- Department of Neurosurgery, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI 53226, USA
Correspondence Address:
Ha Son Nguyen
Department of Neurosurgery, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI 53226, USA
DOI:10.4103/2152-7806.178523
Copyright: © 2016 Surgical Neurology International This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Li L, Patel M, Nguyen HS, Doan N, Sharma A, Maiman D. Primary atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of the spine in an adult patient. Surg Neurol Int 10-Mar-2016;7:27
How to cite this URL: Li L, Patel M, Nguyen HS, Doan N, Sharma A, Maiman D. Primary atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of the spine in an adult patient. Surg Neurol Int 10-Mar-2016;7:27. Available from: http://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint_articles/primary-atypical-teratoidrhabdoid-tumor-of-the-spine-in-an-adult-patient/
Abstract
Background:Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (AT/RT) is an aggressive neoplasm of the central nervous system that generally arises intracranially in patients under 2 years of age. Primary spinal AT/RT in an adult is rare.
Case Description:A 23-year-old female presented with left lower extremity sciatica attributed to a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-documented intradural mass between L2 and L4. The lesion was biopsied (was unresectable) and treated with high-dose chemotherapy (methotrexate, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, etoposide, and cisplatin) with autologous hematopoietic stem cells rescue, followed by 2 months of radiation therapy (36 Gy to craniospinal axis, 20 Gy to lumbar region) with concurrent temozolomide; the latter was discontinued after 3 weeks due to myelosuppression. Tumor relapsed 1 year later at C7–T1 level. She was started on oral metronomic therapy, and bevacizumab was added 2 months later. Three months later, a cervical MRI showed progression of the tumor, along with new lesions in the thoracic/lumbar spine plus intracranial punctate nodular tumors. Following resection of the C7/T1 lesion, she was started on palliative alisertib; a month later, a cranial computed tomography showed progression of her disease with hydrocephalus. Treatment was discontinued, and she expired 12 months after initial diagnosis.
Conclusion:Primary spinal AT/RT in the adult patient is rare. The pathology is associated with early recurrence and a poor prognosis. Although potential benefits of metronomic chemotherapy and alisertib have been reported, the patient in this study did not favorably respond to these modalities.
Keywords: Adult spine tumor, alisertib, atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor, metronomic therapy, primary spine tumor
INTRODUCTION
Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (AT/RT) is an aggressive neoplasm that constitutes approximately 6% of pediatric central nervous system (CNS) tumors.[
CASE PRESENTATION
Clinical presentation
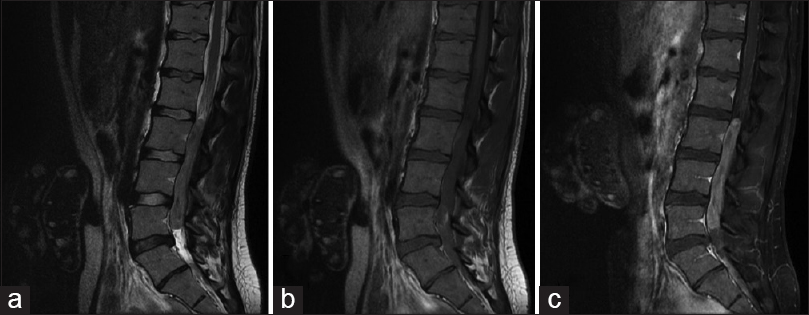
A 23-year-old female presented with left lower extremity sciatica accompanied by numbness and weakness in her left leg and foot plus right leg paresthesias. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine showed an intradural mass from L2 to L4 [
Treatment with radiation and chemotherapy
First, she received chemotherapy (high-dose methotrexate, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, etoposide, and cisplatin) with autologous hematopoietic stem cells rescue. This was followed by 2 months of radiation therapy (36 Gy to craniospinal axis, 20 Gy to lumbar region) with concurrent temozolomide; the latter was discontinued after 3 weeks due to myelosuppression. She underwent disease reevaluation 4 weeks after the completion of radiation, which showed improvement in the spinal tumor and no new metastatic lesions.
