Female insertion in neurosurgery: Evolution of a stigma break
Date of publication: 02-Mar-2021
Background: Utilizing the Brazilian Medical Demography analysis and a literature review, we evaluated how women choose to become neurosurgeons in Brazil and around the world, specifically citing the Europe, the USA, India, and Japan.
Alwitri: The father of modern neurosurgery in Iraq
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2021
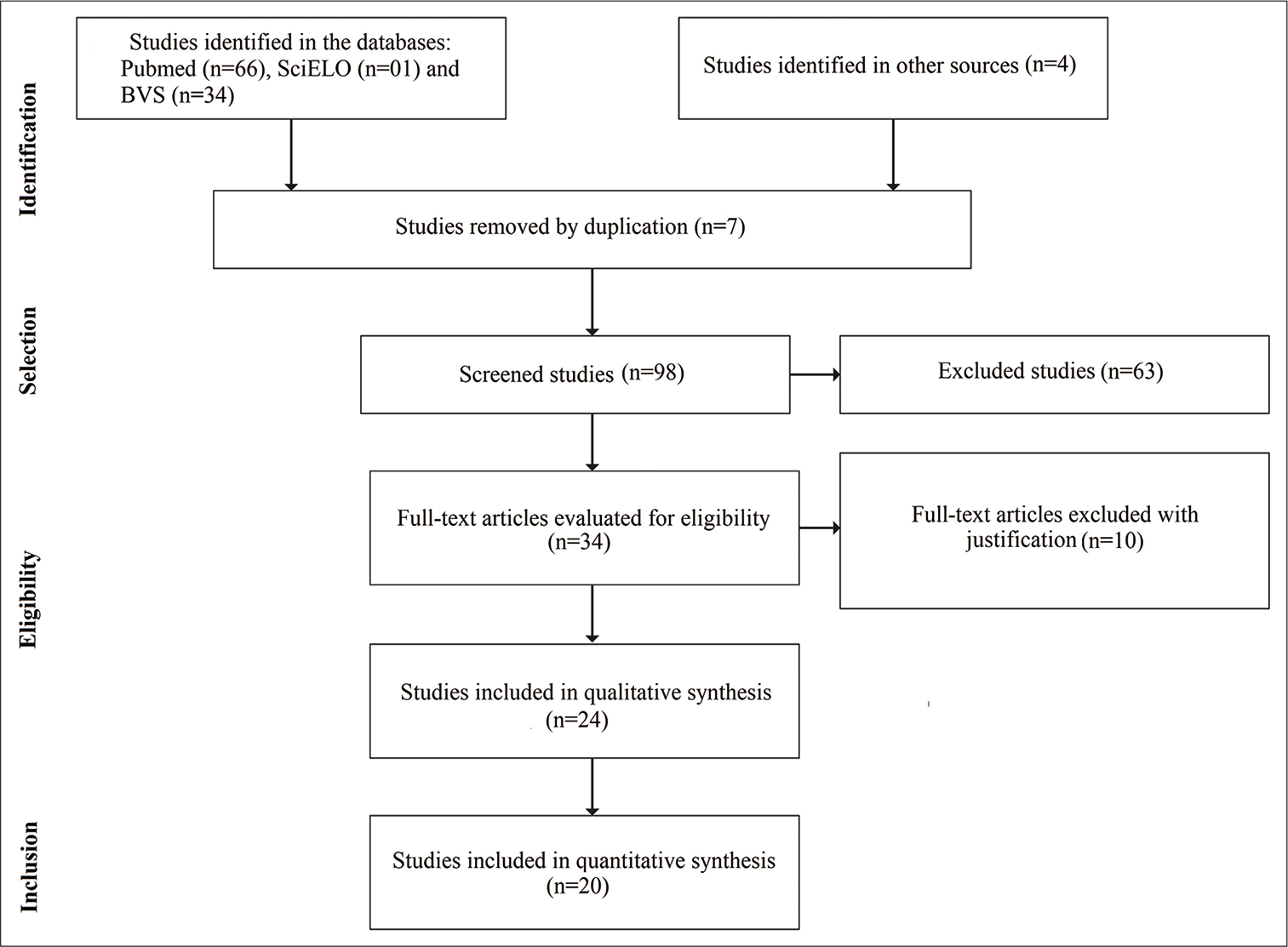
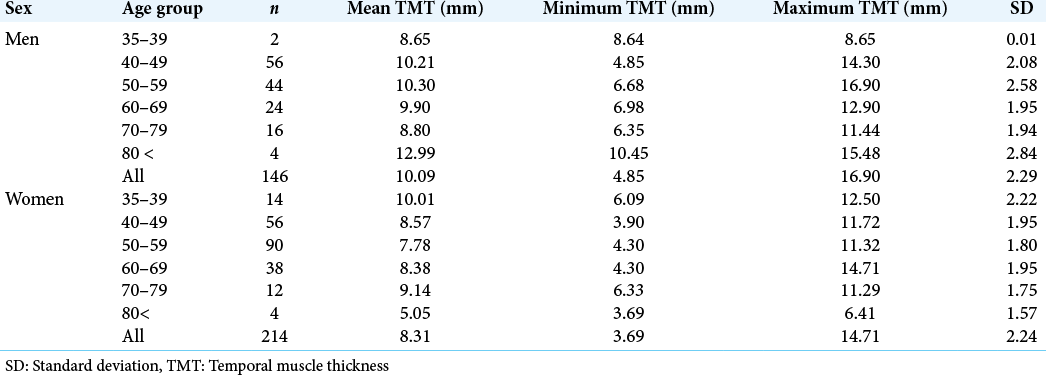
Standard values for temporal muscle thickness in the Japanese population who undergo brain check-up by magnetic resonance imaging
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2021
Background: Skeletal muscle mass is an important factor for various diseases’ outcomes. The psoas muscle cross-sectional area on the abdominal computed tomography (CT), gait speed, and handgrip strength is used to measure it. However, it is difficult to measure the neurological patients’ muscle mass or function because (1) we do not perform abdominal CT. (2) Such patients have impaired consciousness, gait disturbance, paresis, and need of rest. Temporal muscle thickness (TMT) on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is now attractive for skeletal muscle volume indicator, but the reference values are not established. We herein investigated the standard value of the Japanese TMT using the brain check-up database by MRI.
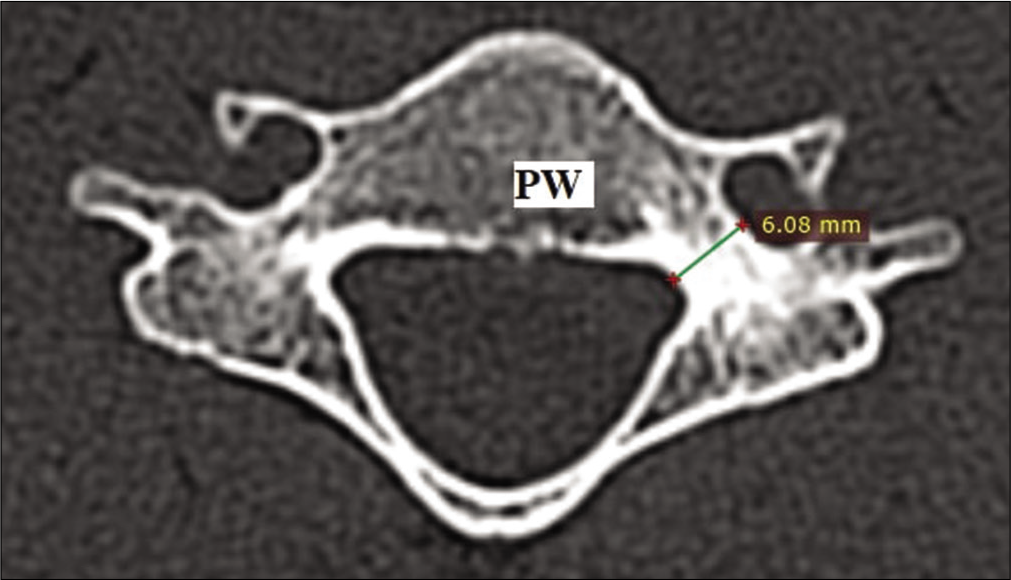
Computed tomographic analysis of cervical spine pedicles in the adult Indian population
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2021
Background: Cervical pedicle screw insertion is a technically demanding procedure that carries the risk of catastrophic damage to surrounding neurovascular structures. Here, we analyzed computed tomography (CT)-based three-dimensional cervical spine pedicle geometry to determine the level and sex-specific morphologic differences in the adult Indian population.
