- Department of Neurosurgery, SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, New York, United States.
- College of Medicine, SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, New York, United States.
Correspondence Address:
Alexander E. Braley
Department of Neurosurgery, SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, New York, United States.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_681_2020
Copyright: © 2020 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Alexander E. Braley1, Carlos Goulart1, Joan Chou2, Michael Galgano1. Resection of a large presacral schwannoma from an all-posterior trans-sacral approach. 25-Nov-2020;11:408
How to cite this URL: Alexander E. Braley1, Carlos Goulart1, Joan Chou2, Michael Galgano1. Resection of a large presacral schwannoma from an all-posterior trans-sacral approach. 25-Nov-2020;11:408. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/?post_type=surgicalint_articles&p=10413
Abstract
Background: Presacral schwannomas vary greatly in size, and symptomatology. Resections may utilize anterior, posterior, or combined 360-degree approaches.
Case Description: A 67-year-old female presented with a progressively enlarging presacral schwannoma originating from the S1 nerve root. Here, we utilized a unique all-posterior, trans-sacral tumor resection technique that did not result in any increased neurological deficit, or warrant fusion (e.g., including operative video). Further, we avoided potential urogenital, vascular, and bowel injuries that are associated with anterior approaches to such lesions.
Conclusion: Here, we described and demonstrated successful resection of a large presacral schwannoma originating from the S1 nerve root that was safely resected utilizing an all-posterior resection without fusion.
Keywords: Presacral schwannoma, Presacral tumor, Schwannoma, Spine oncology
INTRODUCTION
Spinal nerve sheath tumors comprise approximately 30% of the intradural extramedullary tumors and have the capacity to grow to large sizes in the retroperitoneal presacral space.[
