Internal jugular phlebectasia: A systematic review
Date of publication: 19-Jun-2019
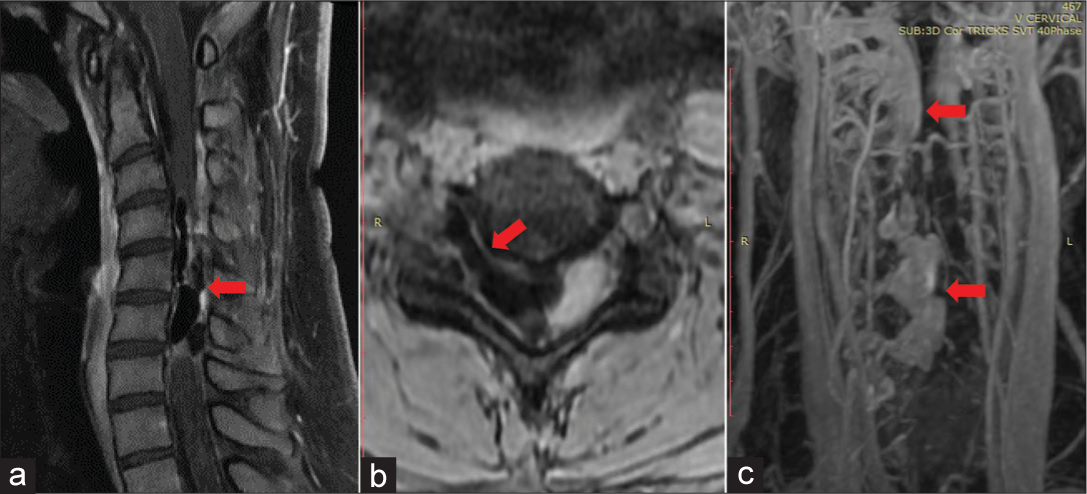
Background: Internal jugular phlebectasia (IJP), the abnormal dilatation of internal jugular vein, is generally considered a benign anomaly. However, because IJP is uncommon, little is known about its natural history, and currently, no consensus on the best treatment modality is available.
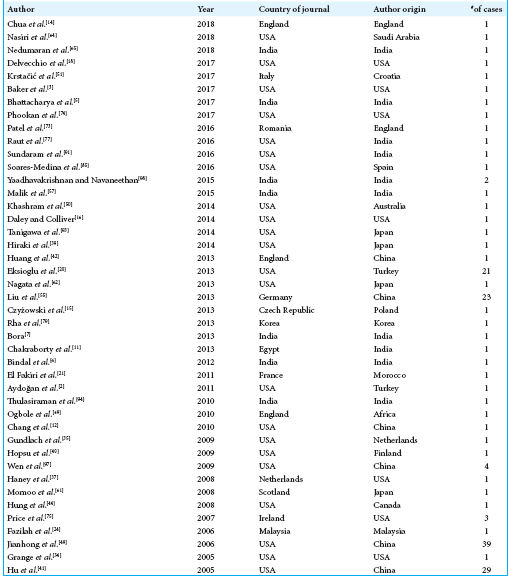
Stent-assisted coil embolization of unruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms with the low-profile visualized intraluminal support stent, with five techniques: Technical note and case report
Date of publication: 19-Jun-2019
Background: Intracranial vertebral artery dissecting aneurysm (VADA) is rare and shows high morbidity and mortality rates when the aneurysm ruptures. Endovascular treatment for VADA is one of the optimal treatments, but the dominant side VA and its branches or perforators need to be preserved. We report a novel and successful stent-assisted coil embolization technique using the low-profile visualized intraluminal support (LVIS) stent, with five technical notes in three consecutive cases of unruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysm (VADA).
