- Department of Neurosurgery, Universidad del Bosque, Bogotá, Colombia
- Department of Neurosurgery, La Cardio Foundation, Bogotá, Colombia
- Department of Neurosurgery, Insituto Nacional de Cancerología, Bogotá, Colombia
- Department of Neurosurgery, Hospital of San José, Bogotá, Colombia.
Correspondence Address:
Juan Pablo Leal Isaza, Department of Neurosurgery, Universidad del Bosque, Bogotá, Colombia.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_724_2023
Copyright: © 2024 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, transform, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Juan Pablo Leal Isaza1, Santiago Vallejo2, Jorge Humberto Aristizabal2, Santiago Andrés Rosales-Camargo3, Juan Pablo Perilla-Estrada4, Diego Quintero Rueda1. The “peel-away” technique for a ventriculoatrial shunt in a 6-month-old patient: A case report. 19-Jan-2024;15:16
How to cite this URL: Juan Pablo Leal Isaza1, Santiago Vallejo2, Jorge Humberto Aristizabal2, Santiago Andrés Rosales-Camargo3, Juan Pablo Perilla-Estrada4, Diego Quintero Rueda1. The “peel-away” technique for a ventriculoatrial shunt in a 6-month-old patient: A case report. 19-Jan-2024;15:16. Available from: https://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/12715/
Abstract
Background: A ventriculoatrial shunt (VAS) proves to be an excellent alternative in the treatment of hydrocephalus. Its usage is a viable option when ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS) is contraindicated in any age of patients.
Case Description: This report highlights a successful case involving a 6-month-old patient who underwent VAS catheter positioning. The child presented with hydrocephalus and biliary atresia, making him a candidate for a liver transplant. Notably, a VPS was considered a relative contraindication in this scenario.
Conclusion: The VAS emerges as a viable option for patients in whom a VPS might be contraindicated. This case demonstrates the successful application of a VAS in a pediatric patient.
Keywords: Hydrocephalus, Pediatrics, Peel-away, Ventricular shunt
INTRODUCTION
The ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS) is typically the primary choice for patients with hydrocephalus. In cases where this procedure is contraindicated, alternative shunts, such as the ventriculoatrial shunt (VAS), prove to be a valuable option.[
VAS becomes a compelling alternative when a VPS has either failed previously or is contraindicated due to abdominal pathology, such as an infectious process.[
In 1981, Ashker and Fox introduced a technique for the percutaneous insertion of the distal catheter into the right atrium in a VAS, known as the “peel-away” technique.[
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
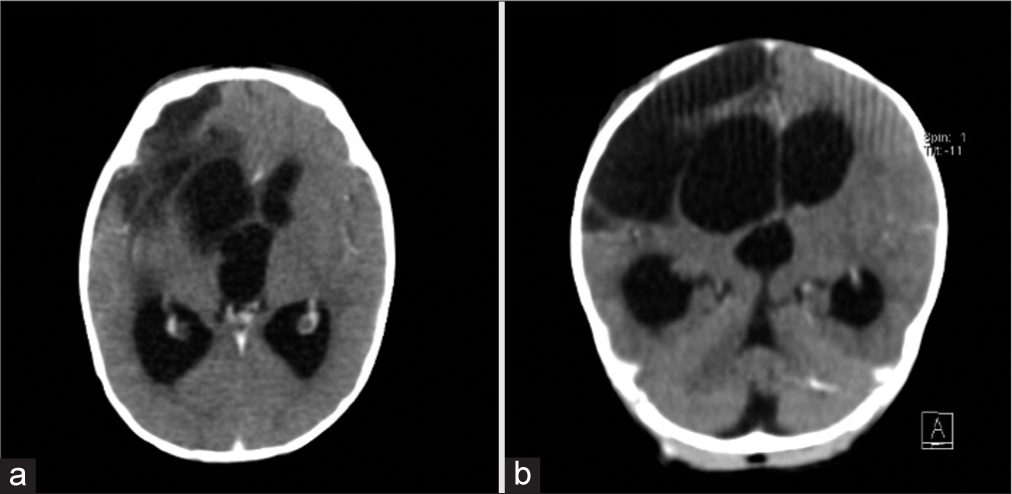
A 6-month-old patient, born prematurely at 27 weeks, diagnosed with bile duct atresia and requiring a liver transplant, experienced intracerebral hemorrhage leading to altered cerebrospinal fluid dynamics and secondary hydrocephalus. The patient underwent multiple surgical procedures, including evacuation of intracerebral hematoma and drainage of intracranial hygromas.
