- Department of Neurosurgery, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Correspondence Address:
G. Lakshmi Prasad, Department of Neurosurgery, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_376_2024
Copyright: © 2024 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Saurabh Beedkar, G. Lakshmi Prasad, Girish Menon. Role of scheduled repeat CT scan in traumatic brain injuries: A prospective observational study. 06-Sep-2024;15:317
How to cite this URL: Saurabh Beedkar, G. Lakshmi Prasad, Girish Menon. Role of scheduled repeat CT scan in traumatic brain injuries: A prospective observational study. 06-Sep-2024;15:317. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/13085/
Abstract
Background: Scheduled CT scan is a routine practice at many centers after traumatic brain injury (TBI), but it has been questioned by few authors. The majority of the studies are reported in mild TBI; however, no specific data exist for the same in moderate and severe TBI.
Methods: This was a single-center and 1-year prospective study. All cases with TBI who underwent scheduled repeat scans were included in the study. Patients who underwent emergency surgery after first computed tomography (CT) and those who expired before repeat CT were excluded from the study. Data included demographics, Glasgow coma scale (GCS) score, initial head CT findings, findings of repeat CT, and the need for any intervention (medical/surgical).
Results: A total of 231 cases were analyzed. The mean time interval for the repeat CT was 7.8 h. One hundred and seventy-one patients underwent scheduled repeat CT (Group 1), 53 patients with GCS >13 were discharged from emergency before the repeat scan (Group 2), and seven cases underwent repeat CT before the scheduled time in view of clinical deterioration (Group 3). The mean age and gender did not vary significantly between the three groups. Mixed lesions predominated in all; however, the proportion significantly differed between groups. In Group 1, two patients required surgery; in Group 3, all patients required a significant change in treatment, whereas none deteriorated or required a repeat scan in Group 2.
Conclusion: In our study, the yield of routine repeat CT scans requiring surgery was 3.5%. Based on the results of our study and the observations from previous studies, we have proposed a few general working statements regarding indications for repeat CT scans in TBI.
Keywords: Follow-up computed tomography scan, Prospective, Repeat computed tomography scan, Scheduled computed tomography scan, Traumatic brain injury
INTRODUCTION
The incidence of traumatic brain injury (TBI) has been reported to be around 350/100,000 population and is also a major cause of permanent disability.[
Radiation exposure is a concern in CT, and to avoid injudicious radiation exposure, researchers have formulated criteria and guidelines for performing CT brain in TBI.[
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This was a single-center and 1-year prospective study from October 2020 to October 2021 conducted in the Department of Neurosurgery, Kasturba Medical College Hospital, Manipal, India. IEC approval was taken before the start of the study (IEC 481/2021 dated 24/10/2021). All patients with TBI who underwent scheduled repeat CT scans within 12 hours of the first scan were included in the study. The following were excluded: patients who had normal findings on the first CT scan, who underwent emergency surgery after the first CT brain, who already had a prior repeat CT scan within 12 h, who expired before the scheduled repeat CT scan, and who underwent repeat CT for nontrauma findings.
We divided the study cohort into three groups: Group 1: patients who had their scheduled repeat CT scan performed as per our protocol; and Group 2: patients who got discharged from the emergency department before the repeat scan, and all of them had a GCS score of 15. The reasons were as follows: not consenting for admission or staying at a nearby place; and Group 3: patients who underwent repeat CT scans before the scheduled time interval in view of a change in neurologic examination (drop in GCS score or pupillary abnormalities). If the patient wishes not to get admitted as in Group 2, then a repeat scan would be performed only if they come back with new symptoms. All patients in Group 2 were followed up, either in the outpatient department (OPD) or telephonically.
The following data were collected and analyzed: age, gender, mechanism of injury, GCS score, associated injuries, radiological data (findings of initial CT, indication for repeat CT, and findings of repeat CT), and need for intervention. The lesions seen on repeat CT were classified as better, same, or worse than the initial findings. Lesions were considered better if there was a resolution of contusion/hematoma or reduction in mass effect and were considered worse if there were new lesions or worsening edema/mass effect or increase in the size of contusions. TBI-related interventions were classified as medical (mannitol/hypertonic saline or hyperventilation) or surgical (craniotomy/decompressive craniectomy). All CT scans were read by attending neurosurgeons. As per the literature, a mild TBI with an intracranial pathology on a CT scan is often termed a complicated mild TBI (cMTBI). Since we included only those cases of mild TBI with abnormal scan findings, the terms mild TBI and cMTBI are used interchangeably.