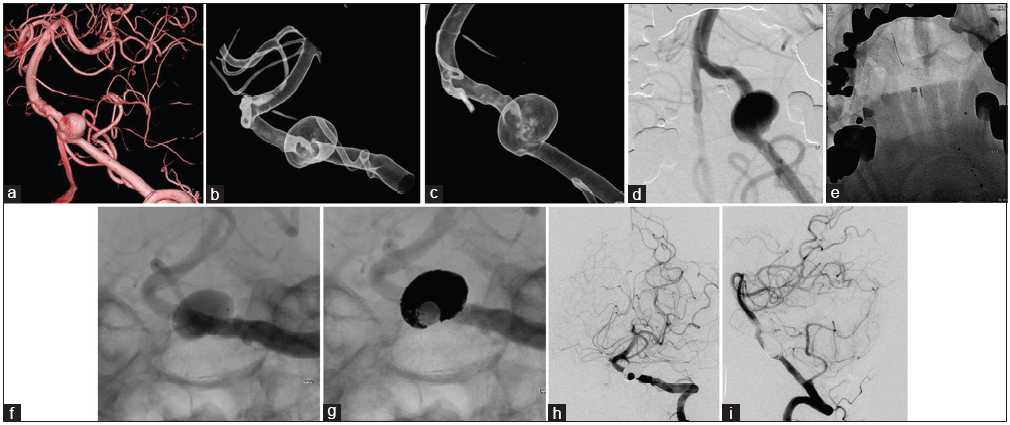
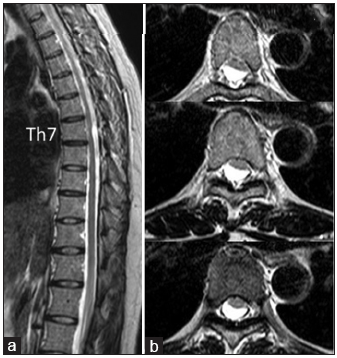
Bone cylinder plug and coil technique for accurate pedicle localization in thoracic spine surgery: A technical note
Date of publication: 19-Jun-2019
Background: Intraoperative identification of the correct level during thoracic spine surgery is essential to avoid wrong-level procedures. Despite technological progress, intraoperative imaging modalities for identifying the correct thoracic spine level remain unreliable and often lead to wrong-level surgery. To counter potential wrong-level operations, here, we have proposed a novel pedicle/bone cylinder marking technique for use in the thoracic spine utilizing biplanar fluoroscopy and confirmed with computed tomography (CT).
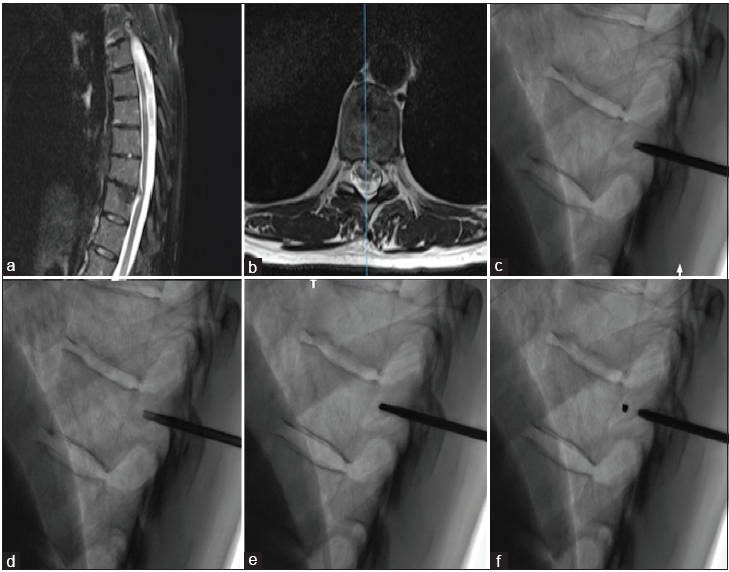
The microsurgical management of benign pineal cysts: Helsinki experience in 60 cases
Date of publication: 19-Jun-2019
Background: Microsurgical resection represents a well-accepted management option for symptomatic benign pineal cysts. Symptoms such as a headache, hydrocephalus, and visual deficiency are typically associated with pineal cysts. However, more recent studies reported over the past years have characterized additional symptoms as a part of the clinical manifestation of this disease and represent additional indications for intervention.
