- Department of Neurosurgery, Tokyo Women’s Medical University Yachiyo Medical Center, Tokyo, Japan
- Department of Neurosurgery, St. Luke’s International Hospital, Tokyo, Japan.
Correspondence Address:
Akitsugu Kawashima, Department of Neurosurgery, St. Luke’s International Hospital, Tokyo, Japan.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_125_2024
Copyright: © 2024 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Takahiro Yokoyama1, Shunsuke Nomura1, Taiichi Ishiguro1, Kenichi Hodotsuka1, Atsushi Kuwano1, Yukiko Tanaka1, Masato Murakami1, Takakazu Kawamata1, Akitsugu Kawashima2. A case of bilateral vertebral artery dissection treated by bilateral surgical occlusion and low-flow bypass. 05-Apr-2024;15:121
How to cite this URL: Takahiro Yokoyama1, Shunsuke Nomura1, Taiichi Ishiguro1, Kenichi Hodotsuka1, Atsushi Kuwano1, Yukiko Tanaka1, Masato Murakami1, Takakazu Kawamata1, Akitsugu Kawashima2. A case of bilateral vertebral artery dissection treated by bilateral surgical occlusion and low-flow bypass. 05-Apr-2024;15:121. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/?post_type=surgicalint_articles&p=12842
Abstract
Background: Bilateral vertebral artery dissection aneurysm (VADA) is a rare condition that leads to severe stroke. However, the surgical strategy for its treatment is controversial because the pathology is very complicated and varies in each case. Here, we report a case of bilateral VADA that was successfully treated with staged bilateral VADA occlusion and low-flow bypass.
Case Description: A Japanese man in his 40s presented with bilateral VADA with subarachnoid hemorrhage. He had only mild headaches without any other neurological deficits. Subsequently, the ruptured left VADA was surgically trapped. However, on postoperative day 11, the contralateral VADA enlarged. The right VADA was then proximally clipped via a lateral suboccipital approach. Furthermore, a superficial temporal artery–superior cerebellar artery bypass was performed through a subtemporal approach in advance to preserve cerebral flow in the posterior circulation. The bilateral VADA was obliterated, and the patient had an uneventful postoperative course during the 1-year and 6-month follow-up period.
