Comparison of postoperative cognitive dysfunction with the use of propofol versus desflurane in patients undergoing surgery for clipping of aneurysm after subarachnoid hemorrhage
Date of publication: 04-Jul-2020
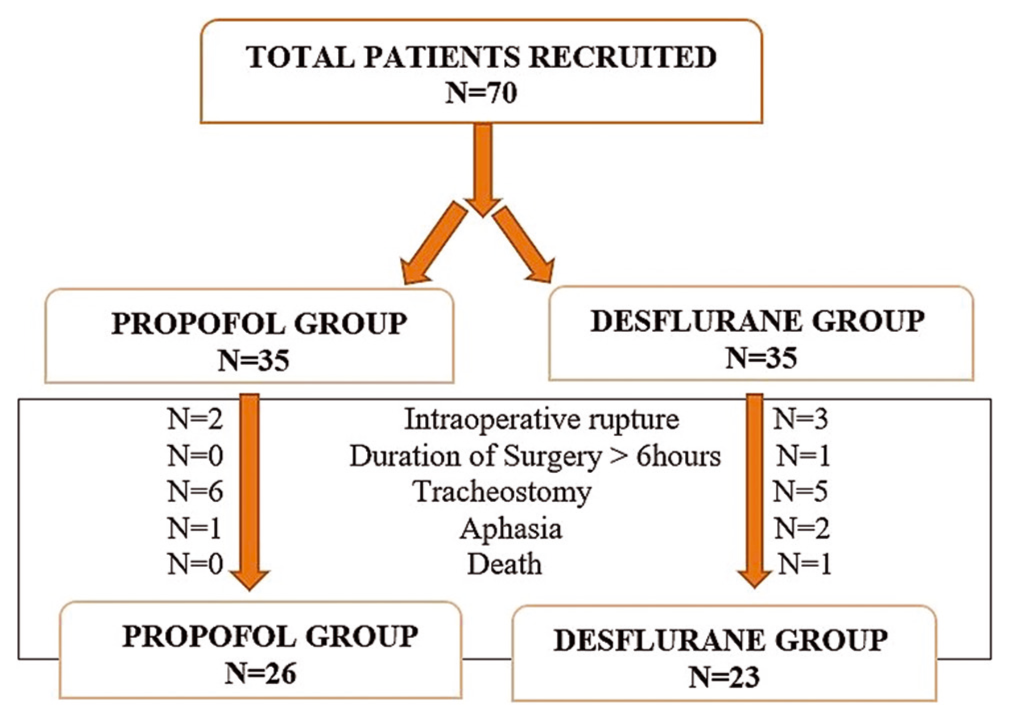
Background: Cerebral aneurysm rupture is a distinct entity among various causes of cerebrovascular accident. Despite the current concept of early surgical clipping to prevent consequences of ruptured aneurysm in good grade subarachnoid hemorrhage patients, 40–50% have postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) on a long- term basis. Here, we compared the effect of two commonly used anesthetic agents on cognitive function following cerebral aneurysmal surgery, i.e., propofol and desflurane.
Dorsal migration of lumbar disc fragments causing cauda equina syndromes: A three case series and literature review
Date of publication: 04-Jul-2020
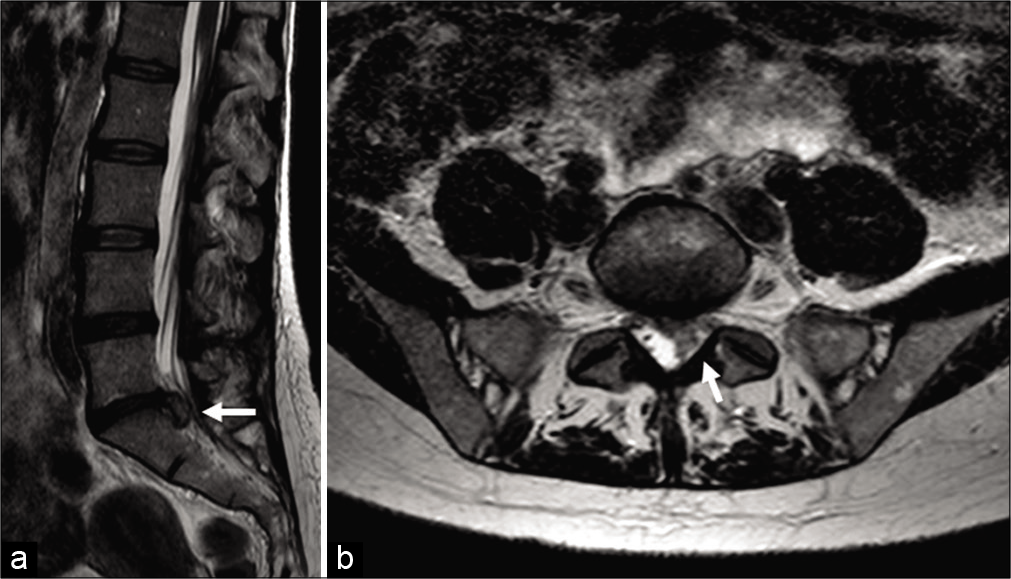
Background: Dorsal migration of an intervertebral lumbar disc fragment is exceedingly rare and may result in spinal cord or cauda equina compression. Radiologically, these lesions may be misdiagnosed as extradural masses or epidural hematomas.
