- Department of Neurological Surgery, Montefiore Medical Center, New York, United States.
- Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Montefiore Medical Center, New York, United States.
- Department of Neurosurgery, Montefiore Medical Center, New York, United States.
Correspondence Address:
Merritt D. Kinon
Department of Neurological Surgery, Montefiore Medical Center, New York, United States.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_707_2020
Copyright: © 2020 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Joshua Alexander Benton1, Rafael De La Garza Ramos1, Yaroslav Gelfand1, Jonathan D. Krystal2, Vijay Yanamadala1, Reza Yassari3, Merritt D. Kinon1. Prolonged length of stay and discharge disposition to rehabilitation facilities following single-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion for acquired spondylolisthesis. 25-Nov-2020;11:411
How to cite this URL: Joshua Alexander Benton1, Rafael De La Garza Ramos1, Yaroslav Gelfand1, Jonathan D. Krystal2, Vijay Yanamadala1, Reza Yassari3, Merritt D. Kinon1. Prolonged length of stay and discharge disposition to rehabilitation facilities following single-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion for acquired spondylolisthesis. 25-Nov-2020;11:411. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/10417/
Abstract
Background: Acquired lumbar spondylolisthesis is often treated with interbody fusion. However, few studies have evaluated predictors for prolonged length of stay (LOS) and disposition to rehabilitation facilities after posterior single-level lumbar interbody fusion for acquired spondylolisthesis.
Methods: The American College of Surgeons National Quality Improvement Program database was queried for adults with acquired spondylolisthesis who underwent single-level lumbar interbody fusion through a posterior approach (posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) or transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion [TLIF]). We utilized multivariate logistic regression analysis to identify predictors of prolonged LOS and disposition in this patient population.
Results: Among 2080 patients identified, 700 (33.7%) had a prolonged LOS (≥4 days), and 306 (14.7%) were discharged postoperatively to rehabilitation facilities. Predictors for prolonged LOS included: American Society of Anesthesiologist (ASA) class ≥3, anemia, prolonged operative time, perioperative blood transfusion, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and return to the operating room. The following risk factors predicted discharge to postoperative rehabilitation facilities: age ≥65 years, male sex, ASA class ≥3, modified frailty score ≥2, perioperative blood transfusion, and prolonged LOS.
Conclusion: Multiple partial-overlapping risk factors predicted prolonged LOS and discharge to rehabilitation facilities after single-level TLIF/PLIF performed for acquired spondylolisthesis.
Keywords: Acquired spondylolisthesis, Discharge, Interbody fusion, Length of stay, Lumbar surgery
INTRODUCTION
Some surgeons utilize single-level posterior-based lumbar interbody fusion (posterior lumbar interbody fusion [PLIF] or transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion [TLIF]) to treat single-level degenerative/acquired lumbar spondylolisthesis. However, these procedures may carry increased perioperative morbidity when compared with laminectomy alone, leading to more prolonged length of stay (LOS) and increased postoperative discharges to rehabilitation facilities (rehab).[
Here, we evaluated the risk factors for postoperative prolonged LOS and discharge to rehabilitation facilities for patients undergoing single-level TLIF and PLIF for acquired degenerative spondylolisthesis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
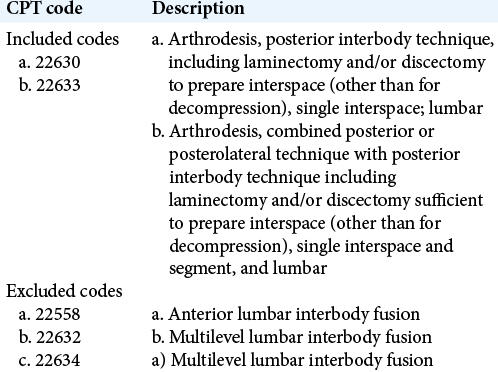
We retrospectively analyzed patients in the American College of Surgeons Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS-NSQIP) database who underwent single-level lumbar posterior-TLIF/PLIF between 2012 and 2016. Inclusion criteria included patients age 18 years and older, and a primary diagnosis of “Acquired Spondylolisthesis” (ICD-9 code 738.4) undergoing PLIF/TLIF [
Clinical data
Multiple clinical criteria, including operative data, the length of surgery, postoperative course, LOS, and discharge data – including discharge to rehabilitation facilities – were evaluated [
Statistical analysis
Univariate analysis and subsequent stepwise multivariate logistic regression models with backward elimination were used to identify the association of independent variables with prolonged LOS and discharge to rehab. Statistical significance was defined as a probability value <0.05 and all statistical analyses were performed using R version 3.6.1 (R Core Team, Vienna, Austria).
