Delayed-onset spinal subdural hematoma after kyphoplasty
Date of publication: 23-May-2025
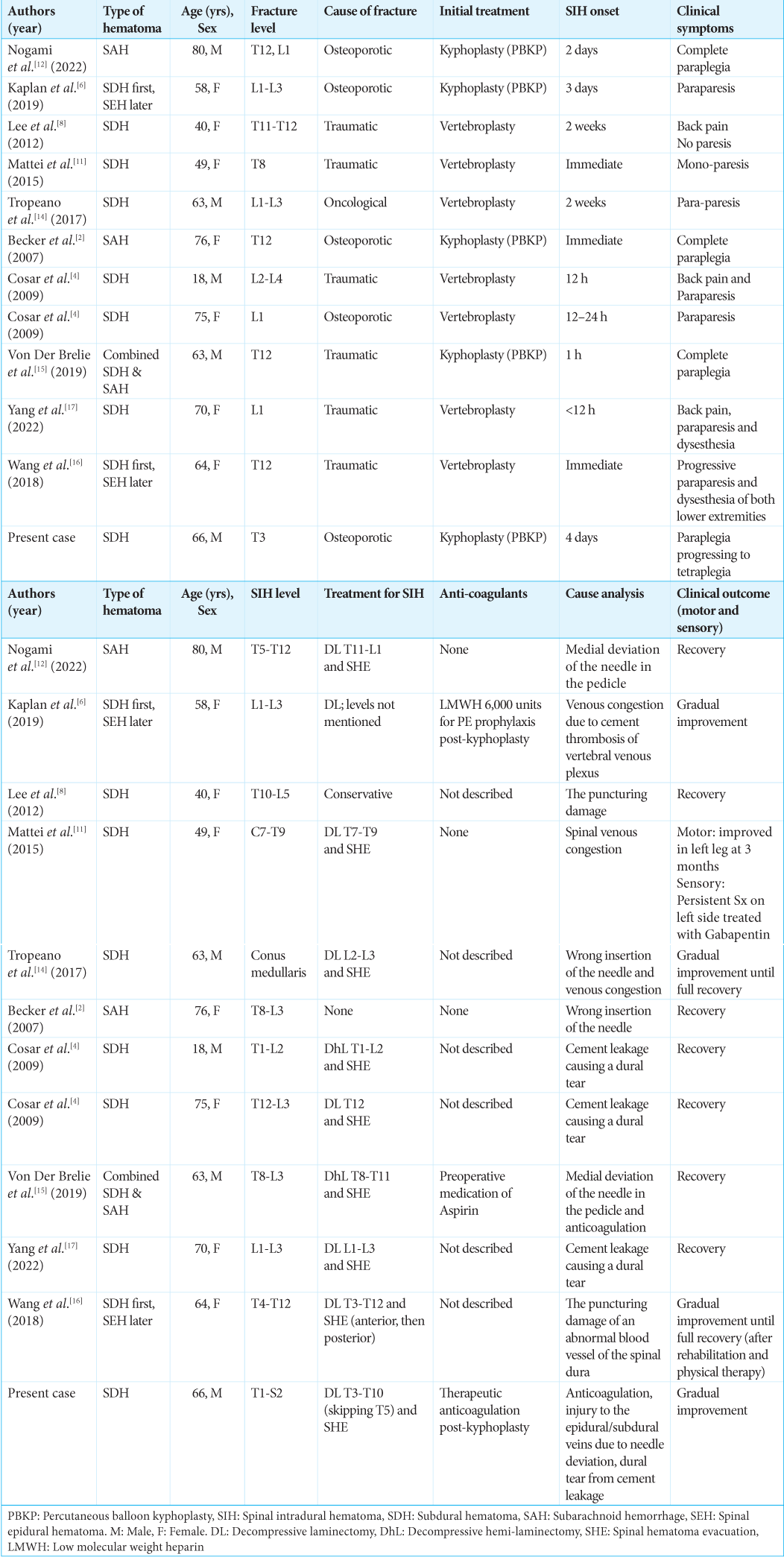
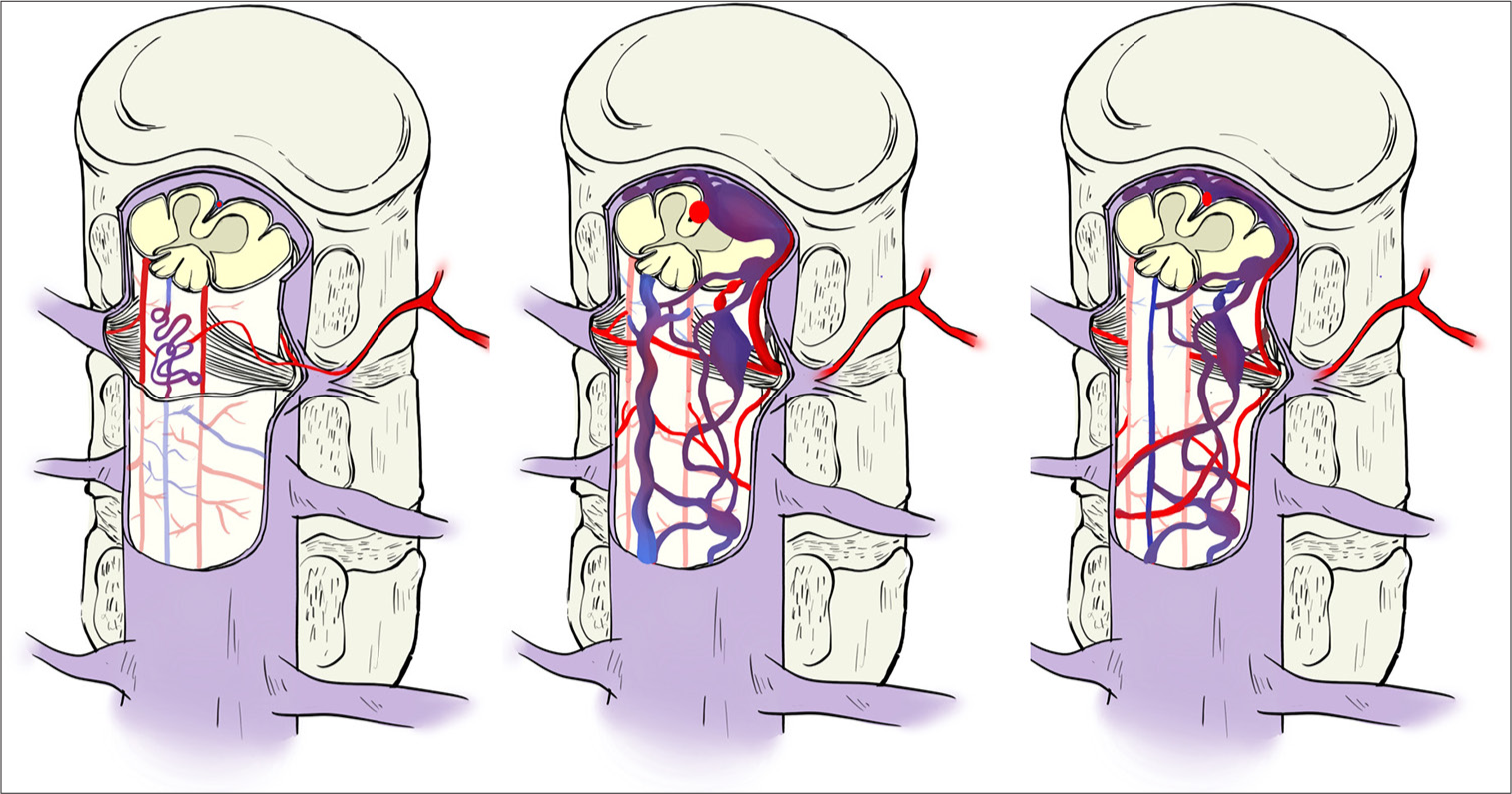
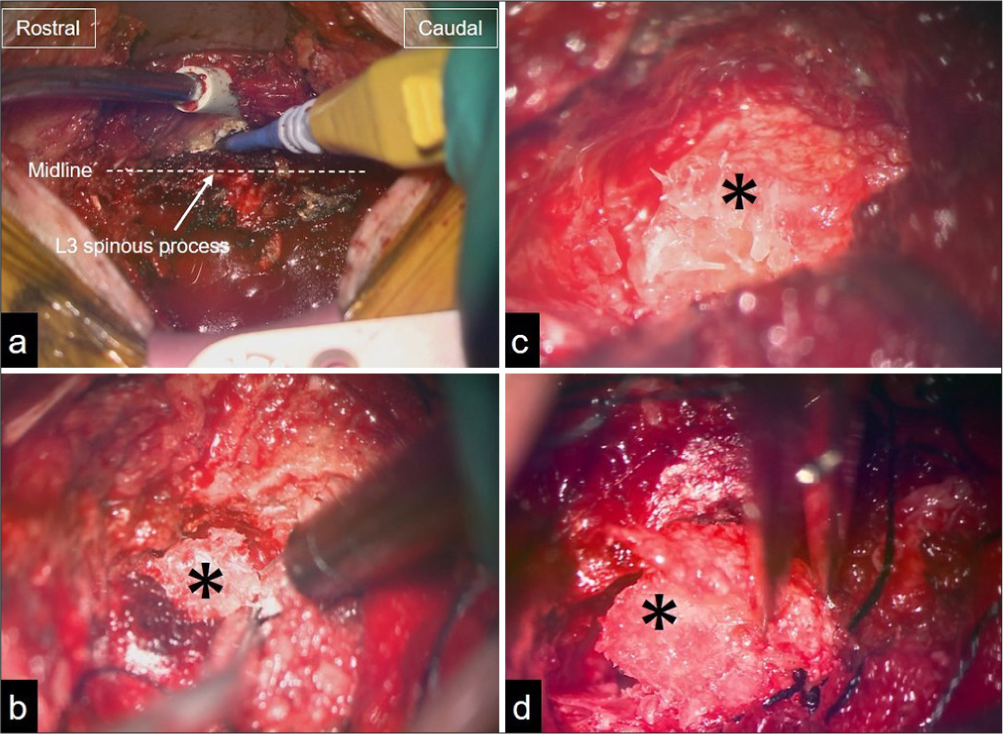
