Endoscopic subdural membranectomy for multi-septated chronic subdural hematoma: Finding a safe solution when middle meningeal artery embolization is not feasible
Date of publication: 30-May-2025
Background: Multi-septated chronic subdural hematoma (mCSDH) is a special type of chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH) that is characterized by a hematoma cavity separated by fibrous septa that hinders adequate drainage. Treatment of mCSDH using minimally invasive endoscopic-assisted techniques that may serve as an addition to the standard technique of burr-hole craniotomy drainage. No prior video on the nuances of endoscopic membranectomy (EM) has been described.
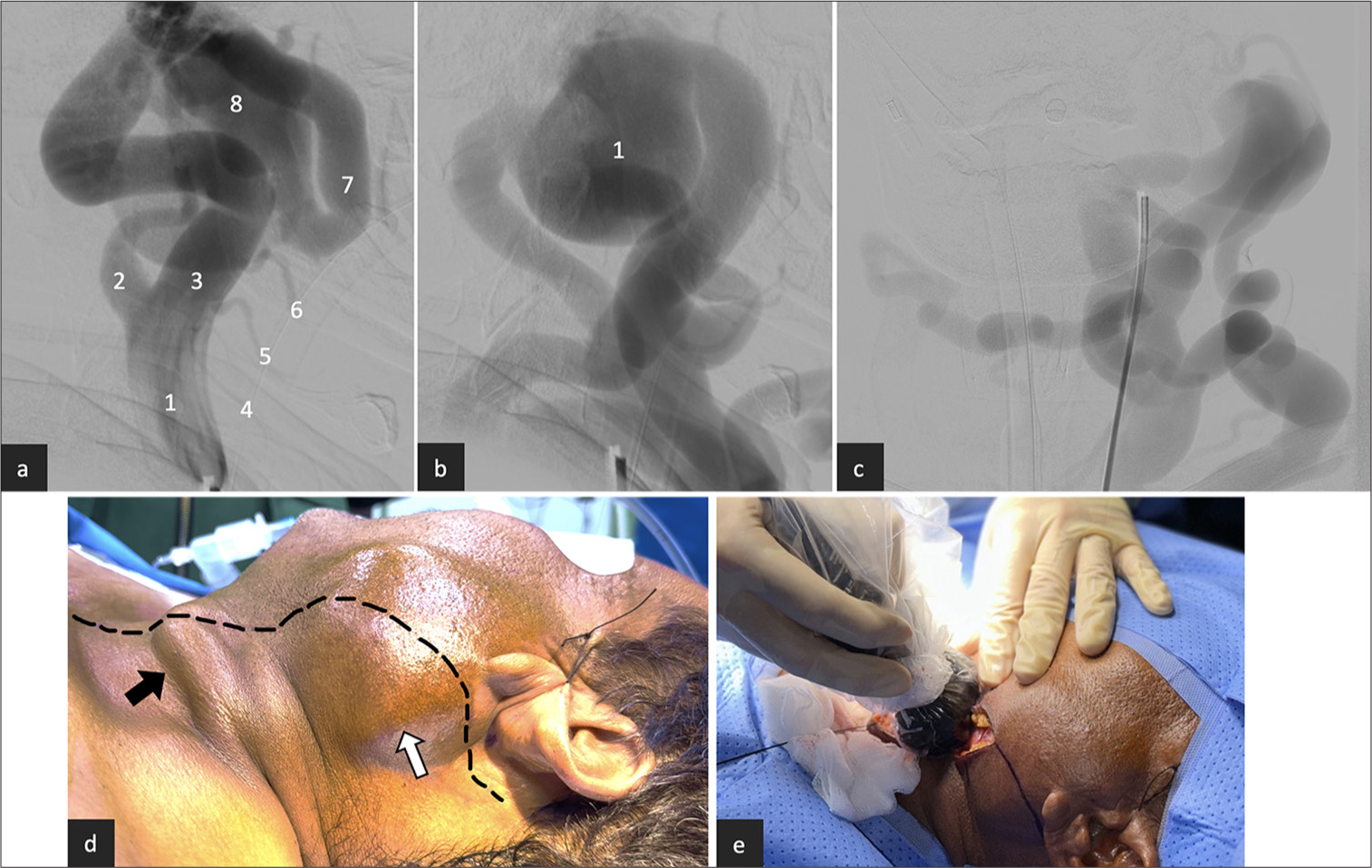
Innovation under pressure: Managing a complex carotid–jugular fistula in a war-zone limited-resources area
Date of publication: 30-May-2025
Background: Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) constitutes a pathological direct connection between an artery and a vein without an intervening capillary bed with a spectrum of high to low-grade malformation. Here, we present an unusual case of congenital neck AFV managed in a resource-limited setting in a war-zone area.
