- Department of Orthopaedics, Seth G.S. Medical College and K.E.M. Hospital, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
- Spine Services, Indian Spinal Injuries Centre, New Delhi, India.
Correspondence Address:
Ashwin Hemant Sathe
Department of Orthopaedics, Seth G.S. Medical College and K.E.M. Hospital, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_773_2020
Copyright: © 2020 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Tushar Narayan Rathod1, Ashwin Hemant Sathe1, Nandan Amrit Marathe1, Abhinav Jogani1, Abhinandan Reddy Mallepally2, Chetan Shende1. Dysplasia and anomalies of atlas result in pediatric torticollis: A case report and literature review. 29-Dec-2020;11:471
How to cite this URL: Tushar Narayan Rathod1, Ashwin Hemant Sathe1, Nandan Amrit Marathe1, Abhinav Jogani1, Abhinandan Reddy Mallepally2, Chetan Shende1. Dysplasia and anomalies of atlas result in pediatric torticollis: A case report and literature review. 29-Dec-2020;11:471. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/?post_type=surgicalint_articles&p=10497
Abstract
Background: Often, the cause of bony torticollis is difficult to determine, especially in cases of multiple craniovertebral junction anomalies.
Case Description: We report a rare case of a dysplastic C1 vertebra (assimilation to the right occiput and C2, a nonseparated left odontoid, and discontinuity in both anterior and posterior arches of the atlas) in a 6-year-old child with progressive torticollis. Notably, the mechanism of torticollis was not a rotatory subluxation of