- Department of Neurosurgery, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Virginia, USA
- Department of Neurosurgery, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, USA
Correspondence Address:
Jeroen R. Coppens
Department of Neurosurgery, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, USA
DOI:10.4103/sni.sni_91_17
Copyright: © 2017 Surgical Neurology International This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Eric Marvin, Asad S. Akhter, Jeroen R. Coppens. Recurrent hemorrhage in hemangioblastoma involving the posterior fossa: Case report. 21-Jun-2017;8:122
How to cite this URL: Eric Marvin, Asad S. Akhter, Jeroen R. Coppens. Recurrent hemorrhage in hemangioblastoma involving the posterior fossa: Case report. 21-Jun-2017;8:122. Available from: http://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/recurrent-hemorrhage-in-hemangioblastoma-involving-the-posterior-fossa-case-report/
Abstract
Background:Hemangioblastomas (HGBs) are the most common primary intra-axial posterior fossa tumor in adults. Although spontaneous hemorrhage of these tumors is exceedingly rare, despite their vascular nature, we describe a case of recurrent hemorrhage with associated tonsillar herniation, and demonstrate that a surgical approach can provide a suitable outcome.
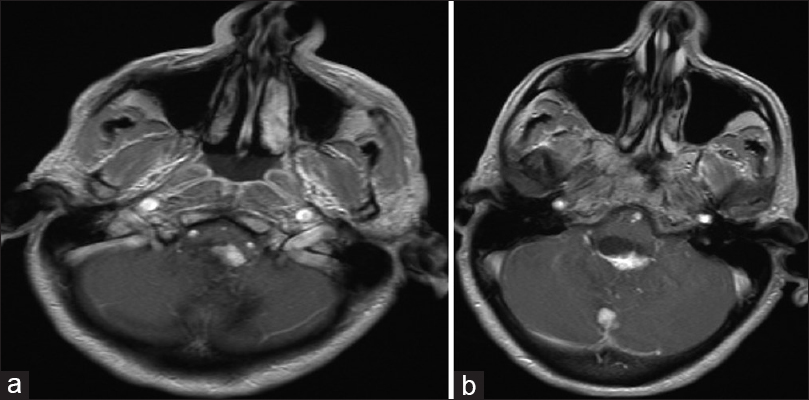
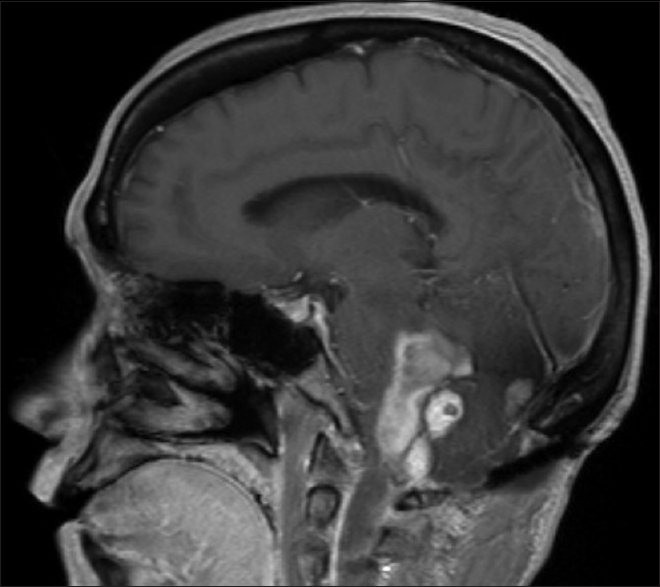
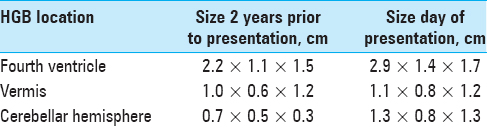
Case Description:A 54-year-old female with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome presented with acute loss of consciousness and Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) was 4. Computed tomographic (CT) images demonstrated large volume subarachnoid hemorrhage of the posterior fossa with intraventricular extension and intraparenchymal hemorrhage involving the right cerebellar tonsil. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) displayed three lesions in the posterior fossa, two near the hemorrhage site. Patient underwent suboccipital craniectomy with a decent recovery followed by radiosurgery as she refused resection. A second hemorrhage occurred ultimately prompting surgical resection of the three posterior fossa lesions, with a reasonable postoperative course.
Conclusion:Hemorrhage of HGBs of the posterior fossa can present in conjunction of tonsillar herniation. Re-hemorrhage appears to be likely if prior acute hemorrhage has occurred. A stepwise approach of surgical decompression and resection may provide the best outcome.
