- Department of Neurosurgery and Spine Surgery, Hanoi Medical University Hospital, Hanoi, Vietnam.
- The Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center, Bach Mai Hospital, Hanoi, Vietnam.
Correspondence Address:
Tam Duc Le, Department of Neurosurgery and Spine Surgery, Hanoi Medical University Hospital, Hanoi, Vietnam.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_687_2021
Copyright: © 2021 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Hung Dinh Kieu1, Duong Ngoc Vuong2, Khoa Trong Mai2, Phuong Cam Pham2, Tam Duc Le1. Long-term outcomes of rotating gamma knife for vestibular schwannoma: A 4-year prospective longitudinal study of 89 consecutive patients in Vietnam. 30-Nov-2021;12:585
How to cite this URL: Hung Dinh Kieu1, Duong Ngoc Vuong2, Khoa Trong Mai2, Phuong Cam Pham2, Tam Duc Le1. Long-term outcomes of rotating gamma knife for vestibular schwannoma: A 4-year prospective longitudinal study of 89 consecutive patients in Vietnam. 30-Nov-2021;12:585. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/?post_type=surgicalint_articles&p=11256
Abstract
Background: Microsurgical total removal of vestibular schwannoma (VS) is the definitive treatment but has a high incidence of postoperative neurological deficits. Rotating Gamma Knife (RGK) is a preferred option for a small tumor. This study aims to evaluate long-term neurological outcomes of RGK for VS.
Methods: This prospective longitudinal study was conducted at the Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center, Bach Mai Hospital, Hanoi, Vietnam. Eighty-nine consecutive patients were enrolled from October 2011 to October 2015 and followed up to June 2017. RGK was indicated for VS measuring
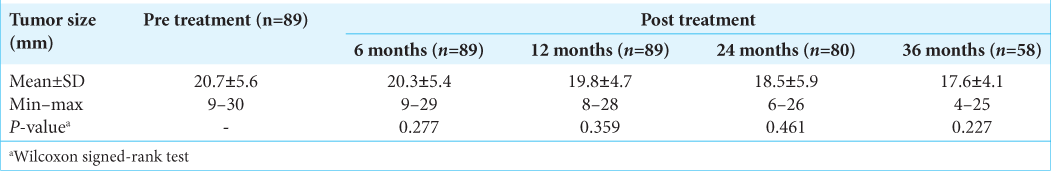
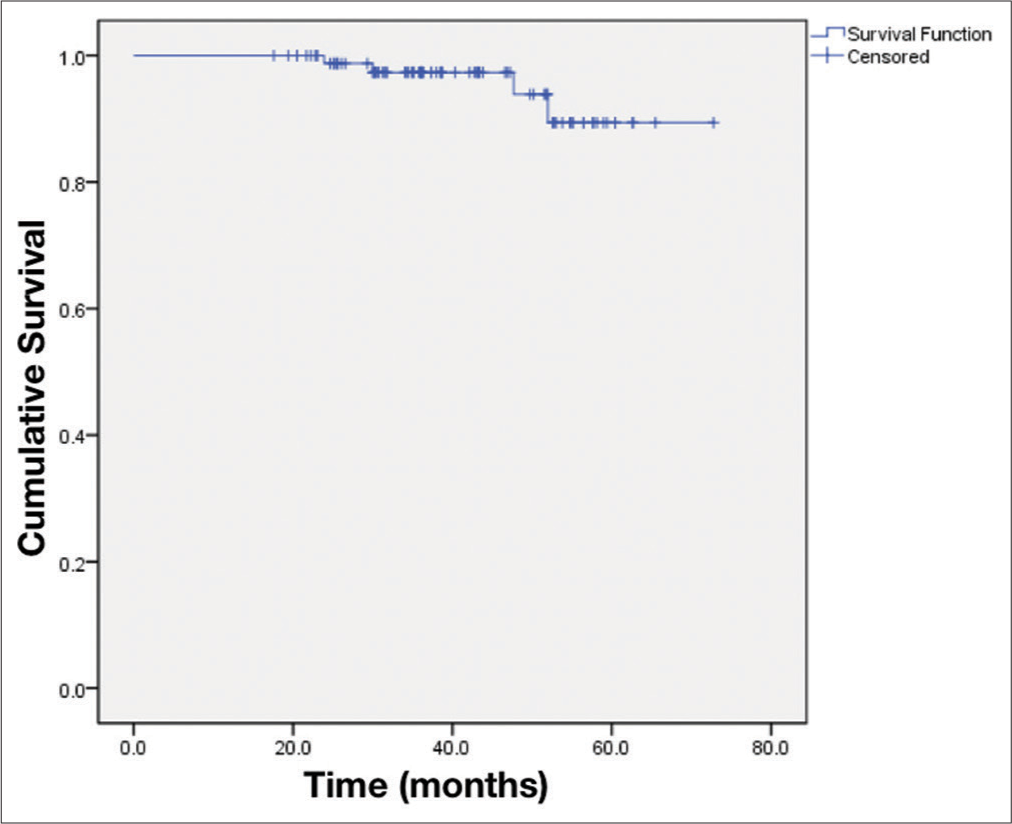
Results: The tumors were measured 20.7 ± 5.6 mm at pre treatment and 17.6 ± 4.1 mm at 3-year post treatment. The mean radiation dose was 13.5 ± 0.9 Gy. Mean follow-up was 40.6 ± 13.3 months. The radiological tumor control rate was achieved 95.5% at 5-year post treatment. The hearing and vestibular functions were preserved in 70.3% and 68.9%, respectively. The facial and trigeminal nerve preservation rates were 94.4% and 73.3%, respectively.
Conclusion: RGK is an effective and safe treatment for VS measuring ≤3 cm with no significant complications during long-term follow-up.
