- Department of Neurosurgery, Social Insurance Tagawa Hospital, Kamihonmachi, Tagawa,
- Department of Neurosurgery, Uchikado Neuro-Spine Clinic, Hakata-Ku Naka, Fukuoka,
- Department of Neurosurgery, Kurume University School of Medicine, Asahi-Machi, Kurume, Japan.
Correspondence Address:
Takehiro Makizono, Department of Neurosurgery, Social Insurance Tagawa Hospital, Kamihonmachi, Tagawa, Japan.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_839_2022
Copyright: © 2022 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Takehiro Makizono1, Hisaaki Uchikado2, Takayasu Ando3, Jin Kikuchi3, Gohsuke Hattori3, Motohiro Morioka3. A case of mid-thoracic osteoporotic vertebral fracture with the inability to belch syndrome. 07-Oct-2022;13:458
How to cite this URL: Takehiro Makizono1, Hisaaki Uchikado2, Takayasu Ando3, Jin Kikuchi3, Gohsuke Hattori3, Motohiro Morioka3. A case of mid-thoracic osteoporotic vertebral fracture with the inability to belch syndrome. 07-Oct-2022;13:458. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/11920/
Abstract
Background: Osteoporotic vertebral fractures (OVF) commonly occur at the thoracolumbar junction, but are less frequently encountered in the mid-thoracic region. Here, a 69-year-old female presented with back pain and the new onset of symptoms characterized by the inability to belch.
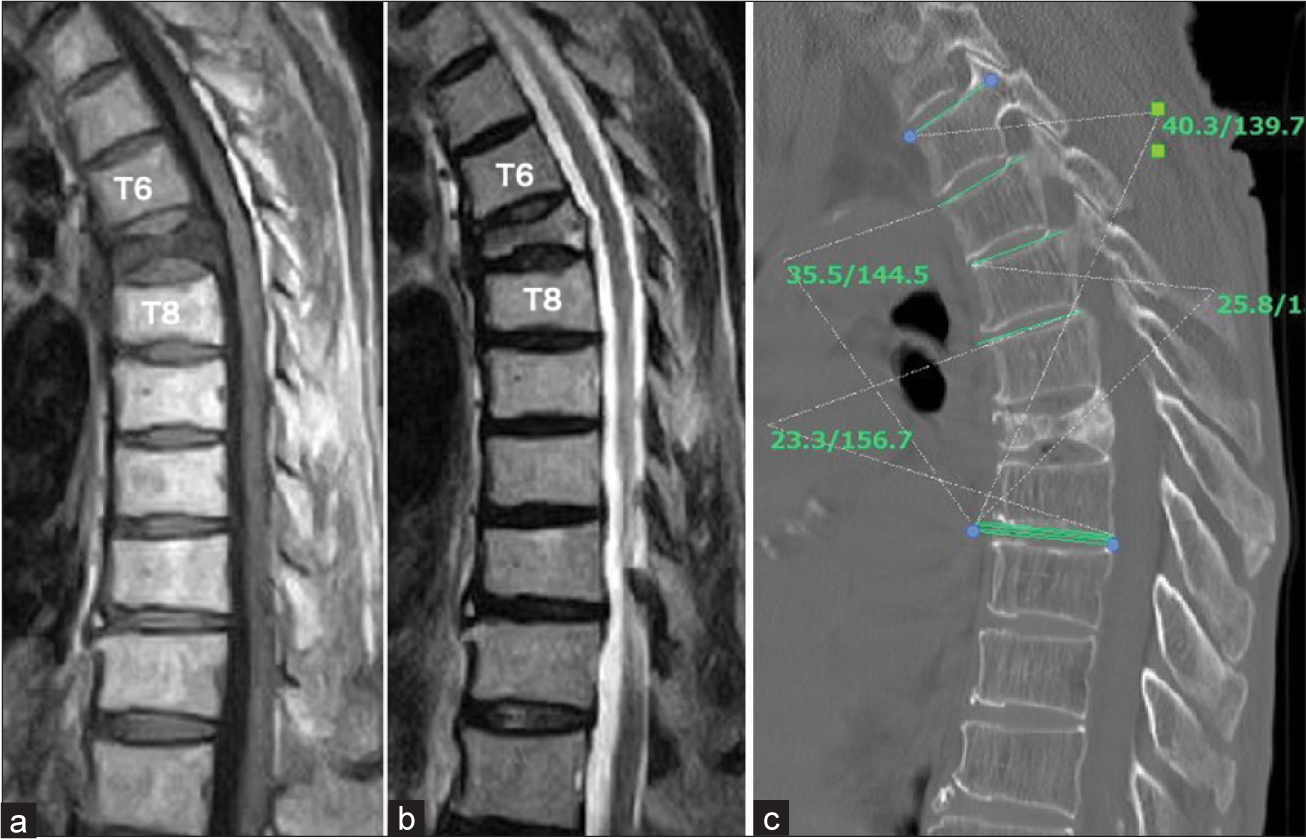
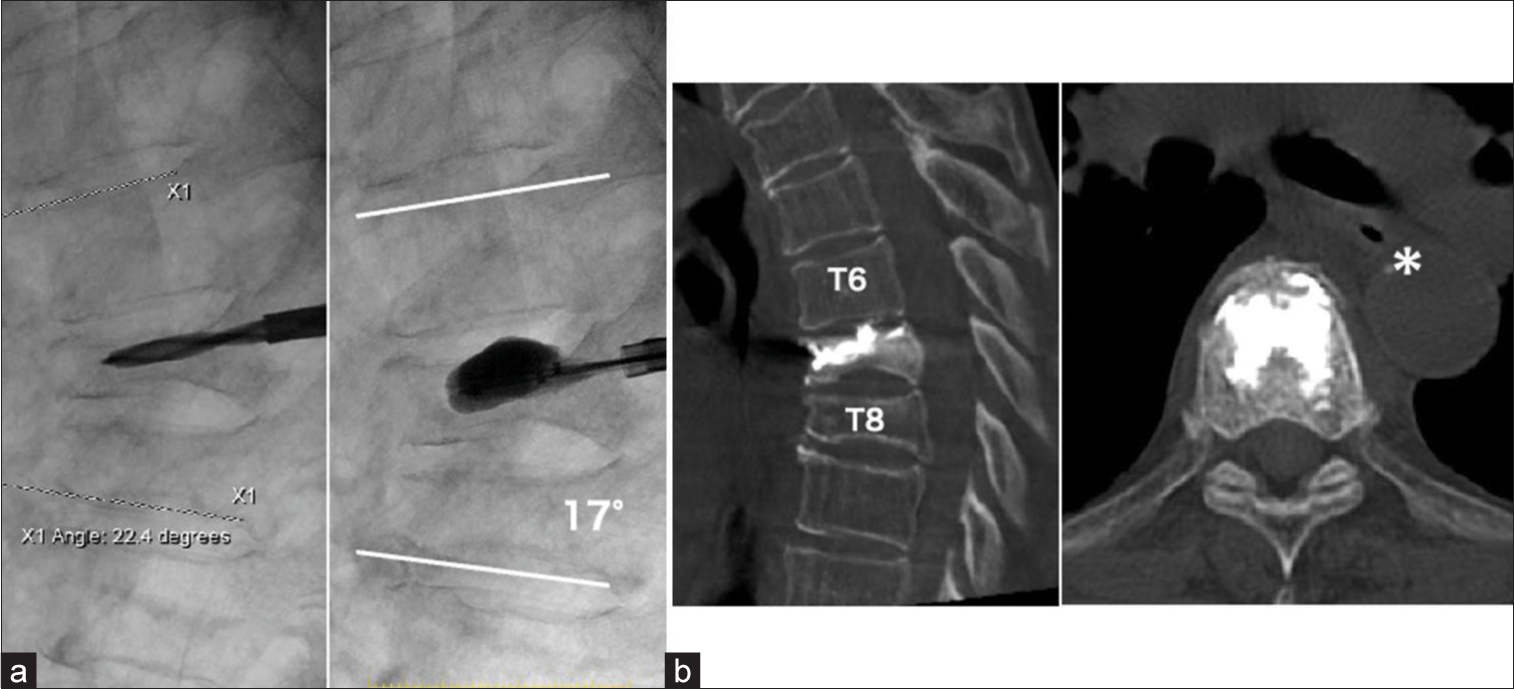
Case Description: A 69-year-old female presented with back pain. 2 months later, she developed anorexia and difficulty belching. The thoracic magnetic resonance (MR) demonstrated a T7 OVF. As she ultimately underwent a balloon kyphoplasty (BKP), as conservative treatment was unsuccessful.
