- Department of Neurosurgery, Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht
- Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
- Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital of Essen, Essen, Germany
Correspondence Address:
Pieter L. Kubben
Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital of Essen, Essen, Germany
DOI:10.4103/2152-7806.208805
Copyright: © 2017 Surgical Neurology International This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Kubben PL, Germans MR, Jabbarli R. Delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage: Comparing and integrating classification systems. Surg Neurol Int 21-Jun-2017;8:121
How to cite this URL: Kubben PL, Germans MR, Jabbarli R. Delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage: Comparing and integrating classification systems. Surg Neurol Int 21-Jun-2017;8:121. Available from: http://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/delayed-cerebral-ischemia-after-subarachnoid-hemorrhage-comparing-and-integrating-classification-systems/
Sir,
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a significant healthcare problem. It is estimated that 30000 Americans suffer from aneurysmal SAH each year. Delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI) is one of the major causes of morbidity and mortality after SAH, and occurs in 20–40% of patients.[
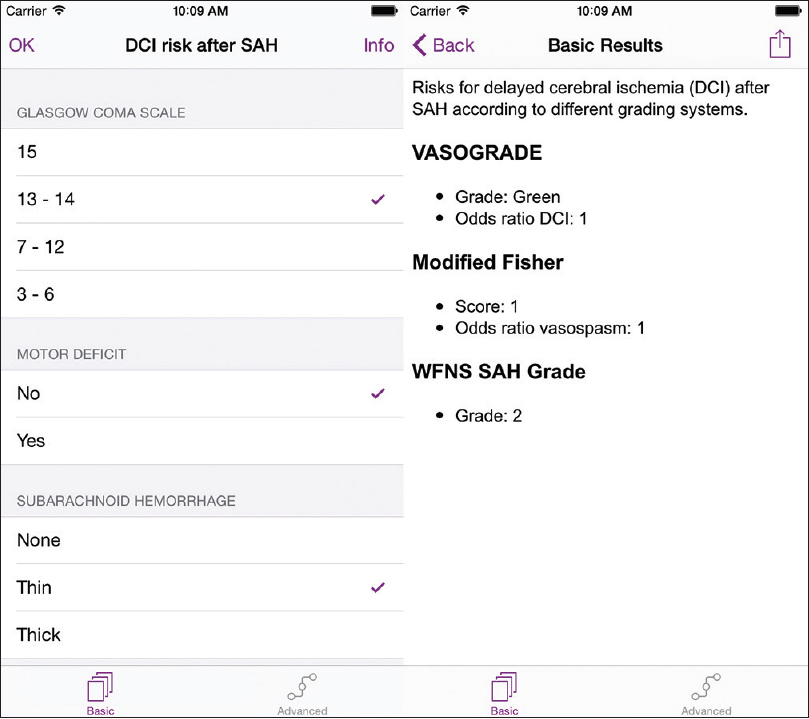
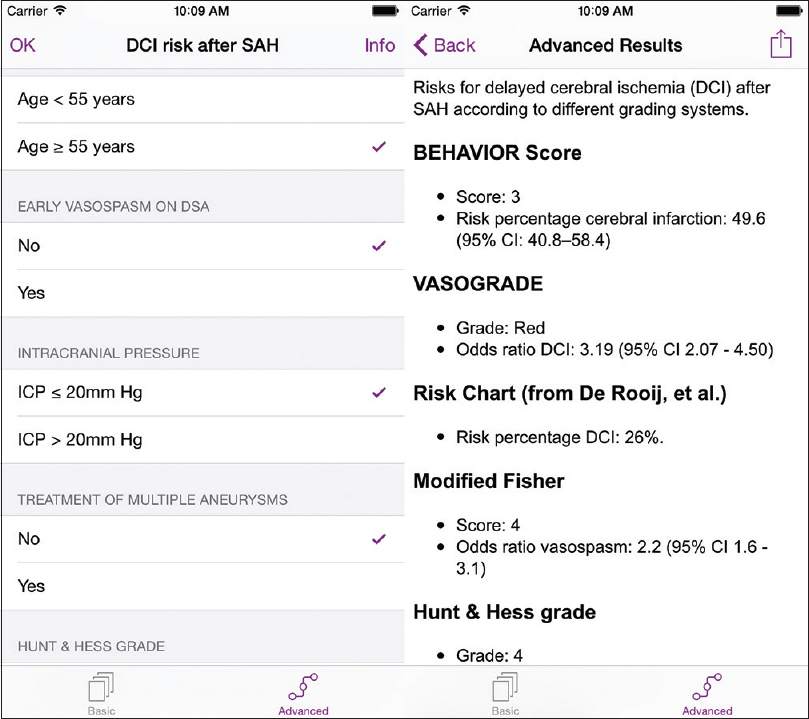
We developed and evaluated a mobile medical app for iOS (Apple Inc, Mountain View, CA) using class 1 CE-marked technology for risk minimization. The app, called SAH DCI, has been evaluated by all authors independently, where the results of the mobile clinical decision support system were compared with manually calculated scores, which were based on the original classification systems. The app provided identical results compared to manual calculation of the relevant classification systems.
The app consists of two screens, a basic module and an advanced module. The basic module asks 4 questions to calculate 3 grading scales (WFNS SAH Grade,[
In conclusion, the SAH DCI app offers clinicians a user-friendly and accurate tool for mobile clinical decision support on DCI after SAH. It combines multiple classification systems for risk calculation that may help to guide treatment, as well as ease and quicken the clinical implication of different SAH scores. Further research and comparative effectiveness studies focusing on different classification systems are needed to extract the main parameters that predict DCI after SAH.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
The first author is the developer of the app. Other authors report no conflict of interest.
References
1. de Oliveira Manoel AL, Jaja BN, Germans MR, Yan H, Qian W, Kouzmina E. The VASOGRADE: A Simple Grading Scale for Prediction of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stroke. 2015. 46: 1826-31
2. de Rooij NK, Greving JP, Rinkel GJE, Frijns CJM. Early Prediction of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Development and Validation of a Practical Risk Chart. Stroke. 2013. 44: 1288-94
3. Fisher CM, Kistler JP, Davis JM. Relation of Cerebral Vasospasm to Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Visualized by Computerized Tomographic Scanning. Neurosurgery. 1980. 6: 1-9
4. Frontera JA, Claassen J, Schmidt JM, Wartenberg KE, Temes R, Connolly ES. Prediction of Symptomatic Vasospasm after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: The Modified Fisher Scale. Neurosurgery. 2006. 59: 21-7
5. Harrod CG, Bendok BR, Batjer HH. Prediction of Cerebral Vasospasm in Patients Presenting with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Review. Neurosurgery. 2005. 56: 633-54
6. Hunt WE, Hess RM. Surgical risk as related to time of intervention in the repair of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1968. 28: 14-20
7. Jabbarli R, Reinhard M, Roelz R, Shah M, Niesen W-D, Kaier K. Early identification of individuals at high risk for cerebral infarction after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: The BEHAVIOR score. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015. 35: 1587-92
8. MacDonald RL. Delayed neurological deterioration after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Nature. 2014. 10: 44-58
9. Teasdale GM, Drake CG, Hunt W, Kassell N, Sano K, Pertuiset B. A universal subarachnoid hemorrhage scale: Report of a committee of the World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. 1988. 51: 1457-7