Keywords: Neurological outcomes, Prospective, Rotating gamma knife, Tumor control rate, Vestibular schwannoma
INTRODUCTION
Vestibular schwannoma (VS), an intracranial extra-axial tumor, is originated from the Schwann cell sheath of either vestibular or cochlear nerve of the eighth cranial nerve. VS comprises about 80% of the cerebellopontine angle tumors and 6–8% of all intracranial tumors. Approximately 65–75% of tumors stem from the inferior branch of the vestibular nerve of the eighth cranial nerve.[
Treatment options of VS include surgical removal of the tumor, controlling tumor growth by stereotactic radiotherapy or radiosurgery, and careful serial observation. Surgical total resection remains the choice of tumor eradication. Despite significant advances and innovations in microsurgery technique, microsurgical excision of VS had many severe complications such as disequilibrium, lower cranial nerve palsies, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, and facial nerve palsy.[
The rotating gamma knife system (RGK) is a hybrid with features of both classical Gamma Knife and linear accelerator-based radiosurgery systems.[
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
This was a prospective longitudinal single-center study. From October 2011 to October 2015, 89 patients with VSs were treated by RGK. The follow-ups lasted until June 2017. These cases were selected consecutively. This study was conducted at the nuclear medicine and Oncology Center, Bach Mai Hospital. Bach Mai Hospital, a tertiary referral hospital, was established in 1911 by the French and is considered one of Vietnam’s largest hospitals. This is an academic and community hospital.
According to our institutional practices, RGK was recommended as the primary treatment for minimally symptomatic VSs measuring <2.2 cm in maximal diameter. In contrast, microsurgical resection was recommended as first-line therapy for patients presenting with debilitating pre treatment symptoms, larger tumors with maximal diameter >3 cm or mass effect on surrounding structures.[
Our Institutional Review Board approved the experimental protocol as well as the informed consent for this study. All patients with VS were consulted by interdisciplinary healthcare professionals, including neurosurgeons, neurologists, radiologists, radiation oncologists, pathologists, and otolaryngologists. The consensus treatment plan was discussed with the patients and their family members.
