- Department of Neurosurgery, Avicenne Military Hospital, Mohammed V University, Rabat,
- Department of Pathology, Avicenne Military Hospital of Marrakech, Marrakech, Morocco.
Correspondence Address:
Ali Akhaddar
Department of Pathology, Avicenne Military Hospital of Marrakech, Marrakech, Morocco.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_383_2020
Copyright: © 2020 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Ali Akhaddar, Issam Rharrassi. Hypertrophic cranial pachymeningitis coinfection with tuberculosis and actinomycosis. Surg Neurol Int 18-Jul-2020;11:201
How to cite this URL: Ali Akhaddar, Issam Rharrassi. Hypertrophic cranial pachymeningitis coinfection with tuberculosis and actinomycosis. Surg Neurol Int 18-Jul-2020;11:201. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/10145/
Abstract
This is a rare case report about hypertrophic cranial pachymeningitis coinfection with tuberculosis and actinomycosis in a 35-year-old male. The patient presented with progressive headache, paraesthesia, and blurred vision. Dural biopsy, histology, and cultures are imperative in pachymeningitis for establishing the diagnosis and guiding treatment.
Keywords: Actinomycosis, Hypertrophic cranial pachymeningitis, Intracranial infection, Pachymeningitis, Tuberculosis
IMAGE REPORT
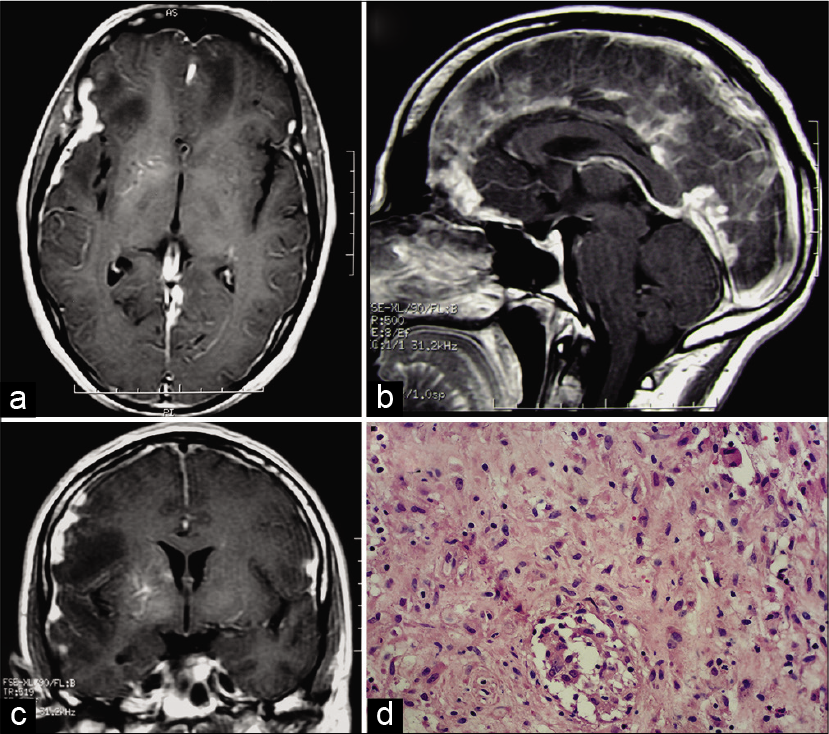
A 35-year-old male presented with progressive headache, paraesthesia, and blurred vision. The MRI showed diffuse meningeal enhancement with thickening, along with areas of brain edema [
Figure 1:
Axial (a), sagittal (b), and coronal (c) cranial magnetic resonance imaging following gadolinium injection showing diffuse meningeal enhancement and thickening, along with areas of brain edema. Dural biopsy revealing epithelioid-giant cell granulomas with caseous necrosis (hematoxylin-eosin staining) (d).
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.