During follow-up, progressive ventricular system dilation was observed, prompting the indication for a ventricular shunt to manage hydrocephalus [
Surgical technique
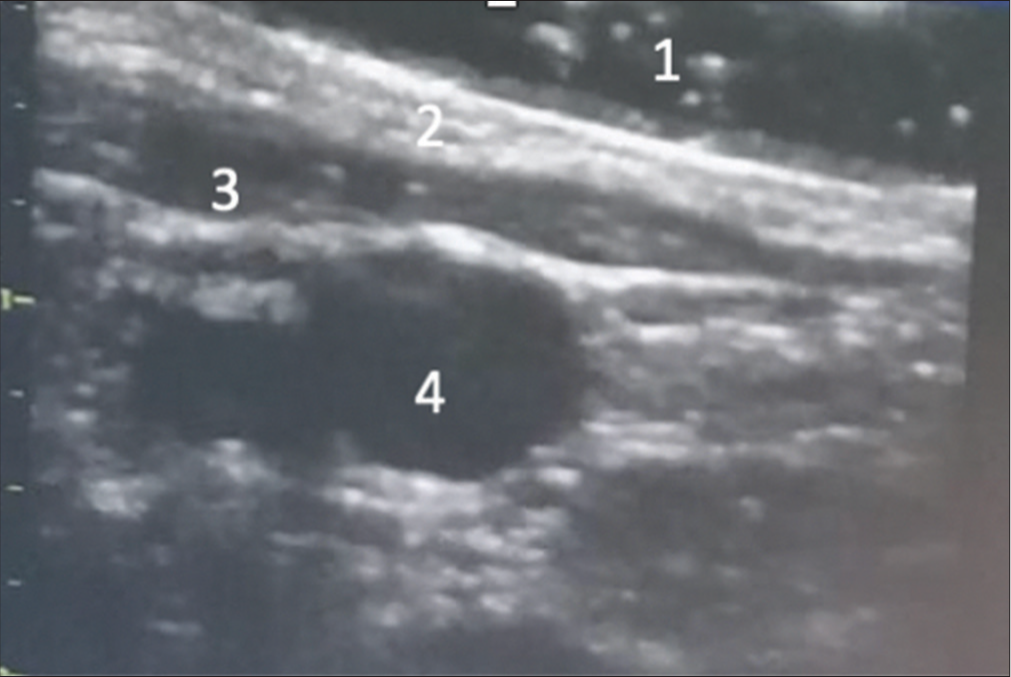
Under general anesthesia, the patient was positioned supine with an interscapular roll. Subsequently, using ultrasound guidance, the internal jugular vein and the internal carotid artery on the right side were identified, and their diameters were measured [
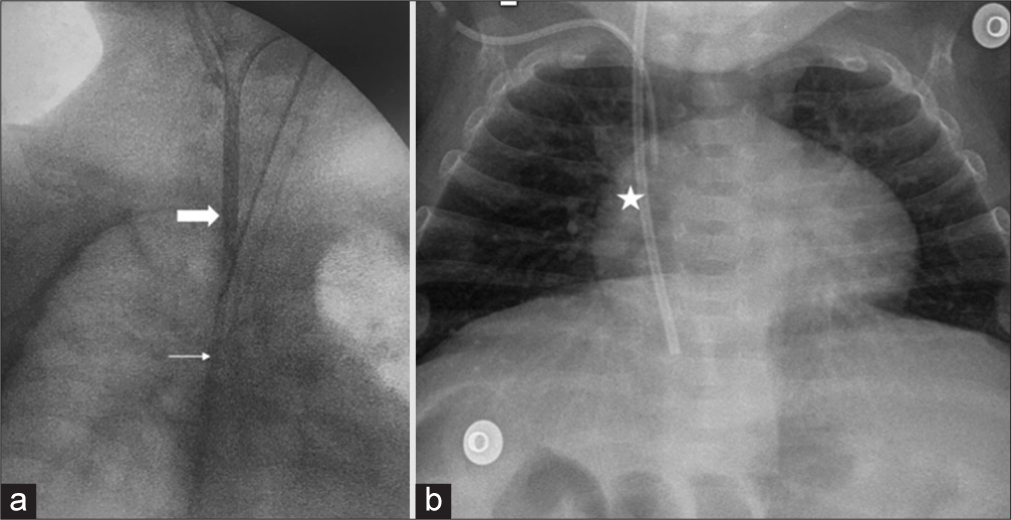
Following aseptic and antiseptic procedures, the internal jugular vein was punctured, and a 7 French “peel-away” catheter was inserted. The procedure was conducted with direct vision under ultrasound guidance, aided by transthoracic echography and electrocardiography wave monitoring. The distal catheter of the VAS was then advanced through the “peel-away” catheter to the right cavoatrial junction, with confirmation of the proper position achieved through intraoperative fluoroscopy [
Finally, a right frontal ventricular access was established, connecting it to the distal system and ensuring proper fixation. Following the procedure, the patient demonstrated symptomatic improvement, and no instances of internal jugular vein thrombosis were documented where the distal catheter was lodged.