On the treatment day, after being administered a local anesthetic for immobilization, the patients underwent the application of a stereotactic head frame. Pre treatment volumetric MRI sequences included 1-mm, axial, T1-weighted, contrast-enhanced images, 1–1.5-mm, axial, T2-weighted volume images, and 3-mm, T2, whole-head imaging. The SRS scenario was planned by the software. Based on the tumor’s contour, site, and size, the different shots (18 mm, 14 mm, 8 mm, and 4 mm) were designed to aim that the 50% isodose line circumscribed the tumor. The 40%, 30%, and 20% isodose lines were evaluated. The dose-volume histograms (DVH) were used to assess the SRS plans. Stereotactic radiosurgery was performed using the Rotating Gamma System Gamma ART-6000™ (American radiosurgery Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). The prescribed SRS dose was 10–16 Gy to the 50% isodose line. The doses for brain stem, cranial nerves (V, VII, and VIII), and cochlea were generally kept below 14 Gy, 12 Gy, and 4 Gy, respectively. Radiation delivery to the brainstem was estimated in a dose-volume fashion (DVH-based). We planned to keep 12 Gy-volume (V12) = 0 and V10 <1 cc to avoid possible issues with focal radionecrosis. In the case of postoperative residual and recurrent tumors, we had difficulty determining cranial nerves (V, VII, and VIII) on MRI. Therefore, empirically estimated doses for these cranial nerves were calculated based on multidisciplinary discussions which included neurosurgeons, radiologists, and radiation oncologists. Post treatment follow-up assessments were performed at 3, 6, 12, 24, and 36 months.
The work has been reported in line with the PROCESS criteria.[
Statistical analysis
The patients were assessed clinically and radiologically. Primary outcomes were radiological tumor control rate, hearing function, vestibular function, facial nerve palsy, and trigeminal neuralgia. Hearing function was evaluated by Gardner-Robertson classification. Facial nerve deficit was clinically assessed using the House-Brackmann index before and after treatment. Different symptomatic outcomes analyzed included lateralized headache, tinnitus, vertigo/dizziness/disequilibrium, trigeminal neuralgia, and secondary malignancies. Radiographic tumor control was defined based on the time from gamma knife radiosurgery (GKRS) until the development of either asymptomatic or symptomatic radiographic progression. Radiographic progression was defined as persistently increased maximal tumor diameter by at least 2 mm than the last MRI within at least 6 months. Trigeminal neuropathy was defined as new facial numbness or trigeminal neuralgia as reported in the patient chart. It was recorded as either present or absent. The rate of new trigeminal neuropathy was calculated as the percentage of patients with trigeminal neuropathy at follow-up. Vestibular nerve dysfunction was assessed by the presence or absence of balance difficulty before and after treatment. The vestibular nerve dysfunction was new if it was reported after but not before GKRS, and it was written as worse if the patient record explicitly stated that the functioning was worse after GKRS.
Data analysis was performed using STATA® version 14.0 (StataCorp., Lakeway Drive College Station, Texas, USA). Statistical significance was set arbitrarily at P < 0.05. The quantitative variables were presented as mean ± standard deviation if the data were normal distribution and were shown as the median and interquartile range if the data were non-normal distribution. The qualitative variables were presented as frequency and proportions. We used the Wilcoxon signed-rank test to compare the difference between the two paired groups. Kaplan– Meier estimator evaluated radiological progression-free survival.
Ethical considerations
The Institutional Review Board at Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center of Bach Mai Hospital and Hanoi Medical University, Hanoi, Vietnam, approved data collection, analysis, and publication of this study. The study was performed within ethical standards. All potential participants were given information on the study’s purpose, the associated risks, and benefits and were required to provide written informed consent before inclusion in the study. Parents or legal guardians provided written consent for participants aged <18 years.