Statistical tests
All statistical tests were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software (version 29.0). Qualitative variables were tested using the Chi-square test, and quantitative variables (for testing three groups) were tested using analysis of variance test. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
Among a total of 328 cases, 98 cases were excluded and the remaining 231 cases were included in the study and analyzed. Males predominated, and the most common age groups were 3rd and 5th decades. The mean time interval for the repeat CT from the first scan was 7.8 h (range, 6–12 h).
There were 171 patients in Group 1, 53 in Group 2, and seven patients in Group 3. In our series, we did not have any patients in Group 2 who returned to the hospital with new symptoms warranting a scan. Many of them consulted our OPD for suture removal (for a sutured lacerated wound) or regular follow-up, and the remaining patients were followed up telephonically.
The mean age and gender did not vary significantly between the three groups; however, the severity of TBI varied. In Group 1, there was a predominance of moderate TBI. Group 2 comprised mild TBI alone (cMTBI), whereas Group 3 had more severe TBI cases, and this difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).
With regard to radiology, mixed lesions predominated in all three groups; however, the proportion varied significantly between them (P < 0.05). Basal cisterns were preserved in >90% of cases in Group 1, whereas it was compressed in >40% of Group 3 patients (P < 0.05). Twenty-eight cases had changes in the CT findings, and this was statistically different between Groups 1 and 3 (P < 0.05) (Group 2 was not considered. No repeat scan was done in those patients).
Among them, nine cases had worsened, whereas 19 cases showed improvement in CT findings. In Group 1, there were 12 patients with isolated EDHand; two out of those 12 (16.6%) cases needed surgery in view of new scan findings. Of the seven patients in Group 3, five underwent surgery, and two received additional anti-edema measures for the changes noted on repeat CT scans.
Overall, on statistical analysis, we found that age and gender did not differ between the groups, while the severity of TBI, proportion of mixed lesions, basal cistern effacement, and radiological changes in the new scan were significantly different between the groups.
The clinicoradiological characteristics between the three groups (with statistical results) are shown in
Illustrations
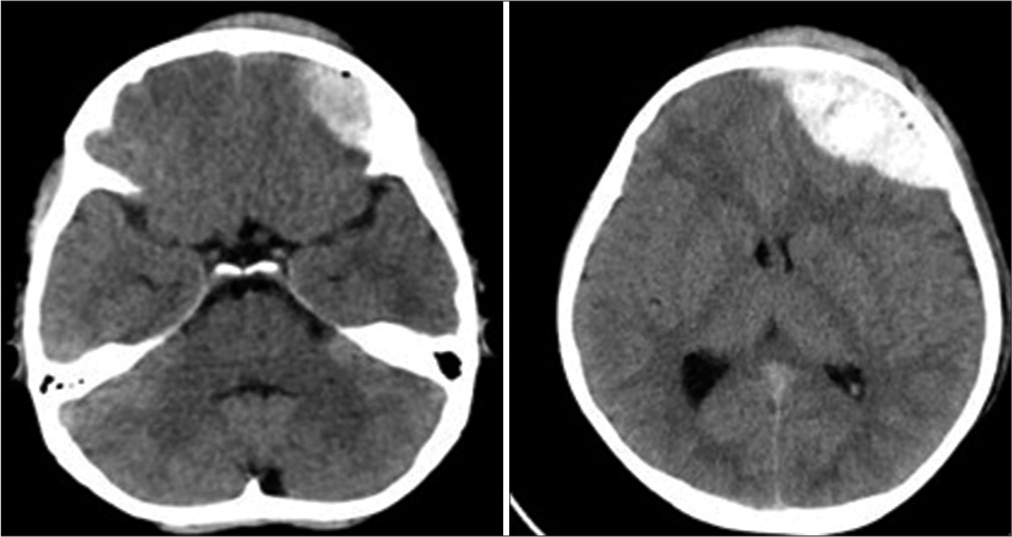
Figure 4:
A 55-year-old male with Glasgow Coma scale (GCS) 12 on admission and computed tomography showing thin frontal subdural hematoma (SDH) and contusion with preserved basal cisterns (top panel). He deteriorated in GCS score with pupillary asymmetry and repeated scan showing worsening of the SDH and compressed basal cisterns (bottom panel).