Intradural spinal arachnoid cyst contributing to sudden paraparesis
Date of publication: 19-Jun-2019
Background: Spinal arachnoid cysts are cystic lesions filled with cerebrospinal fluid that contributes to neurological deficits depending on their size/location within the spinal canal. Here, we report a patient with a spinal subarachnoid cyst who suddenly developed paraparesis.
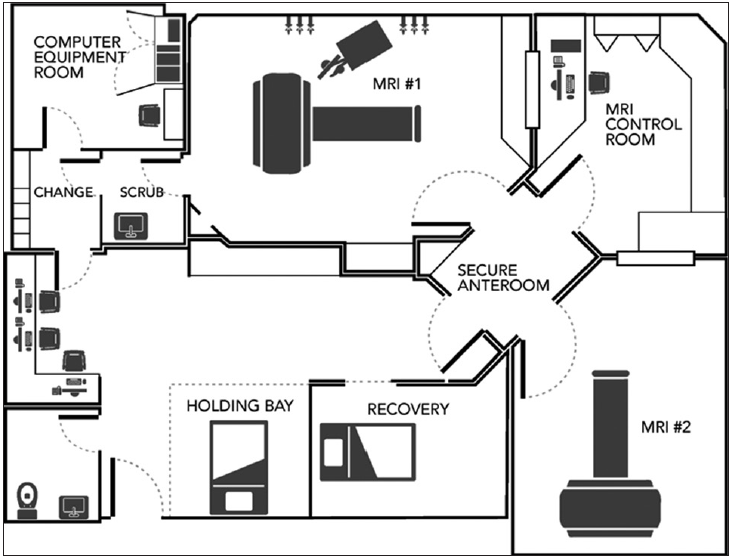
The interventional magnetic resonance imaging suite: Experience in the design, development, and implementation in a pre-existing radiology space and review of concepts
Date of publication: 19-Jun-2019
Background: Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (ioMRI) has led to significant advancements in neurosurgery with improved accuracy, assessment of the extent of resection, less invasive surgical alternatives, and real-time confirmation of targeting as well delivery of therapies. The costs associated with developing ioMRI units in the surgical suite have been obstacles to the expansion of their use. More recently, the development of hybrid interventional MRI (iMRI) units has become a viable alternative. The process of designing, developing, and implementing operations for these units requires the careful integration of environmental, technical, and safety elements of both surgical and MR practices. There is a paucity of published literature providing guidance for institutions looking to develop a hybrid iMRI unit, especially with a limited footprint in the radiology department.
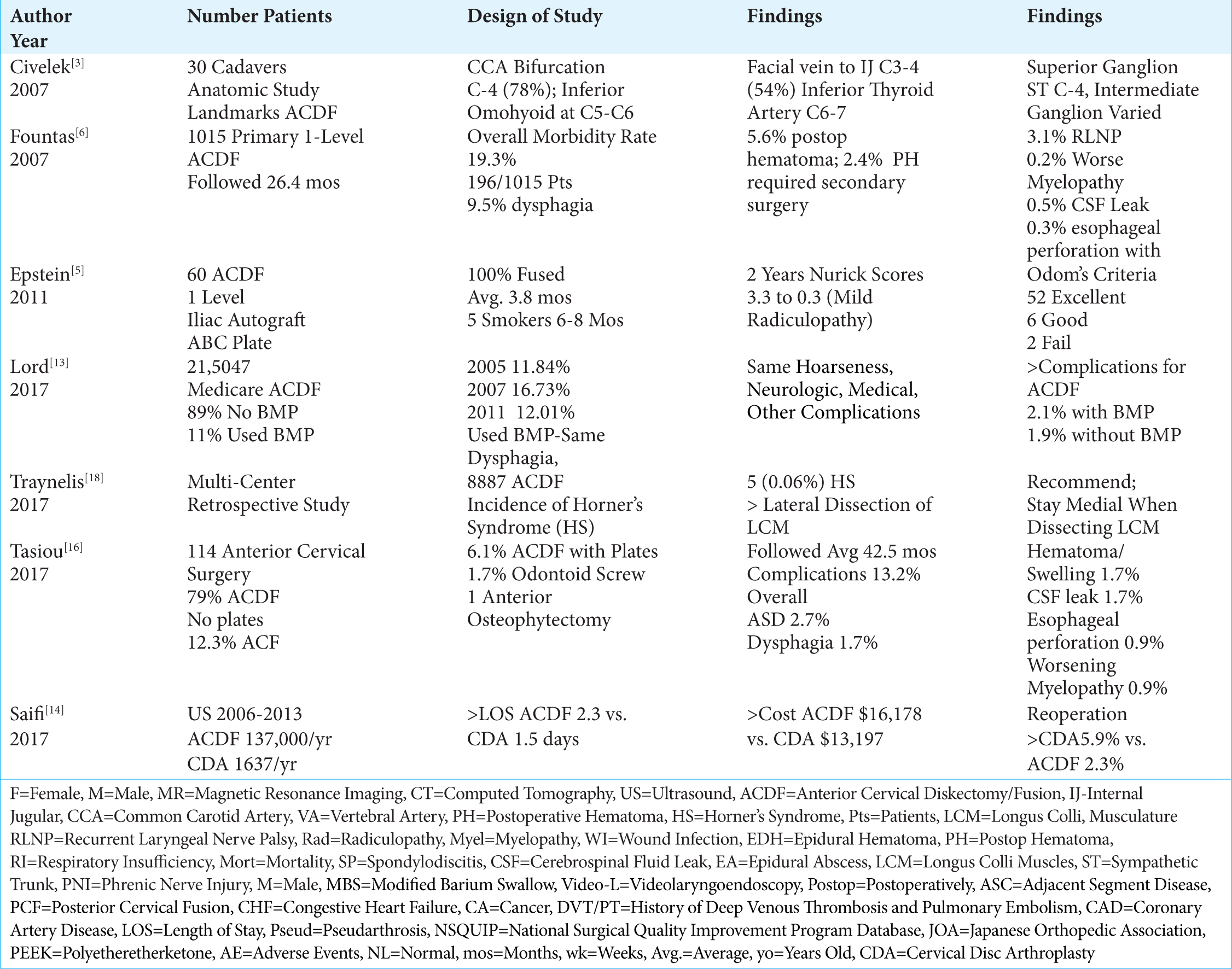
A Review of Complication Rates for Anterior Cervical Diskectomy and Fusion (ACDF)
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2019
Background:There are multiple complications reported for anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion (ACDF), one of the most common cervical spine operations performed in the US (e.g. estimated at 137,000 ACDF/year).
A case involving a giant aberrant craniocervical arteriovenous malformation
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2019
Background:Spinal cord arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) comprise about 3%–4% of primary intraspinal masses and are only rarely found external to the C2–C7 cervical vertebral foramen.
Endoscopic resection of the third ventricular epidermoid cysts: A case review and review of literature
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2019
Background:Epidermoid cysts are benign, congenital lesions that originate from ectodermal cells, they are most commonly found in the cerebellopontine angle, but rarely in the ventricular system. There is limited literature regarding the different microsurgical techniques utilized to approach these lesions.
A noninvasive method for the estimation of increased intracranial pressure in patients with severe traumatic brain injury using optic nerve sheath diameter measured on computed tomography head
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2019
Background:Measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) using ocular ultrasonography has shown a promise in predicting increased intracranial pressure (ICP). However, this method is dependent on operator technique and equipment availability. We propose an alternative method of measuring ONSD and Marshall score grading by utilizing initial computed tomography (CT) head obtained on admission. We believe that such a technique could help predict patients requiring an invasive ICP monitor on admission.