Conclusion: Bilateral VADA can be successfully treated with staged bilateral VADA obstruction and low-flow bypass. In this case, as the posterior communicating arteries were the fetal type and the precommunicating segments of the posterior cerebral arteries (P1) were hypoplastic, a low-flow bypass was used to supply the basilar and cerebellar arteries, except the posterior cerebral and posterior inferior cerebellar arteries. Furthermore, low-flow bypass is a less invasive option than high-flow bypass.
Keywords: Bilateral vertebral dissection, Direct surgery, Low-flow bypass, Proximal clipping, Subarachnoid hemorrhage, Trapping
INTRODUCTION
The prevalence rate of fusiform aneurysms, including vertebral artery dissection aneurysms (VADA), is reportedly <0.1%.[
CASE DESCRIPTION
A man in his early 40s with no past medical history presented with a mild headache that had persisted for two days. He was diagnosed with a SAH that corresponded to the World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies Grade I.[
Figure 1:
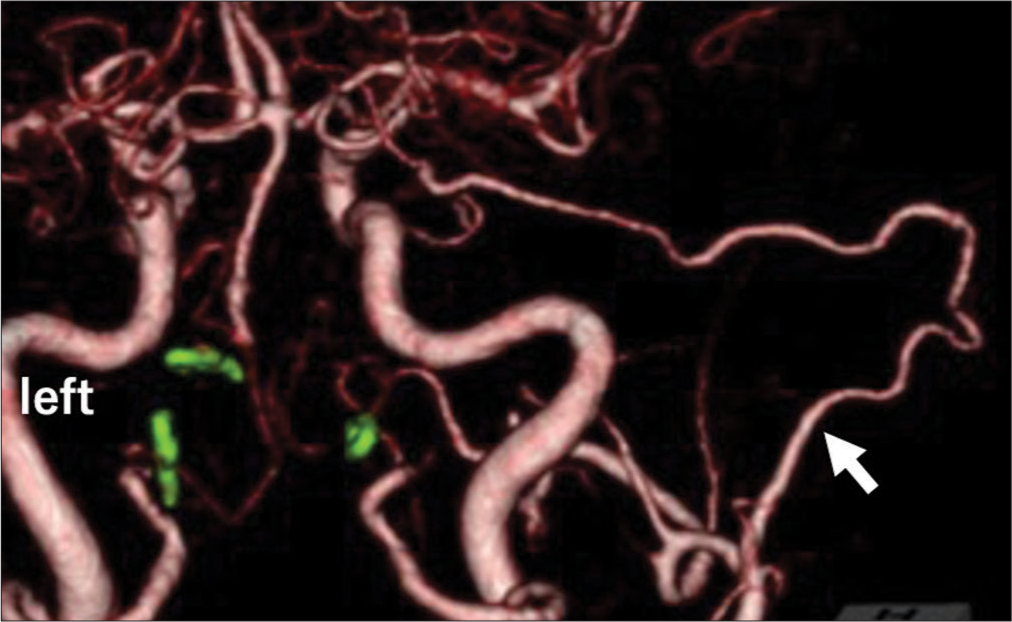
(a) Posterior view of computed tomography angiography on admission demonstrates bilateral vertebral dissection aneurysm (arrows); (b) Posterior view of computed tomography angiography on hospital days 3 (arrows); (c) Posterior view of computed tomography angiography on hospital days 11 reveals that the right vertebral dissection aneurysm is rapidly enlarging (arrows); (d) A lateral view of right vertebral angiography reveals a perforating artery to the medulla oblongata from the distal part of the right vertebral dissection aneurysm (arrows) and hypoplastic precommunicating segment of the posterior cerebral arteries.
Figure 2:
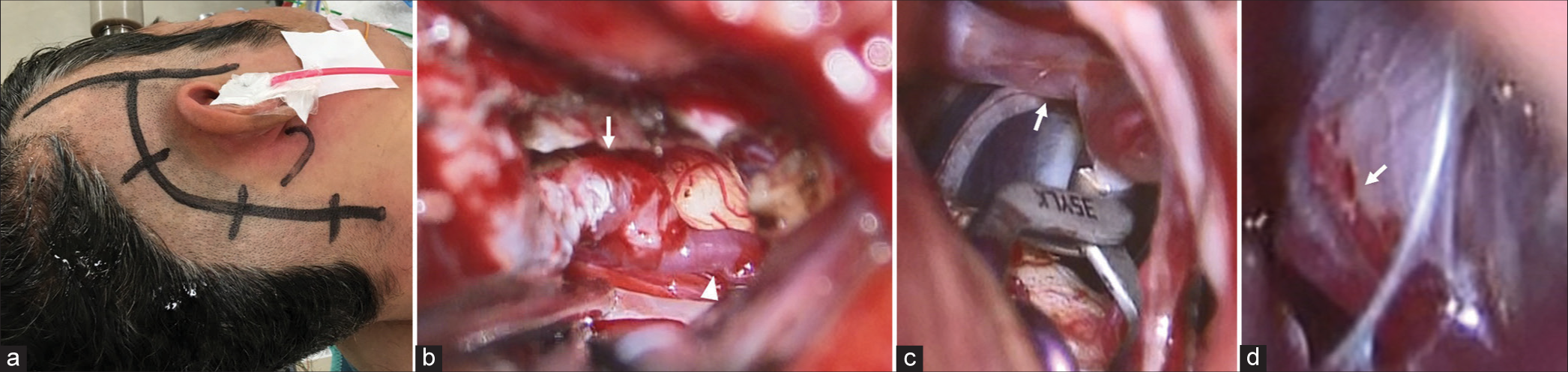
(a) Skin incision line for right superficial temporal artery–superior cerebellar artery (SCA) bypass and proximal clipping of the right vertebral dissection aneurysm; (b) Intraoperative findings of a right superficial temporal artery (arrows)–SCA (arrows head) bypass. The interruption time of a right SCA during the bypass was 28 min; (c) Intraoperative findings of proximal clipping distal to the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (arrows); (d) Intraoperative findings of right vertebral dissection aneurysm and the perforator from the distal part to the brain stem (arrows).