DISCUSSION
The hazards of radiation are well known, and the most severe ones include the risk of secondary malignancy due to DNA damage.[
Studies against a routine repeat CT scan
In their prospective 1-year study by Sifri et al., the authors included 130 adult patients with minimal head injury (HI) (LOC, amnesia, GCS>13) and IC bleed. A repeat CT scan was done within 24 hours of admission. Around 3/4ths of them (n = 99) had a normal neurologic examination at the time of their repeat cranial CT. They observed that none required immediate neurosurgical intervention or had delayed neurologic deterioration related to their head injury after the repeat CT scan, and the negative predictive value (NPV) of a normal neurologic examination was 100%. They concluded that repeat CT in patients with minimal HI and a normal neurologic examination is therefore not indicated.[
Connon et al. conducted a 20-month prospective study and included all adult blunt trauma patients. They categorized brain CT as “routine” or “indicated” and included 591 patients, of whom around 80% were mild TBI. Among them, 401 were discharged without a repeat scan (similar to Group 2 in our study), and the remaining 190 patients had undergone 305 repeat scans. They noted that 28 patients had changes in CT findings necessitating change in management, and all of them belonged to the “indicated” category. The authors concluded that the decision to perform routine repeat CT brain should be reconsidered, and repeat CT brain is indicated in patients with deteriorating neurological status, especially younger and more severely head-injured patients. [
Studies supporting repeat CT scan
Kaups et al. conducted a 5-year retrospective study. The mean time to 2nd CT was 22.6 h. Sixteen patients had intervention after repeat CT. They concluded that elevated ICP, hypotension, and coagulopathy were risk factors.[
Stein et al. conducted a review including only mild TBI. They included articles published between 1980 and 2006. A decision tree was assembled to compare whether routine repeat CT was cost-effective versus selective CT after clinical deterioration. They observed that awaiting clinical deterioration in patients with mild TBI with initial abnormal CT is not cost-effective as compared to routine repeat scans. They concluded that, despite the difference being not statistically significant, routine follow-up scanning is slightly more cost-effective, especially in younger patients.[
In their 6-month prospective study, Doddamani et al. analyzed 201 patients and observed that 20% showed a change in management. However, the information about neurological changes is unclear in their paper. They concluded that repeat CT scans were of value in detecting new lesions or enlargement of existing lesions resulting in change of management in a significant proportion of patients.[
In our study, the positive yield of the scheduled repeat CT scan requiring surgical intervention due to a silent progression of hematoma was 3.5%. In isolated EDH, younger patients had a change in management following the scheduled repeat CT scan. In mixed lesions and no clinical deterioration, routine repeat CT showed changes in lesions but none required any change in management. In isolated traumatic SAH, DAI, tentorial SDH, fractures, and none required any change in management after routine repeat CT brain.
In our study, we included patients with all GCS scores which are not very commonly seen in other studies. In the first group of studies (opposing a routine repeat scan), except two studies by da Silva et al. and Connon et al.,[
Due to the inherent heterogeneity involved in TBI and also conflicting results from the previous studies, it would be very difficult to formulate guidelines regarding a routine repeat scan after TBI. However, based on the observations of our prospective study and the previous studies, the following general statements may be proposed. We want to reiterate the fact that these are not guidelines or recommendations but may serve as important points for future larger studies.
In an isolated SAH, falcine, and tentorial SDH, repeat CT is not required (Cooper et al.[ In mild TBI with an initial abnormal CT (cMTBI), repeat CT is necessary only if clinical deterioration except in cases of isolated EDH and younger pts, in whom a routine CT may be beneficial (from our observations and Stein et al.[ In other GCS scores with an initial abnormal scan, repeat CT is probably beneficial and should be performed (Doddamani et al.,[
Strengths of the study
Ours was a prospective study from a single center, and we included patients with all GCS scores which are not commonly seen in previous studies.
Limitations
The relatively lesser number of cases was the major limitation of our study. Other than younger age and isolated EDH, we could not identify any specific factors that could predict deterioration and requirement of repeat scan.
CONCLUSION
We prospectively analyzed patients with TBI to assess the impact of a scheduled repeat CT scan at our center. In our study, the yield of the scheduled repeat CT scan requiring surgery was 3.5%. Based on the results of our study and the observations from previous studies, we have proposed a few general working statements regarding indications for repeat CT scans in TBI. Well-designed and prospective multicentric trials, including all categories of TBI patients, are necessary to provide reliable answers.
Ethical approval
IEC approval of Kasturba Medical College was taken for the study. No.: IEC 481/2021 dated 24/10/2021.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Journal or its management. The information contained in this article should not be considered to be medical advice; patients should consult their own physicians for advice as to their specific medical needs.
