rotational angiography.
Conclusion: We propose that UHR-CTA is a reliable postoperative assessment method for intracranial clipping surgeries.
Keywords: Cerebral aneurysm, Computed tomography angiography, Digital subtraction angiography, Ultra-high-resolution computed tomography
INTRODUCTION
Clipping surgery is one of the established treatments for intracranial aneurysms.[
The ultra-high-resolution computed tomography (UHR-CT) system recently became available, and we recently reported usefulness of UHR-CT in the detection of the subcallosal artery.[
CASE DESCRIPTION
A patient underwent clipping surgery for an unruptured aneurysm. Two titanium alloy clips (Sugita Aneurysm Clip; Mizuho, Tokyo, Japan) were used for obliteration of the aneurysm. He/she underwent CTA using the UHR-CT system (Aquilion Precision; Canon Medical Systems, Otawara, Japan) after surgery [
Figure 1:
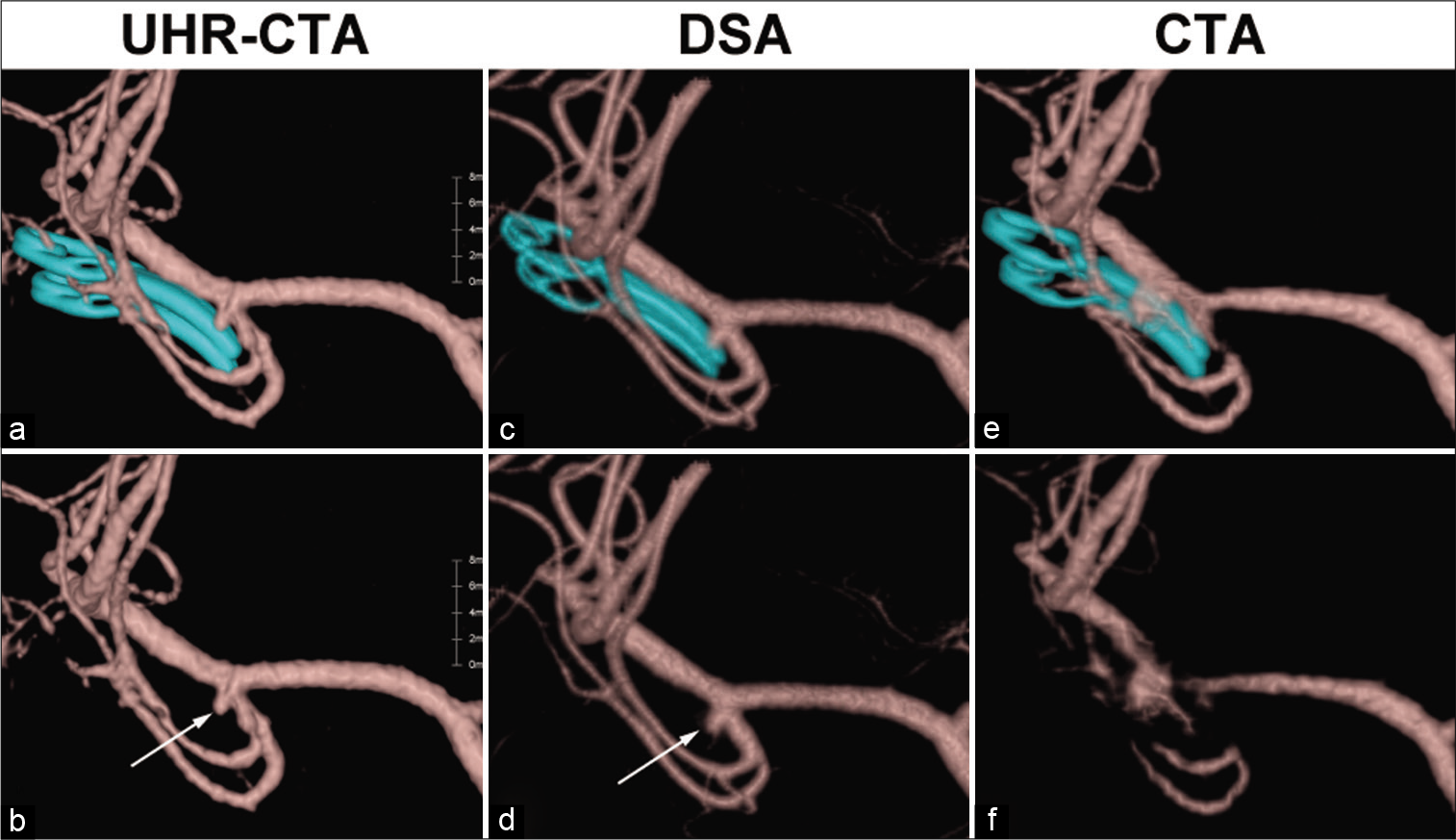
Small recurrent aneurysm after the clipping surgery. The volume rendering image on (a and d) ultra-high-resolution computed tomographic angiography (UHR-CTA) is comparable to (b and e) on digital subtraction angiography (DSA), and (c and f) on conventional CTA. The image from conventional CTA had considerably less optimal quality. The aneurysmal clips were removed manually in (d, e and f). Note that UHR-CTA and DSA were performed in 2020, whereas conventional CTA was performed in 2019. Arrows in (d and e) indicate small remnant of the aneurysm after clipping surgery.