C1-C2, but differential growth between C1-C2. The child underwent a successful C1-C2 Goel and Harms fusion with reduction/correction of the torticollis.
Conclusion: Torticollis caused by differential growth between the C1 and C2 vertebrae resulting in a nonrotatory subluxation/torticollis in a 6-year-old child, was successfully managed with a C1-C2 Goel and Harm’s fusion.
Keywords: Dysplasia, Occipitalization, Torticollis
INTRODUCTION
Torticollis may result from a congenital craniovertebral junction (CVJ) anomaly. Here, in a 6-year-old child with progressive torticollis, we recognized a dysplastic C1 vertebra showing assimilation to the right occiput and C2, accompanied by a nonseparated left odontoid, and discontinuity in both anterior and posterior arches of the atlas. This was successfully managed with a C1-C2 Goel and Harm’s fusion.
CASE DESCRIPTION
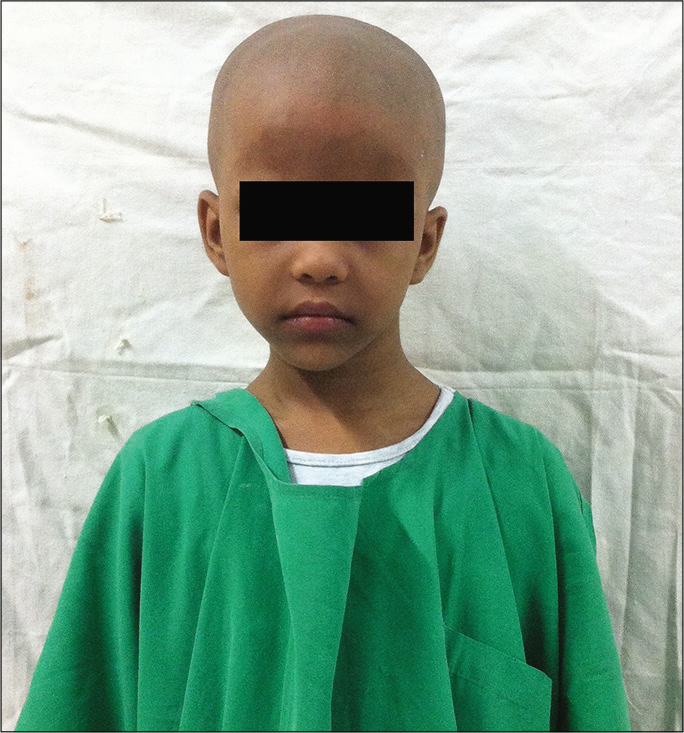
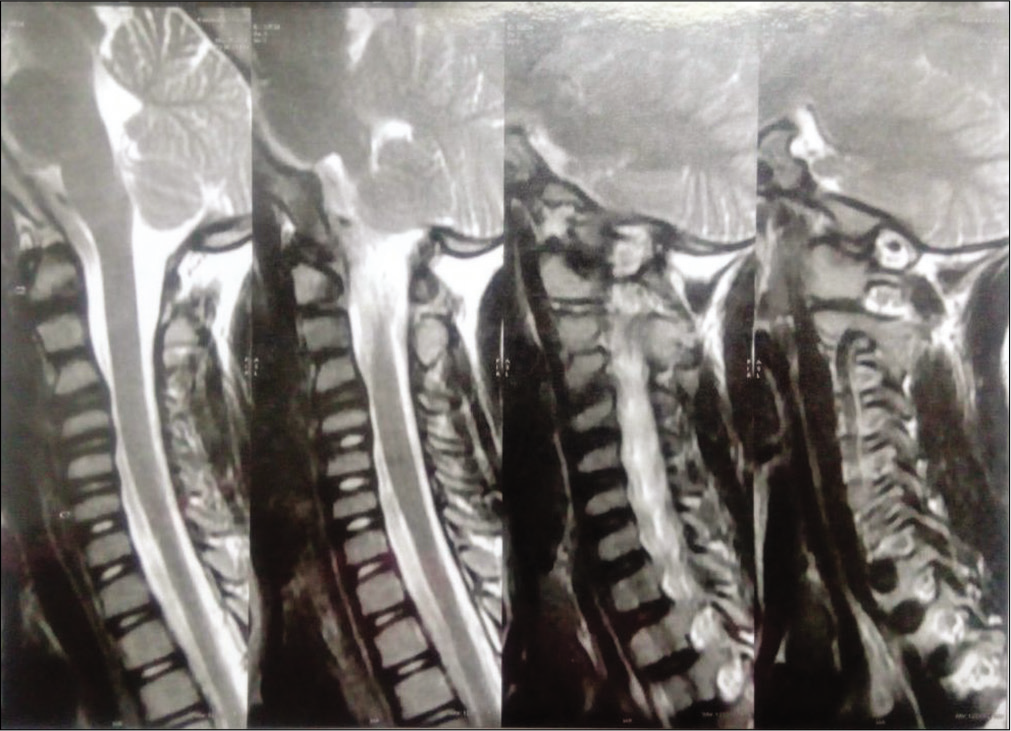
A 6-year-old female presented with a 3-year history of a progressive torticollis toward the right side. It was associated with facial asymmetry including a smaller right eye [
Figure 3:
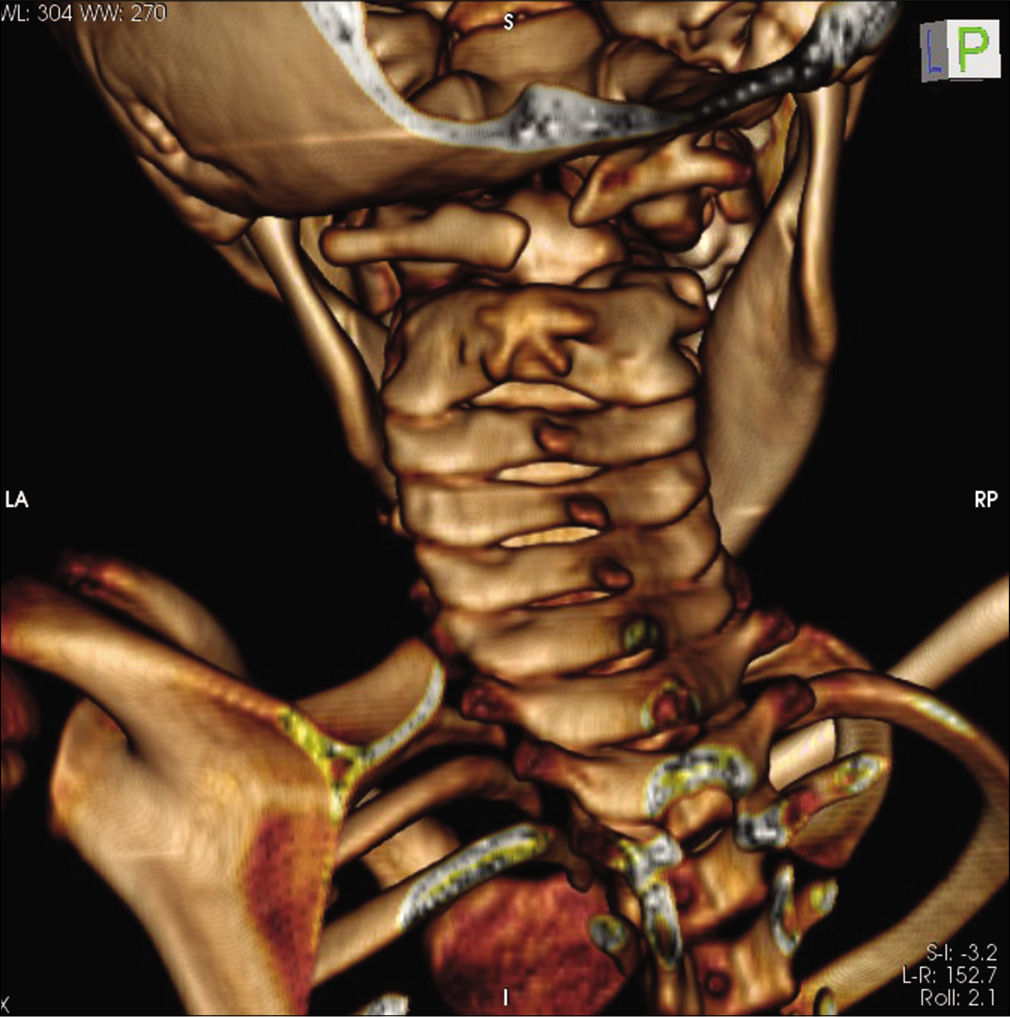
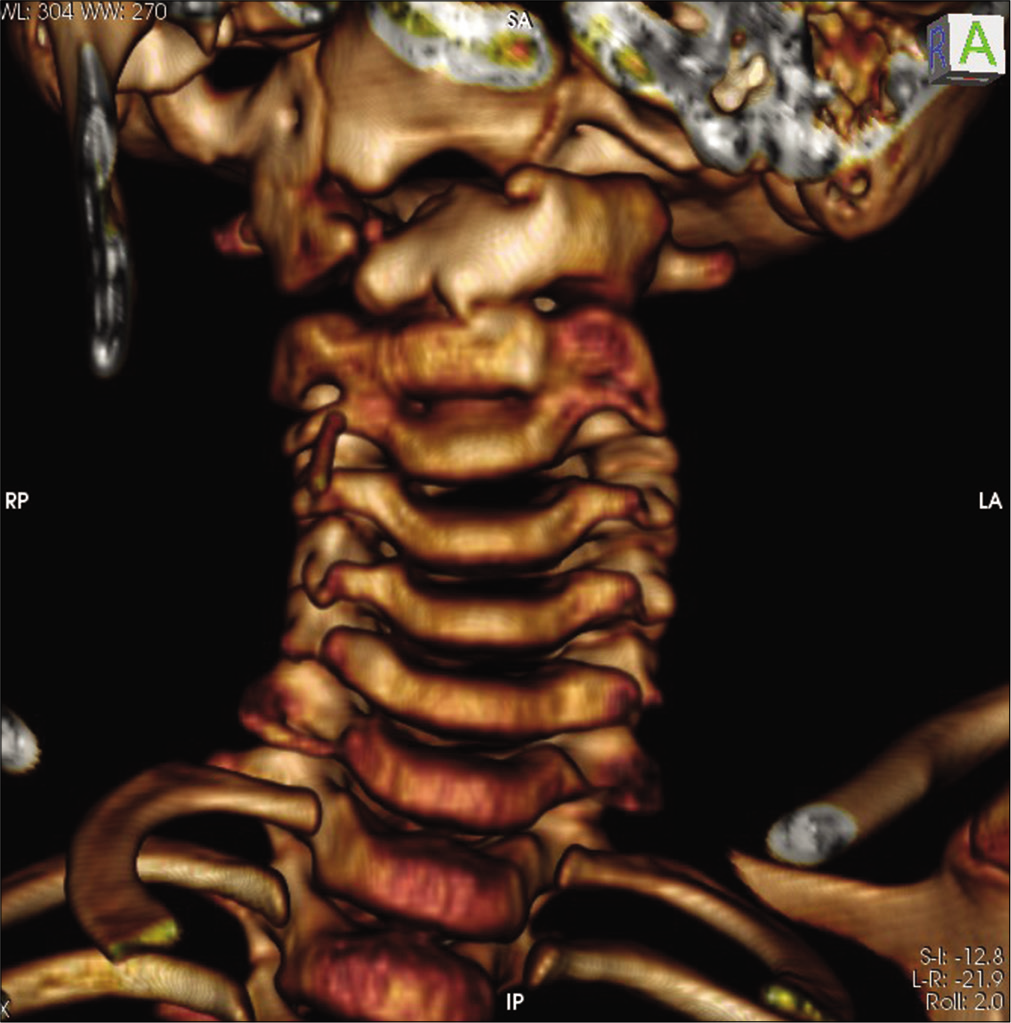
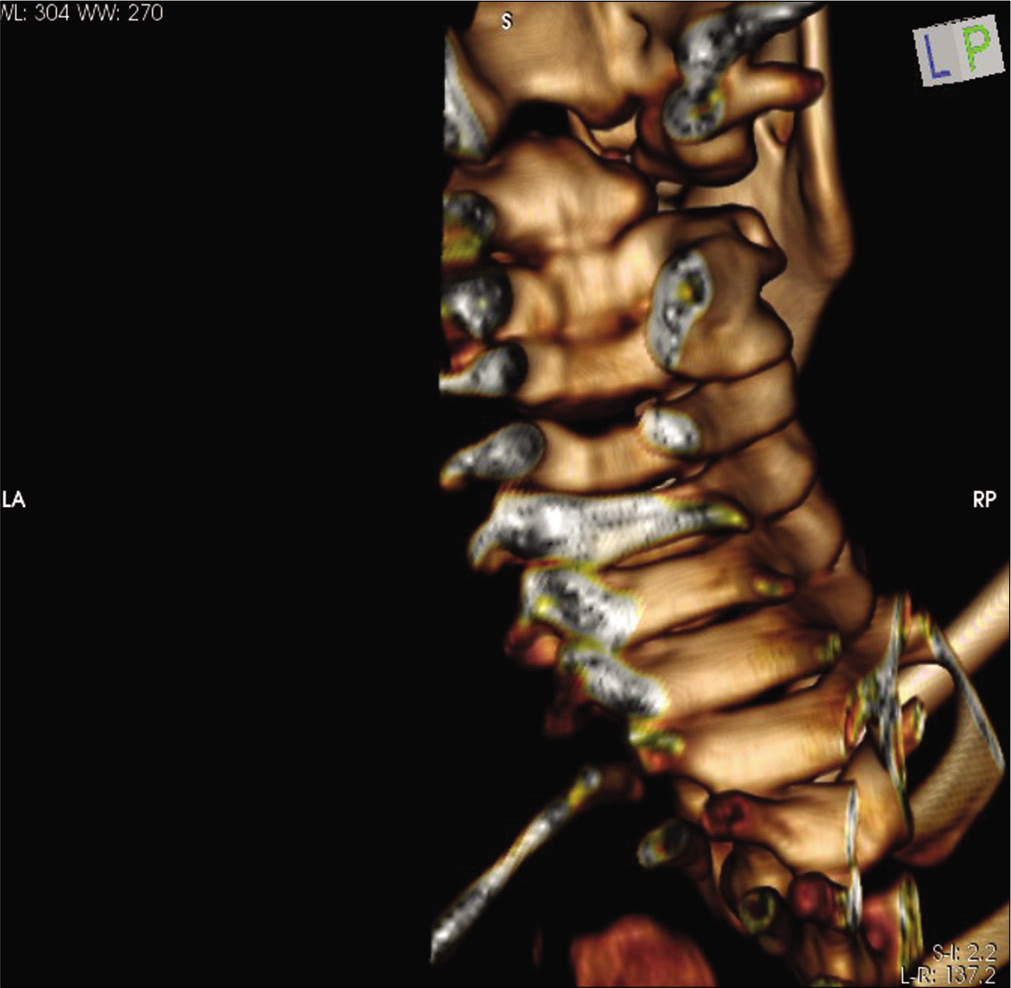
3D CT scan showing occipitalization of the right side of lateral mass of C1, discontinuity in anterior arch of C1, left side lateral mass of C1 with residual anterior arch of C1 showed fusion with body of C2 anteriorly with minimal space between left lateral mass of C1 and C2 in contrast to the right side.