Conclusion: OVF should be suspected in elderly females with the inability to belch accompanied by chest and back pain. The diagnosis is best established with a spinal MR imaging and should be followed by BKP.
Keywords: Balloon kyphoplasty, Gastroesophageal reflux disease, Inability to belch, Mediastinal triangle, Osteoporotic vertebral fracture, Spinal deformity
INTRODUCTION
In Japan, the number of osteoporosis patients has reached 10 million, is still increasing resulting in a poorer quality of life, and increased morbidity/mortality.[
CASE REPORT
A 69-year-old female presented with chest and severe upper back pain, but neurologically intact. The first chest computed tomography (CT) was interpreted as normal [
DISCUSSION
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is known to be a post OVF spinal deformity gastrointestinal symptom, and vertebral body fractures and kyphosis at the thoracolumbar junction are considered contributing risk factors.[
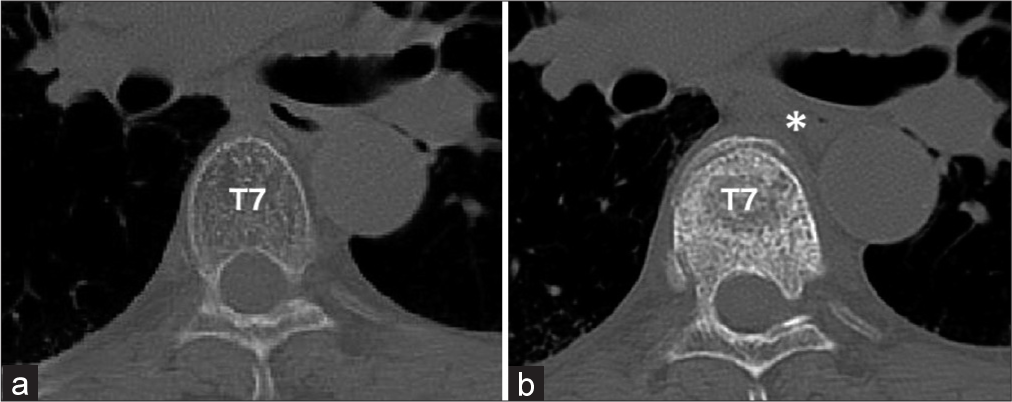
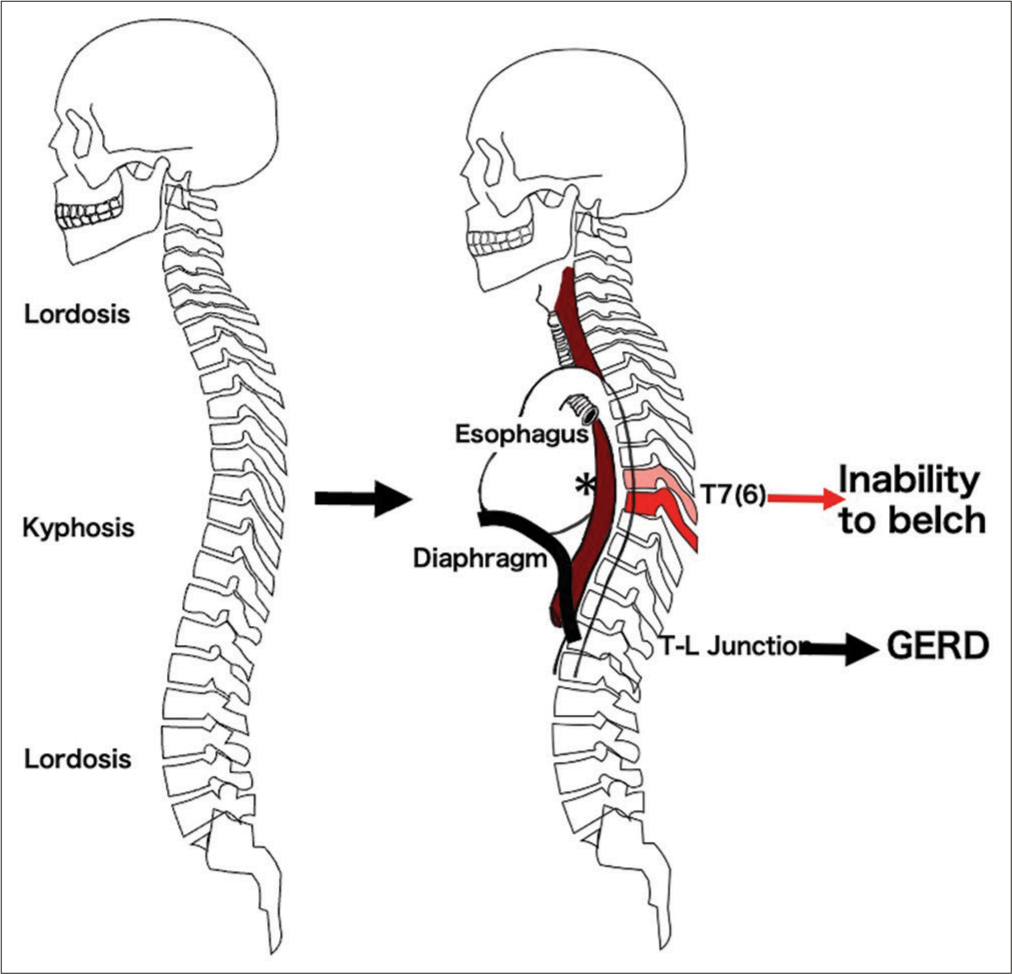
In this case report, the patient did not have GERD, but rather, the inability to belch that was attributed to her T7 OVF. The wedge kyphosis deformity of the mid-thoracic spine (i.e., T7 in this case) likely caused a localized minor narrowing of the esophagus, leading to air entrapment and making it difficult to belch [
Figure 4:
In humans, kyphotic deformation occurs in the middle thoracic spine due to aging (Left).[
CONCLUSION
