- Department of Neurological Surgery, Juntendo University Urayasu Hospital, Urayasu, Chiba, Japan.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_605_2020
Copyright: © 2020 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Shinichiro Teramoto, Satoshi Tsutsumi, Hisato Ishii. Traumatic acute epidural hematoma caused by injury of the diploic channels. 08-Oct-2020;11:333
How to cite this URL: Shinichiro Teramoto, Satoshi Tsutsumi, Hisato Ishii. Traumatic acute epidural hematoma caused by injury of the diploic channels. 08-Oct-2020;11:333. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/10320/
Abstract
Background: Traumatic acute epidural hematomas (EDHs) commonly develop by rupture of the meningeal arteries. EDH caused by an injury of the diploic channel (DC) has not been reported.
Case Description: A 21-year-old man suffered a head injury while falling off the skateboard. At presentation, the patient was drowsy but did not exhibit any focal neurological deficits. Cranial computed tomography (CT) revealed a biconvex intracranial hematoma with 18-mm thickness in the high parietal region and a linear fracture that involved both the outer and inner tables and passed above the hematoma. A well-developed and large DC was observed near the hematoma. Patient’s consciousness level decreased at 12 h after admission with considerable growth of the hematoma. A frontoparietal craniotomy revealed an EDH. The dura mater and the meningeal arteries underneath the hematoma were intact. The medial bone cut caused brisk bleeds from the large DC. Postoperative CT revealed the cut of the DC and other finer DCs exhibiting air density and lying near the fracture. Based on these findings, we assumed that the EDH was developed by an injury of the DCs.
Conclusion: Traumatic EDH can develop by an injury of the DCs. Careful observation of patient’s neurological status and precise interpretation of neuroimages is important to identify venous EDHs.
Keywords: Acute epidural hematoma, Diploic channel, Traumatic, Venous hemorrhage
INTRODUCTION
Traumatic acute epidural hematomas (EDHs) are well-known entities that develop in approximately 2% of all head injuries, with mortality rates ranging from 1.2% to 33%.[
CASE PRESENTATION
A 21-year-old, previously healthy man, suffered a head injury while falling off the skateboard and was transported to our hospital. The patient lost consciousness for 1 min immediately after the injury. At presentation, the patient was drowsy and exhibited a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 13 without any focal neurological deficits. Cranial CT revealed a biconvex intracranial hematoma with 18-mm maximum thickness in the left high parietal region and a linear fracture coursing parallel to the sagittal suture [