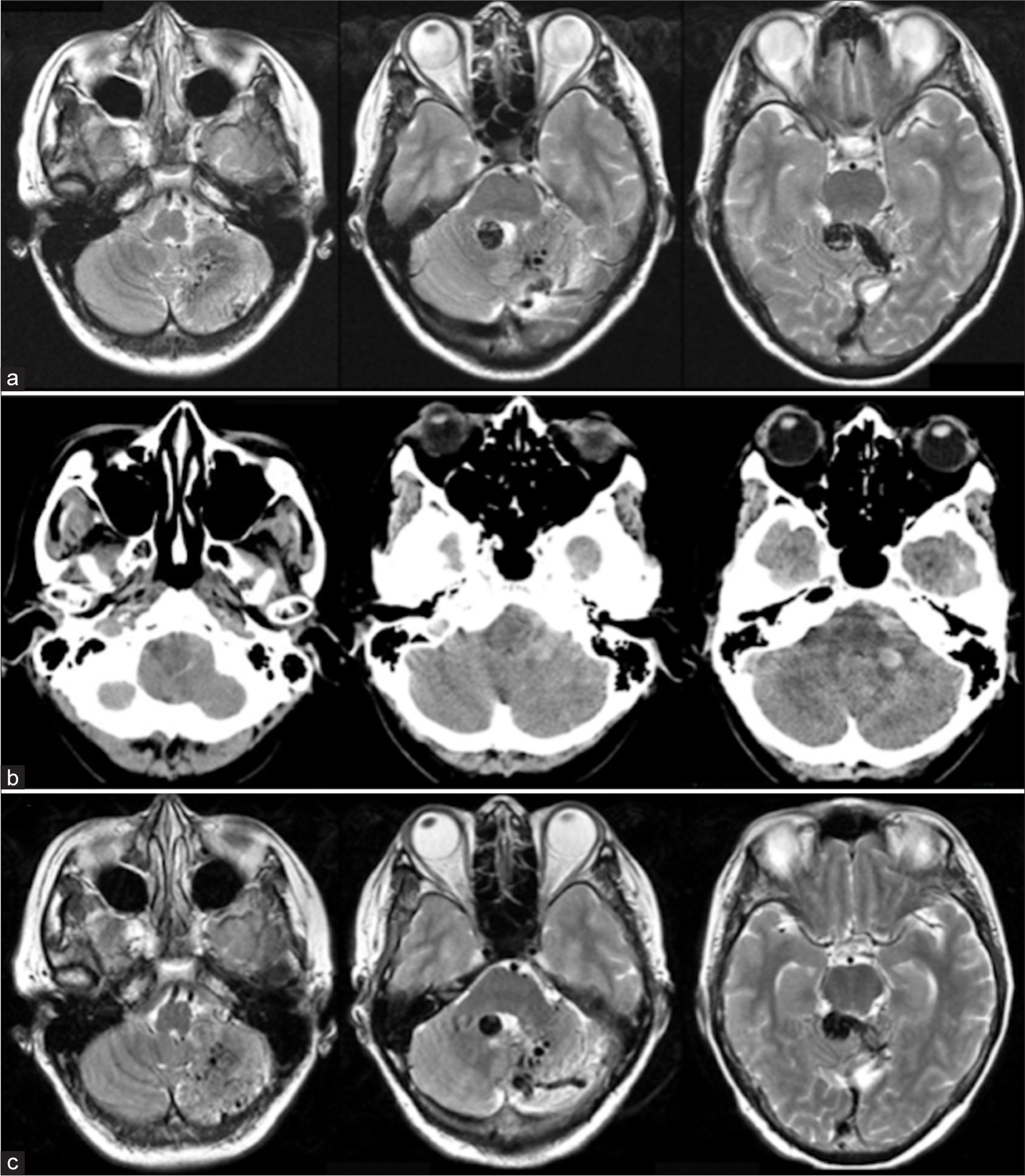
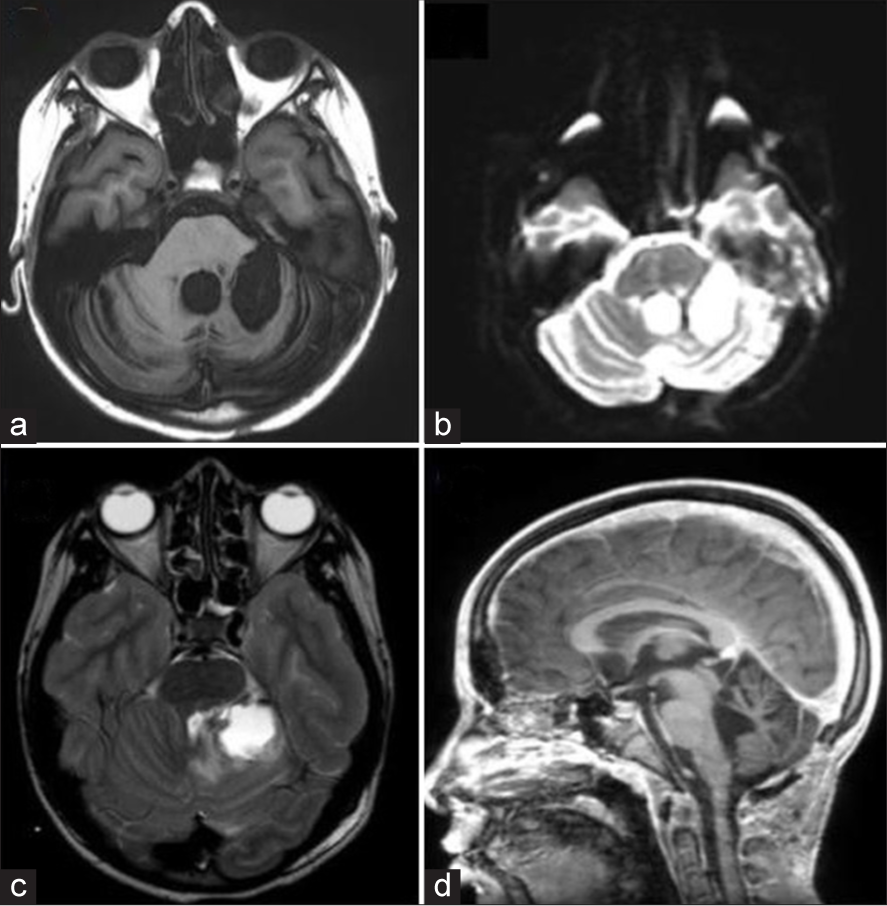
Infratentorial cerebral proliferative angiopathy: A rare entity with high risk of hemorrhage
Date of publication: 30-May-2025
Background: Cerebral proliferative angiopathy (CPA) is a rare vascular disease characterized by nonfocal angiogenic activity. Numerous case reports have been published; however, despite there are a few reported cases of infratentorial CPA (or cerebellar proliferative angiopathy), no comprehensive review of this condition has been conducted.
Diffuse midline H3K27-altered glioma in an atypical location mimicking a medulloblastoma
Date of publication: 30-May-2025
Background: Diffuse midline glioma (DMG) with H3 histones in lysine 27 (H3K27) mutation is an aggressive central nervous system tumor that primarily affects children. It often presents with nonspecific neurological symptoms and can mimic other posterior fossa tumors, such