- Department of Neurosurgery, Ibrahim Cardiac Hospital and Research Institute (A Centre for Cardiovascular, Neuroscience and Organ Transplant Units), Shahbag, Dhaka, Bangladesh
- Department of Neurosurgery, Dhaka Medical College Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Correspondence Address:
Nazmin Ahmed, Department of Neurosurgery, Ibrahim Cardiac Hospital and Research Institute (A Centre for Cardiovascular, Neuroscience and Organ Transplant Units), Shahbag, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_719_2023
Copyright: © 2023 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Nazmin Ahmed1, Md. Isma Azam2. Isolated fourth ventricle craniopharyngioma: Representative case illustration and review of literature. 08-Dec-2023;14:416
How to cite this URL: Nazmin Ahmed1, Md. Isma Azam2. Isolated fourth ventricle craniopharyngioma: Representative case illustration and review of literature. 08-Dec-2023;14:416. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/12663/
Abstract
Background: Sella and suprasellar areas are frequently affected by craniopharyngiomas. In this article, eight occurrences have been documented. One is new, and the remaining seven are from previously published articles. Their prevalence in the posterior fossa without expansion from the suprasellar area is unusual.
Case Description: We present a case of a primary 4th ventricular craniopharyngioma of the posterior fossa in a 16-year-old male with no association with Gardner’s syndrome. He presented with sudden deterioration of consciousness level and was diagnosed as having a homogeneously contrast enhancing lesion occupying the 4th ventricle with obstructive hydrocephalus. The patient underwent emergency placement of external ventricular drain followed by complete removal of the tumor on the next day by midline suboccipital craniotomy with telovelar approach. Histopathological features were consistent with the adamantinomatous variety of craniopharyngioma. He had complete neurological recovery and no evidence of tumor recurrence in 1-year follow-up.
Conclusion: The craniopharyngioma in our case was distinct because it was a solid tumor with no cystic component, exhibited homogeneous contrast enhancement in neuroimaging, developed in the fourth ventricle, and reached the level of foramen magnum, features that had rarely been documented previously. We also reviewed the literature on reported cases of 4th ventricular craniopharyngioma to strengthen knowledge in this area and highlight the embryological basis of ectopic craniopharyngioma.