Relapse 1 year later
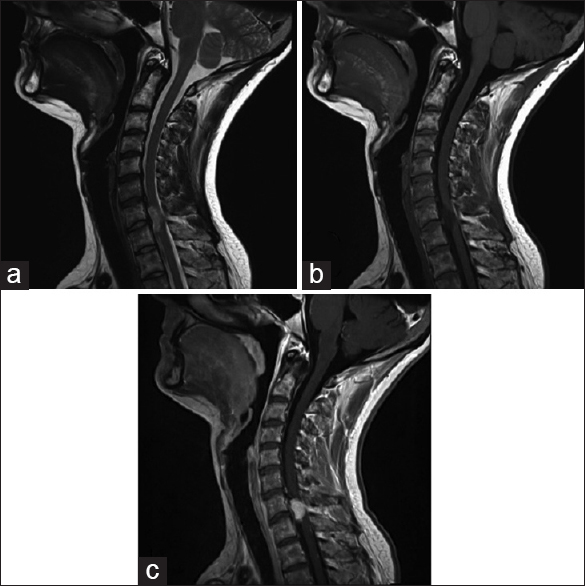
The patient relapsed 1 year later, demonstrating a metastasis on the left at the C7–T1 level [
DISCUSSION
History
In the 1970s, AT/RT was formerly labeled as a malignant RT due to similarities to Wilms’ tumor.[
Epidemiology of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor
AT/RT largely develops in children <2 years of age arising in the cerebellum, followed by the ventricles, frontal lobe, and brainstem.[
Rare spinal cord lesions
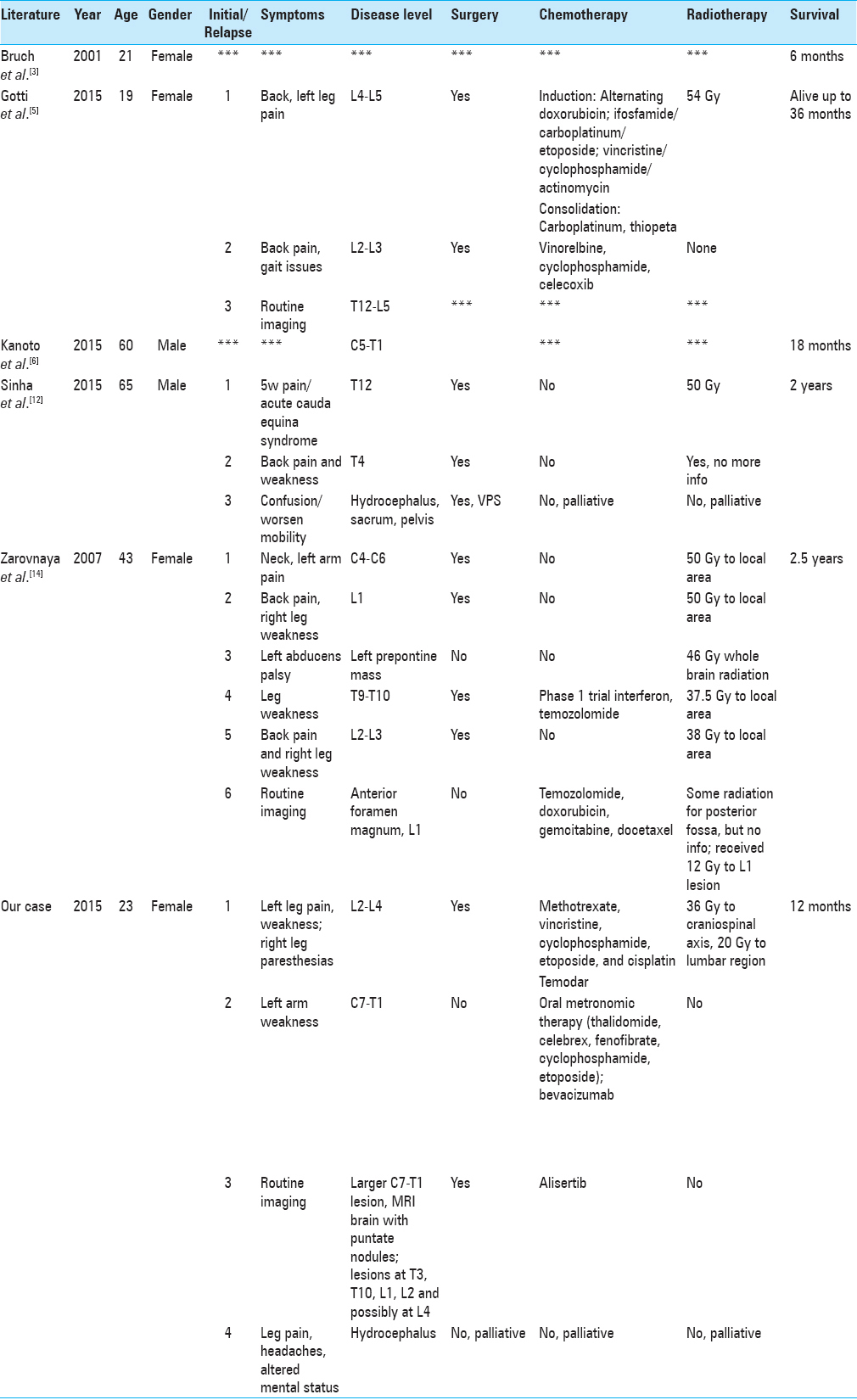
Findings within the spinal cord are rare. In particular, there have been only five prior cases of primary spinal AT/RT in adult patients[
No standard protocol for treatment atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (primary/relapsing)
There is no standard protocol for the treatment of primary and relapsing AT/RT. Immediate multimodal treatment has been advocated, including gross tumor resection, followed by high-dose chemotherapy with autologous hematopoietic stem cells rescue and radiotherapy.[
CONCLUSION
There is no standardized treatment for primary spinal AT/RT in adults. Most of the treatment protocols are derived from the pediatric population where data are inadequate. Primary spinal AT/RT in adults is rare and is associated with early recurrence and a poor prognosis. Although potential benefits of metronomic chemotherapy and alisertib have been reported, the patient in this study did not favorably respond to these modalities.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. André N, Abed S, Orbach D, Alla CA, Padovani L, Pasquier E. Pilot study of a pediatric metronomic 4-drug regimen. Oncotarget. 2011. 2: 960-5
2. Beckwith JB, Palmer NF. Histopathology and prognosis of Wilms tumors: Results from the First National Wilms’ Tumor Study. Cancer. 1978. 41: 1937-48
3. Bruch LA, Hill DA, Cai DX, Levy BK, Dehner LP, Perry A. A role for fluorescence in situ hybridization detection of chromosome 22q dosage in distinguishing atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors from medulloblastoma/central primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Hum Pathol. 2001. 32: 156-62
4. Gnoni A, Silvestris N, Licchetta A, Santini D, Scartozzi M, Ria R. Metronomic chemotherapy from rationale to clinical studies: A dream or reality?. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015. 95: 46-61
