- Department of Neurosurgery, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Correspondence Address:
Arash Fattahi
Department of Neurosurgery, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
DOI:10.4103/sni.sni_225_18
Copyright: © 2018 Surgical Neurology International This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Alireza Tabibkhooei, Arash Fattahi, Feizollah Ebrahimnia. Gliosarcoma with long progression free survival: A case report and literature review. 05-Nov-2018;9:227
How to cite this URL: Alireza Tabibkhooei, Arash Fattahi, Feizollah Ebrahimnia. Gliosarcoma with long progression free survival: A case report and literature review. 05-Nov-2018;9:227. Available from: http://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/9059/
Abstract
Background:Gliosarcoma (GS) is a primary rare malignant brain tumor that accounts 4% of all high-grade glial tumor of the brain.
Case Description:We present a 45-year-old female admitted to our center with progressive headache since 1 month ago concomitant with nausea and emesis and generalized weakness. Imaging revealed a large solid mass with well-defined margin and some cystic portions that enhanced brightly with contrast. We decided to operate the patient via right parietal craniotomy and we totally resected all visible portions of the mass, as en bloc resection. The histopathological report of the mass was GS. We are following the patient up to now, for about 50 months, and she is good without any compliant or neurologic deficit. All follow-up magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) did not show any tumor recurrence.
Conclusion:Aiming to achieve longer progression-free survival in cases of GS, we recommend resecting all portions of the mass as much as possible, so named en bloc resection, and then refer the patients for appropriate and timely chemoradiotherapy.
Keywords: En bloc resection, gliosarcoma, overall survival, progression-free survival
BACKGROUND
Gliosarcoma (GS) is a primary rare malignant brain tumor that contains both gliomatous and sarcomatous (mesenchymal) components and accounts 4% of all high-grade glial tumor of the brain.[
CASE DESCRIPTION
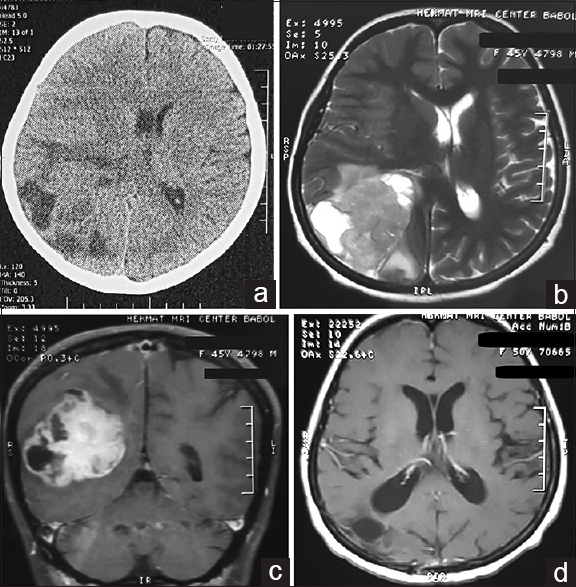
We present a 45-year-old female admitted to our center with progressive headache since 1 month ago concomitant with nausea, emesis, and generalized weakness. She had minimal headache since 2 years ago and, on admission clinical examination, we did not find any neurologic deficits. Also, the patient had bilateral pupillary edema on fundoscopy. She had bilateral positive Hoffmann's sign. On first brain computed tomography (CT), we saw a large heterogeneous mass with some vasogenic edema at right parieto-occipital region with 0.5 cm midline shift that compressed right occipital horn of lateral ventricle [
Figure 1
Preoperative brain computed tomography scan (a) of the patient revealed a large heterogeneous mass at right parieto-occipital region with some vasogenic edema that produces a 0.5 cm midline shift of the brain. On the brain magnetic resonance imaging, we found a solid-cystic hyper-intense mass on T2 sequences (b) that it is brightly enhanced after injection of gadolinium (c). Follow-up brain magnetic resonance imaging with gadolinium revealed no remnant of tumor (d)
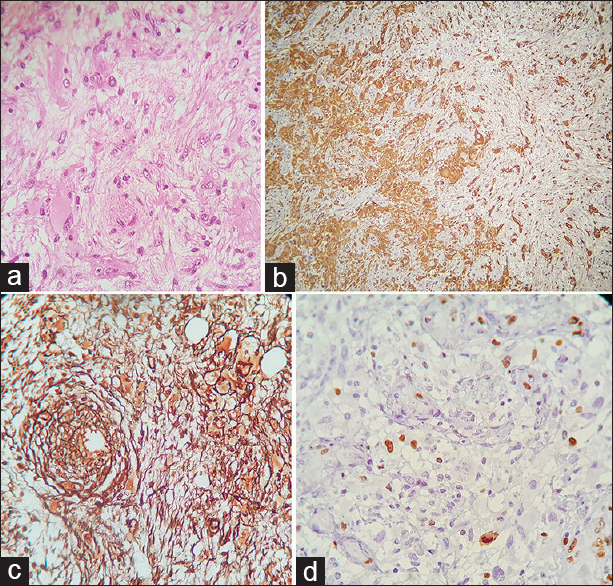
According to very large mass effect, we decided to operate the patient via right parietal craniotomy. The tumor had a more firm consistency compared with adjacent normal brain tissue and it was well demarcated and we totally resected all visible portions of the mass, as en bloc resection. The histopathological report of the mass was GS [Figure
Figure 2