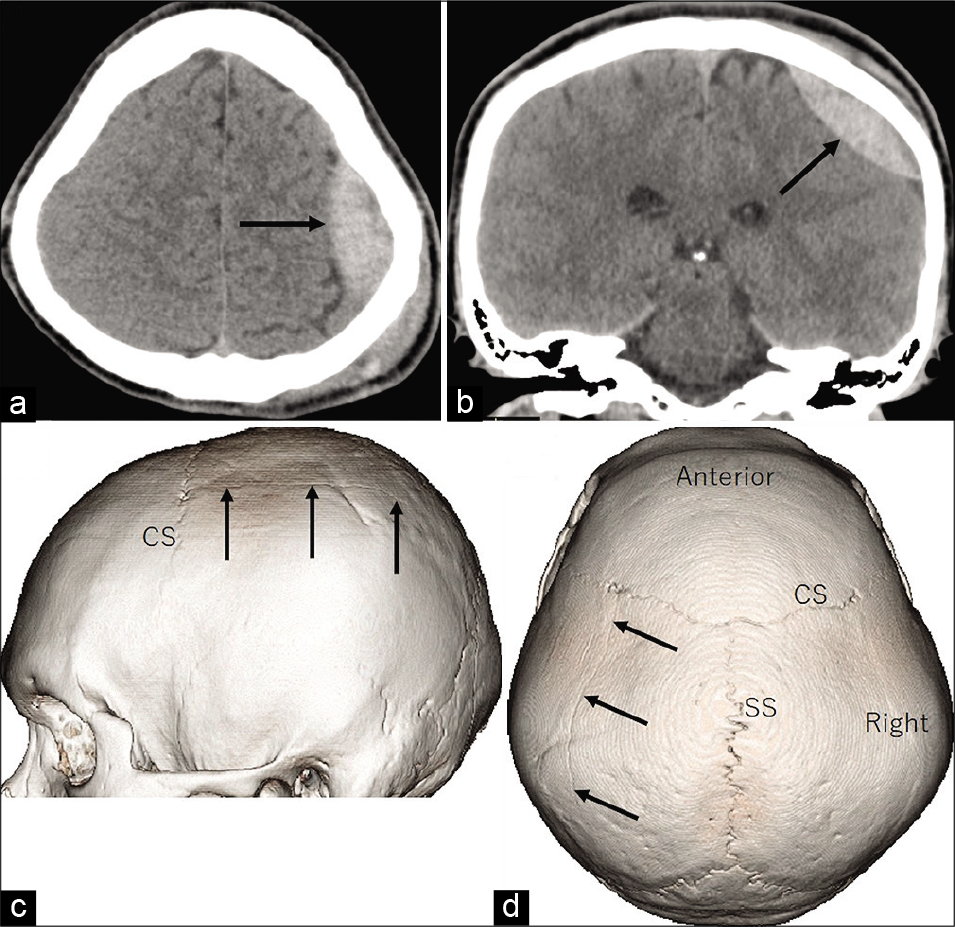
Figure 1:
Axial (a) and coronal (b) computed tomography scans at presentation show a biconvex hematoma with 18-mm thickness in the left high parietal region (arrow). Lateral (c) and superior (d) views of the three-dimensional computed tomography scans show a linear fracture in the left parietal bone passing parallel to the sagittal suture. CS : coronal suture.
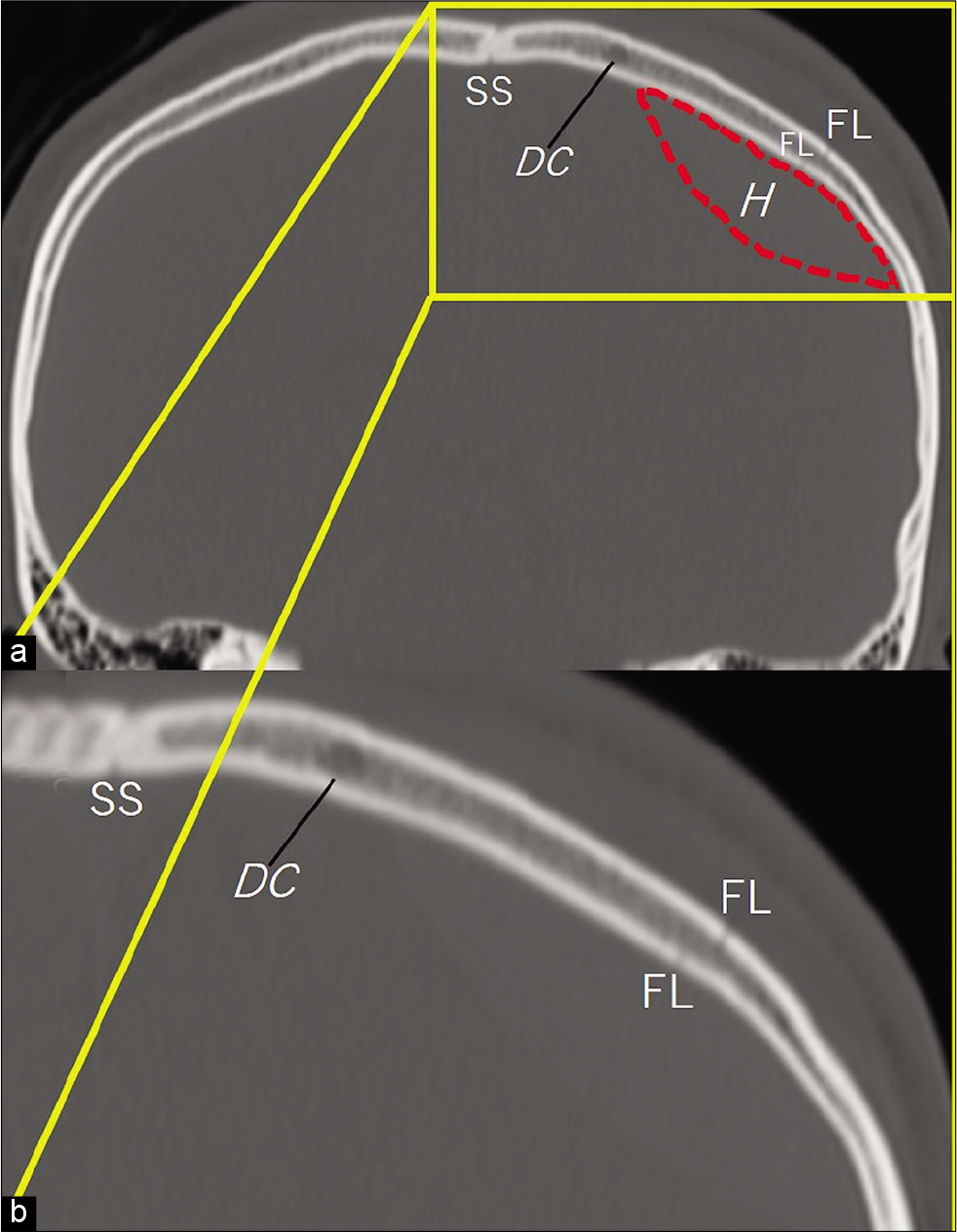
Figure 2:
(a) Bone target coronal computed tomography scan show a fracture line passing above the thickest part of an intracranial hematoma (h). A well-developed and large diploic channel is observed near the hematoma. (b) Bone target coronal computed tomography showing the magnified view of the boxed area in A. SS : Sagittal suture. DC: Diploic channel, FL: Fracture line, H: Hematoma
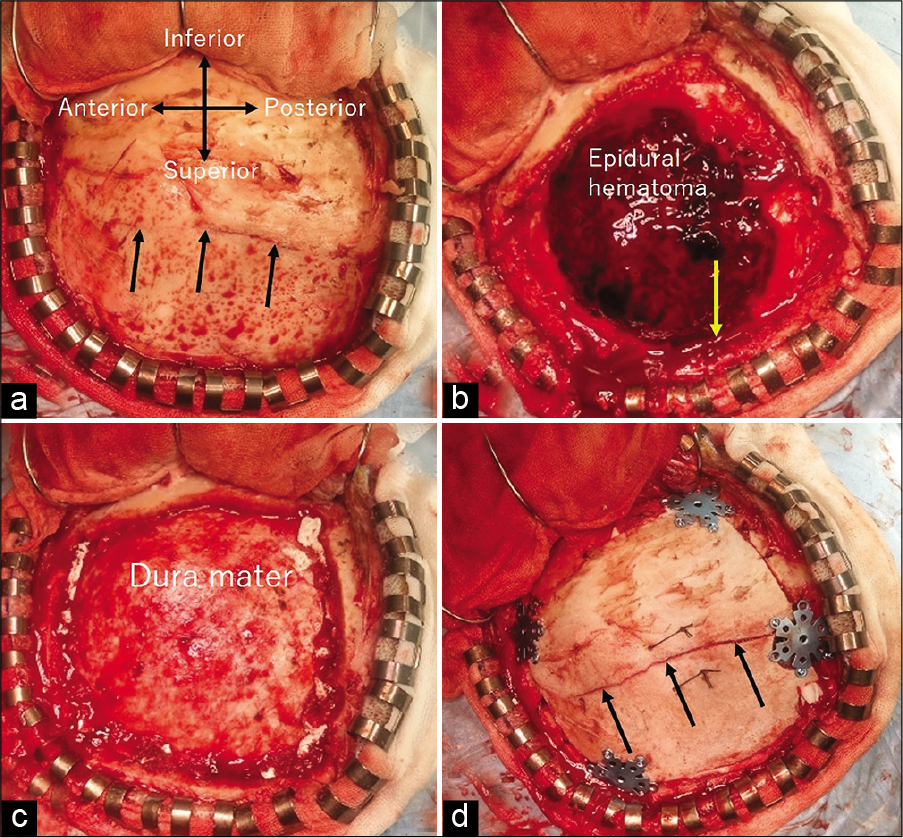
Figure 4:
Intraoperative photographs on reflecting the scalp flap (a), immediately after removal of the bone flap (b), after the evacuation of the epidural hematoma (c), and after fixing the bone flap back into the original place (d) are depicted. Abnormal vasculature or injury of the dural arteries is not observed. Arrow in (b) indicates the site of a large diploic channel that was cut by the medial bone fracture caused brisk bleeds. Arrows in (a) and (d) indicate the fracture line.
