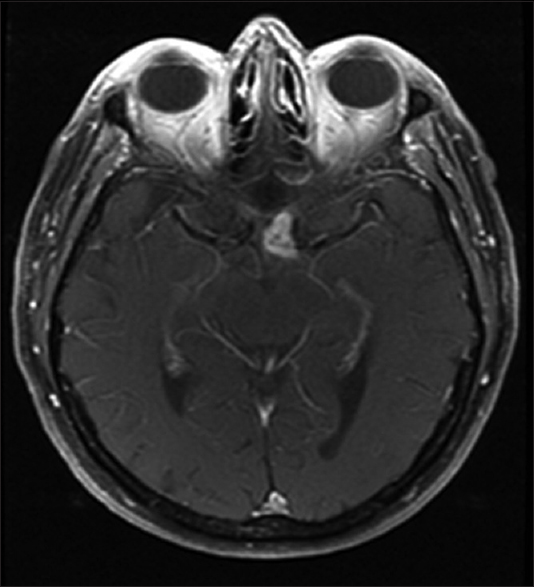
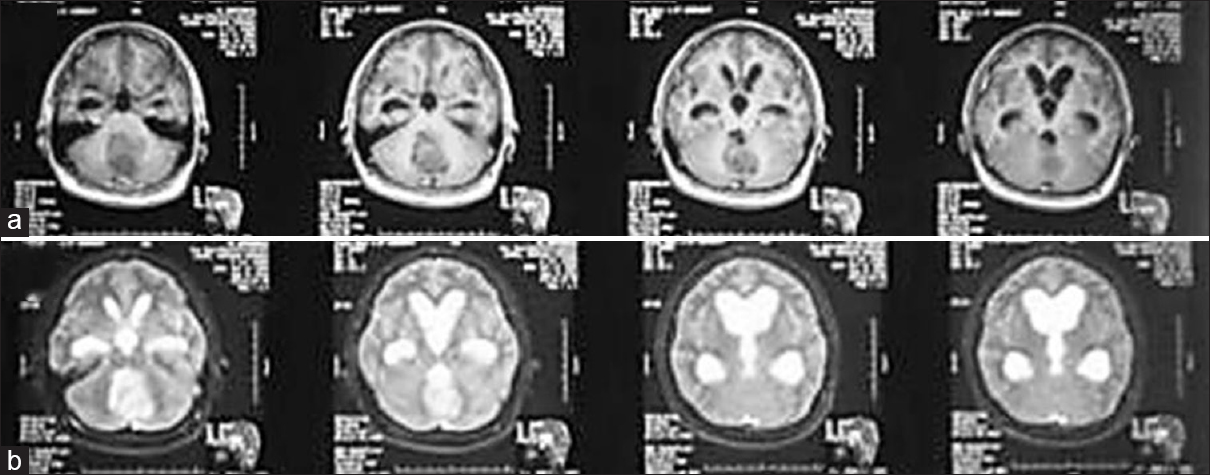
Glioblastoma multiforme of the optic chiasm: A rare case of common pathology
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:Malignant optic and chiasmatic gliomas are extremely rare, and are classified pathologically as anaplastic astrocytoma or glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). Approximately 40 cases of optic GBM in adults have been reported in the literature, and only five of them were described to originate from the optic chiasm.
