- Department of Neurosurgery, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, United States.
- Department of Neurology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, United States.
Correspondence Address:
Joseph S. Kass, Department of Neurology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, United States.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_421_2022
Copyright: © 2022 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Dominic J. Kizek1, Eric A. Goethe1, Patrick J. Karas1, Jeffrey M. Treiber1, Ali Jalali1, Shankar P. Gopinath1, Joseph S. Kass2. Neurolymphomatosis of the brachial plexus from atypical primary central nervous system lymphoma lesions: A case report and review of the literature. 14-Oct-2022;13:464
How to cite this URL: Dominic J. Kizek1, Eric A. Goethe1, Patrick J. Karas1, Jeffrey M. Treiber1, Ali Jalali1, Shankar P. Gopinath1, Joseph S. Kass2. Neurolymphomatosis of the brachial plexus from atypical primary central nervous system lymphoma lesions: A case report and review of the literature. 14-Oct-2022;13:464. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/11934/
Abstract
Background: Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is an aggressive and extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma limited to the neuroaxis. In immunocompetent individuals, PCNSL is more common in older adults and lacks the association with the Epstein–Barr virus found in individuals with AIDS-associated PCNSL. Because the clinical presentation and radiographic findings of PCNSL are highly variable, stereotactic brain biopsy is typically required for definitive diagnosis. High-dose methotrexate, in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents with or without whole brain radiation, is the mainstay of treatment.
Case Description: A 70-year-old HIV-negative woman presented with confusion, acute flaccid left arm weakness, and left hand numbness. Head computed tomography without contrast demonstrated a 1 cm hyperdense round lesion in the suprasellar cistern that prompted further evaluation. Gadolinium-enhanced brain magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated enhancing lesions with heterogeneous signal intensity in the suprasellar, pineal, and right periatrial regions that did not explain the limb weakness and numbness. Serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) studies were unrevealing, and a diagnosis of PCNSL was made following stereotactic biopsy. The patient’s liver cirrhosis precluded chemotherapy, but treatment with whole-brain radiation was pursued.
Conclusion: The myriad clinical presentations and insidious course of PCNSL contribute to diagnostic difficulties, delays in treatment, and poor outcomes. Stereotactic brain biopsy is the primary method of PCNSL diagnosis since malignant cells are typically not detected in CSF. PCNSL should be considered in the differential diagnosis when immunocompetent elderly patients present with multiple intracranial lesions, even in the presence of lower motor neuron findings.
Keywords: Case report, Multifocal, Neurolymphomatosis, Primary central nervous system lymphoma
INTRODUCTION
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma accounting for 1% of all lymphomas and 2% of all central nervous system (CNS) tumors.[
CASE REPORT
A 70-year-old woman with atrial fibrillation, liver cirrhosis, Type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and venous thrombus treated with enoxaparin presented with a 5-day history of weakness in the left arm, numbness in the left fourth and fifth digits and medial palmar surface, and confusion. The patient also reported chronic vision loss in the right eye and denied headache or recent trauma.
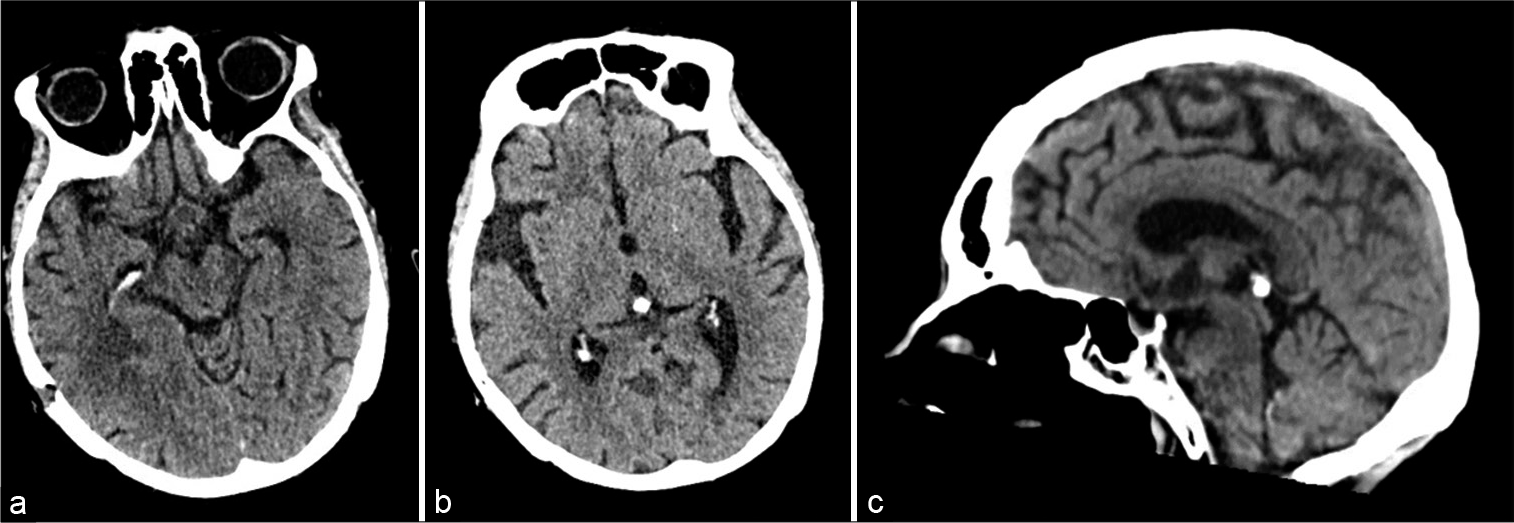
On initial examination, the patient was alert; oriented to person, place, and time; and disoriented to situation. Cranial nerve testing revealed reduced visual acuity in the right eye. Motor strength testing revealed 4/5 strength in the left triceps, left wrist flexors and extensors, and left finger flexors and 3/5 strength in the left finger extensors. Reflex testing revealed an absent left triceps reflex. Sensation testing revealed decreased sensation to pinprick and light touch in the fourth and fifth digits of the left hand. There was no dysmetria or dysdiadokokinesia. Head computed tomography (CT) without contrast demonstrated a 1 cm hyperdense round lesion in the suprasellar cistern [