Phantom study
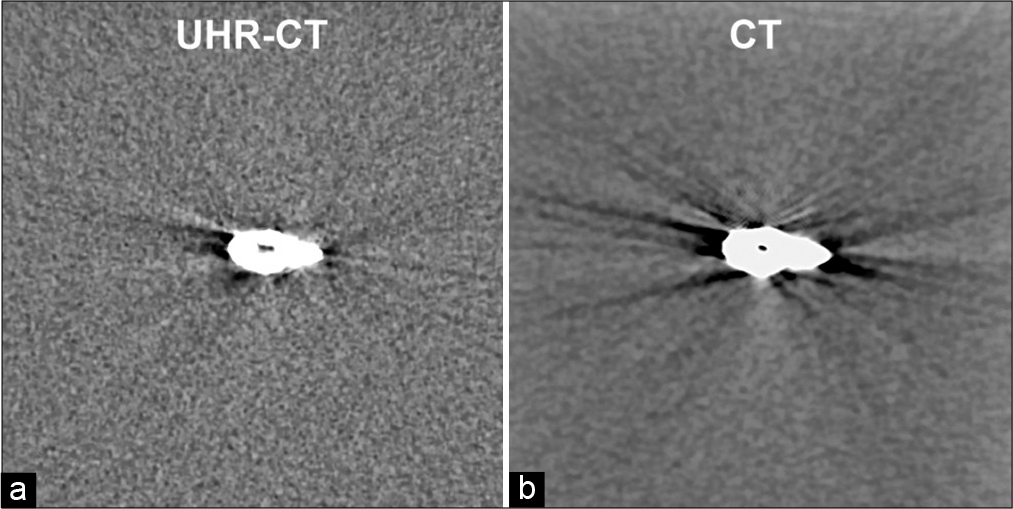
Using the same scanning parameters for UHR-CTA and conventional CTA, we performed the phantom studies (supplementary manuscript). The in vitro study demonstrated that the artifacts from the aneurysmal clip were less intense the image obtained in UHR-CT [
DISCUSSION
This is the first report demonstrating the efficacy of UHRCTA in evaluating aneurysms after clipping surgery, which successfully suppressed the artifacts from the clips.
The UHR-CT system has two distinct features that explain the quality improvement. First is the high spatial resolution. UHR-CT can provide images with a matrix of 1024 × 1024 and 0.25 mm section thickness,[
A recent meta-analysis indicated that CTA was not as accurate as DSA in ruling out postclipping remnant aneurysms;[
Declaration of patient consent
Institutional Review Board (IRB) permission obtained for the study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Manuscript
The following scanning parameters were used for the ultra-high-resolution computed tomography angiography (CTA): tube voltage = 120 kV, tube current = 240 mA, collimation = 0.25 mm × 160, beam pitch factor = 0.569, rotation speed = 0.75 s, slice thickness = 0.25 mm, slice interval = 0.25 mm, scanning FOV = 320 mm, and reconstruction kernel = forward-projected model-based iterative reconstruction solution (FIRST) algorithm. The image matrix size was 1024 × 1024 matrix and display field of view (FOV) of 200 mm.
The conventional CT scanning parameters were as follows: tube voltage = 120 kV, collimation = 0.5 mm × 320, 1.5 s/rot, slice thickness = 0.5 mmSR, slice interval = 0.25 mm, scan coverage = 160 mm of volume per rotation, and reconstruction kernel = FC44. Scanning FOV = 240 mm. CT-AEC was set on the condition that the standard deviation of 0.5 mm thickness images was equal to 7. Iterative and noise-reduction filters (AIDR3D enhanced mild), and a single energy metal artifact reduction algorithm were applied. The display FOV was 200 mm.
The above scanning parameters are used in the proposed phantom study and the clinical evaluations of the cerebral CT angiography in our institute.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
References
1. Golitz P, Struffert T, Ganslandt O, Lang S, Knossalla F, Doerfler A. Contrast-enhanced angiographic computed tomography for detection of aneurysm remnants after clipping: A comparison with digital subtraction angiography in 112 clipped aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2014. 74: 606-13
2. Kaufmann TJ, Huston J, Mandrekar JN, Schleck CD, Thielen KR, Kallmes DF. Complications of diagnostic cerebral angiography: Evaluation of 19, 826 consecutive patients. Radiology. 2007. 243: 812-9
3. Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, Clarke M, Sneade M, Yarnold JA. International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: A randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet. 2005. 366: 809-17
4. Sakuma I, Tomura N, Kinouchi H, Takahashi S, Otani T, Watarai J. Postoperative three-dimensional CT angiography after cerebral aneurysm clipping with titanium clips: Detection with single detector CT. Comparison with intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography. Clin Radiol. 2006. 61: 505-12
5. Sato Y, Endo T, Kayano S, Nemoto H, Shimada K, Ito A. Comparison between ultra-high-resolution computed tomographic angiography and conventional computed tomographic angiography in the visualization of the subcallosal artery. Surg Neurol Int. 2021. 12: 528
6. Uricchio M, Gupta S, Jakowenko N, Levito M, Vu N, Doucette J. Computed tomography angiography versus digital subtraction angiography for postclipping aneurysm obliteration detection. Stroke. 2019. 50: 381-8
7. Yanagawa M, Hata A, Honda O, Kikuchi N, Miyata T, Uranishi A. Subjective and objective comparisons of image quality between ultra-high-resolution CT and conventional area detector CT in phantoms and cadaveric human lungs. Eur Radiol. 2018. 28: 5060-8