References
1. AbdelFattah KR, Eastman AL, Aldy KN, Wolf SE, Minei JP, Scott WW. A prospective evaluation of the use of routine repeat cranial CT scans in patients with intracranial hemorrhage and GCS score of 13 to 15. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012. 73: 685-8
2. Bee TK, Magnotti LJ, Croce MA, Maish GO, Minard G, Schroeppel TJ. Necessity of repeat head CT and ICU monitoring in patients with minimal brain injury. J Trauma. 2009. 66: 1015-8
3. Brenner DJ, Doll R, Goodhead DT, Hall EJ, Land CE, Little JB. Cancer risks attributable to low doses of ionizing radiation: Assessing what we really know. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. 100: 13761-6
4. Brown CV, Zada G, Salim A, Inaba K, Kasotakis G, Hadjizacharia P. Indications for routine repeat head computed tomography (CT) stratified by severity of traumatic brain injury. J Trauma. 2007. 62: 1339-44
5. Bullock MR, Chesnut R, Ghajar J, Gordon D, Hartl R, Newell DW. Surgical management of traumatic parenchymal lesions. Neurosurgery. 2006. 58: S25-46 discussion Si-iv
6. Carney N, Totten AM, O’Reilly C, Ullman JS, Hawryluk GW, Bell MJ. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury, fourth edition. Neurosurgery. 2017. 80: 6-15
7. Connon FF, Namdarian B, Ee JL, Drummond KJ, Miller JA. Do routinely repeated computed tomography scans in traumatic brain injury influence management? A prospective observational study in a level 1 trauma center. Ann Surg. 2011. 254: 1028-31
8. Cooper SW, Bethea KB, Skrobut TJ, Gerardo R, Herzing K, Torres-Reveron J. Management of traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage by the trauma service: Is repeat CT scanning and routine neurosurgical consultation necessary?. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2019. 4: e000313
9. da Silva PS, Reis ME, Aguiar VE. Value of repeat cranial computed tomography in pediatric patients sustaining moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. J Trauma. 2008. 65: 1293-7
10. Devulapalli KK, Talbott JF, Narvid J, Gean A, Rehani B, Manley G. Utility of repeat head CT in patients with blunt traumatic brain injury presenting with small isolated falcine or tentorial subdural hematomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018. 39: 654-7
11. Doddamani RS, Gupta SK, Singla N, Mohindra S, Singh P. Role of repeat CT scans in the management of traumatic brain injury. Indian J Neurotrauma. 2012. 9: 33-9
12. GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborato. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019. 18: 459-80
13. Haydel MJ, Preston CA, Mills TJ, Luber S, Blaudeau E, DeBlieux PM. Indications for computed tomography in patients with minor head injury. N Engl J Med. 2000. 343: 100-5
14. Kaups KL, Davis JW, Parks SN. Routinely repeated computed tomography after blunt head trauma: Does it benefit patients?. J Trauma. 2004. 56: 475-80 discussion 480-1
15. Mettler FA, Huda W, Yoshizumi TT, Mahesh M. Effective doses in radiology and diagnostic nuclear medicine: A catalog. Radiology. 2008. 248: 254-63
16. Mower WR, Hoffman JR, Herbert M, Wolfson AB, Pollack CV, Zucker MI. Developing a clinical decision instrument to rule out intracranial injuries in patients with minor head trauma: Methodology of the NEXUS II investigation. Ann Emerg Med. 2002. 40: 505-14
17. Nagesh M, Patel KR, Mishra A, Yeole U, Prabhuraj AR, Shukla D. Role of repeat CT in mild to moderate head injury: An institutional study. Neurosurg Focus. 2019. 47: E2
18. Sifri ZC, Homnick AT, Vaynman A, Lavery R, Liao W, Mohr A. A prospective evaluation of the value of repeat cranial computed tomography in patients with minimal head injury and an intracranial bleed. J Trauma. 2006. 61: 862-7
19. Stein SC, Fabbri A, Servadei F. Routine serial computed tomographic scans in mild traumatic brain injury: When are they cost-effective?. J Trauma. 2008. 65: 66-72
20. Stiell IG, Lesiuk H, Wells G, McKnight R, Brison R, Clement C. The Canadian CT Head Rule Study for patients with minor head injury: Rationale, objectives, and methodology for phase I (derivation). Ann Emerg Med. 2001. 38: 160-9
21. Stippler M, Keith S, Nelton EB, Parsons CS, Singleton J, Bilello LA. Pathway-based reduction of repeat head computed tomography for patients with complicated mild traumatic brain injury: Implementation and outcomes. Neurosurgery. 2021. 88: 773-8