Surgical management
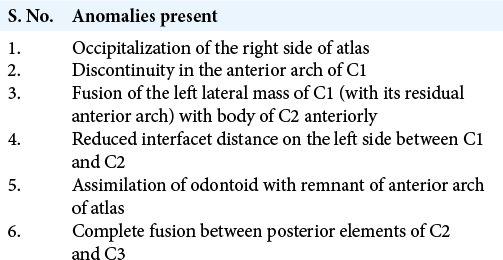
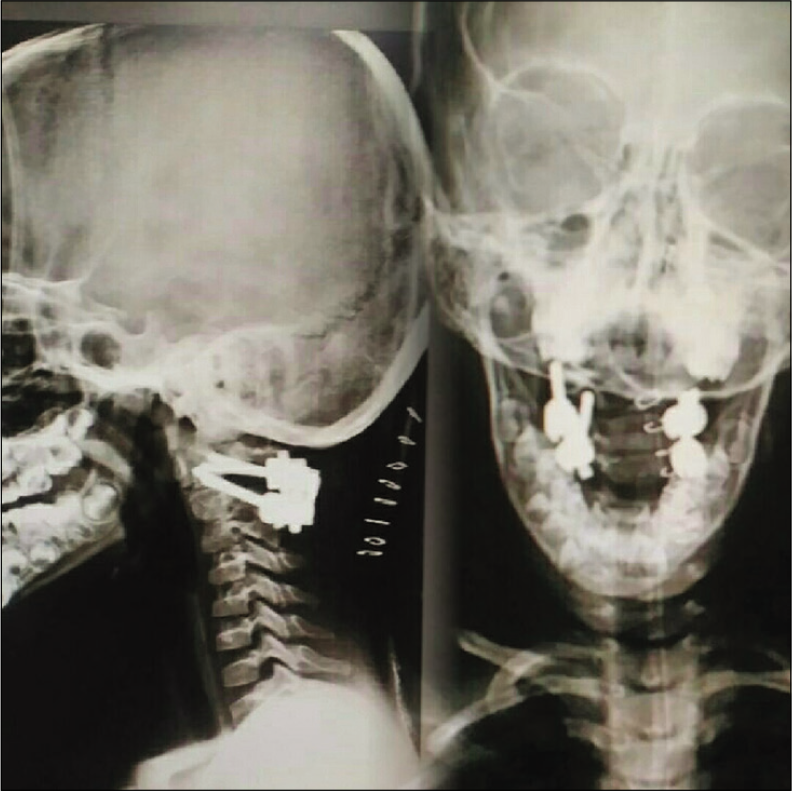
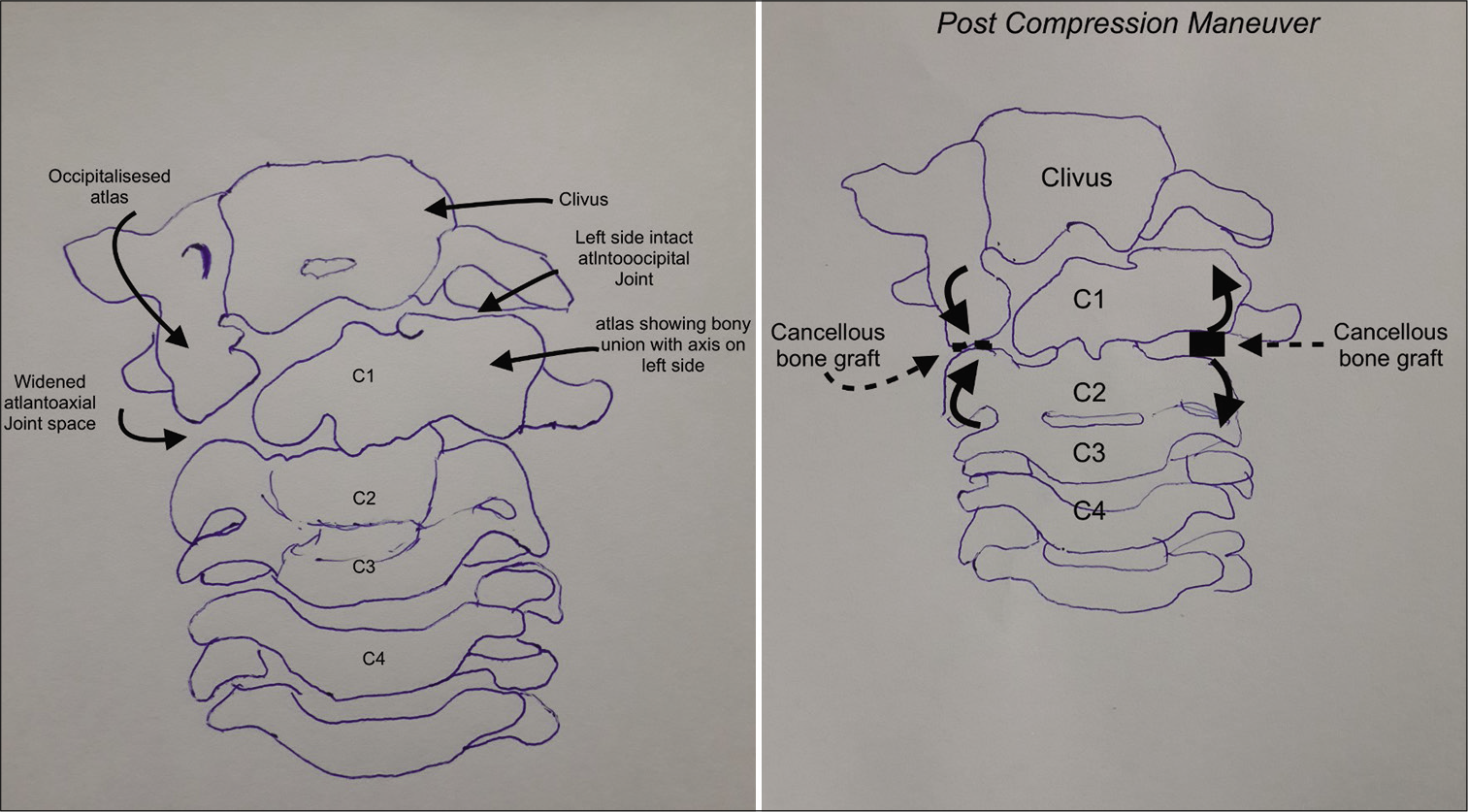
The progressive torticollis was treated with a C1 and C2 Goel and Harm fusion. During the surgery, on the right side, the interfacet space between C1 and C2 was large in contrast to the left side. Articular cartilage was debrided and cancellous bone grafting (e.g., harvested from the posterior iliac crest) was performed.
Similar steps were followed on the left side. Next, C1 lateral mass and C2 pedicle screw were inserted with increased attention to the dysplastic C1 and C2 anatomy. The screw trajectory on the right side was kept high in sagittal plane to adjust for occipitalization of the right lateral mass of the atlas. As there was fusion between the C1 and C2 bodies, we passed larger bilateral pedicle screws into the C2 vertebral body [
Intraoperative reduction/compression was performed on the right side between the C1 and C2 screws to correct the torticollis [
DISCUSSION
It is extremely rare to find dysplastic C1 vertebrae causing torticollis without rotatory subluxation of C1 and C2. A report by Geipel[
Cave had classified atlantoaxial congenital fusion into three types: (1) fusion of a separated odontoid process with the anterior atlantal arch; (2) complete (bilateral) fusion of atlas and axis; and (3) incomplete (unilateral) fusion, with or without some degree of assimilation.[
Previously published literature has reports about bipartite atlas. However, in our case, atlas cannot be called bipartite, as defect on anterior side was not in midline and there was unilateral assimilation of atlas with axis and occiput. As C2-C3 had fused from both anterior and posterior side symmetrically, it did not have any effect on torticollis caused at CVJ.