Histopathologic finding revealed a biphasic tumor with alternating between glial and mesenchymal differentiation (a, H and E × 400). Immunohistochemically (IHC), we see G-FAP positive portions (negative for reticulin, b × 100) and in concomitant with reticulin-riched portions (negative for G-FAP, c × 400) in other sites. Also, we can see positive staining for Ki-67 (d × 400)
DISCUSSION
The GS, as known Feigin tumor, is a rare and malignant glioma.[
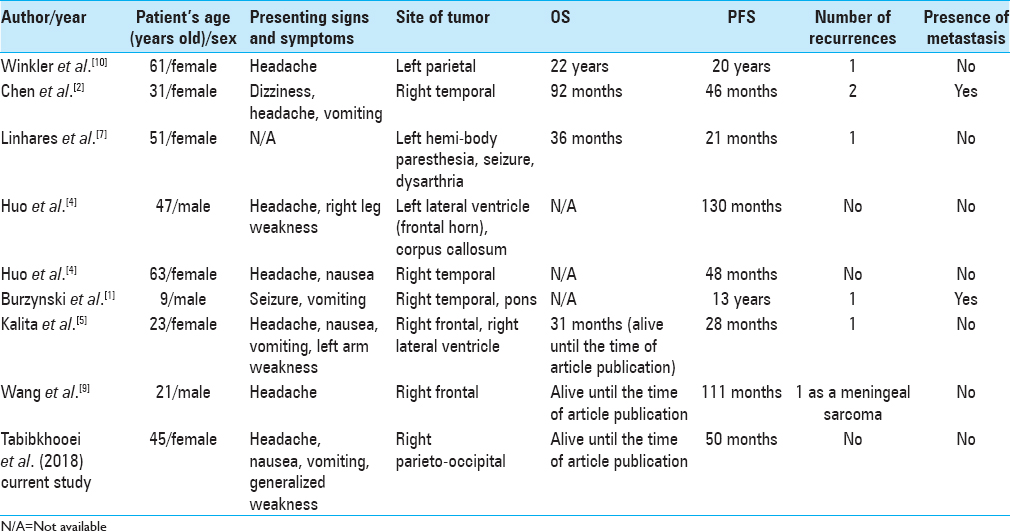
In the literature, we found only eight reports of GS with OS >2 years [
Although in almost all cases, infiltrative nature of gliomatous tumors hinder to remove all portions of them, because of sarcomatous components of GS, differences in consistency of tumoral tissue compared with brain tissue assist to define a relatively well-demarcated plane between them during surgery. In addition, en bloc resection with preservation of tissue planes during dissection prevents missing any tumor component intermingled with brain parenchyma at the time of dissection. Finally, location of the lesion in non-eloquent area of brain lets intraoperative manipulations and more feasible en bloc tumor removal. We think all these factors together in association with appropriate and timely adjuvant therapy helps surgeon to give the most chance of PFS to the patient with GS.
CONCLUSION
We present a patient with GS that has a long PFS after surgical treatment. Aiming to achieve longer PFS in cases of GS and regarding to more distinct consistency, we recommend resecting all portions of the mass, as much as possible, to reach en bloc resection and then refer the patients for appropriate and timely chemoradiotherapy.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form the patient(s) has/have given his/her/their consent for his/her/their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Burzynski SR, Janicki TJ, Burzynski GS, Marszalek A. Long-term survival (>13 years) in a child with recurrent diffuse pontine gliosarcoma: A case report. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014. 36: e433-9
2. Chen L, Xiao H, Xu L, Zou Y, Zhang Y, Xu M. A case study of a patient with gliosarcoma with an extended survival and spinal cord metastases. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2012. 62: 391-5
3. Feigin IH, Gross SW. Sarcoma arising in glioblastoma of the brain. Am J Pathol. 1955. 31: 633-53
4. Huo Z, Yang D, Shen J, Li Y, Wu H, Meng Y. Primary gliosarcoma with long-survival: Report of two cases and review of literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. 7: 6323-32
5. Kalita O, Zlevorova M, Megova M, Vaverka M, Trojanec R, Tuckova L. A patient with primary intraventricular gliosarcoma and long-term survival-A case report. Klin Onkol. 2016. 29: 454-9
6. Karsy M, Gelbman M, Shah P, Balumbu O, Moy F, Arslan E. Established and emerging variants of glioblastoma multiforme: Review of morphological and molecular features. Folia Neuropathol. 2012. 50: 301-21
7. Linhares P, Martinho O, Carvalho B, Castro L, Lopes JM, Vaz R. Analysis of a synchronous gliosarcoma and meningioma with long survival: A case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol Int. 2013. 4: 151-
8. Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007. 114: 97-109
9. Wang Z, Kong QT, Wu XH, Zhu XX. Long-term survival in gliosarcoma with radiation-induced meningeal sarcomas: Case report and molecular features. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015. 11: 651-
10. Winkler PA, Buttner A, Tomezzoli A, Weis S. Histologically repeatedly confirmed gliosarcoma with long survival: Review of the literature and report of a case. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2000. 142: 91-5