RESULTS
Variables associated with prolonged LOS
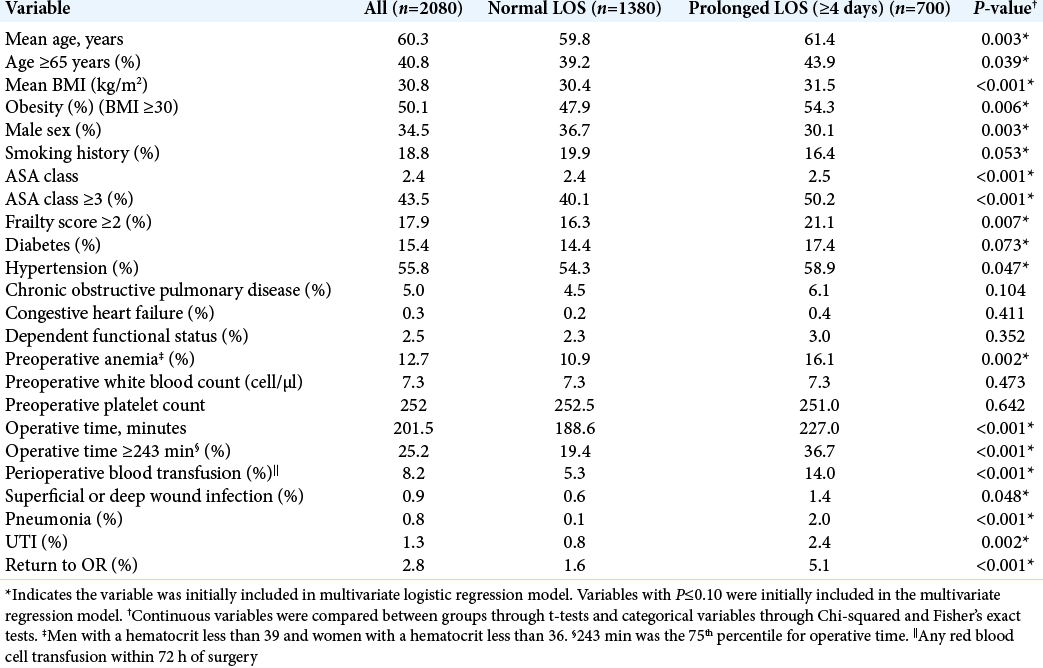
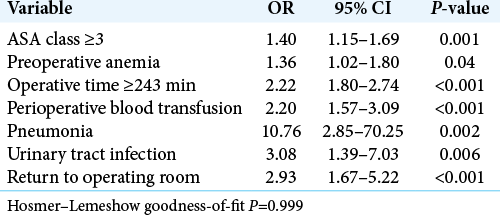
Of the 2080 patients in this study, 700 (33.7%) had a prolonged LOS (e.g., greater than or equal to 4 days) [
Variables associated with discharge to rehabilitation centers
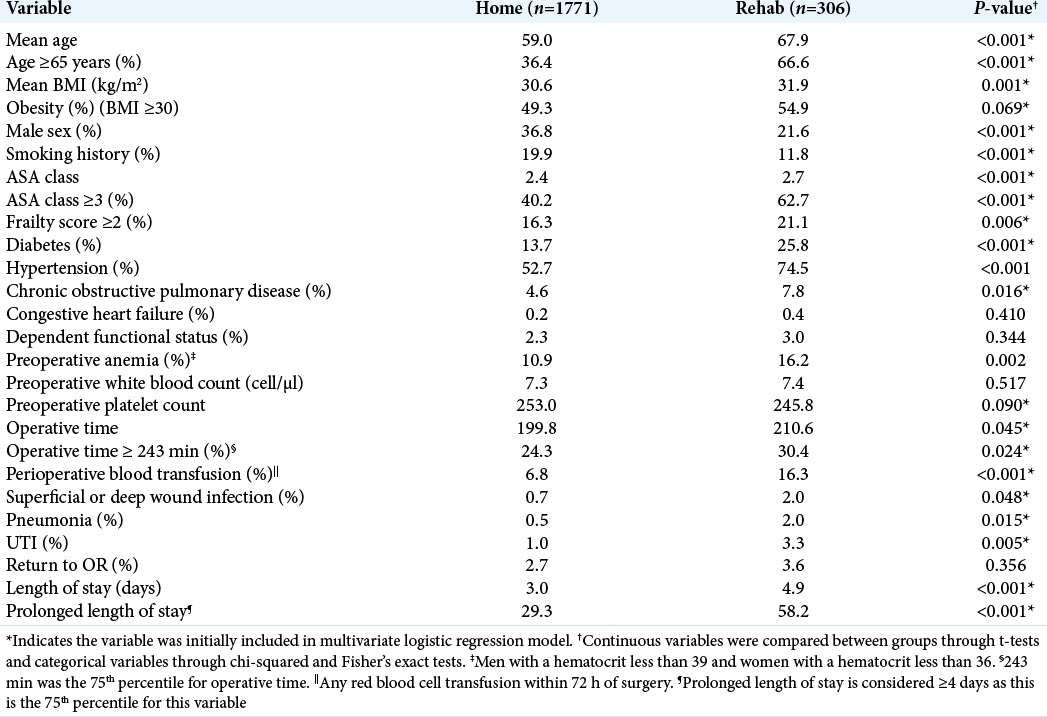
Among 2077 patients, 306 (14.7%) were discharged to rehabilitation centers [
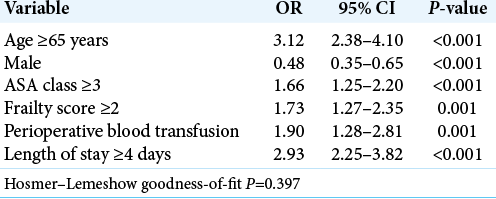
After multivariate logistic regression, analysis independent predictors of discharge to rehab included; age ≥65 years, male sex, ASA class ≥3, frailty score ≥2, perioperative blood transfusion, and prolonged LOS [
DISCUSSION
Following single-level PLIF/TLIF for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis, it was important to understand what risk factors predisposed patients to prolonged postoperative LOS and discharges to rehabilitation facilities. The following factors helped predict prolonged LOS for TLIF/ PLIF: ASA class ≥3, prolonged operative time, preoperative anemia, perioperative blood transfusion, postoperative pneumonia and UTI, and return to the operating room. Postoperative risk factors predicting discharge to rehab facilities included; age ≥65 years, male sex, ASA class ≥3, frailty score ≥2, perioperative blood transfusion, and prolonged LOS.
Literature review
Prior studies of TLIF/PLIF procedures identified similar risk factors associated with discharge to rehab centers; ASA ≥3 class, age ≥65, and male gender.[
Other variables impacting outcomes of TLIF/PLIF
Other clinical variables negatively impacted outcomes of TLIF/ PLIF. First, diabetes increased the morbidity and mortality rates in this and other studies due to it negatively impacting patients’ immune responses and associated chronic inflammation.[
CONCLUSION