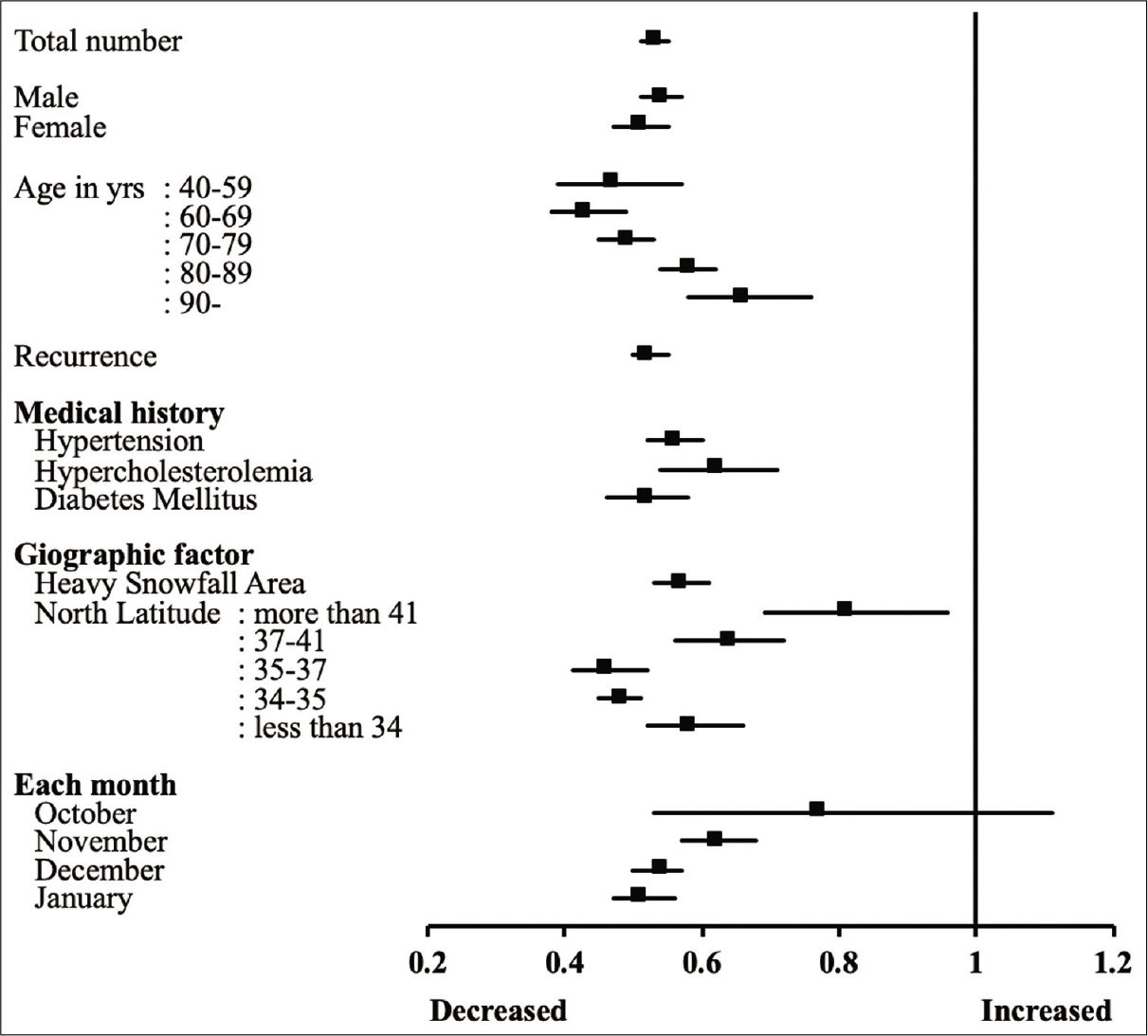
Snowfall reduces the risk of chronic subdural hematoma onset: Analysis of an administrative database in Japan
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2021
Background: Chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH) is a frequently observed disease in neurosurgical practice. Although first snowfall has been considered to increase the onset of CSDH, few reports have assessed the relationship between snowfall and CSDH. In this study, we aimed to investigate the relationship between CSDH onset and first snowfall events.
