- Department of Neurosurgery, Umberto I General Hospital, Marche Polytechnic University, Ancona, Italy.
- Department of Emergency Surgery, Umberto I General Hospital, Marche Polytechnic University, Ancona, Italy.
Correspondence Address:
Davide Nasi
Department of Neurosurgery, Umberto I General Hospital, Marche Polytechnic University, Ancona, Italy.
DOI:10.25259/SNI_485_2019
Copyright: © 2019 Surgical Neurology International This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-Share Alike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.How to cite this article: Davide Nasi, Paolo Ruscelli, Maurizio Gladi, Fabrizio Mancini, Maurizio Iacoangeli, Mauro Dobran. Ultra-early surgery in complete cervical spinal cord injury improves neurological recovery: A single-center retrospective study. 18-Oct-2019;10:207
How to cite this URL: Davide Nasi, Paolo Ruscelli, Maurizio Gladi, Fabrizio Mancini, Maurizio Iacoangeli, Mauro Dobran. Ultra-early surgery in complete cervical spinal cord injury improves neurological recovery: A single-center retrospective study. 18-Oct-2019;10:207. Available from: http://surgicalneurologyint.com/surgicalint-articles/9715/
Abstract
Background: This study evaluated how the neurological outcome in patients operated on cervical spinal cord injury (SCI) was positively influenced by ultra-early surgery (UES).
Methods: Between 2010 and 2017, 81 patients with traumatic cervical SCI were assigned to the UES group (
Results: Forty-seven of 81 (58.02%) patients exhibited improved neurological function 12 months postoperatively; better outcomes were observed in the UES (29 of 40 [72.5%]) versus ES groups (18 of 41 [43.9%]) (P = 0,009). For the 26 patients with complete cervical SCI (ASIA A), ultra-early surgical decompression was associated with significantly greater neurological improvement versus ES (61.53% vs. 7.69%; P = 0.003). Further, more neurological improvement correlated with the younger age, better ASIA grade at admission, and ultra-early surgical timing (P = 0.037, P = 0.017, and P = 0.005, respectively), while CCI was correlated with improvement only in the univariate analysis (P = 0.005).