as medulloblastoma, on imaging. Due to its poor prognosis and rapid progression, early recognition and accurate diagnosis are crucial for patient management.
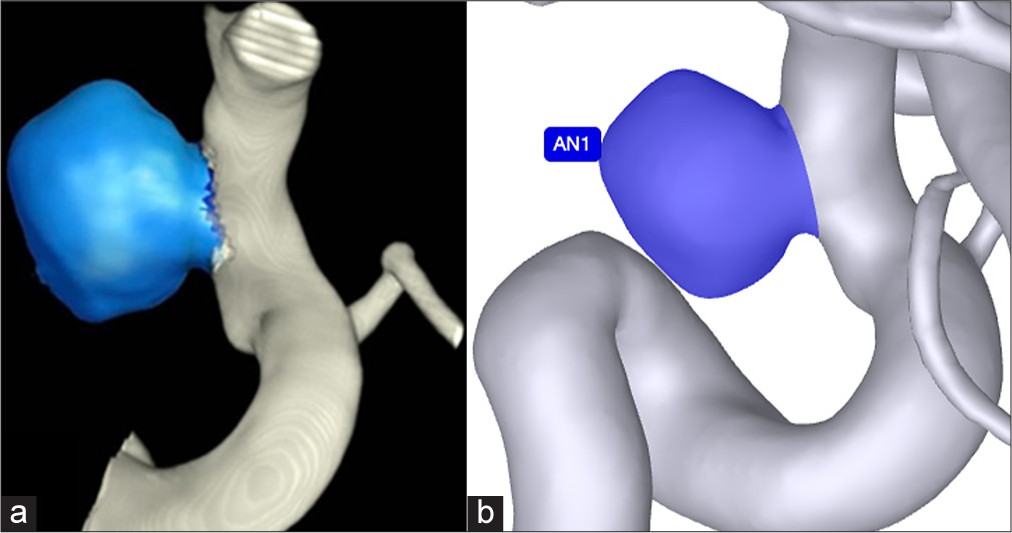
Enhancing precision in aneurysm volume measurement: A comparative study of techniques including an artificial intelligence-based method for endovascular coiling
Date of publication: 30-May-2025
Background: Durable occlusion after endovascular coiling can be compromised by recanalization, underscoring the need for accurate cerebral aneurysm assessment. Precise volume measurement not only informs treatment decisions and detects subtle aneurysm growth but also refines calculations of packing density, historically linked to occlusion success. This study compares three volume-measurement approaches-traditional two-dimensional (2D) estimation, a semi-automated three-dimensional (3D) technique, and an artificial intelligence (AI)-based 3D method.