Keywords: Craniopharyngioma, Ectopic craniopharyngioma, Fourth ventricle, Primary posterior fossa
INTRODUCTION
Craniopharyngiomas make up 1.2–4.6% of all intracranial tumors. They are uncommon, benign, extra-axial, largely cystic, and slow-growing epithelial tumors of the central nervous system. They often start in the suprasellar region of the brain’s infundibulohypophysial axis and spread to affect the hypothalamus, optic chiasm, cranial nerves, third ventricle, and blood arteries.[
Although few craniopharyngiomas are seen in the infrasellar, intrasellar, or anterior regions, the tumor is often suprasellar in position. There are two possible types of posterior fossa craniopharyngiomas: recurrence/extension and the exceedingly uncommon initial tumor (de novo). A relatively high 50% recurrence rate is seen in craniopharyngiomas. In addition, it has significant rates of survival (65–100%: 10-year survival, 83–96%: 5-year survival) as well as morbidity.[
In this article, we have described a rare example of a de novo fourth ventricle craniopharyngioma that reached the foramen magnum and was completely excised. We also showed the schematic picture of development of craniopharyngioma [
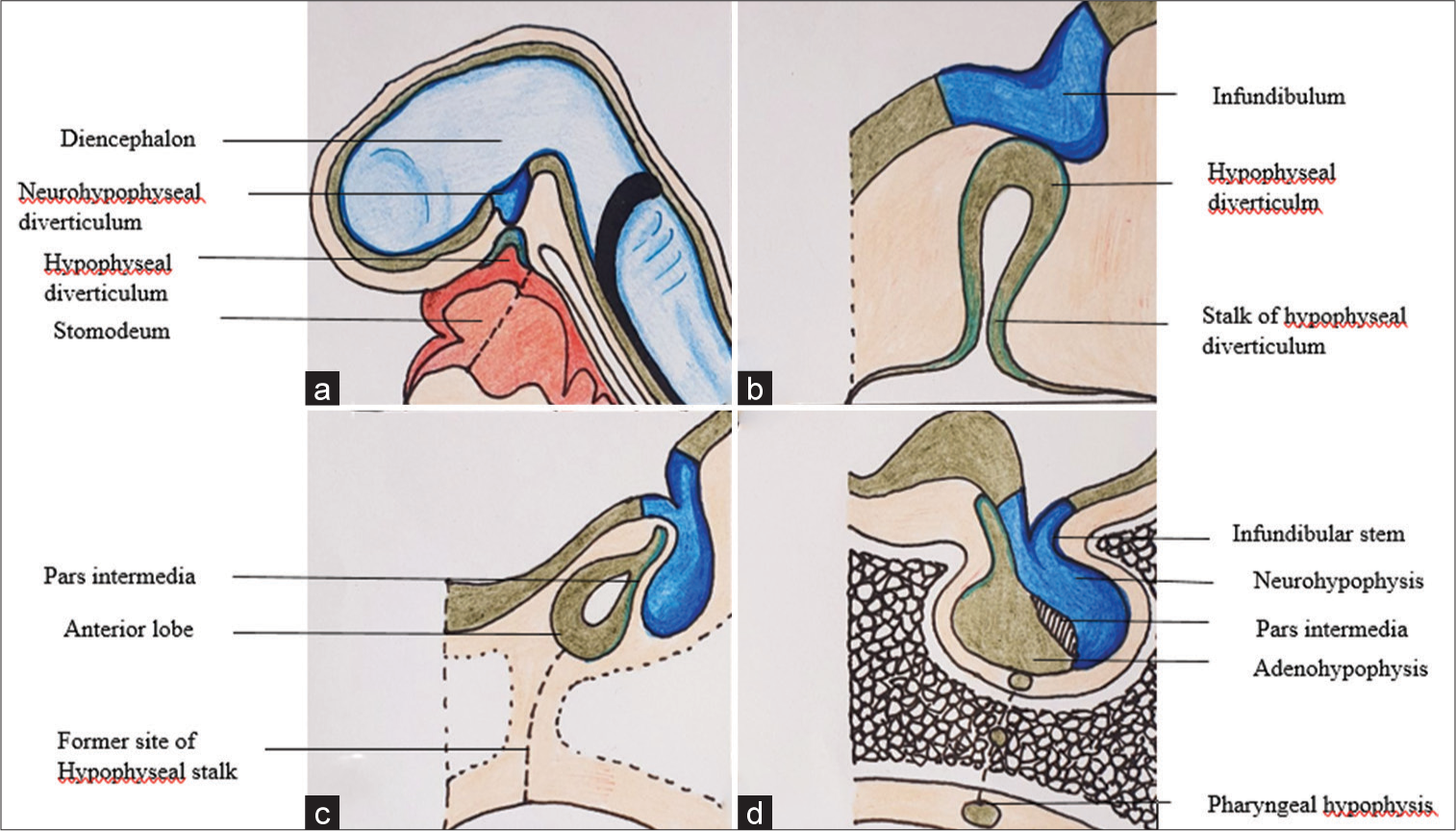
Figure 1:
Schematic picture demonstrates (a) development of the pituitary gland from neurohypophyseal diverticulum originating from diencephalon and hypophyseal diverticulum from primitive stomodeum; (b) progressive elongation of the diverticulum gives rise to infundibulum and stalk respectively; (c) after the development of the anterior lobe (adenohypophysis), former site of hypophyseal stalk illustrated; and (d) this remnant of hypophyseal stalk may give rise to ectopic craniopharyngioma.
CASE REPORT
History and physical examination
A 16-year-old man who had previously been in good condition arrived at the hospital’s emergency with a 30-h history of altered consciousness. He experienced a headache and had trouble walking for four weeks before the presentation. The occipital area was the site of a persistent headache accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and diplopia. His Glasgow Coma Scale was 12 out of 15, and he did not have facial paralysis, papilledema, or any other neurological impairments.