Conclusion: Ultra-early surgical timing in SCI patients appeared to be the most important factor determining the extent of postoperative neurological improvement, particularly regarding motor function recovery.
Keywords: Spinal cord injury, Spine trauma, Surgical decompression, Timing of operation, Traumatic cervical spinal cord injury
INTRODUCTION
Cervical spinal cord injuries represent 20–33% of total spinal injuries, most of which occur at the subaxial levels.[
MATERIALS AND METHODS
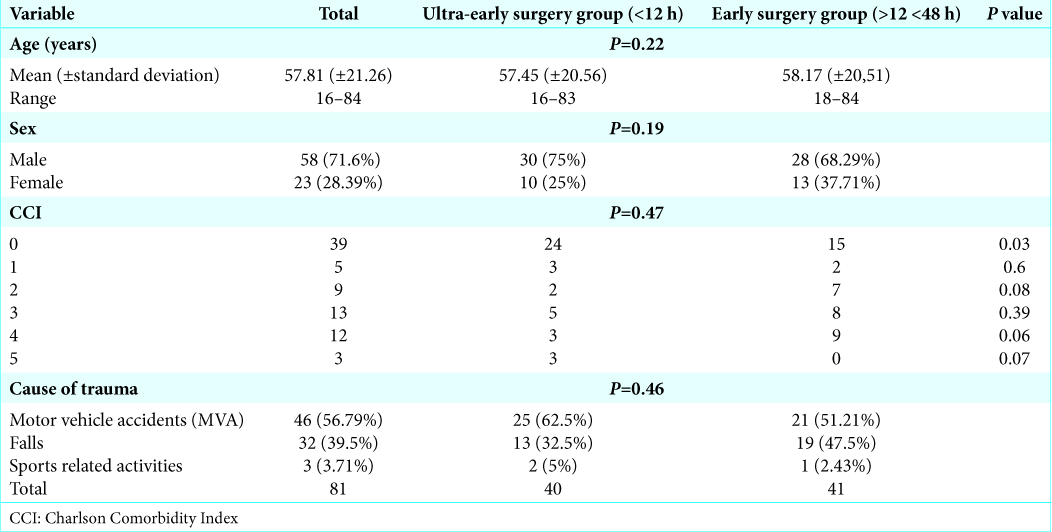
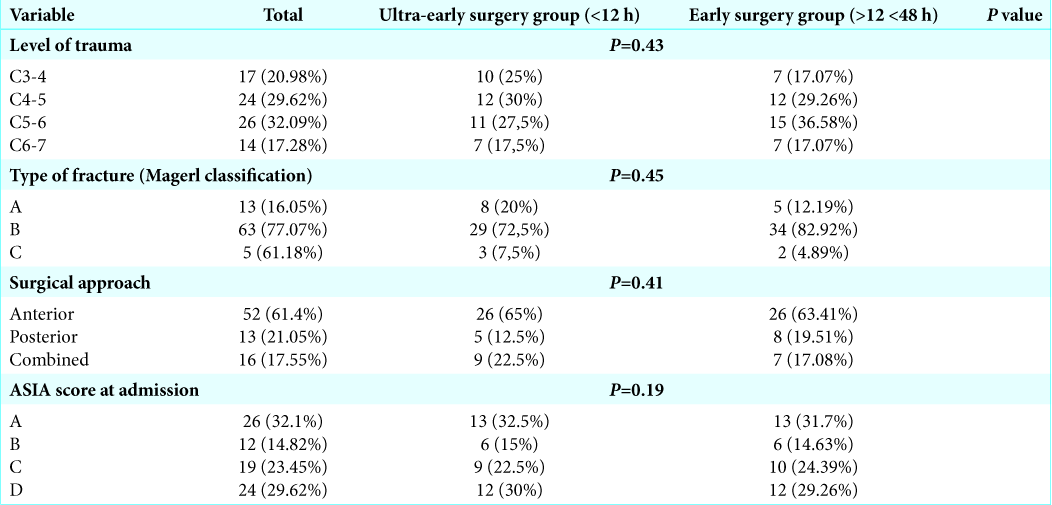
From 2010 to 2017, 81 patients presented with traumatic cervical spinal cord injuries. There were 58 males and 23 females who averaged 57.81 years of age (range 16–84). To determine whether timing of surgery improved postoperative outcomes, 40 patients were assigned to the ultra-ES (UES) group (< 12 h after injury; UES) versus 41 in the ES group (surgery between 12 and 48 h after injury).[
Definition of UES versus ES
“UES” intervention was defined by surgery performed within 6–12 h range,[
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software (version 20; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). The univariate analysis of data was carried out by the Pearson Chi-square test for discrete variables, the t-test for the continuous ones. Logistic regression was used for the multivariate analysis. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. All patients granted their permission for this study before surgery.
RESULTS
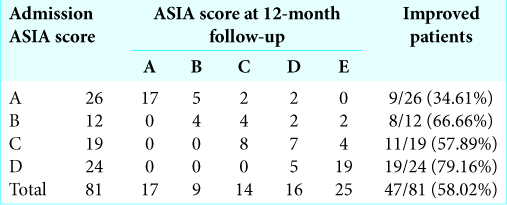
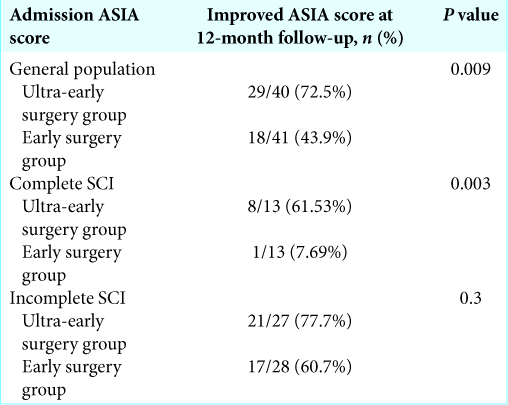
Forty-seven patients of 81 (58.02%) showed improved neurological function 12 months postoperatively [
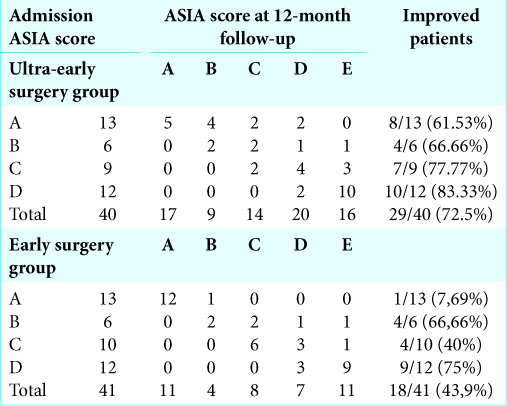
Among the 26 patients with complete cervical SCI (ASIA A), ultra-early surgical decompression was significantly associated with neurological improvement (61.53%) versus ES (7.69 %; P = 0.003).