The patient’s limb weakness and numbness localized to either the C7/8 nerve roots or the middle and lower trunks of the brachial plexus. Our differential diagnosis included a lateralized mass in the extradural or intradural extramedullary spinal canal or idiopathic brachial neuritis. While the patient had several risk factors for embolic stroke, including atrial fibrillation and diabetes, the specific patterns of sensory loss in the left upper extremity and loss of the left triceps reflex were more suggestive of either nerve root or brachial plexus pathology. On hospital day 2, the patient developed a pupil-sparing right CN III palsy. The next day, the right pupil became dilated to 4 mm and nonreactive to light.
The new cranial nerve palsy combined with the previously seen lesion on head CT without contrast broadened the differential diagnosis to include neoplastic, infectious, and inflammatory etiologies, especially those with a predilection for invading the subarachnoid space. Considerations included leptomeningeal disease from metastatic carcinoma or lymphoma as well as PCNSL due to the patient’s age and multifocal nature of her symptoms, as well as tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, or cryptococcosis, and sarcoidosis. The patient then underwent gadolinium-enhanced brachial plexus, brain, and spine MRI in addition to lumbar punctures and several blood tests.
The patient’s Vitamin B12, Vitamin B6, folate, and lead levels were within normal limits. RPR was nonreactive and HIV-1 was negative. Hemoglobin A1c was mildly elevated to 6.7%. The ophthalmology service performed a slit-lamp examination, which showed only rare drusen. Gadolinium-enhanced brachial plexus and spine MRI were unrevealing. Gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI demonstrated enhancing lesions with heterogeneous signal intensity in the suprasellar, pineal, and right periatrial regions concerning for a lymphoproliferative, infectious, or inflammatory process and no evidence of ischemic stroke [
Figure 2:
(a) Initial axial T1-weighted and gadolinium-enhanced brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrating enhancing lesions with heterogeneous signal intensity in the suprasellar and right periatrial regions. (b) Initial axial T1-weighted and gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI demonstrating enhancing lesion with heterogeneous signal intensity in the pineal region. (c) Initial sagittal T1-weighted and gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI demonstrating enhancing lesions with heterogeneous signal intensity in the suprasellar and pineal regions.
Figure 3:
(a) Follow-up axial T1-weighted and gadolinium-enhanced brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrating enhancing lesions with heterogeneous signal intensity in the suprasellar and right periatrial regions with interval increase in size. (b) Follow-up axial T1-weighted and gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI demonstrating enhancing lesion with heterogeneous signal intensity in the pineal region with interval increase in size. (c) Follow-up sagittal T1-weighted and gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI demonstrating enhancing lesions with heterogeneous signal intensity in the suprasellar and pineal regions with interval increase in size.
The patient was treated with whole-brain radiation (30 Gy in 10 fractions) rather than high-dose methotrexate due to the patient’s decompensated liver cirrhosis.[
Figure 4:
(a) Follow-up axial head computed tomography (CT) without contrast demonstrating near-complete resolution of the lesions in the suprasellar and right periatrial regions after whole-brain radiation. (b) Follow-up axial head CT without contrast demonstrating near-complete resolution of the lesion in the pineal region after whole-brain radiation. (c) Follow-up sagittal head CT without contrast demonstrating near-complete resolution of the lesions in the suprasellar and pineal regions after whole-brain radiation.