RESULTS
Participants and descriptive data
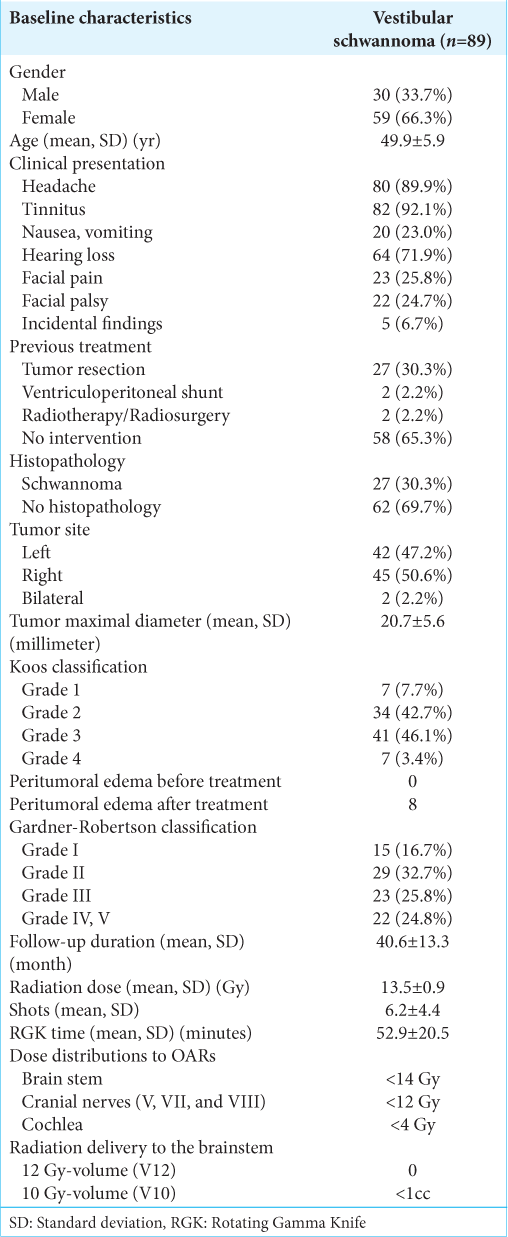
A total of 89 patients with VS were treated by RGK. Thirtyone patients were lost to follow-up after 4 years, precluding a longer period of surveillance. Patient characteristics and descriptive data are tabulated in [
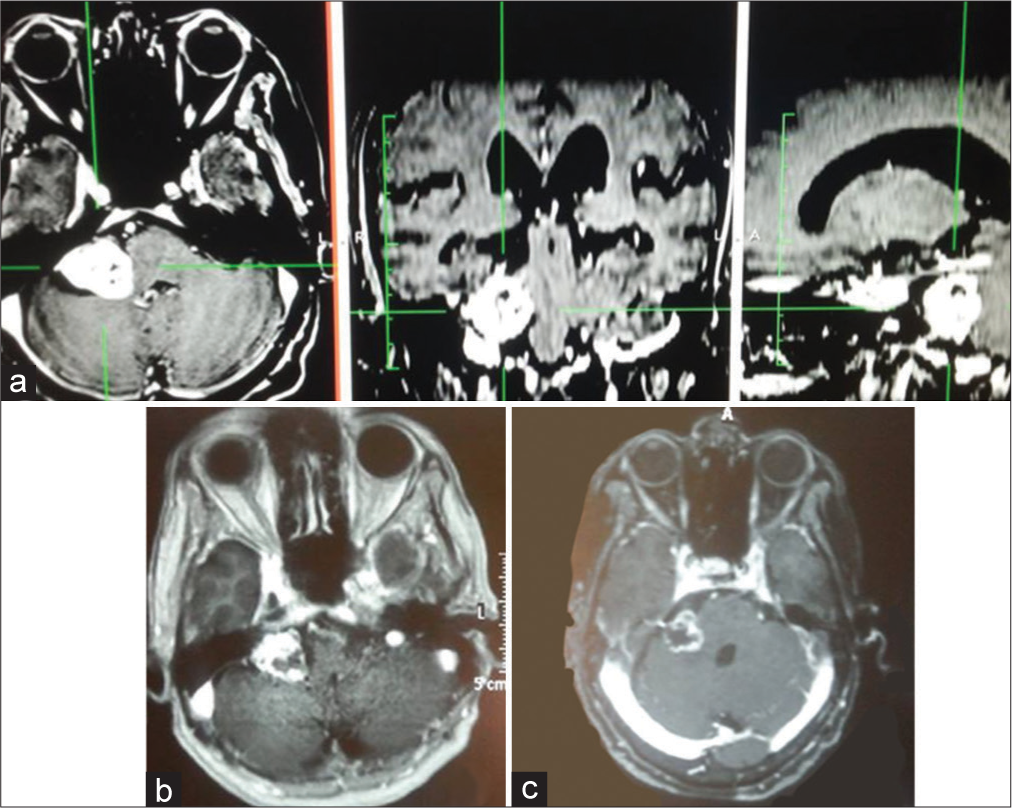
Figure 1:
A 71-year-old female presented to our hospital with a complaint of headache and hearing loss on the right side for 12 months before admission. (a) Brain MRI showed a right vestibular schwannoma with Koos Grade III. MRI showed tumor necrosis and a remarkable decrease in size at 6-month (b) and 24-month (c) post treatment.