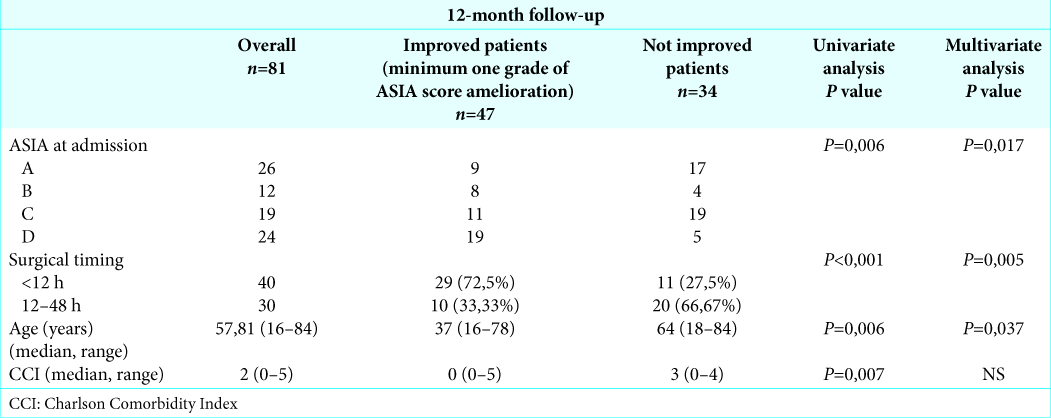
Further, greater neurological improvement was positively correlated with younger age, higher ASIA grade at admission, and ultra-early surgical timing both in the univariate and multivariate analysis (P = 0.037, P = 0.017, and P = 0.005, respectively), except for evaluation of the charlson comorbidity index (CCI) that correlated with improvement only in the univariate analysis (P = 0.005) [
DISCUSSION
In this study, we compared the postoperative results for patients with SCI treated within 12 h (40 patients; UES group; UES) versus between 12 and 48 h (41 patients; ES group 12–48 h; ES).
There is still no clearly accepted definition of early or late surgery for SCI.[
Efficacy of Ultra-early cervical surgery following SCI
Here, we confirmed better neurological improvement for patients having ultra-early (72.5%) versus early 12–48 h (43.9%) surgery.[
Benefits of UES
We and other have observed that patients in the more severe ASIA grades (e.g., Grade A) benefit more from UES (e.g., avoid secondary ischemic injury). In a recent meta- analysis, the rate of ≥ 2 ASIA grade improvement in patients with complete SCI operated within 24 h was 22.6%; this number was similar to those in our series (4/13; 30.76%).[
Better preoperative ASIA grade influenced outcomes for SCI patient
The ASIA grade on admission influenced the postoperative outcome both in the univariate than in the multivariate analysis.[
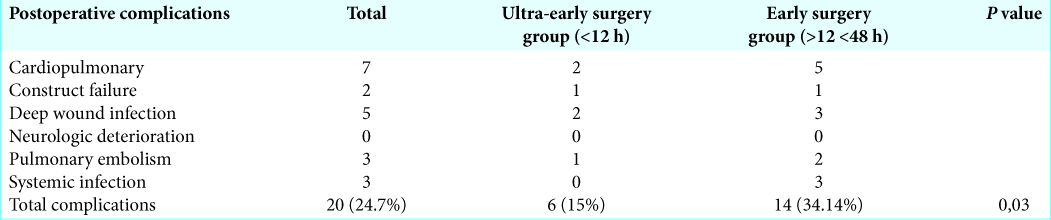
Controversy regarding complication rates for UES versus ES for SCI
In the past, several authors reported that ES was associated with a higher rate of complications (e.g., attributed often to polytrauma). This issue may explain the frequent postoperative surgical site infections in emergency surgery.[
CONCLUSION
Here, for patients with cervical SCI, better outcomes were observed following ultra-early (<12 hours) versus early (12–48 h) cervical decompression/fusion. Better preoperative ASIA grades on admission in younger patients also closely positively correlated with improved outcomes.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Dobran M, Iacoangeli M, Di Somma LG, Di Rienzo A, Colasanti R, Nocchi N. Neurological outcome in a series of 58 patients operated for traumatic thoracolumbar spinal cord injuries. Surg Neurol Int. 2014. 5: S329-32
2. Dobran M, Mancini F, Nasi D, Scerrati M. A case of deep infection after instrumentation in dorsal spinal surgery: The management with antibiotics and negative wound pressure without removal of fixation. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. 2017: 220792-
3. Dobran M, Marini A, Gladi M, Nasi D, Colasanti R, Benigni R. Deep spinal infection in instrumented spinal surgery: Diagnostic factors and therapy. G Chir. 2017. 38: 124-9