Keywords: Intracranial hemorrhage, hemangioblastoma, von Hippel-Lindau
INTRODUCTION
Hemangioblastomas (HGBs) are the most common primary intra-axial posterior fossa tumor in adults.[
CASE HISTORY
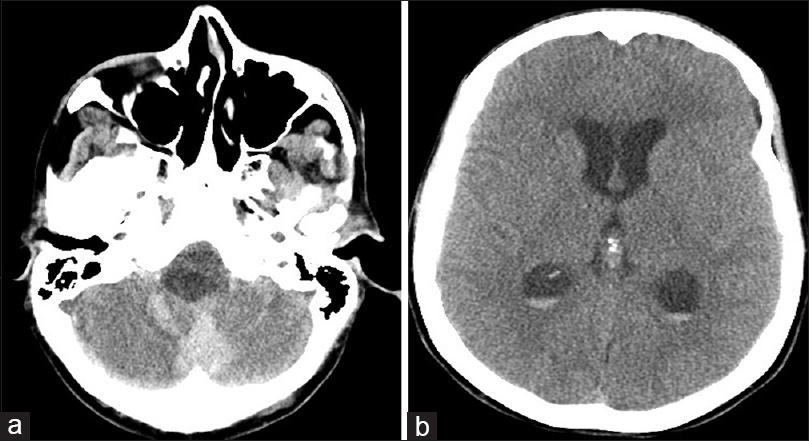
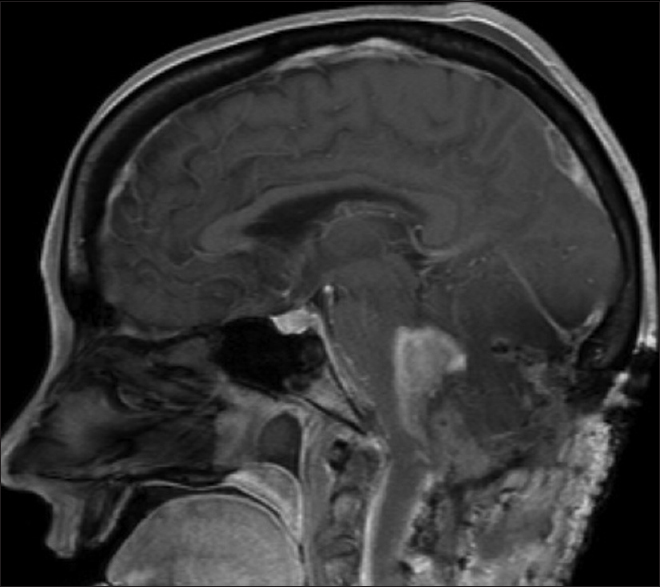
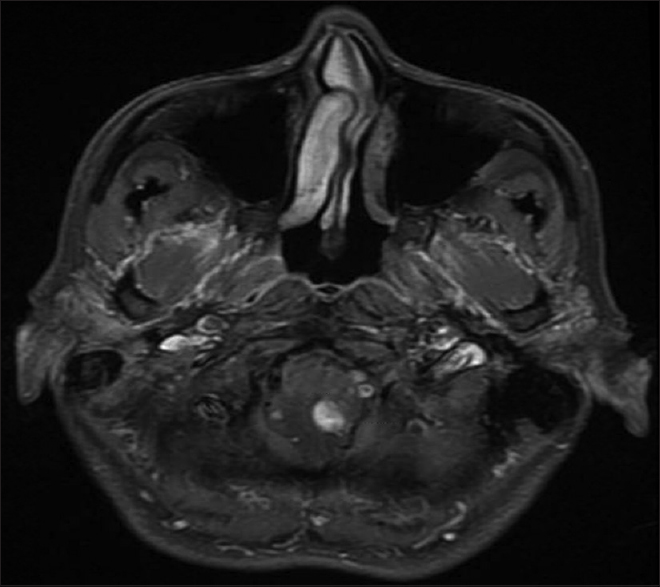
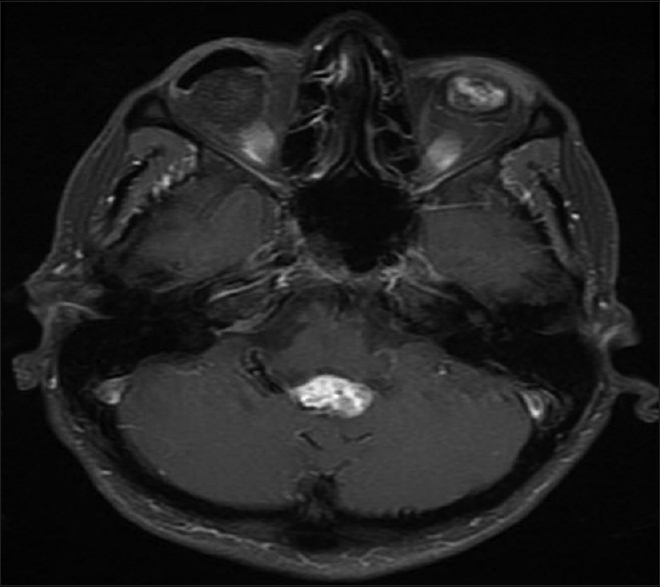
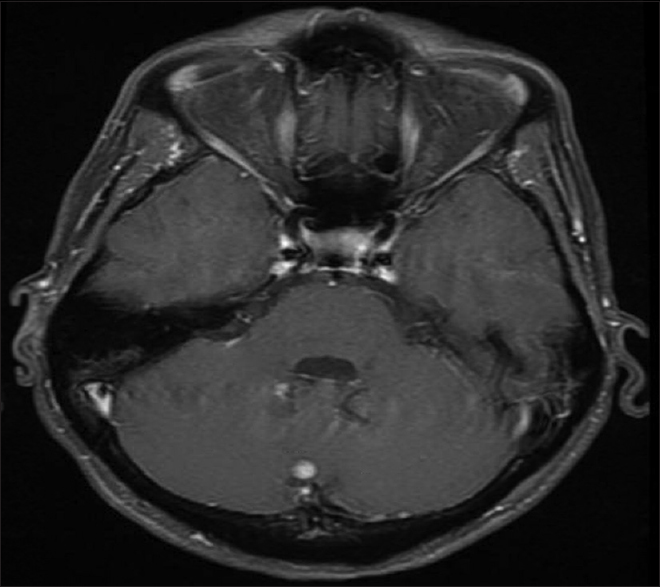
A 54-year-old female with known VHL presented to the emergency department with acute altered mental status, which was followed by respiratory distress requiring intubation. Her past medical history was significant for sequelae of VHL including breast cysts, retinal detachment causing blindness, multiple pancreatic cysts, a kidney cyst, thoracolumbar resection of a spinal HGB, a right globe prosthesis, left phthisis bulbi, gastrointestinal arteriovenous malformation (AVM), partial nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma, and hypertension. Her Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) was 4. Computed tomographic (CT) image [
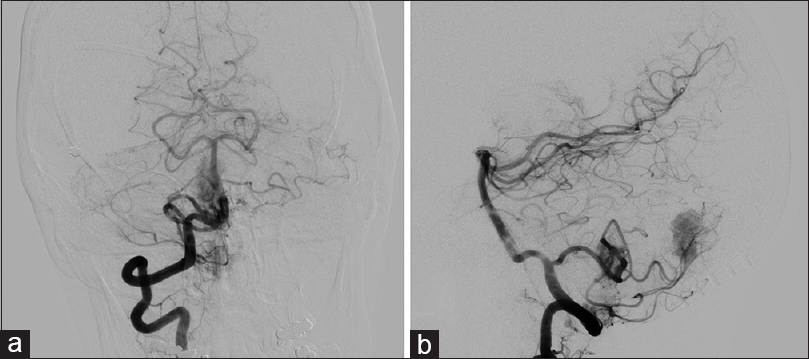
Figure 4
(a) Anteroposterior view of cerebral angiogram with right vertebral artery injection demonstrating two separate areas of tumor blush from the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. (b) Lateral view of cerebral angiogram with right vertebral artery injection demonstrating two separate areas of tumor blush from the posterior inferior cerebellar artery
DISCUSSION
HGBs are the most common primary intra-axial posterior fossa tumor in adults.[
The proposed mechanisms of hemorrhage from a HGB may include hemorrhagic infarction from stenosis or occlusion of vessels by endothelial proliferation or tumor emboli, rupture of thin fragile vessels due to direct invasion of the vessels from tumor cells, vessel rupture due to loss of perivascular support tissue, rupture of fragile neovasculature, venous occlusion, and vascular degeneration due to radiation and/or chemotherapy.[
The risk of hemorrhage in hemangioblastoma (HGB) has been suggested to be linked to their size. Glasker et al. calculated a 0.0024 risk of spontaneous hemorrhage per person per year in patients with HGBs.[
Solid HGBs are often more vascular during surgery[
Partially debulked HGBs may also cause hemorrhage.[
We recommend complete resection of the HGB in case of hemorrhage, given their risk of subsequent hemorrhage. A staged approach may be necessary to perform decompression first, followed by a definitive resection once brain swelling has subsided.