Neuroimaging
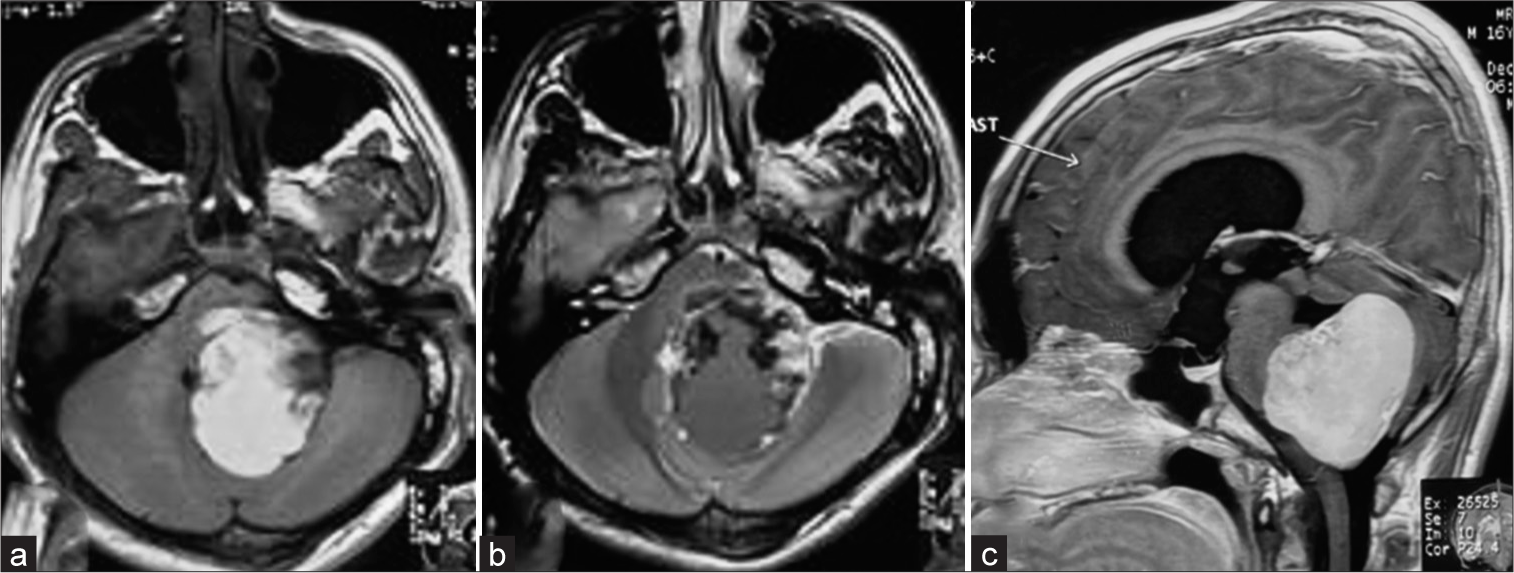
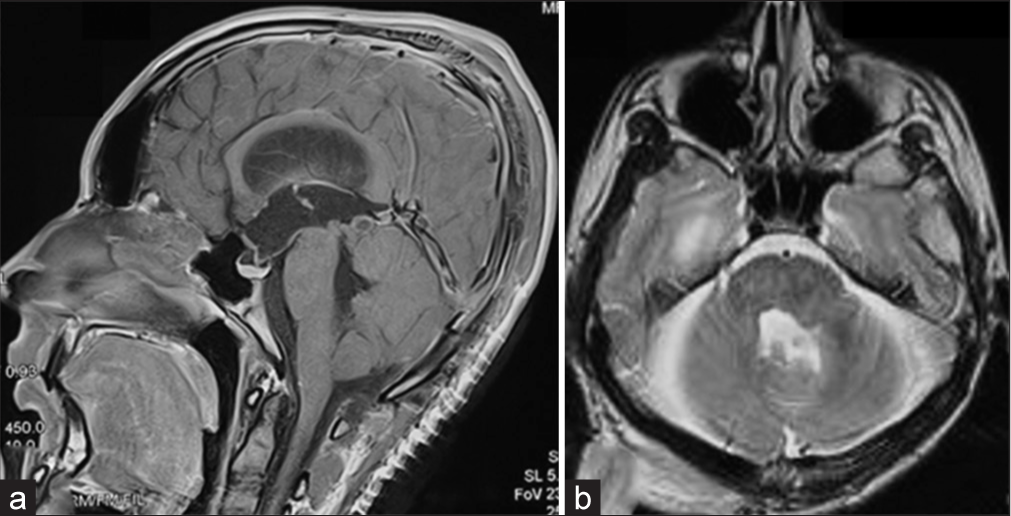
A solid lesion measuring 5 cm in the craniocaudal plane and 4.5 × 3.5 cm in the axial plane was detected using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [
Figure 3:
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, T1WI axial section demonstrated a 4.5 × 3.5 cm heterogeneously hyperintense lesion occupying the 4th ventricle, extending toward the left cerebellopontine cistern. (a) The mass effect is evidenced by compressing the pons, left middle cerebellar peduncle, and cerebellar hemisphere. (b) The lesion becomes mixed intensity in T2WI, having an irregular hyperintense rim. (c) After administration of contrast, there is intense homogeneous contrast enhancement.