DISCUSSION
We report a case of bilateral VADA that was successfully treated with staged bilateral VADA occlusion and low-flow bypass. The management strategies for bilateral VADA with SAH are controversial. Here, we present an effective surgical option for the treatment of bilateral VADA. The indications for bypass in the treatment of bilateral VADA were selected individually. Some previous studies have reported strategies to preserve perfusion in the basilar and cerebellar arteries. Ota et al. and Saito et al. reported an efficient treatment of bilateral VADA using high-flow bypass. [
CONCLUSION
We describe a patient with bilateral VADA successfully treated with staged bilateral VADA obstruction and low-flow bypass. In such cases, as perfusion of the PCA is supplied by adequate antegrade flow via PCOMs, low-flow bypass is sufficient to maintain the circulation of the basilar and cerebellar arteries. Based on collateral flow, low-flow bypass may be considered a potential treatment option for bilateral VADA occlusion, as it tends to be less invasive than high-flow bypass.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Journal or its management. The information contained in this article should not be considered to be medical advice; patients should consult their own physicians for advice as to their specific medical needs.
References
1. Aihara M, Naito I, Shimizu T, Matsumoto M, Asakura K, Miyamoto N. Predictive factors of medullary infarction after endovascular internal trapping using coils for vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2018. 129: 107-13
2. Anson JA, Lawton MT, Spetzler RF. Characteristics and surgical treatment of dolichoectatic and fusiform aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1996. 84: 185-93
3. Endo H, Matsumoto Y, Kondo R, Sato K, Fujimura M, Inoue T. Medullary infarction as a poor prognostic factor after internal coil trapping of a ruptured vertebral artery dissection. J Neurosurg. 2013. 118: 131-9
4. Kono K, Shintani A, Fujimoto T, Terada T. Stent-assisted coil embolization and computational fluid dynamics simulations of bilateral vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms presenting with subarachnoid hemorrhage: Case report. Neurosurgery. 2012. 71: E1192-200
5. Motoyama Y, Takamura Y, Park HS, Miyasaka T, Wada T, Yamada S. Appropriate flow reduction for unilateral ruptured vertebral artery dissection by proximal clipping to prevent rebleeding and medullary infarction. World Neurosurg. 2019. 130: e627-33
6. Murai Y, Matano F, Yokobori S, Onda H, Yokota H, Morita A. Treatment strategies of subarachnoid hemorrhage from bilateral vertebral artery dissection: A case report and literature review focusing on the availability of stent placement. World Neurosurg. 2017. 106: 1050.e11
7. Ota N, Tanikawa R, Eda H, Matsumoto T, Miyazaki T, Matsukawa H. Radical treatment for bilateral vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms by reconstruction of the vertebral artery. J Neurosurg. 2016. 125: 953-63
8. . Report of world federation of neurological surgeons committee on a universal subarachnoid hemorrhage grading scale. J Neurosurg. 1988. 68: 985-6
9. Saito N, Kamiyama H, Takizawa K, Takebayashi S, Asano T, Kobayashi T. Management strategy for bilateral complex vertebral artery aneurysms. Neurosurg Rev. 2016. 39: 289-95
10. Tatsuya I, Koji Y, Hidenori A, Taichi I, Go M, Takakazu K. Stent-assisted coil embolisation for bilateral vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms presenting with subarachnoid haemorrhage. Neuroradiol J. 2016. 29: 473-8
11. van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJ, van Gijn J. Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke. 1988. 19: 604-7
12. Zhang Y, Tian Z, Zhu W, Liu J, Wang Y, Wang K. Endovascular treatment of bilateral intracranial vertebral artery aneurysms: An algorithm based on a 10-year neurointerventional experience. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020. 5: 291-301