CONCLUSION
Despite their vascular nature, symptomatic hemorrhage from HGB is an uncommon event. This case illustrates multiple posterior fossa HGBs leading to an acute event with tonsillar herniation. A staged approach with decompression followed by resection of the HGB can be safe in that situation. Re-hemorrhage of a HGB seems to be likely if a prior acute hemorrhage has occurred, and surgical resection should be emphasized over other treatment options.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Adegbite AB, Rozdilsky B, Varughese G. Supratentorial capillary hemangioblastoma presenting with fatal spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 1983. 12: 327-30
2. Al-Najar M, Al-Hadidy A, Saleh A, Al-Tamimi A, Al-Darawish A, Obeidat F. Sporadic Lateral Ventricular Hemangioblastoma presenting with Intraventricular and Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2013. 13: 597-600
3. Berlis A, Schumacher M, Spreer J, Neumann HP, van Velthoven V. Subarachnoid haemorrhage due to cervical spinal cord haemangioblastomas in a patient with von Hippel-Lindau disease. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2003. 145: 1009-13
4. Bishop FS, Liu JK, Chin SS, Fults DW. Recurrent cerebellar hemangioblastoma with enhancing tumor in the cyst wall: Case report. Neurosurgery. 2008. 62: E1378-9
5. Browne TR, Adams RD, Roberson GH. Hemangioblastoma of the spinal cord. Review and report of five cases. Arch Neurol. 1976. 33: 435-41
6. Cerejo A, Vaz R, Feyo PB, Cruz C. Spinal cord hemangioblastoma with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 1990. 27: 991-3
7. Chauvet D, Silhouette B, Engrand N, Pradier F, Piotin M, Lot G. Multiple spinal hemangioblastomas complicated with postoperative remote cerebellar hemorrhage: Review of the literature of two rare entities. World Neurosurg. 2014. 81: 843. e841-4
8. Chun YI, Cho J, Moon CT, Koh YC. Delayed fatal cerebellar hemorrhage caused by hemangioblastoma after successful radiosurgical treatment. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010. 152: 1625-7
9. Dayes LA, Purtzer TJ, Shahhal I, Cojocaru T, Knierim D, Soloniuk D. Acute spontaneous cerebellar hemorrhage. J Natl Med Assoc. 1986. 78: 495-9
10. de San Pedro JR, Rodriguez FA, Niguez BF, Sanchez JF, Lopez-Guerrero AL, Murcia MF. Massive hemorrhage in hemangioblastomas Literature review. Neurosurg Rev. 2010. 33: 11-26
11. Djindjian M. Successful removal of a brainstem hemangioblastoma. Surg Neurol. 1986. 25: 97-100
12. Ene CI, Morton RP, Ferreira M, Sekhar LN, Kim LJ. Spontaneous Hemorrhage from Central Nervous System Hemangioblastomas. World Neurosurg. 2015. 83: 1180-e1113-87
13. Friedrich CA. Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. A pleomorphic condition. Cancer. 1999. 86: 2478-82
14. Fujii H, Higashi S, Hashimoto M, Shouin K, Hayase H, Kimura M. Hemangioblastoma presenting with fourth ventricular bleeding. Case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1987. 27: 545-9
15. Gekka M, Yamaguchi S, Kazumata K, Kobayashi H, Motegi H, Terasaka S. Hemorrhagic onset of hemangioblastoma located in the dorsal medulla oblongata presenting with tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy and neurogenic pulmonary edema: A case report. Case Rep Neurol. 2014. 6: 68-73
16. Glasker S, Bender BU, Apel TW, Natt E, van Velthoven V, Scheremet R. The impact of molecular genetic analysis of the VHL gene in patients with haemangioblastomas of the central nervous system. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999. 67: 758-62
17. Glasker S, Van Velthoven V. Risk of hemorrhage in hemangioblastomas of the central nervous system. Neurosurgery. 2005. 57: 71-
18. Gluf WM, Dailey AT. Hemorrhagic intramedullary hemangioblastoma of the cervical spinal cord presenting with acute-onset quadriparesis: Case report and review of the literature. J Spinal Cord Med. 2014. 37: 791-4
19. Hashimoto K, Nozaki K, Oda Y, Kikuchi H. Cerebellar hemangioblastoma with intracystic hemorrhage - Case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1995. 35: 458-61