Adult medulloblastoma: A rare case report and literature review
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
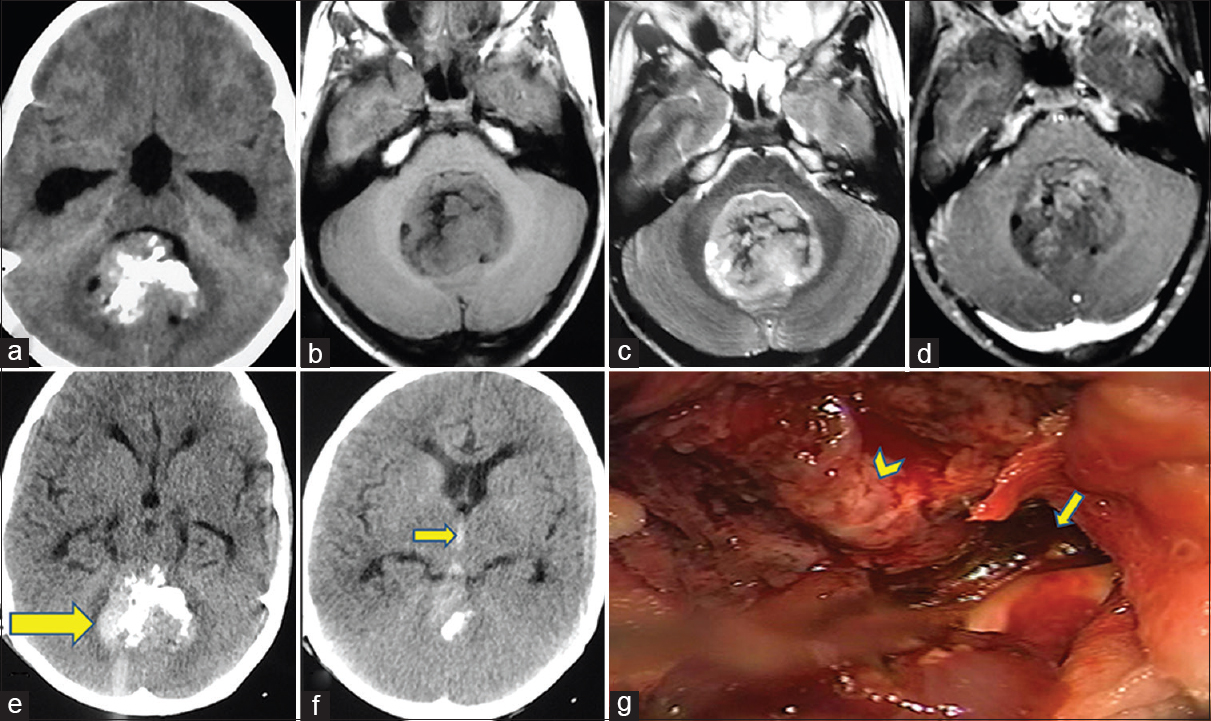
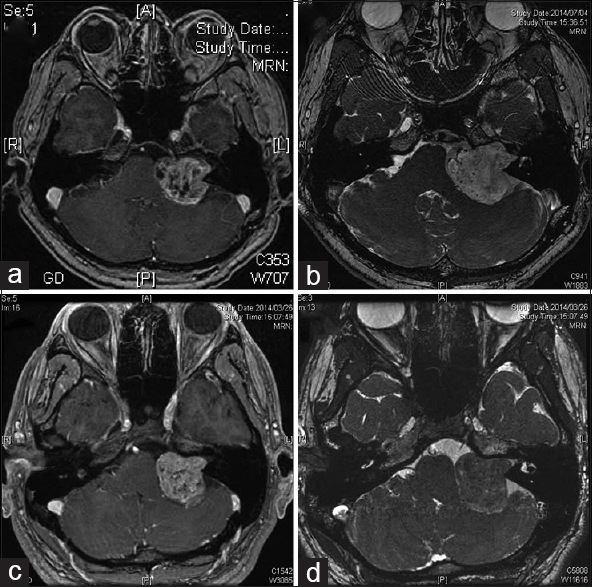
Background:Medulloblastoma is a highly malignant embryonal tumor which commonly arises in the cerebellum. It is relatively rare and accounts for less than 2% of all primary brain tumors. The tumor primarily occurs in childhood; however, rarely, it may be found in adult population. In addition, medulloblastoma in adult population shows features which are quite distinct from the pediatric group.