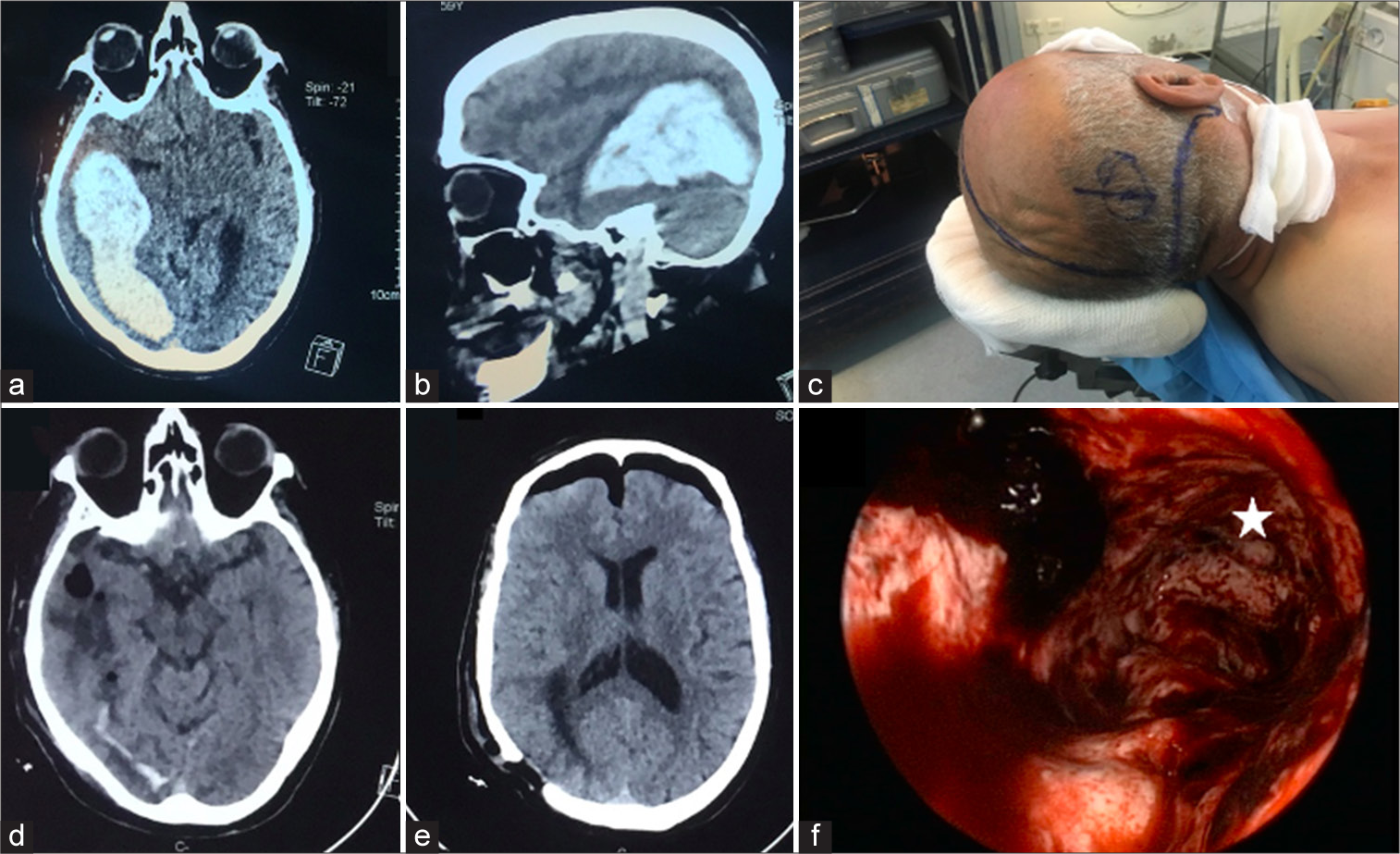
Background: Spinal subdural hematoma (SDH) is a very rare complication of percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty. Here, a 66-year-old male developed delayed-onset spinal SDH following kyphoplasty.
Treatment of 23 spinal perimedullary arteriovenous fistulas in a single center: A simple and practical treatment strategy
Date of publication: 23-May-2025
Background: The aim of the study is to present our strategy for stratifying patients with spinal perimedullary arteriovenous fistulas (PMAVFs) and apply the appropriate treatment.