4. Dobran M, Marini A, Nasi D, Gladi M, Liverotti V, Costanza MD. Risk factors of surgical site infections in instrumented spine surgery. Surg Neurol Int. 2017. 8: 212-
5. Fehlings MG, Tetreault LA, Wilson JR, Aarabi B, Anderson P, Arnold PM. A clinical practice guideline for the management of patients with acute spinal cord injury and central cord syndrome: Recommendations on the timing (≤24 hours versus >24 hours) of decompressive surgery. Global Spine J. 2017. 7: 195S-202S
6. Fehlings MG, Vaccaro A, Wilson JR, Singh A, W Cadotte D, Harrop JS. Early versus delayed decompression for traumatic cervical spinal cord injury: Results of the surgical timing in acute spinal cord injury study (STASCIS). PLoS One. 2012. 7: e32037-
7. Furlan JC, Noonan V, Cadotte DW, Fehlings MG. Timing of decompressive surgery of spinal cord after traumatic spinal cord injury: An evidence-based examination of pre-clinical and clinical studies. J Neurotrauma. 2011. 28: 1371-99
8. Hachem LD, Ahuja CS, Fehlings MG. Assessment and management of acute spinal cord injury: From point of injury to rehabilitation. J Spinal Cord Med. 2017. 40: 665-75
9. Katoh S, el Masry WS, Jaffray D, McCall IW, Eisenstein SM, Pringle RG. Neurologic outcome in conservatively treated patients with incomplete closed traumatic cervical spinal cord injuries. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996. 21: 2345-51
10. Kim M, Hong SK, Jeon SR, Roh SW, Lee S. Early (≤48 hours) versus late (>48 hours) surgery in spinal cord injury: Treatment outcomes and risk factors for spinal cord injury. World Neurosurg. 2018. 118: e513-25
11. Nasi D, Dobran M, Di Rienzo A, di Somma L, Gladi M, Moriconi E. Decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury: The role of cranioplasty and hydrocephalus on outcome. World Neurosurg. 2018. 116: e543-9
12. Nasi D, Dobran M, Iacoangeli M, Di Somma L, Gladi M, Scerrati M. Paradoxical brain herniation after decompressive craniectomy provoked by drainage of subdural hygroma. World Neurosurg. 2016. 91: 673-4
13. Ter Wengel PV, De Witt Hamer PC, Pauptit JC, van der Gaag NA, Oner FC, Vandertop WP. Early surgical decompression improves neurological outcome after complete traumatic cervical spinal cord injury: A meta-analysis. J Neurotrauma. 2019. 36: 835-44
14. Ter Wengel PV, Feller RE, Stadhouder A, Verbaan D, Oner FC, Goslings JC. Timing of surgery in traumatic spinal cord injury: A national, multidisciplinary survey. Eur Spine J. 2018. 27: 1831-8
15. Wyndaele M, Wyndaele JJ. Incidence, prevalence and epidemiology of spinal cord injury: What learns a worldwide literature survey?. Spinal Cord. 2006. 44: 523-9