Surgical procedure
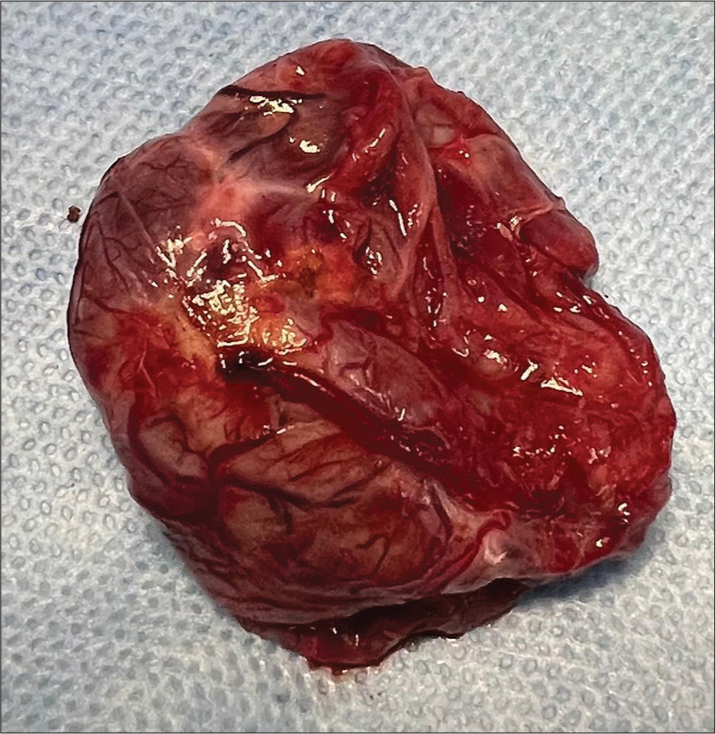
The first procedure was the emergency external ventricular drain (EVD) insertion since the patient’s state of consciousness quickly declined. The patient recovered consciousness after the EVD, and his condition stabilized. He underwent a posterior fossa craniotomy and complete tumor excision by telovelar approach on the next day. After the opening of the dura in a “Y”-shaped fashion, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was sucked from the cisterna magna to relax the brain. On gross inspection, the tumor was brownish red, lobulated with numerous engorged blood vessels mimicking a solid variety of hemangioblastoma [
Postoperative period and follow-up
A solid lesion with squamous epithelium and isolated peripheral palisading was identified by histopathology. Extensive fibrosis, cholesterol clefts, ongoing inflammation, calcification, cystic alterations, and isolated osteoid development is all seen on the wall. There were isolated areas of reactive gliosis in the cerebellum. These characteristics were indicative of a craniopharyngioma of the adamantinomatous type. The patient’s postoperative period was uneventful. An MRI performed after surgery revealed no signs of tumor residual or hydrocephalus [
DISCUSSION
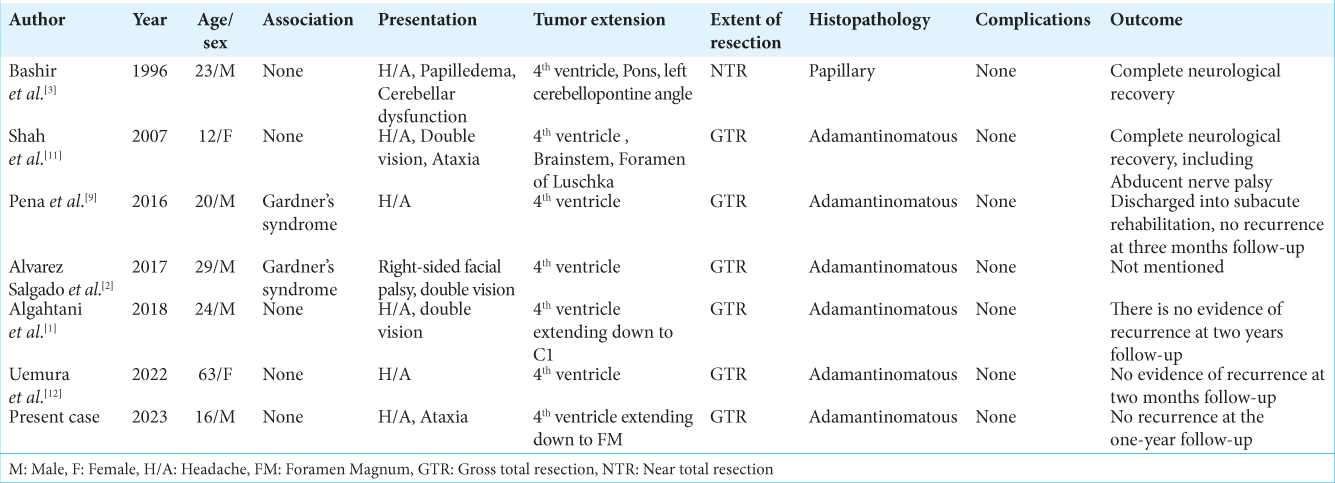
Other than the present case, we have reviewed seven more cases here published between 1996 and 2022 of primary posterior fossa craniopharyngioma located within the 4th ventricle, as shown in
Management
Gross total resection was the surgical technique that was most frequently employed. However, Bashir et al. achieved near-total removal of the tumor due to dense adherence of the cyst wall to the brainstem.[
Embryogenesis of ectopic craniopharyngiomas
The origin of craniopharyngioma from the remnant of the obliterated craniopharyngeal duct was first proposed on the basis of the presence of squamous epithelium clusters at the junction of the infundibulum and pituitary in 1904.[
CONCLUSION
Less than 20 cases of primary posterior fossa craniopharyngioma have been reported, making it an uncommon condition. The rarity of a craniopharyngioma coming from the fourth ventricle is much higher. We have documented the 8th instance of this kind. In the differential diagnosis of CPA and fourth ventricular tumors in adolescent and adult patients, craniopharyngioma should be considered. A good prognosis is linked to complete resection and early diagnosis.