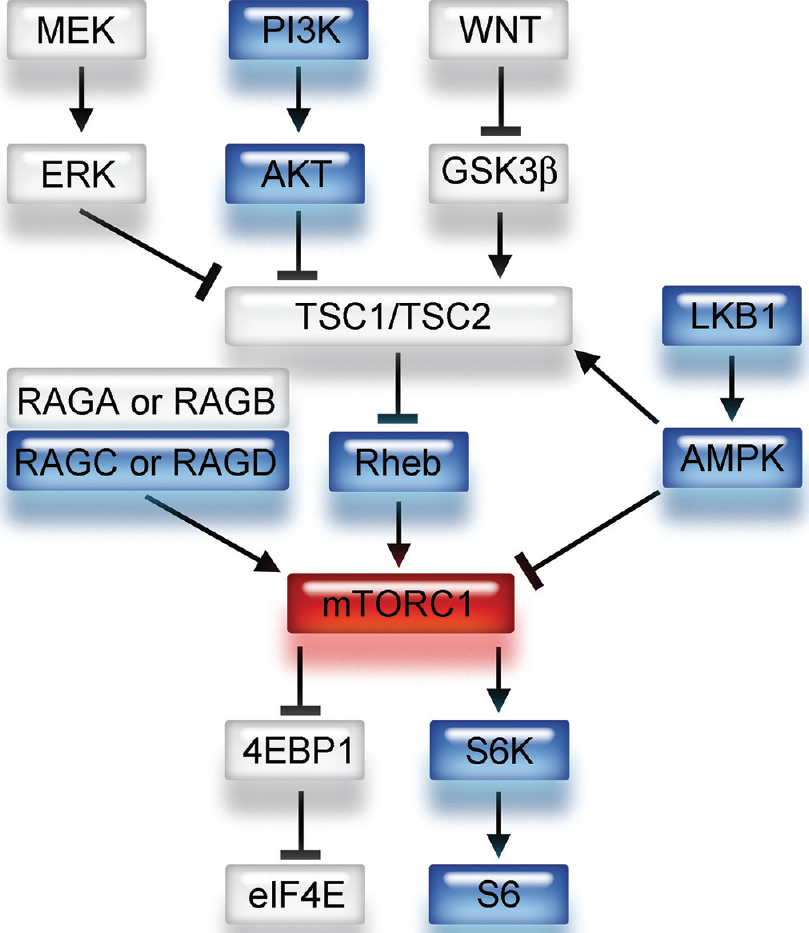
mTORC1 signaling in primary central nervous system lymphoma
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 1 (mTORC1) acts as a downstream effector of phosphatidyl-inositol-3 kinase, which is frequently hyperactivated in glioblastoma multiforme and links to cell signaling in cellular proliferation, differentiation, metabolism, and survival. Although many studies have suggested the importance of mTORC1 in tumorigenesis, its role remains unclear in brain tumors other than glioblastoma.
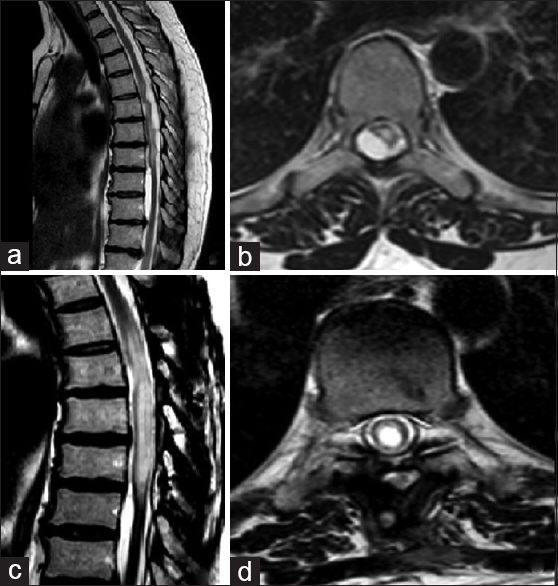
Intramedullary cyst formation after removal of multiple intradural spinal arachnoid cysts: A case report
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:A rare cause of spinal cord compression is spinal arachnoid cysts. Symptoms are caused by spinal cord compression, however, asymptomatic patients have been also reported. Treatment options depend upon symptom severity and clinical course.
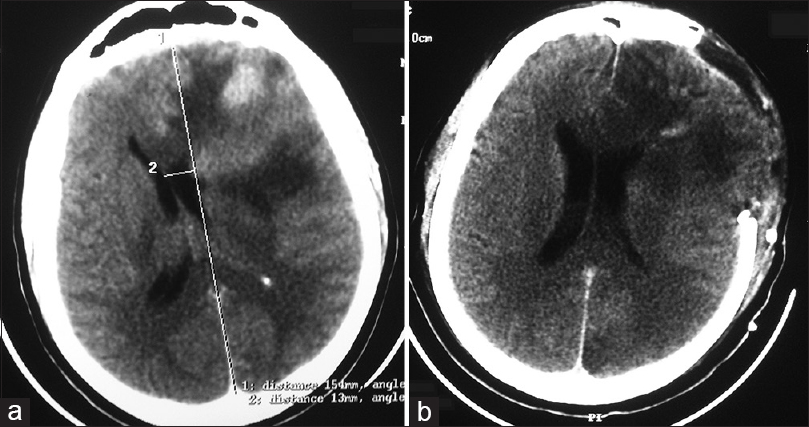
Diagnosing early upward cerebellar herniation by computed tomography: A diagnostic boom, a savior
Date of publication: 29-Jun-2016
The outermost “dura-like membrane” of vestibular schwannoma
Date of publication: 29-Jun-2016
Background:The membranous structure of vestibular schwannoma is an important factor in its surgical treatment. Herein, we report intraoperative and microscopic findings relating to an outermost dura-like membrane in cases of vestibular schwannoma and the importance of these findings.