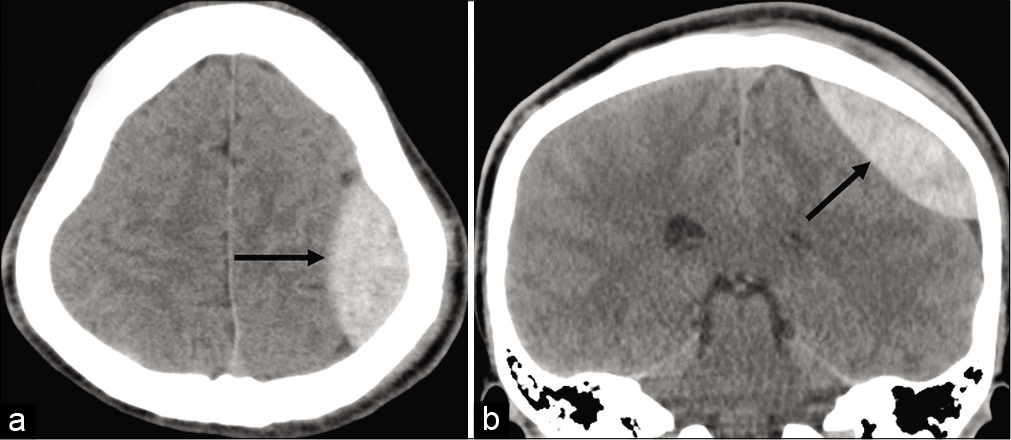
Figure 5:
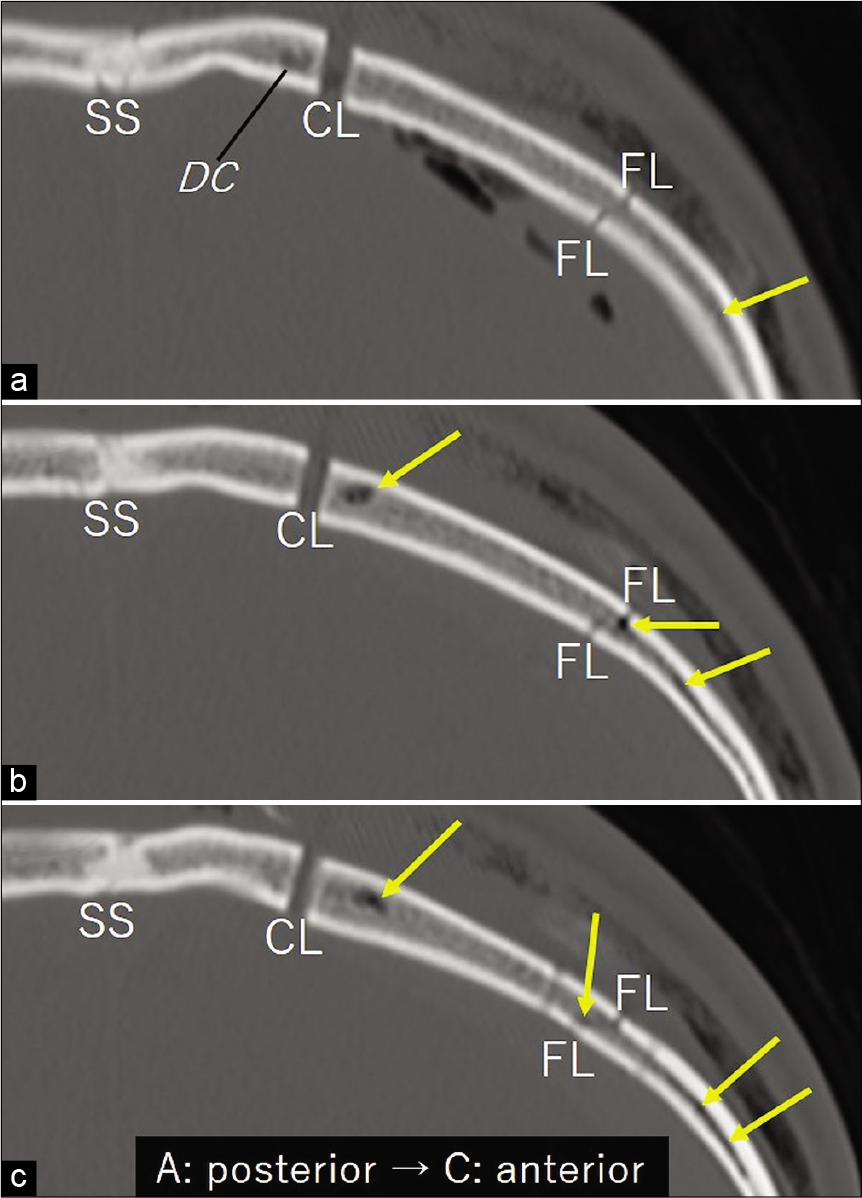
(a-c) Serial bone target coronal computed tomography scans performed immediately after surgery shows the cut of a large diploic channel (DC) by the medial bone cut and other finer DCs lying in the bone flap and exhibiting air density (arrows). CL: craniotomy line, FL: fracture line, SS: sagittal suture.
DISCUSSION
Traumatic acute EDHs usually develop by ruptures of the meningeal arteries. However, based on the time course of the patient’s neurological status and neuroimaging and intraoperative findings, we assumed that the present EDH developed by injuries of the DCs. Direct anatomical connections between a well-developed and large DC that was cut during the medial bone cut and finer DCs lying near the fracture line were not demonstrated. However, postoperative CT images were highly suggestive of such connections. These DCs are presumed to correspond with the previously documented, the occipitoparietal route of the calvarial DCs that consistently connect the superior sagittal sinus and transverse sinus-sigmoid sinus junctional region.[
Anatomically, the part of the meningeal artery coursing through the high parietal region is a fine peripheral vessel that transmits a tiny amount of blood flow.[
CONCLUSION
