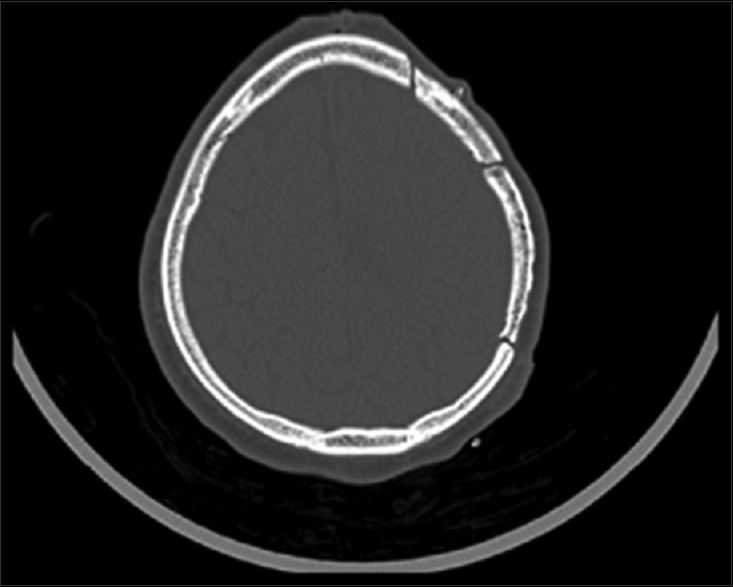
Cranial autologous bone flap resorption after a cranioplasty: A case report
Date of publication: 19-Mar-2018
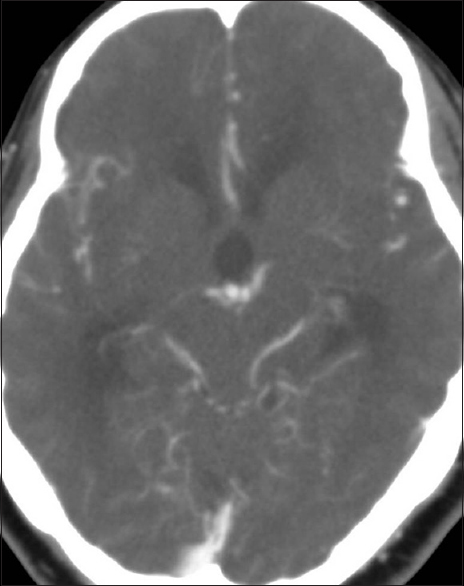
Background:Craniectomies and cranioplasty are common neurosurgical procedures performed after brain trauma, ischemia, tumor resection, or infection. Post-cranioplasty autologous bone flap resorption may occur in patients after delayed cranial reconstruction. The occurrence is usually low when bone flaps are stored in subcutaneous abdominal tissue. We report a unique case of post-cranioplasty cranial bone flap.
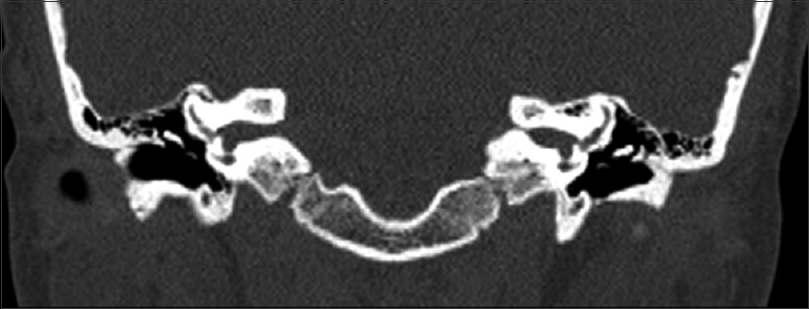
Internal auditory canal exostosis: A technical case report
Date of publication: 19-Mar-2018
Background:Exostoses of the internal auditory canal is a rare finding that may present with disabling symptoms of dizziness, hearing loss, and vestibular dysfunction based on the extent of cranial nerve compression. The purpose of this case report is to discuss the presentation and outcomes in a patient who presented with this disorder.
Lower complication and reoperation rates for laminectomy rather than MI TLIF/other fusions for degenerative lumbar disease/spondylolisthesis: A review
Date of publication: 07-Mar-2018
Background:Utilizing the spine literature, we compared the complication and reoperation rates for laminectomy alone vs. instrumented fusions including minimally invasive (MI) transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) for the surgical management of multilevel degenerative lumbar disease with/without degenerative spondylolisthesis (DS).
Spinal case of the month with short perspective: How would you treat this L3-L4 synovial cyst?