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patient’s identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Journal or its management. The information contained in this article should not be considered to be medical advice; patients should consult their own physicians for advice as to their specific medical needs.
References
1. Algahtani AY, Algahtani HA, Jamjoom AB, Samkari AM, Marzuk YI. De novo craniopharyngioma of the fourth ventricle: Case report and review of literature. Asian J Neurosurg. 2018. 13: 62-5
2. Álvarez Salgado JA, González-Llanos Fernández de Mesa F, Villaseñor Ledezma JJ, Cañizares Méndez ML, Paredes Sansinenea I, Rodríguez de Lope-Llorca A. Ectopic craniopharyngioma and Gardner’s syndrome: Case report and literature review. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2016. 28: 97-101
3. Bashir EM, Lewis PD, Edwards MR. Posterior fast craniopharyngioma. Br J Neurosurg. 1996. 10: 613-5
4. Ganz JC. Craniopharyngiomas. Prog Brain Res. 2022. 268: 217-27
5. John AA, Marsh H, Rossettie SS, Ray CN, Freedman KA, Baronia BC. Ectopic craniopharyngioma of the orbit: Illustrative case. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2022. 3: CASE21544
6. Kuo BR, Erickson CA. Regional differences in neural crest morphogenesis. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. 4: 567-85
7. Mueller HL, Merchant TE, Warmuth-Metz M, Martinez-Barbera JP, Puget S. Primer’craniopharyngioma’. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019. 5: 75
8. Ortega-Porcayo LA, Ponce-Gómez JA, Martínez-Moreno M, Portocarrero-Ortíz L, Tena-Suck ML, Gómez-Amador JL. Primary ectopic frontotemporal craniopharyngioma. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015. 9: 57-60
9. Pena AH, Chaudhry A, Seidman RJ, Peyster R, Bangiyev L. Ectopic craniopharyngioma of the fourth ventricle in a patient with Gardner syndrome. Clin Imaging. 2016. 40: 232-6
10. Sadler TW, editors. Langman’s medical embryology. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2022. p.
11. Shah GB, Bhaduri AS, Misra BK. Ectopic craniopharyngioma of the fourth ventricle: Case report. Surg Neurol. 2007. 68: 96-8
12. Uemura H, Tanji M, Natsuhara H, Takeuchi Y, Hoki M, Sugimoto A. The association of ectopic craniopharyngioma in the fourth ventricle with familial adenomatous polyposis: Illustrative case. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2022. 3: CASE21572