Outcomes
Headache, tinnitus, and vertigo improved significantly post treatment [
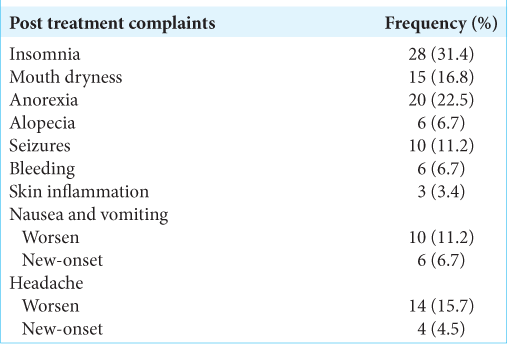
Regarding post treatment complaints, insomnia (31.4%), anorexia (22.5%), and headache (20.2%) were the most common [
DISCUSSION
KEY RESULTS
For 4 years, 89 patients with VS were treated by RGK. The mean radiation dose was 13.5 ± 0.9 Gy. The mean duration of follow-ups was 40.6 ± 13.3 months. The radiological tumor control rate was 95.5% at 4-year post treatment. The most relieving symptoms were headache (89.9–5.6%) and tinnitus (92.1– 52.8%). The hearing function and vestibular function were preserved in 70.3% and 68.9%, respectively. The facial and trigeminal nerve preservation rates were 94.4% and 73.3%, respectively.
Interpretations
Radiation dose selection and tumor control rate
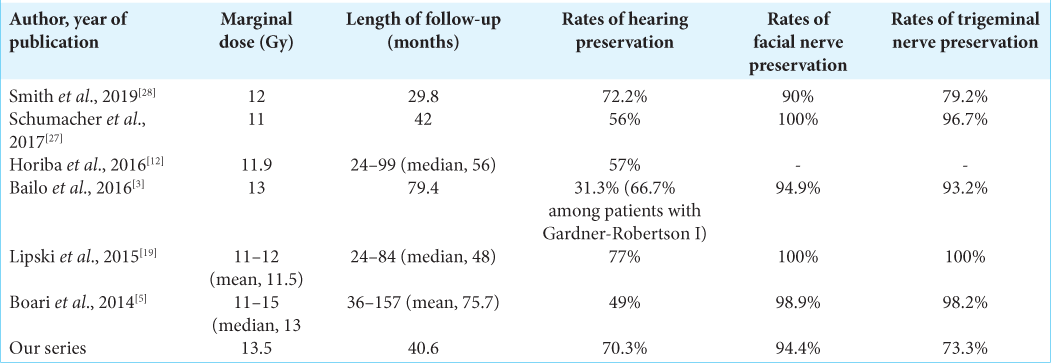
Prescription doses must balance between late perilesional toxicity and effective tumor control. In theory, low-dose rates may reduce focal toxicity by better preserving surrounding normal tissues, potentially compromising tumor control. In our study, the mean radiation dose was 13.5 Gy (range 10–16 Gy). This is in good agreement with Lunsford (mean 13 Gy), Boari (mean 13 Gy, range 11–15 Gy),[
Functional neurological preservation
[
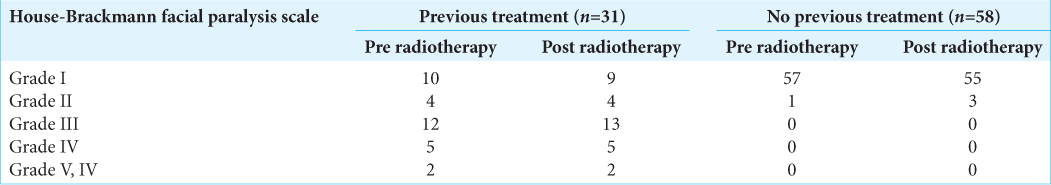
Pretreatment facial nerve palsy was observed in 24.7% of cases, in which 23.6% of patients had a previous surgical resection. Notwithstanding this, new-onset of transient facial nerve palsy post treatment was reported in four cases with one case recovering after 24 months. The latter is also in keeping with findings from other groups where facial nerve preservation was in the range of 95–100%.[
Due to posterior compression of VS, 3/89 (3.3%) cases had a new-onset of trigeminal neuralgia. This value was scarcely distinguishable from previous results.[
Complications
Regarding the safety of RGK, no mortality case was reported even in elderly patients with severe comorbidities. Insomnia (31.4%) and anorexia (22.5%) were the most common complaints. Nevertheless, headache, insomnia, and anorexia were usually relieved by medication (usually within three days). Despite this, symptoms lasted up to 1 month in some patients. Brain edema was determined by magnetic imaging resonance. In this context, edema was reported as a complication of radiosurgery when it got worse or fully evolved after treatment, usually at a rate of 3-month post radiosurgery. In this study, eight cases had post treatment brain edema (21.6%), generally presenting with headache, nausea, and vomiting. All of all these particular cases were treated with corticoid therapy and their symptoms relieved after several weeks to 1 month. This is also in keeping with Bailo et al., observing signs of adverse radiation effect in 6/59 cases.[
Limitations
It is plausible that several limitations might have influenced the results obtained. The first limitation was a small number of patients and a relatively short follow-up after radiosurgery. Inherent selection biases associated with nonrandomized treatment assignments were another flaw. Despite that, prospective data gave reasonable tumor control and cranial nerve function preservation rates compared to previously published reports. Another drawback was the loss of patients to follow-up over time. Patients’ compliance at long-term follow-up was variable, particularly for patients living far from our center and the poor patients; this limitation could not be easily overcome, even by scheduling subsequent examinations at hospital discharge.