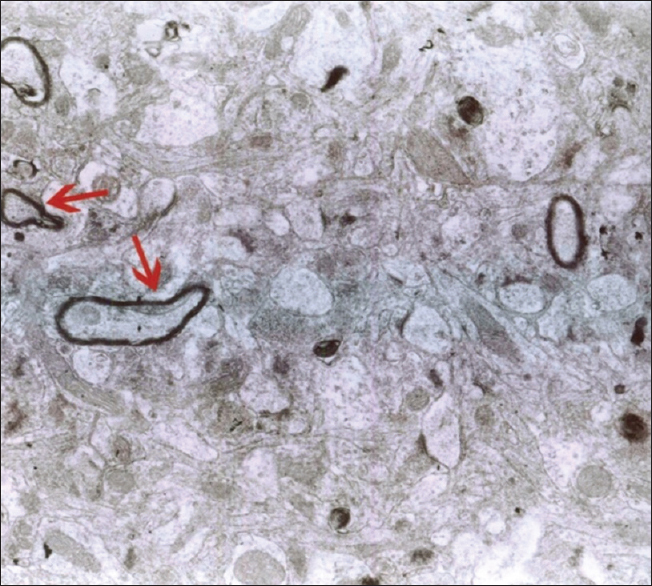
The effects of 30 mT electromagnetic fields on hippocampus cells of rats
Date of publication: 29-Jun-2016
Background:Despite the use of electromagnetic waves in the treatment of some acute and chronic diseases, application of these waves in everyday life has created several problems for humans, especially the nerve system. In this study, the effects of 30mT electromagnetic fields (EMFs) on the hippocampus is investigated.
Postoperative cerebral myiasis: A rare cause of wound dehiscence in developing countries
Date of publication: 23-Jun-2016
Background:Cerebral myiasis is a rare parasitic disease, especially in postoperative neurological surgery.
Free market or socialized medicine for the future of US health care?
Date of publication: 23-Jun-2016
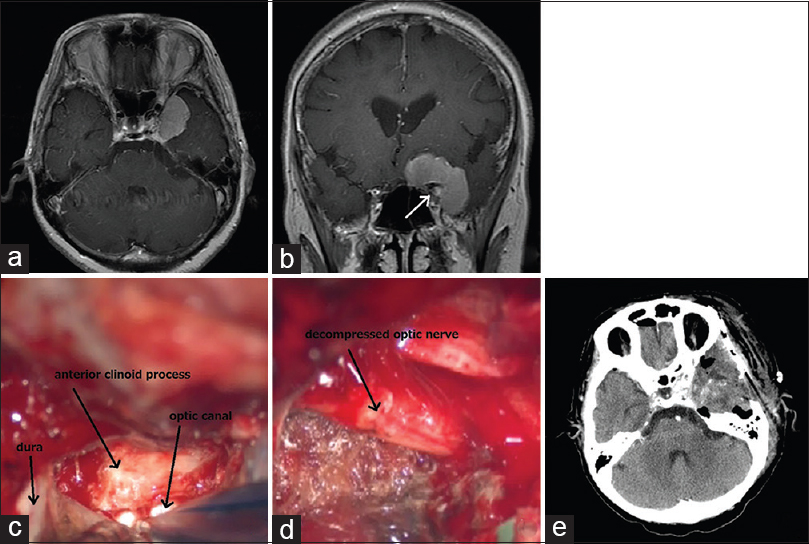
Improvement of long-term blindness caused by compression from inner-third sphenoid wing meningioma after optic canal decompression: An extremely rare case report
Date of publication: 23-Jun-2016
Background:There has been no previous case report of a patient whose visual acuity improved after long-term blindness caused by tumor invasion into the optic canal.