DISCUSSION
PCNSL can present with a variety of signs and symptoms. In this case, the patient’s initial presentation was secondary to distal neurolymphomatosis of the brachial plexus. The intracranial findings, with dominant lesions in the suprasellar and pineal regions, are atypical for the disease and could not explain the limb findings. We compare our experience with this patient to that reported in the literature.
PCNSL arises in the brain parenchyma, spinal cord, cranial nerves, eyes, or meninges; therefore, it can present with virtually any constellation of neurologic symptoms. The most common presenting symptoms are focal neurologic deficit (70%), altered mental status (43%), increased intracranial pressure (33%), seizures (14%), and vitreous involvement (4%).[
PCNSL should be included in the differential diagnosis for all patients with imaging findings demonstrating multiple intracranial lesions. The typical gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI of a patient with PCNSL shows isointense to hypointense lesions on T2 sequences that enhance intensely and homogeneously with well-defined boarders on T1 with gadolinium sequences. PCNSL lesions also often demonstrate restricted diffusion on diffusion-weighted imaging.[
The frontal and parietal lobes are the most commonly involved sites followed by the periventricular region, corpus callosum, basal ganglia, and cerebellum.[
In both case reports of neurolymphomatosis of the brachial plexus secondary to PCNSL, diagnosis of brachial plexus involvement could be made using gadolinium-enhanced brachial plexus MRI that showed hyperintense thickening of the brachial plexus on T2 sequences that enhance intensely and homogeneously.[
In patients who are not optimal surgical candidates because of either medical comorbidities or the deep or eloquent location of their lesions, a lumbar puncture may aid in diagnosis if the leptomeninges are involved. Analyzing CSF for neoplastic lymphocytes using either cytomorphologic or polymerase chain reaction analysis reveals evidence of leptomeningeal dissemination in only 15–20% of cases.[
CONCLUSION
PCNSL is a rare, aggressive, and extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the neuroaxis with myriad clinical manifestations that complicate and potentially delay diagnosis. Diagnosis is most commonly made through stereotactic brain biopsy following an investigative path of gadolinium-enhanced brain and spine MRI, body imaging to exclude systemic lymphoma, slit-lamp examination, and CSF analysis. We present a 70-year-old woman with rapid onset of motor and sensory disturbances, clinically localized to the brachial plexus, who subsequently developed a CN III palsy. Gadolinium-enhanced brachial plexus, brain, and spine MRI demonstrated enhancing masses in the suprasellar, pineal, and right periatrial regions that did not explain the neurologic deficits, and CSF studies were nondiagnostic. Stereotactic brain biopsy confirmed PCNSL. An insidious course and nonspecific presentation contribute to the difficulty of diagnosing PCNSL and initiating treatment with chemotherapy and/or radiation in a timely fashion.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patient’s identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Bataille B, Delwail V, Menet E, Vandermarcq P, Ingrand P, Wager M. Primary intracerebral malignant lymphoma: Report of 248 cases. J Neurosurg. 2000. 92: 261-6
2. Choi YJ, Shin JA, Kim YH, Cha SJ, Cho JY, Kang SH. Neurolymphomatosis of brachial plexus in patients with nonhodgkin’s lymphoma. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2013. 2013: 492329
3. Ferreri AJ, Marturano E. Primary CNS lymphoma. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2012. 25: 119-30
4. Fischer L, Martus P, Weller M, Klasen HA, Rohden B, Röth A. Meningeal dissemination in primary CNS lymphoma: Prospective evaluation of 282 patients. Neurology. 2008. 71: 1102-8
5. Grommes C, DeAngelis LM. Primary CNS lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2017. 35: 2410-8
6. Gupta A, Johnson M, Hussain A. Pineal gland lymphoma: Case report and literature review. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2015. 5: 51
7. Han CH, Batchelor TT. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2017. 23: 1601-18
8. Hoang-Xuan K, Bessell E, Bromberg J, Hottinger AF, Preusser M, Ruda R. Diagnosis and treatment of primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompetent patients: Guidelines from the European association for neuro-oncology. Lancet Oncol. 2015. 16: e322-32
9. Mustafa R, Klein CJ, Martinez-Thompson J, Johnson AC, Engelstad JK, Spinner RJ. Recurrent brachial neuritis attacks in presentation of B-cell lymphoma. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018. 2: 382-6
10. Schwingel R, Reis F, Zanardi V, Queiroz L, França M. Atypical sites of lymphoma in the central nervous system. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2011. 69: 566-7
11. Tarabay A, Cossu G, Berhouma M, Levivier M, Daniel RT, Messerer M. Primary pituitary lymphoma: An update of the literature. J Neurooncol. 2016. 130: 383-95