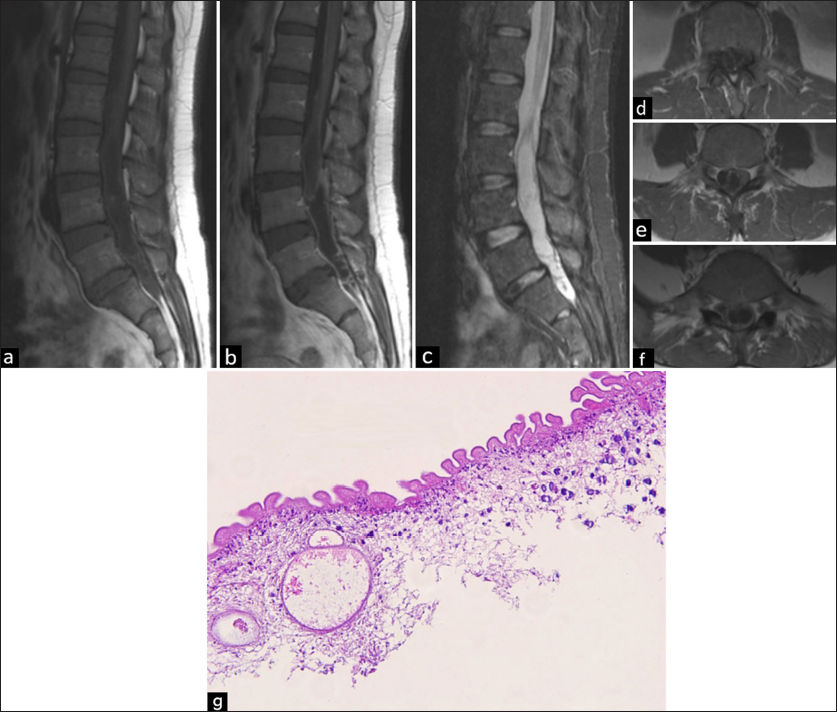
A rare case of lumbar intraspinal osteolipoma presenting with a sciatic pain
Date of publication: 23-May-2025
Background: Osteolipoma constitutes <1% of all lipomas. They are only rarely located in the spine. Here, we report an extremely rare lumbar intraspinal osteolipoma, along with a review of its clinical and radiological features.
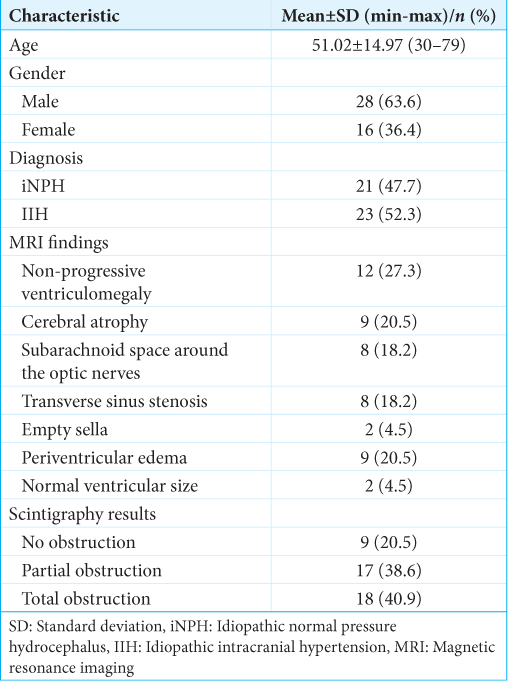
Diagnostic efficacy of radionuclide scintigraphy in detecting lumboperitoneal shunt obstructions in idiopathic hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension
Date of publication: 23-May-2025
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic effectiveness of radionuclide scintigraphy (RS) in detecting lumboperitoneal shunt (LPS) obstructions in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) and idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH).
Posterior fossa hemorrhagic complication after tuberculum sellae meningioma surgery through transcranial corridor: A proposed hypothesis
Date of publication: 23-May-2025
Road map to enhanced recovery protocol for endonasal endoscopic approach to pituitary adenomas: Surgical short-term outcome and experience of a single ENT/neurosurgery collaboration
Date of publication: 23-May-2025
Background: The endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach has become standard for the management of pituitary adenomas. This approach has been shown to facilitate early recovery and discharge from the hospital. The early recovery protocol has many advantages for both patients and the healthcare system in terms of patient satisfaction and cost-effectiveness.