Occipitalization of the atlas occurs as a result of the failure of segmentation between the fourth occipital sclerotome and the first cervical sclerotome.[
The distinguishing feature in our case was the torticollis caused by differential growth between C1 and C2. (minimal growth due to fusion of C1 and C2 on the left half and continuous growth on the right side between occipitalized C1 lateral mass and C2). Our patient underwent a C1-C2 fusion using the Goel and Harm technique to reduce the torticollis and achieve stability [
CONCLUSION
Torticollis caused by anomalous/differential growth of C1-C2 vertebrae resulting in a nonrotatory subluxation is exceedingly rare. Here, a 6-year-old female with a dysplastic C1 and multiple other congenital anomalies required a C1-C2 Goel and Harm fusion to reduce the torticollis.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Publication of this article was made possible by the James I. and Carolyn R. Ausman Educational Foundation.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Cave AJ. On fusion of atlas and axis vertebra. J Anat. 1930. 64: 337-43
2. Dubousset J. Torticollis in children caused by congenital anomalies of the atlas. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986. 68: 178-88
3. Geipel P. Studies on the fissure formation of the atlas and epistropheus. Zentralbl Allg Pathol. 1955. 94: 19-84
4. Menezes AH. Craniocervical developmental anatomy and its implications. Childs Nerv Syst. 2008. 24: 1109-22