CONCLUSION
In this group of patients, RGK proved to be effective and safe in the management of VS mearing <3 cm. Tumor control throughout follow-up was comparable to other studies; no significant neurological complications were observed at long-term either. Further multicentric prospective studies with larger cohorts are warranted to validate the findings of this paper.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patients identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Agha RA, Sohrabi C, Mathew G, Franchi T, Kerwan A, O’Neill N. The PROCESS 2020 guideline: Updating consensus preferred reporting of CasE series in surgery (PROCESS) guidelines. Int J Surg. 2020. 84: 231-5
2. Andrews DW, Suarez O, Goldman HW, Downes MB, Bednarz G, Corn BW. Stereotactic radiosurgery and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for the treatment of acoustic schwannomas: Comparative observations of 125 patients treated at one institution. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001. 50: 1265-78
3. Bailo M, Boari N, Franzin A, Gagliardi F, Spina A, del Vecchio A. Gamma knife radiosurgery as primary treatment for large vestibular schwannomas: Clinical results at long-term follow-up in a series of 59 patients. World Neurosurg. 2016. 95: 487-501
4. Bailo M, Boari N, Gagliardi F, Franzin A, Piloni M, Spina A. Gamma knife radiosurgery for residual and recurrent vestibular schwannomas after previous surgery: Clinical results in a series of 90 patients and review of the literature. World Neurosurg. 2017. 98: 60-72
5. Boari N, Bailo M, Gagliardi F, Franzin A, Gemma M, del Vecchio A. Gamma Knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma: Clinical results at long-term follow-up in a series of 379 patients. J Neurosurg. 2014. 121: 123-42
6. Carratalá IL, García VE, Alborch MO, de Paula Vernetta C, Algarra JM. Radiosurgery as treatment for acoustic neuroma. Ten years’ experience. Acta Otorrinolaringol (English Ed). 2014. 65: 327-31
7. Coughlin AR, Willman TJ, Gubbels SP. Systematic review of hearing preservation after radiotherapy for vestibular schwannoma. Otol Neurotol. 2018. 39: 273-83
8. Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD, Linskey ME, Duma CM, Kondziolka D. Gamma knife radiosurgery for acoustic tumors: Multivariate analysis of four year results. Radiother Oncol. 1993. 27: 91-8
9. Goetsch SJ, Murphy BD, Schmidt R, Micka J, De Werd L, Chen Y. Physics of rotating gamma systems for stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999. 43: 689-96
10. Haque R, Wojtasiewicz TJ, Gigante PR, Attiah MA, Huang B, Isaacson SR. Efficacy of facial nerve-sparing approach in patients with vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg. 2011. 115: 917-23
11. Hasegawa T, Kida Y, Kato T, Iizuka H, Kuramitsu S, Yamamoto T. Long-term safety and efficacy of stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas: Evaluation of 440 patients more than 10 years after treatment with Gamma Knife surgery. J Neurosurg. 2013. 118: 557-65
12. Horiba A, Hayashi M, Chernov M, Kawamata T, Okada Y. Hearing preservation after low-dose gamma knife radiosurgery of vestibular schwannomas. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2016. 56: 186-92