Concomitant trigeminal and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: Illustrative case and scoping review
Date of publication: 30-May-2025
Background: Cranial neuralgias are characterized by sharp lancinating pain that occurs on specific regions served by cranial nerves. Glossopharyngeal neuralgia (GPN) and trigeminal neuralgia (TN) are disorders for which etiology, epidemiology, and pain regions differ. On the other hand, the treatment stays the same as microvascular decompression, which serves as a safe approach for these entities.
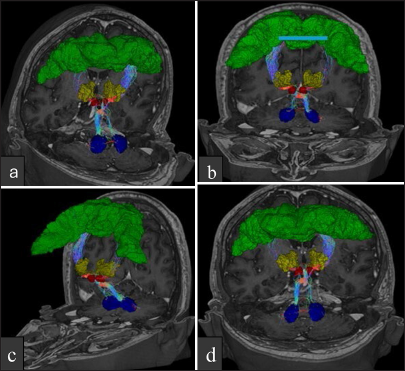
Dentato-rubro-thalamic tract tractography: Constrained spherical deconvolution versus diffusion tensor imaging for essential tremor deep brain stimulation targeting
Date of publication: 30-May-2025
Background: This study aimed to compare diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and constrained spherical deconvolution (CSD) techniques in the segmentation of the dentate-rubro-thalamic tract (DRTT), evaluating their anatomical accuracy and applicability for surgical planning in deep brain stimulation (DBS) for essential tremor surgery in two patients.
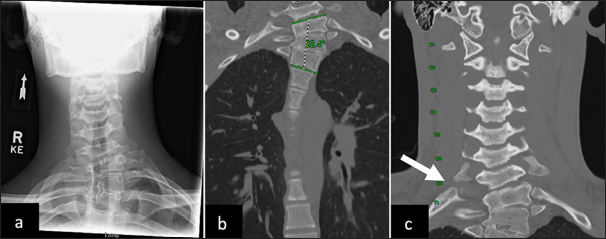
Thoracic outlet syndrome associated with cervicothoracic scoliosis
Date of publication: 30-May-2025
Background: Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a debilitating neurologic condition that is commonly encountered in routine neurosurgical practice. It causes severe pain, paresthesias, and weakness in the affected limb and can negatively impact patients’ quality of life. Classically, TOS is caused by compression of the neurovascular bundle in the thoracic outlet region, often by soft tissue or bony anomalies. A relationship to cervicothoracic scoliosis has not been previously reported. The purpose of this case series is to report on the clinical and radiographic findings, surgical interventions, and clinical outcomes in patients with TOS and concurrent cervicothoracic scoliosis. We hypothesize that the abnormal cervicothoracic curvature may contribute to compression within the thoracic outlet.
Pseudoaneurysm development in extracranial-intracranial bypass surgery: Diagnostic challenges and surgical solutions
Date of publication: 30-May-2025
Background: Pseudoaneurysm formation at the anastomotic site of extracranial-intracranial (EC-IC) bypass surgery is a rare but potentially severe complication. Due to its unpredictable nature and associated risks, early detection and appropriate management are crucial. However, the rarity of this condition makes diagnosis and treatment challenging. This review explores the pathophysiology, risk factors, diagnostic strategies, and management options for pseudoaneurysms in EC-IC bypass procedures.
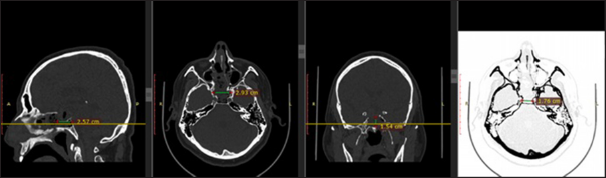
Prevalence of anatomical variants in preoperative computed tomography imaging for surgical planning of the endonasal transsphenoidal corridor
Date of publication: 30-May-2025
Background: The endonasal transsphenoidal approach is a fundamental technique for the resection of pituitary tumors. Anatomical variability of the sphenoid sinus and its relationship with neurovascular structures can influence surgical planning and outcomes.