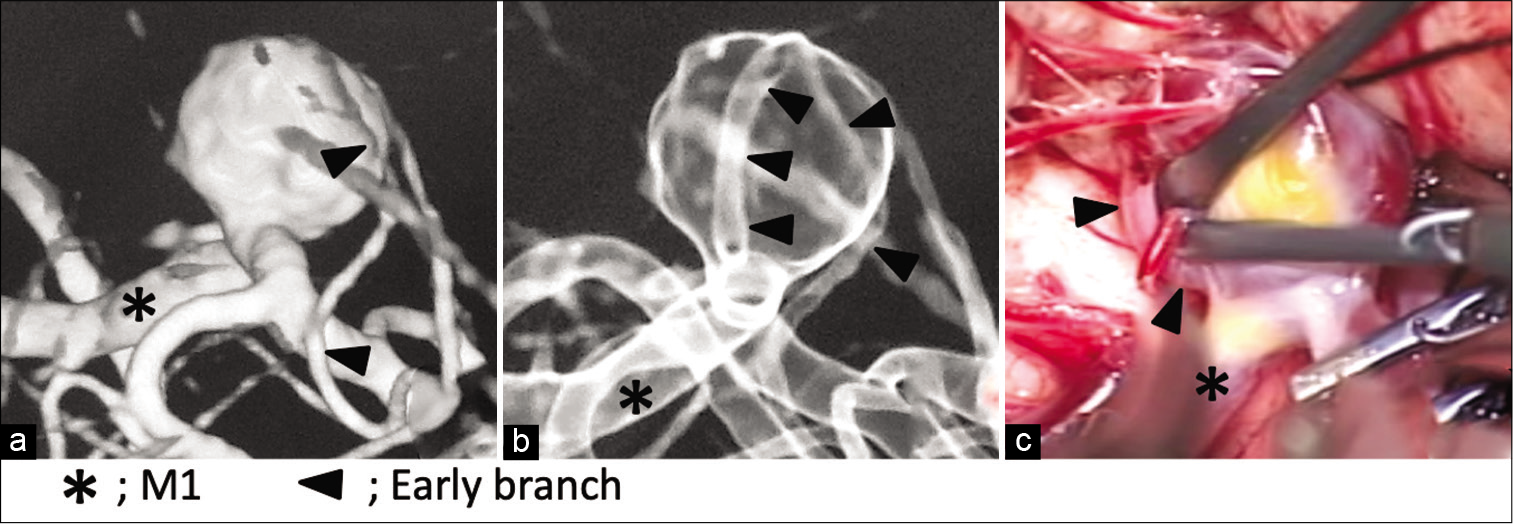
Preoperative simulation of a middle cerebral artery aneurysm clipping using a rotational three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2021
Background: In recent years, young neurosurgeons have had few opportunities to gain experience with clipping surgeries. The first author was sometimes surprised that she could not predict the anatomical relationships between the aneurysm and vessels during actual surgery. This study investigated the differences between the expected and actual operative findings during clipping surgery for aneurysms of the middle cerebral artery.
