- Department of Neurosurgery, Takeda General Hospital, Kyoto, Japan.
- Department of Neurology, Uji Takeda Hospital, Kyoto, Japan.
Correspondence Address:
Masahiro Kawanishi
Department of Neurology, Uji Takeda Hospital, Kyoto, Japan.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_795_2020
Copyright: © 2021 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Masahiro Kawanishi1, Hidekazu Tanaka1, Yutaka Itoh1, Kunio Yokoyama1, Makoto Yamada1, Akira Sugie1, Akari Miyake2. Intradural extramedullary hemangioblastoma of the thoracic cord: A case report. 30-Mar-2021;12:126
How to cite this URL: Masahiro Kawanishi1, Hidekazu Tanaka1, Yutaka Itoh1, Kunio Yokoyama1, Makoto Yamada1, Akira Sugie1, Akari Miyake2. Intradural extramedullary hemangioblastoma of the thoracic cord: A case report. 30-Mar-2021;12:126. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/10684/
Abstract
Background: Spinal hemangioblastomas account for 1–3% of all spinal cord tumors and are mostly intramedullary in location. Here, we report an intradural extramedullary hemangioblastoma of the thoracic spine, occurring in in a patient without von Hippel-Lindau disease.
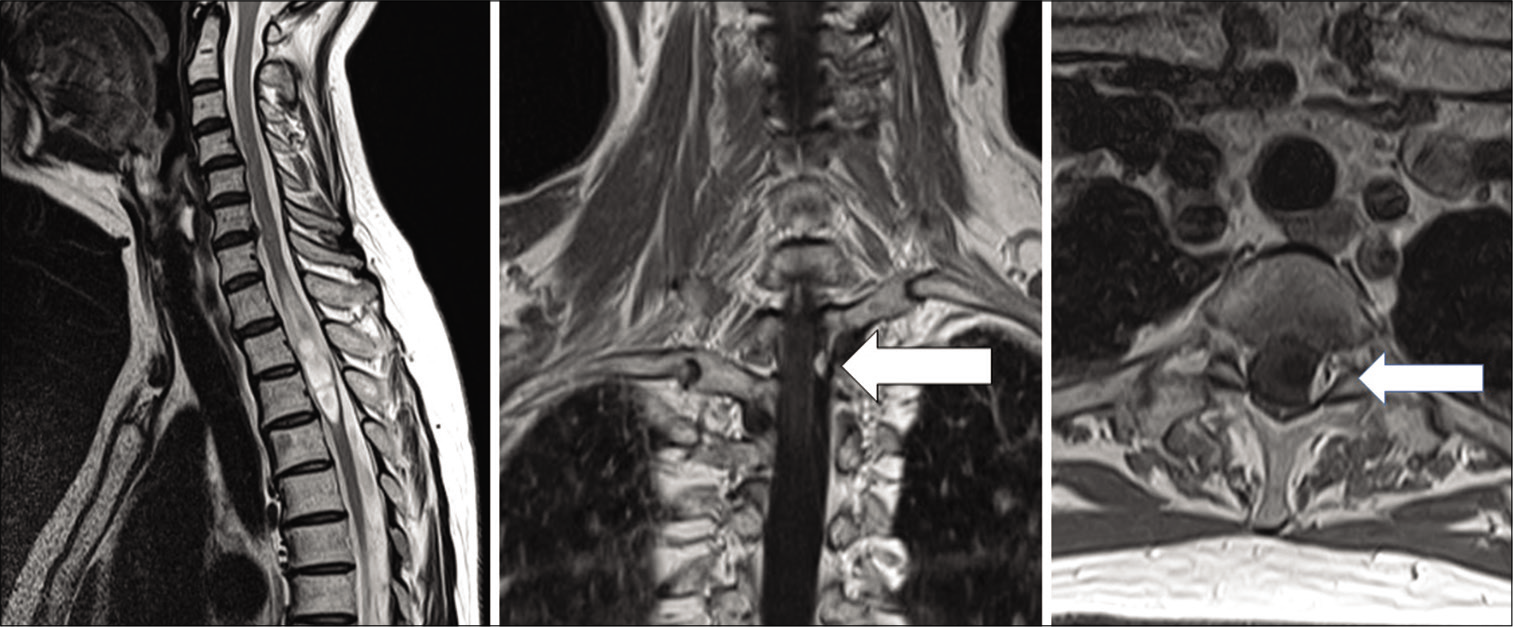
Case Description: A 58-year-old female had a 5-year history of progressive left lower extremity weakness. When the MR demonstrated an intradural/extramedullary lesion with a syrinx at the T2-3 level, she successfully underwent gross total tumor excision following which she neurologically improved.