Patients with back pain who have gastroesophageal symptoms such as the inability to belch may have a mid-thoracic OVF. In these cases, MR studies of the thoracic spine should be performed followed by the early performance of a BKP.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Gulias-Soidan D, Fraga-Manteiga D, Mosquera-Rodriguez VX, Marini-Diaz M, Lopez-Bargiela P, González-Martín C. The importance of the mediastinal triangle in traumatic lesions of the Aorta. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. 55: 263
2. Ikeda Y, Sudo A, Yamada T, Uchida A. Mortality after vertebral fractures in a Japanese population. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2010. 18: 148-52
3. Masharawi Y, Salame K, Mirovsky Y, Peleg S, Dar G, Steinberg N. Vertebral body shape variation in the thoracic and lumbar spine: Characterization of its asymmetry and wedging. Clin Anat. 2008. 21: 46-54
4. Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Sasaki H, Kamo K, Shimada Y. Impact of spinal kyphosis on gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms in patients with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2009. 20: 1193-8
5. Ohba T, Ebata S, Koyama K, Haro H. Prevalence and key radiographic spinal malalignment parameters that influence the risk for gastroesophageal reflux disease in patients treated surgically for adult spinal deformity. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018. 18: 8
6. Prince RL, Devine A, Dick IM. The clinical utility of measured kyphosis as a predictor of the presence of vertebral deformities. Osteoporos Int. 2007. 18: 621-7