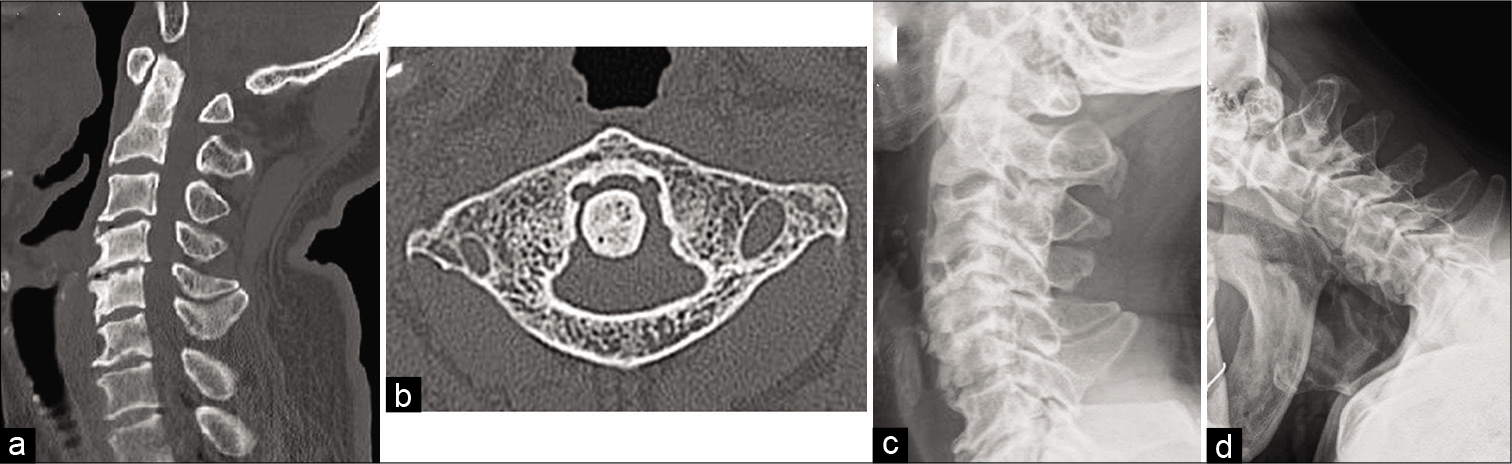
A surgical case of C1 arch stenosis: A case report and review of literature
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2021
Background: Isolated symptomatic cervical stenosis of the atlas is quite rare; there have been 11 cases reported in literature.
A titanium implant for Chiari malformation Type 1 surgery
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2021
Background: Concepts of Chiari malformation Type 1 (CM1) surgery in the present time significantly different. The most common complications are pseudomeningocele (12%) and postoperative CSF leak (5%). The development of pseudomeningocele may be associated with inappropriate restoration of bone and muscles relations.
Seizure outcome in moyamoya after indirect revascularization in pediatric patients: Retrospective study and literature review
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2021
Background: Moyamoya disease (MMD) is a unique cerebrovascular disorder characterized by progressive stenosis of anterior cerebral circulation. Moyamoya is not an uncommon disease in Saudi Arabia. Although a less common symptom of the disease, the incidence of seizure in MMD ranges from 6 to 30%. Indirect revascularization through Encephaloduroarteriosynangiosis technique is one of the surgical treatment options for MMD. In our cohort, we aim to evaluate seizure outcome in pediatric patients with moyamoya.