Traumatic EDH can develop by injury of the DCs. Careful observation of patient’s neurological status and precise interpretation of neuroimages is important to identify venous EDHs.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Domenicucci M, Signorini P, Strzelecki J, Delfini R. Delayed post-traumatic epidural hematoma. A review. Neurosurg Rev. 1995. 18: 109-22
2. Kissel P, Boggan JE, Wagner FC. CT evolution of an acute venous epidural hematoma. J Emerg Med. 1989. 7: 365-8
3. Martins C, Yasuda A, Campero A, Ulm AJ, Tanriover N, Rhoton AL. Microsurgical anatomy of the dural arteries. Neurosurgery. 2005. 56: 211-51
4. Rehman L, Khattak A, Naseer A, Mushtaq . Outcome of acute traumatic extradural hematoma. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2008. 18: 759-62
5. Soon WC, Marcus H, Wilson M. Traumatic acute extradural haematoma-indications for surgery revisited. Br J Neurosurg. 2016. 30: 233-4
6. Tsutsumi S, Nakamura M, Tabuchi T, Yasumoto Y, Ito M. Calvarial diploic venous channels: An anatomic study using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Surg Radiol Anat. 2013. 35: 935-41
7. Yoshioka S, Kuwayama K, Satomi J, Nagahiro S. Transarterial N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate embolization of an intraosseous dural arteriovenous fistula associated with acute epidural hematoma: Technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2015. 11: E468-71