Date of publication: 07-Mar-2018
Background:In this new section, Case of the Month with Short Perspective from Surgical Neurology International, we want to see how various spine surgeons would approach different spinal pathologies. In this first case, an elderly male presented with 3 years of lower back pain and progressive neurogenic claudication with bilateral radiculopathy that had exacerbated over the prior 6 months. An outside physician performed a magnetic resonance (MR) study of the lumbar spine that showed a massive synovial cyst filling the spinal canal (e.g., large bilateral cysts) at the L3-L4 level with grade I spondylolisthesis. The MR and CT studies also both demonstrated moderate L2-L3, and severe L3-L4 stenosis.
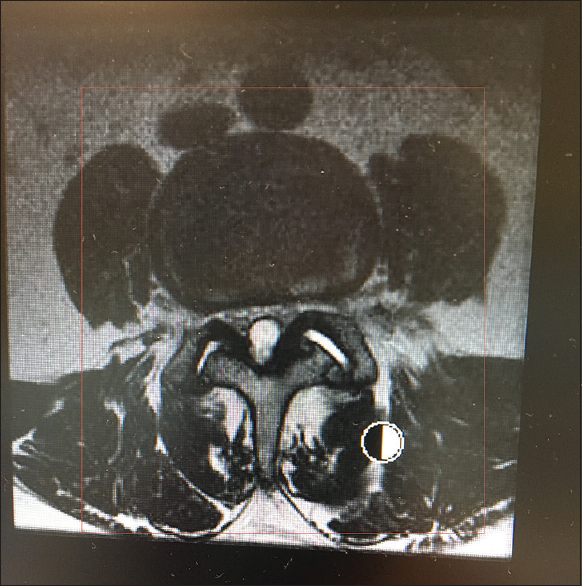
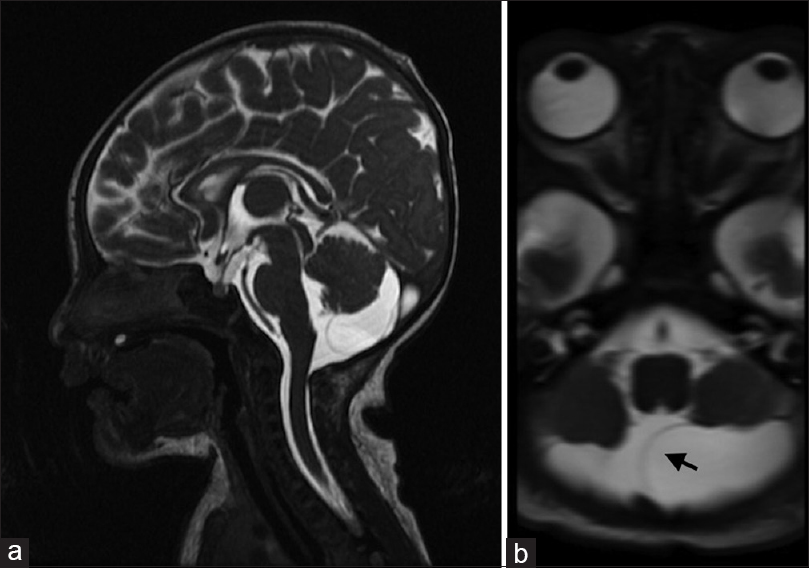
Rare case of a rapidly enlarging symptomatic arachnoid cyst of the posterior fossa in an infant: A case report and review of the literature
Date of publication: 07-Mar-2018
Background:Intracranial arachnoid cysts are space-occupying lesions that typically remain stable or decrease in size over time. Cysts in infants younger than 1 year of age are remarkably different from those in older children and adults in terms of cyst localization and enlargement. Arachnoid cysts of the posterior fossa (PFACs) are very rare in infants and do not typically grow or present with clinical symptoms, such that surgical treatment is generally considered to be unnecessary. Here, we describe an extremely rare case of an infant with a rapidly enlarging symptomatic PFAC that was successfully treated with surgery.
Obstructive hydrocephalus and facial nerve palsy secondary to vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia: Case Report
Date of publication: 07-Mar-2018
Background:Symptomatic hydrocephalus due to vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia is a rare occurrence.