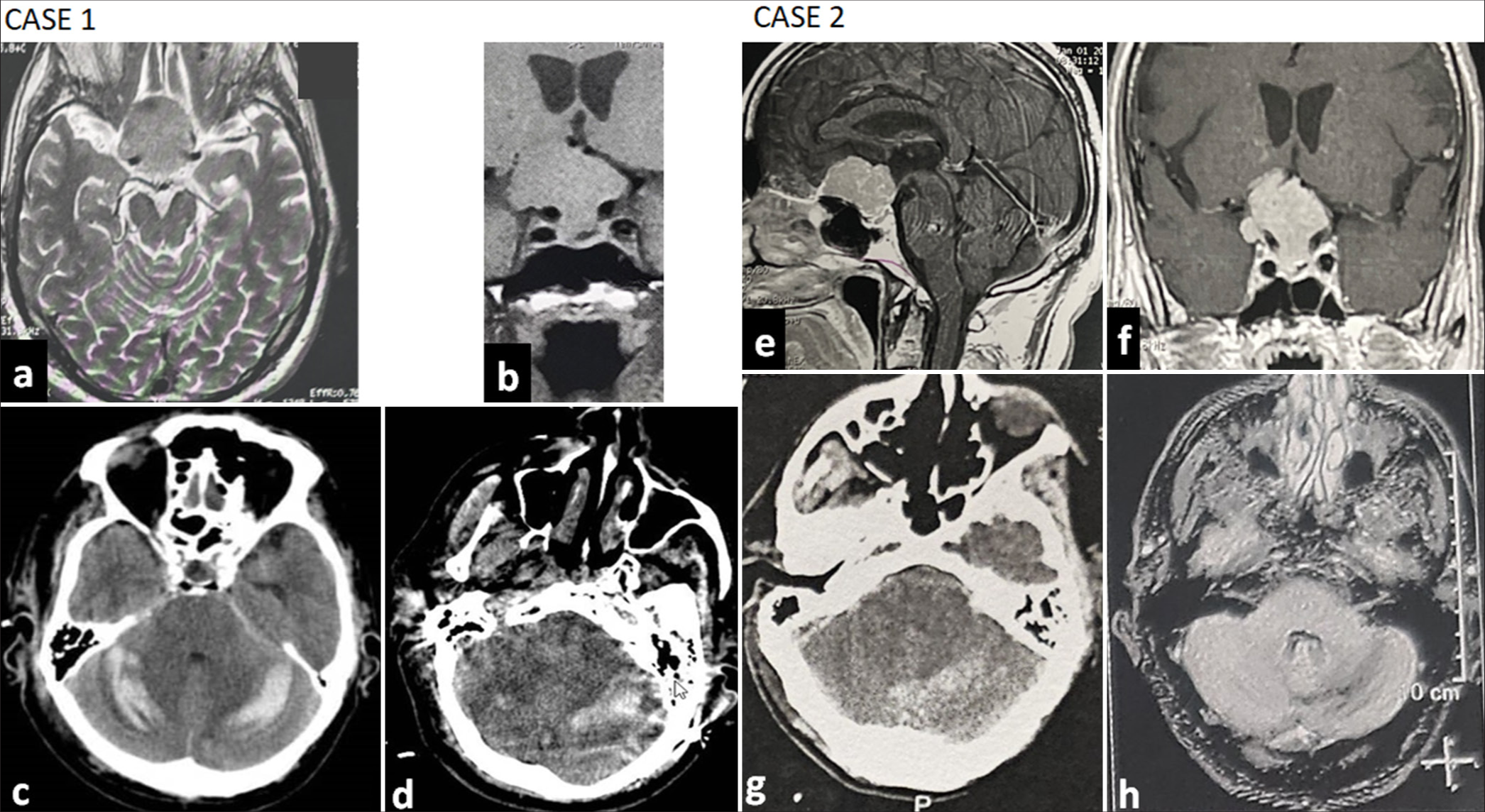
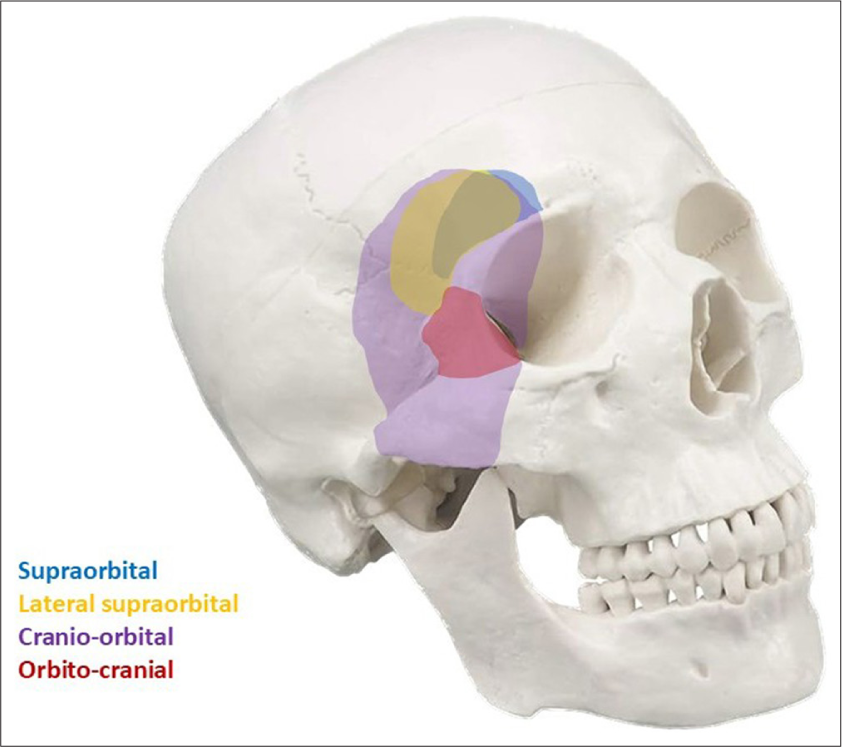
Cranial-orbital approaches for vascular pathology: A review of surgical approach selection and technical considerations
Date of publication: 23-May-2025
Background: Modified cranial approaches for vascular pathology are sometimes necessary to enhance exposure and can be tailored by the pathology treated and surgical conditions. The authors outline these approaches, comparing the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Patient selection criteria and preliminary outcome of the first 20 endoscopic evacuation of intracerebral hematoma in a tertiary hospital center
Date of publication: 23-May-2025
Background: Evacuation of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) using endoscopic, minimally invasive surgery is becoming the main technique in the surgical treatment of this devastating disease, given the overall improved outcomes reported. We report our experience with patient selection and preliminary results of the first 20 patients with ICH treated with endoscopic evacuation.
Disseminated and migratory sparganosis in the central nervous system: A case report and literature review of combined spinal and intracranial involvement
Date of publication: 16-May-2025
Background: Central nervous system (CNS) sparganosis is an exceptionally rare parasitic infection caused by the larvae of Spirometra species. Its migratory nature and nonspecific clinical presentation often lead to misdiagnosis, posing significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. While CNS involvement typically affects either the brain or spinal cord, disseminated cases involving both regions are exceedingly rare.
Resection of a rare lumbar epithelioid schwannoma
Date of publication: 16-May-2025
Background: Schwannomas, along with meningiomas, constitute the most common type of intradural extramedullary tumors. They are rare, typically benign tumors that originate from Schwann cells. Symptoms and signs attributed to these tumors may include back/radicular pain, focal motor and/or sensory deficits, and bowel/bladder dysfunction. It is essential to obtain pathological confirmation of this lesion and to differentiate it from other benign (i.e., neurofibromas, lipomas, ganglion cysts, meningiomas, and giant cell tumors), and/ or infrequently malignant lesions (i.e., malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors, and sarcomas). Epithelioid Schwannomas/Benign Epithelioid Schwannomas (BES) is a benign, rare histologic subtype of schwannoma that resembles epithelial cells and lacks classic features such as Antoni A and Antoni B areas.