13. Huang CW, Tu HT, Chuang CY, Chang CS, Chou HH, Lee MT. Gamma Knife radiosurgery for large vestibular schwannomas greater than 3 cm in diameter. J Neurosurg. 2018. 128: 1380-7
14. Khrais T, Romano G, Sanna M. Nerve origin of vestibular schwannoma: A prospective study. J Laryngol Otol. 2008. 122: 128-31
15. Komatsuzaki A, Tsunoda A. Nerve origin of the acoustic neuroma. J Laryngol Otol. 2001. 115: 376-9
16. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, McLaughlin MR, Flickinger JC. Long-term outcomes after radiosurgery for acoustic neuromas. N Engl J Med. 1998. 339: 1426-33
17. Kondziolka D, Mousavi SH, Kano H, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD. The newly diagnosed vestibular schwannoma: Radiosurgery, resection, or observation?. Neurosurg Focus. 2012. 33: E8
18. Kumon Y, Kohno S, Ohue S, Watanabe H, Inoue A, Iwata S. Usefulness of endoscope-assisted microsurgery for removal of vestibular schwannomas. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2012. 73: 42-7
19. Lipski SM, Hayashi M, Chernov M, Levivier M, Okada Y. Modern Gamma Knife radiosurgery of vestibular schwannomas: Treatment concept, volumetric tumor response, and functional results. Neurosurg Rev. 2015. 38: 309-18
20. Lunsford LD, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Maitz A, Kondziolka D. Radiosurgery of vestibular schwannomas: Summary of experience in 829 cases. J Neurosurg. 2013. 102: 195-9
21. McClelland S, Guo H, Okuyemi KS. Morbidity and mortality following Acoustic neuroma excision in the United States: Analysis of racial disparities during a decade in the radiosurgery era. Neuro Oncol. 2011. 13: 1252-9
22. Murphy ES, Barnett GH, Vogelbaum MA, Neyman G, Stevens GH, Cohen BH. Long-term outcomes of Gamma Knife radiosurgery in patients with vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg. 2011. p. 114432-40
23. Nonaka Y, Fukushima T, Watanabe K, Friedman AH, Sampson JH, McElveen JT. Contemporary surgical management of vestibular schwannomas: Analysis of complications and lessons learned over the past decade. Neurosurgery. 2013. 72: ons103-15
24. Régis J, Pellet W, Delsanti C, Dufour H, Roche PH, Thomassin JM. Functional outcome after gamma knife surgery or microsurgery for vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg. 2002. 97: 1091-100
25. Régis J, Roche P, Delsanti C, Thomassin J, Ouaknine M, Gabert K. Modern management of vestibular schwannomas. Prog Neurol Surg. 2007. 20: 129-41
26. Sarmiento JM, Patel S, Mukherjee D, Patil CG. Improving outcomes in patients with vestibular schwannomas: Microsurgery versus radiosurgery. J Neurosurg Sci. 2013. 57: 23-44
27. Schumacher AJ, Lall RR, Lall RR, Iii AN, Ayer A, Sejpal S. Low-dose gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas: Tumor control and cranial nerve function preservation after 11 Gy. J Neurol Surgery. Part B Skull Base. 2017. 78: 2-10
28. Smith DR, Saadatmand HJ, Wu CC, Black PJ, Wuu YR, Lesser J. Treatment outcomes and dose rate effects following gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas. Clin Neurosurg. 2019. 85: E1084-94
29. Wangerid T, Bartek J, Svensson M, Förander P. Long-term quality of life and tumour control following gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2014. 156: 389-96