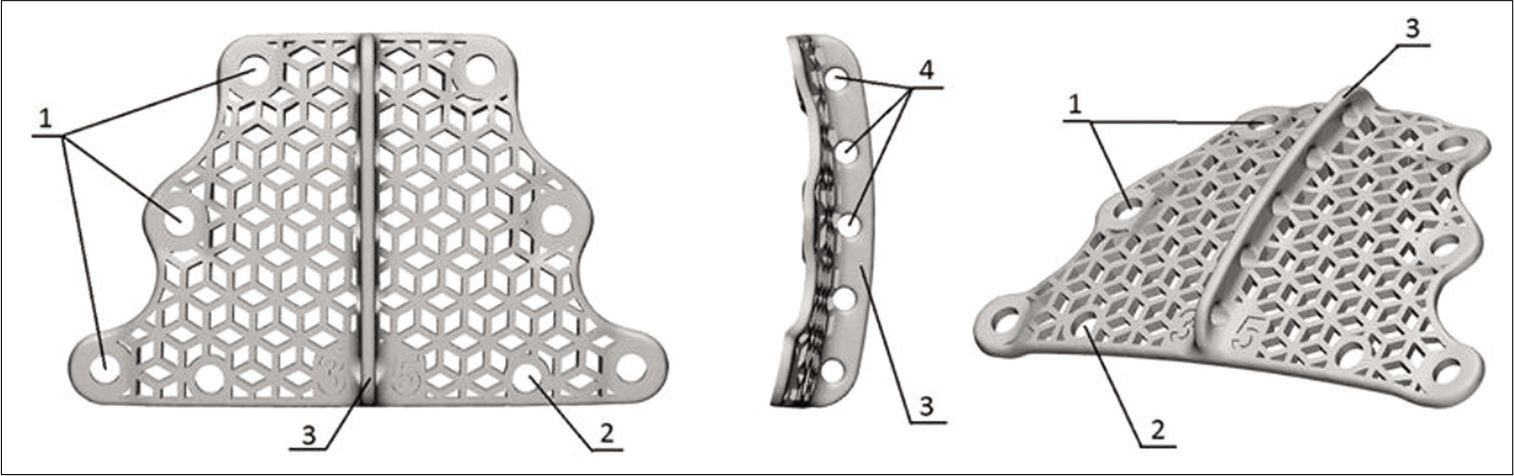
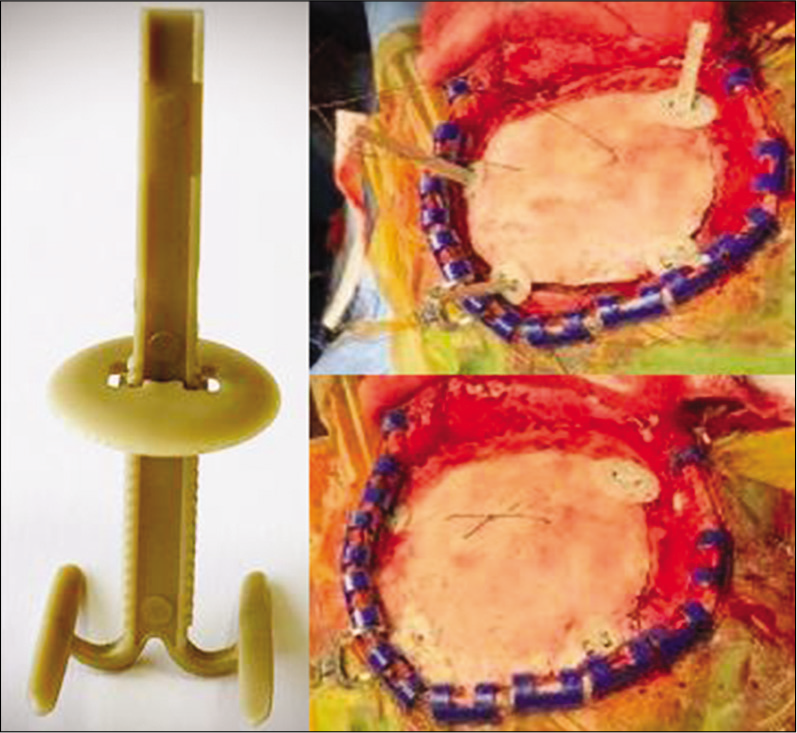
A new device for bone cranial flap fixation: Technical note and surgical remarks. A multicentric experience
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2021
Background: Fixation of bone flaps after craniotomy is a routine part of every neurosurgical procedure. The ideal fixation device should be safe, reliable, biologically inert, easy to use, and inexpensive and should not produce artifacts on neuroimaging. The authors describe a new device that meets these criteria.