The optimal approaches should depend on the size, anatomic location, body habitus, and comorbidities of the patients.[
Posterior approaches reduces the risk of injury to bowel, allow for more direct resection of presacral tumors with clearer operative visualization, but reduce the ability to control potential large-vessel injury.[
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
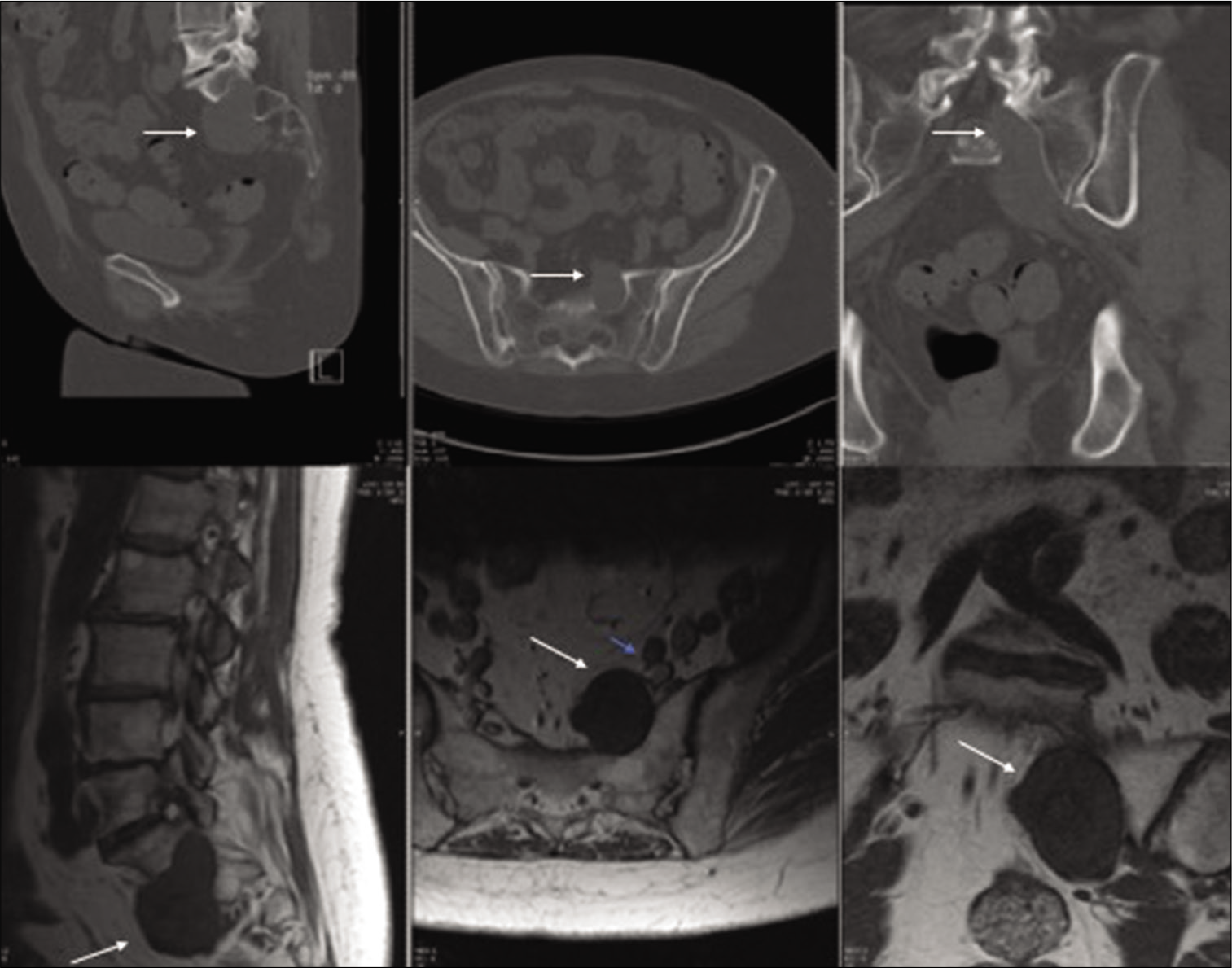
A 67-year-old female, with a history of schwannomatosis, had been followed for 8 years with a left S1 foraminal schwannoma. She had developed progressive symptoms (e.g., left S1 distribution: pain, plantar flexor weakness, and sensory loss) with the evidence of increased growth into the presacral space on enhanced MR studies (e.g., 2.2 × 3.0 × 5.0 cm) [
Surgery
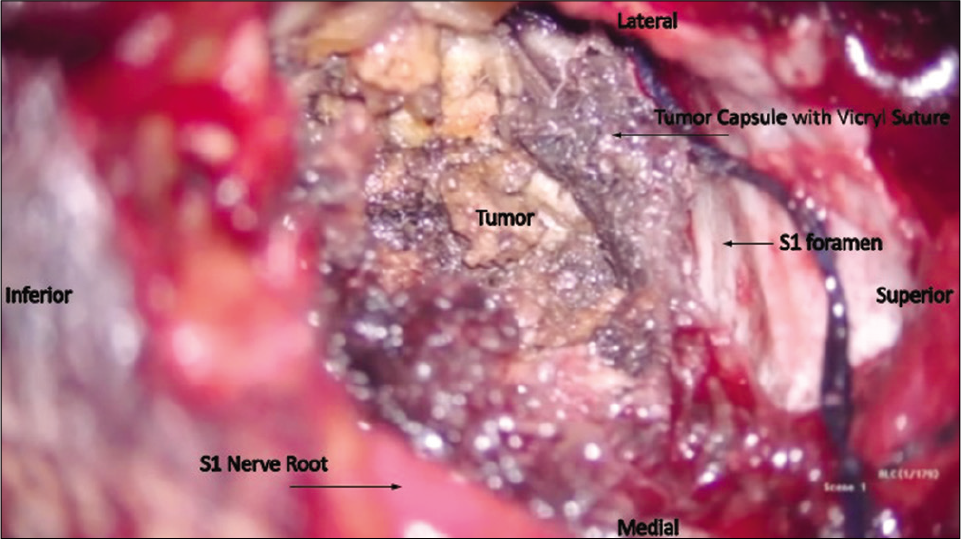
Utilizing intraoperative neuromonitoring, a traditional midline incision was accompanied by subperiosteal dissection of the paraspinal musculature off the L5, S1, and S1 laminae. The inferior L5 lamina was removed to expose the origin of the tumor, while the dorsal S1 foramen was enlarged with the drill. The tumor capsule was then incised, and tumor was debulked, and dissected away from the surrounding structures [
Video 1
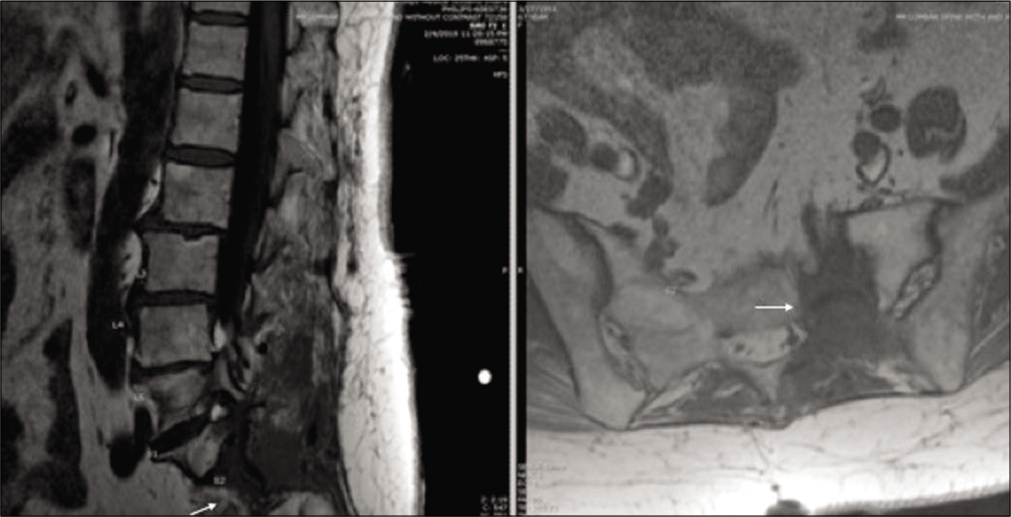
Postoperatively the patient had no new motor/sensory deficits, and the preoperative pain was significantly reduced. Postoperative imaging demonstrated gross total resection of the tumor, and she was discharged home uneventfully after a short hospital stay [
DISCUSSION
There are many operative alternatives for resecting presacral schwannomas; anterior, posterior, or combined 360-degree approaches.
Anterior approaches require minimal muscle dissection, do not violate the sacroiliac joint, do not require laminectomy or arthrodesis, and are less painful. However, there is an increased the risk of injury to adjacent urogenital, vascular, and bowel structures, and they additionally require an access surgeon.[