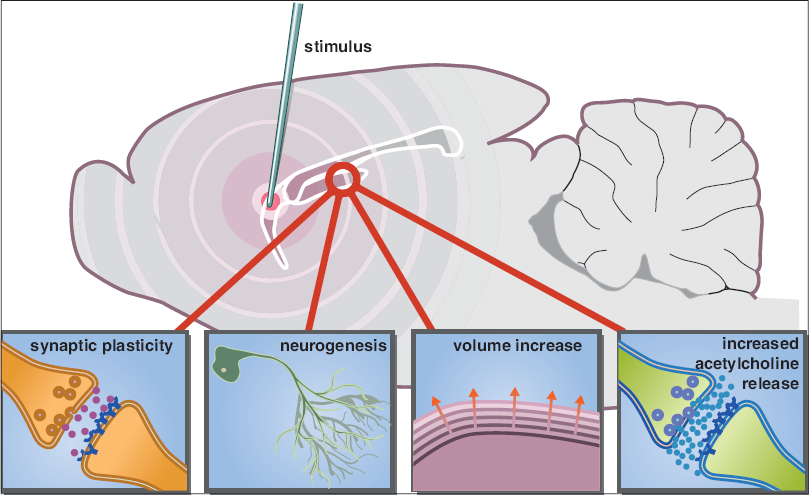
Deep brain stimulation for Alzheimer's Disease: An update
Date of publication: 07-Mar-2018
Background:Dementia is among the leading causes of severe and long-term disability worldwide, decreasing the quality of life of individuals and families. Moreover, it induces an enormous economic burden on societies. The most prevalent cause of dementia is Alzheimer's disease (AD). Because current treatment options for AD are limited, deep brain stimulation (DBS) has been considered.
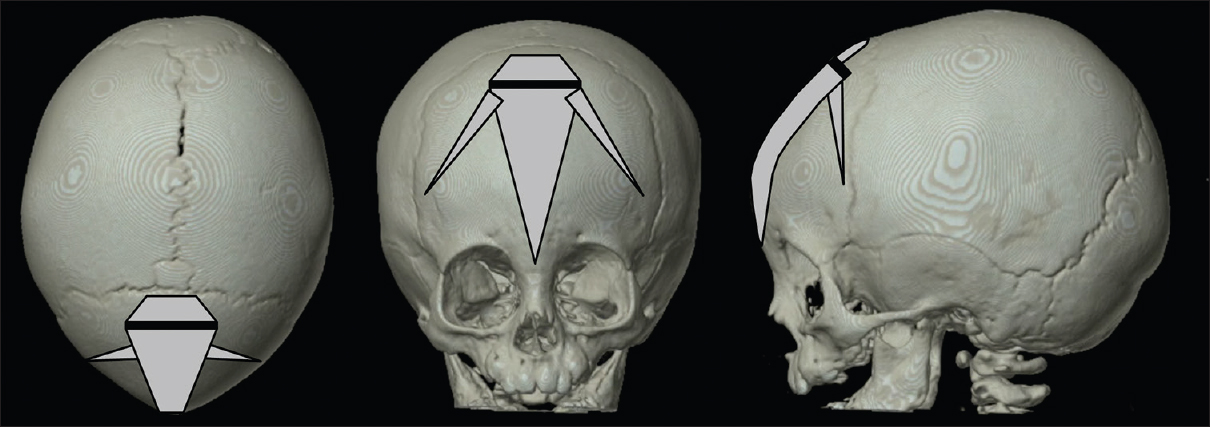
Endoscopy-assisted craniosynostosis surgery followed by helmet therapy
Date of publication: 07-Mar-2018
Background:Surgical methods to treat craniosynostosis have evolved from a simple strip craniectomy to a diverse spectrum of partial or complete cranial vault remodeling with excellent results but often with high comorbidity. Therefore, minimal invasive craniosynostosis surgery has been explored in the last few decades. The main goal of minimal invasive craniosynostosis surgery is to reduce the morbidity and invasiveness of classical surgical procedures, with equal long-term results, both functional as well as cosmetic.
Rhabdomyolysis following minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: Case report
Date of publication: 01-Mar-2018
Background:Rhabdomyolysis results from the release of large quantities of muscle cell contents into plasma resulting in a classic triad of symptoms – muscle pain, weakness, and brown urine. Only a handful of rhabdomyolysis cases occurring after spinal surgery have been reported.
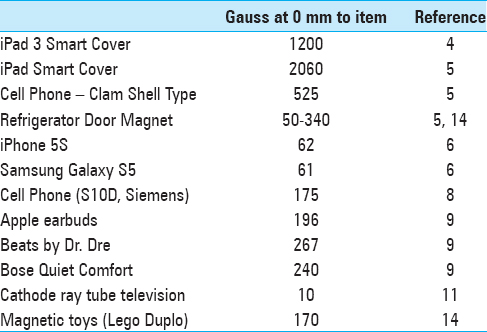
Maladjustment of programmable ventricular shunt valves by inadvertent exposure to a common hospital device
Date of publication: 01-Mar-2018
Background:Programmable ventricular shunt valves are commonly used to treat hydrocephalus. They can be adjusted to allow for varying amounts of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow using an external magnetic programming device, and are susceptible to maladjustment from inadvertent exposure to magnetic fields.