DISCUSSION
The VPS presents similar complications to the VAS, such as infection and malfunction, with comparable rates.[
Complications, such as changes in length, have been reported in VASs in pediatric patients, ranging from 43% to 63%.[
In our presented case, the risk of infection and contamination of the peritoneal catheter was associated with the need for the patient to undergo surgical intervention in the abdominal cavity for a liver transplant due to bile duct atresia. While a VPS is not an absolute contraindication in liver transplant patients, it is preferable to opt for other types of shunts to mitigate potential complications[
Performing the VAS procedure percutaneously, as done in our case, offers several advantages over open cervical dissection, including reduced surgical time, a smaller incision, and a lower probability of vascular lesions during surgery.[
The insertion of the catheter using the “peel-away” technique is more commonly performed in the adult population. However, its utilization is infrequent in the pediatric population, and to our knowledge, our case represents the youngest patient recorded in the literature.
CONCLUSION
Hydrocephalus remains one of the most prevalent challenges faced by neurosurgeons in their daily practice within the pediatric population. While VPS continues to be the preferred surgical intervention, VAS emerges as a valuable alternative for patients in whom the former is contraindicated. The utilization of minimally invasive techniques, such as distal catheter insertion through a peel-away catheter guided by ultrasonography, proves to be a swift, effective, and minimally invasive method.
In this case, we present the application of this technique in a patient under six months of age, yielding optimal short-term results. It is crucial to recognize that this type of procedure should be undertaken selectively, emphasizing the importance of thoroughly evaluating the pros and cons, especially in challenging cases like the one discussed here.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Journal or its management. The information contained in this article should not be considered to be medical advice; patients should consult their own physicians for advice as to their specific medical needs.
References
1. Aloddadi M, Alshahrani S, Alnaami I. Endovascular retrieval of detached ventriculoatrial shunt into pulmonary artery in pediatric patient: Case report. J Pediatr Neurosci. 2018. 13: 78-80
2. Ashker K, Fox JL. Percutaneous technique for insertion of an atrial catheter for CSF shunting. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 1981. 55: 488-90
3. Bakhaidar M, Wilcox JT, Sinclair DS, Diaz RJ. Ventriculoatrial shunts: Review of technical aspects and complications. World Neurosurg. 2022. 158: 158-64
4. Erdogan H, Altun A, Kuruoglu E, Kaya AH, Dagcinar A. Difficulties of distal catheter insertion of ventriculoatrial shunting in infants and little children. Turk Neurosurg. 2018. 28:
5. Faybush E, Mulligan DC, Birch BD, Sirven JI, Balan V. Liver transplant in a patient with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Liver Transplant. 2005. 11: 467-8
6. Gmeiner M, Wagner H, van Ouwerkerk WJ, Sardi G, Thomae W, Senker W. Long-term outcomes in ventriculoatrial shunt surgery in patients with pediatric hydrocephalus: Retrospective single-center study. World Neurosurg. 2020. 138: e112-8
7. Gutiérrez-González R, Rivero-Garvía M, Márquez-Rivas J. Ventriculovascular shunts via the femoral vein: A temporary feasible alternative in pediatric hydrocephalus. J Pediatr Surg. 2010. 45: 2274-7
8. Hung AL, Vivas-Buitrago T, Adam A, Lu J, Robison J, Elder BD. Ventriculoatrial versus ventriculoperitoneal shunt complications in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017. 157: 1-6
9. Nulsen FE, Spitz EB. Treatment of hydrocephalus by direct shunt from ventricle to jugular vain. Surg Forum. 1951. 2: 399-403
10. O’Shea PA. Inferior vena cava and hepatic vein thrombosis as a rare complication of ventriculoatrial shunt. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1978. 48: 143-5
11. Park KJ, Lim YC, Yoon SH. Shunt revision to ventriculoatrial shunt due to long-term abdominal distension complicated by neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis and cerebrospinal fluid overproduction after ventriculoperitoneal shunt for the management of post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus: A case report. Nerve. 2019. 5: 90-3
12. Paulsen AH, Lundar T, Lindegaard KF. Pediatric hydrocephalus: 40-year outcomes in 128 hydrocephalic patients treated with shunts during childhood. Assessment of surgical outcome, work participation, and health-related quality of life. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015. 16: 633-41
13. Symss NP, Oi S. Is there an ideal shunt? A panoramic view of 110 years in CSF diversions and shunt systems used for the treatment of hydrocephalus: From historical events to current trends. Childs Nerv Syst. 2015. 31: 191-202