5. Gotti G, Biassoni V, Schiavello E, Spreafico F, Antonelli M, Calareso G. A case of relapsing spinal atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (AT/RT) responding to vinorelbine, cyclophosphamide, and celecoxib. Childs Nerv Syst. 2015. 31: 1621-3
6. Kanoto M, Toyoguchi Y, Hosoya T, Kuchiki M, Sugai Y. Radiological image features of the atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor in adults: A systematic review. Clin Neuroradiol. 2015. 25: 55-60
7. Lau CS, Mahendraraj K, Chamberlain RS. Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors: A population-based clinical outcomes study involving 174 patients from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database (1973-2010). Cancer Manag Res. 2015. 7: 301-9
8. Moeller KK, Coventry S, Jernigan S, Moriarty TM. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of the spine. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. 28: 593-5
9. Rickert CH, Paulus W. Epidemiology of central nervous system tumors in childhood and adolescence based on the new WHO classification. Childs Nerv Syst. 2001. 17: 503-11
10. Rorke LB, Packer RJ, Biegel JA. Central nervous system atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors of infancy and childhood: Definition of an entity. J Neurosurg. 1996. 85: 56-65
11. Schrey D, Carceller Lechón F, Malietzis G, Moreno L, Dufour C, Chi S. Multimodal therapy in children and adolescents with newly diagnosed atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor: Individual pooled data analysis and review of the literature. J Neurooncol. 2016. 126: 81-90
12. Sinha P, Ahmad M, Varghese A, Parekh T, Ismail A, Chakrabarty A. Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumour of the spine: Report of a case and literature review. Eur Spine J. 2015. 24: S472-84
13. Wetmore C, Boyett J, Li S, Lin T, Bendel A, Gajjar A. Alisertib is active as single agent in recurrent atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors in 4 children. Neuro Oncol. 2015. 17: 882-8
14. Zarovnaya EL, Pallatroni HF, Hug EB, Ball PA, Cromwell LD, Pipas JM. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of the spine in an adult: Case report and review of the literature. J Neurooncol. 2007. 84: 49-55