20. Hayashi S, Takeda N, Komura E. Symptomatic cerebellar hemorrhage from recurrent hemangioblastoma during delivery. Case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2010. 50: 1105-7
21. Ho VB, Smirniotopoulos JG, Murphy FM, Rushing EJ. Radiologic-pathologic correlation: Hemangioblastoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992. 13: 1343-52
22. Irie K, Kuyama H, Nagao S. Spinal cord hemangioblastoma presenting with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1998. 38: 355-8
23. Kikuchi K, Kowada M, Sasaki J, Yanagida N. Cerebellar hemangioblastoma associated with fatal intratumoral hemorrhage: Report of an autopsied case. No Shinkei Geka. 1994. 22: 593-7
24. Koda M, Mannoji C, Itabashi T, Kita T, Murakami M, Yamazaki M. Intramedullary hemorrhage caused by spinal cord hemangioblastoma: A case report. BMC Res Notes. 2014. 7: 823-
25. Kormos RL, Tucker WS, Bilbao JM, Gladstone RM, Bass AG. Subarachnoid hemorrhage due to a spinal cord hemangioblastoma: Case report. Neurosurgery. 1980. 6: 657-60
26. Lemeta S, Aalto Y, Niemela M, Jaaskelainen J, Sainio M, Kere J. Recurrent DNA sequence copy losses on chromosomal arm 6q in capillary hemangioblastoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2002. 133: 174-8
27. Liu A, Wang JM, Li GL, Sun YL, Sun SB, Luo B. Clinical and pathological analysis of benign brain tumors resected after Gamma Knife surgery. J Neurosurg. 2014. 121: 179-87
28. Maddock IR, Moran A, Maher ER, Teare MD, Norman A, Payne SJ. A genetic register for von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Med Genet. 1996. 33: 120-7
29. Maeda YY, Takahama S, Yonekawa H. Four dominant loci for the vascular responses by the antitumor polysaccharide, lentinan. Immunogenetics. 1998. 47: 159-65
30. Mills SA, Oh MC, Rutkowski MJ, Sughrue ME, Barani IJ, Parsa AT. Supratentorial hemangioblastoma: Clinical features, prognosis, and predictive value of location for von Hippel-Lindau disease. Neuro Oncol. 2012. 14: 1097-104
31. Minami M, Hanakita J, Suwa H, Suzui H, Fujita K, Nakamura T. Cervical hemangioblastoma with a past history of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol. 1998. 49: 278-81
32. Moon BH, Park SK, Han YM. Large solid hemangioblastoma in the cerebellopontine angle: Complete resection using the transcondylar fossa approach. Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2014. 2: 128-31
33. Neumann HP, Eggert HR, Scheremet R, Schumacher M, Mohadjer M, Wakhloo AK. Central nervous system lesions in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992. 55: 898-901
34. Neumann HP, Eggert HR, Weigel K, Friedburg H, Wiestler OD, Schollmeyer P. Hemangioblastomas of the central nervous system. A 10-year study with special reference to von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. J Neurosurg. 1989. 70: 24-30
35. Nishimura Y, Hara M, Natsume A, Takemoto M, Fukuyama R, Wakabayashi T. Intra-extradural dumbbell-shaped hemangioblastoma manifesting as subarachnoid hemorrhage in the cauda equina. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2012. 52: 659-65
36. Orita T, Abiko S, Aoki H, Hatano M. Hemangioblastoma with massive bleeding. Case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1985. 25: 398-403
37. Schar RT, Vajtai I, Sahli R, Seiler RW. Manifestation of a sellar hemangioblastoma due to pituitary apoplexy: A case report. J Med Case Rep. 2011. 5: 496-
38. Tago M, Terahara A, Shin M, Maruyama K, Kurita H, Nakagawa K. Gamma knife surgery for hemangioblastomas. J Neurosurg. 2005. 102: 171-4
39. Wakai S, Inoh S, Ueda Y, Nagai M. Hemangioblastoma presenting with intraparenchymatous hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1984. 61: 956-60
40. Wang Z, Hu J, Xu L, Malaguit J, Chen S. Intratumoral hemorrhage in a patient with cerebellar hemangioblastoma: A case report and review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. 94: e497-
41. Yu JS, Short MP, Schumacher J, Chapman PH, Harsh GRt. Intramedullary hemorrhage in spinal cord hemangioblastoma. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1994. 81: 937-40