Conclusion: Here, we report a rare case of an intradural/extramedullary thoracic hemangioblastoma successfully excised at the T 2-3 level in a patient without von Hippel-Lindau disease.
Keywords: Cyst, Extramedullary spinal tumor, Hemangioblastoma
INTRODUCTION
Spinal hemangioblastomas account for 1–3% of all spinal cord tumors and are typically intramedullary in location.[
CASE REPORT
Clinical presentation
A 58-year-old female presented with a 5-year history of progressive left lower extremity weakness. On examination, she exhibited hypesthesia and hypalgesia in both lower extremities accompanied by diffuse hyperreflexia and bilateral Babinski signs. The accompanying laboratory and radiographic studies rule out the presence of von Hippel-Lindau disease.
MR documentation
The MR demonstrated a homogenously, contrast enhancing intradural/extramedullary tumor accompanied by edema and a syrinx at the T2-T3 level [
Surgery
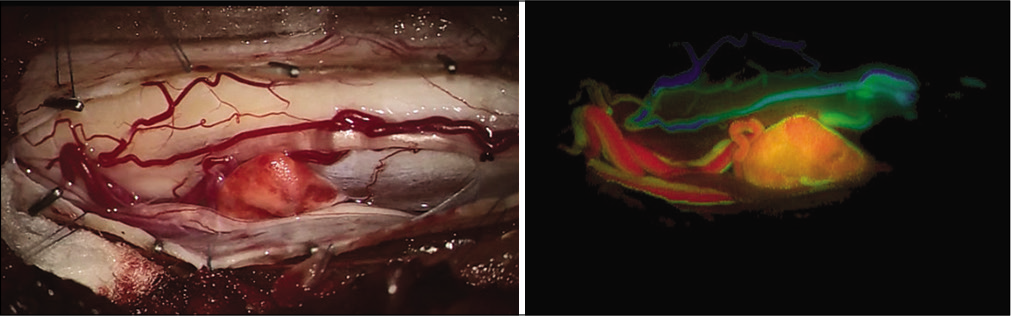
Under MEP and SEP monitoring, the patient underwent gross total excision of the intradural/extramedullary mass. On opening the dura and arachnoid, a triangular, small, orange mass could be seen located between the thoracic roots [
Five days postoperatively, the patient was discharged with only slight residual left lower extremity weakness. No residual tumor mass was observed on follow-up MR studies. The final histologic diagnosis was consistent with a hemangioblastoma.
DISCUSSION
Spinal hemangioblastomas are rare tumors and mostly occur with von Hippel-Lindau disease.[
Ideal treatment
The ideal treatment for these lesions is gross total surgical excision.[
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Deng X, Wang K, Wu L, Yang C, Yang T, Zhao L. Intraspinal hemangioblastomas: Analysis of 92 cases in a single institution: Clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014. 21: 260-9
2. Imagama S, Ito Z, Wakao N, Sakai Y, Kato F, Yukawa Y. Differentiation of localization of spinal hemangioblastomas based on imaging and pathological findings. Eur Spine J. 2011. 20: 1377-84
3. Taniguchi S, Ogikubo O, Nakamura T, Yamagishi I, Hayakawa K, Otsuka T. A rare case of extramedullaryintradural hemangioblastoma in the thoracic spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009. 34: E969-72
4. Toyoda H, Seki M, Nakamura H, Inoue Y, Yamamoto Y, Takaoka K. Intradural extramedullary hemangioblastoma differentiated by MR images in the cervical spine: A case report and review of the literature. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004. 17: 343-7
5. Yasargil MG, Antic J, Laciga R, de Preux J, Fideler RW, Boone SC. The microsurgical removal of intramedullary spinal hemangioblastomas. Report of twelve cases and a review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 1976. 3: 141-8
6. Yasuda T, Hasegawa T, Yamato Y, Kobayashi S, Togawa D, Banno T. Relationship between spinal hemangioblastoma location and age. Asian Spine J. 2016. 10: 309-13