Approximately one-third of patients undergoing posterior single-level interbody fusions (TLIF/PLIF) for acquired spondylolisthesis experience a prolonged LOS, and nearly one-seventh (e.g., around 14.7%) are discharged to rehabilitation facilities. Surgeons can better optimize their patient selection and surgical planning for TLIF/PLIF by better understanding of these risk factors.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patients identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Epstein NE, Schwall G, Reillly T, Insinna T, Bahnken A, Hood DC. Surgeon choices, and the choice of surgeons, affect total hospital charges for single-level anterior cervical surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011. 36: 905-9
2. Goz V, Weinreb JH, Schwab F, Lafage V, Errico TJ. Comparison of complications, costs, and length of stay of three different lumbar interbody fusion techniques: An analysis of the nationwide inpatient sample database. Spine J. 2014. 14: 2019-27
3. Guzman JZ, Iatridis JC, Skovrlj B, Cutler HS, Hecht AC, Qureshi SA. Outcomes and complications of diabetes mellitus on patients undergoing degenerative lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014. 39: 1596-604
4. Malik AT, Kim J, Yu E, Khan SN. Discharge to inpatient care facility after anterior lumbar interbody fusion: Incidence, predictors, and postdischarge outcomes. World Neurosurg. 2019. 122: e584-90
5. Passias PG, Poorman GW, Bortz CA, Qureshi R, Diebo BG, Paul JC. Predictors of adverse discharge disposition in adult spinal deformity and associated costs. Spine J. 2018. 18: 1845-52
6. Purvis TE, Goodwin CR, de la Garza-Ramos R, Ahmed AK, Lafage V, Neuman BJ. Effect of liberal blood transfusion on clinical outcomes and cost in spine surgery patients. Spine J. 2017. 17: 1255-63
7. Seicean A, Seicean S, Alan N, Schiltz NK, Rosenbaum BP, Jones PK. Preoperative anemia and perioperative outcomes in patients who undergo elective spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013. 38: 1331-41
8. Vincent AM, Callaghan BC, Smith AL, Feldman EL. Diabetic neuropathy: Cellular mechanisms as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011. 7: 573-83
9. Weaver DJ, Malik AT, Jain N, Yu E, Kim J, Khan SN. The modified 5-item frailty index: A concise and useful tool for assessing the impact of frailty on postoperative morbidity following elective posterior lumbar fusions. World Neurosurg. 2019. 124: e626-32