We utilized a posterior transforaminal approach to minimize the risk of injury to the presacral structures, while also carefully avoiding compromise the sacroiliac joint. Cipolleschi et al. similarly successfully utilized a posterior extraforaminal approach and avoided fusion in their patient who was discharged on postoperative day 3.[
Utilizing a traditional midline incision and transforaminal approach allowed for internal debulking of the S1 presacral schwannoma while minimizing blood loss, avoiding destabilization, and decreasing the perioperative risks.
CONCLUSION
Our patient had an excellent following a posterior-only resection of a S1 presacral schwannoma.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patients identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Videos available on:
www.surgicalneurologyint.com
References
1. Acciarri N, Staffa G, Poppi M. Giant sacral schwannoma: Removal by an anterior, transabdominal approach. Br J Neurosurg. 1996. 10: 489-92
2. Cipolleschi E, Wembagher GC, Barni I, Romoli S. Minimally invasive posterior extraforaminal approach for presacral schwannoma of L5. J Neurosurg Sci. 2018. 63: 488-90
3. Dorsi MJ, Belzberg AJ. Paraspinal nerve sheath tumors. Neurosurg Clin North Am. 2004. 15: 217-22
4. Emohare O, Stapleton M, Mendez A. A minimally invasive pericoccygeal approach to resection of a large presacral schwannoma: Case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015. 23: 81-5
5. Jatal S, Pai VD, Rakhi B, Saklani AP. Presacral schwannoma: Laparoscopic resection, a viable option. Ann Transl Med. 2016. 4: 176
6. Lee BH, Hyun SJ, Park JH, Kim KJ. Single Stage posterior approach for total resection of presacral giant schwannoma: A technical case report. Korean J Spine. 2017. 14: 89-92
7. Saxena D, Pandey A, Bugalia RP, Kumar M, Kadam R, Agarwal V. Management of presacral tumors: Our experience with posterior approach. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015. 12: 37-40