Cervical intramedullary spinal cavernoma in setting of unresolved myelopathy: A case report
Date of publication: 04-Jul-2020
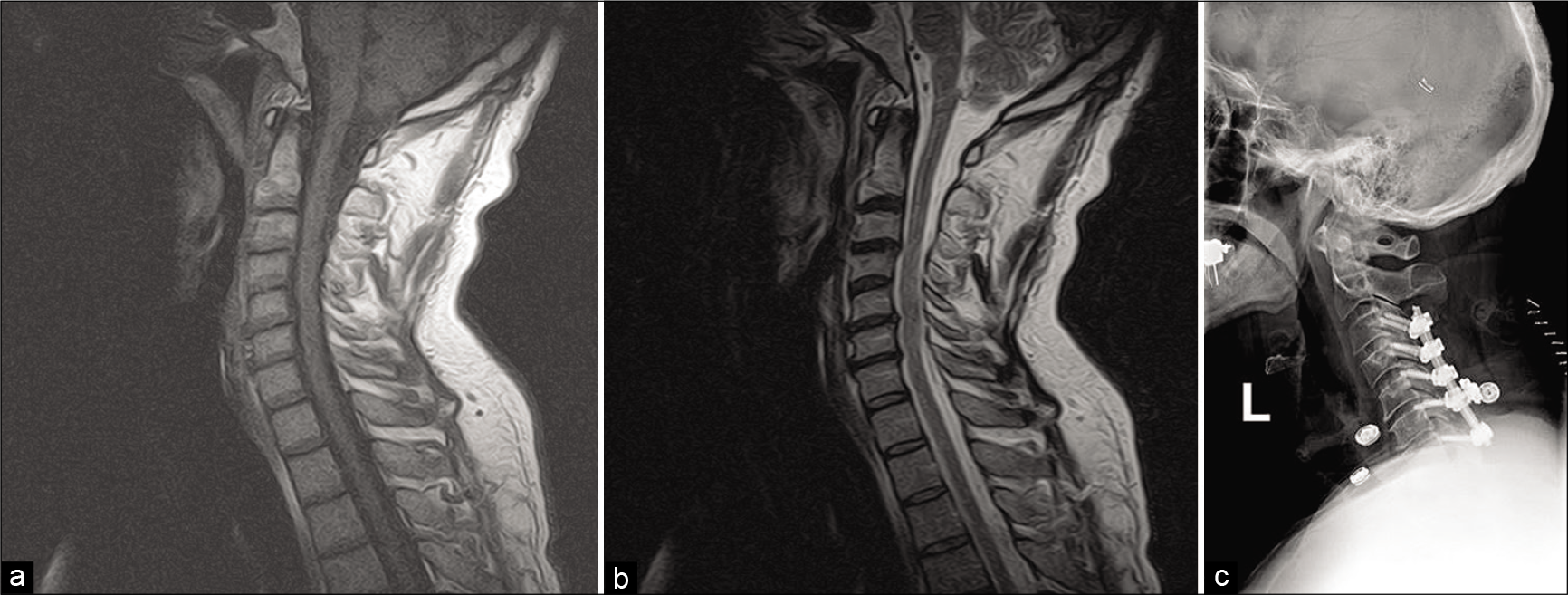
Background: Spinal cavernous malformations are rare, accounting for approximately 5–12% of all spinal cord vascular lesions. Fortunately, improvements in imaging technologies have made it easier to establish the diagnosis of intramedullary spinal cavernomas (ISCs).
Glioblastoma with primitive neuronal component: A case report and considerations of fluorescence-guided surgery
Date of publication: 04-Jul-2020
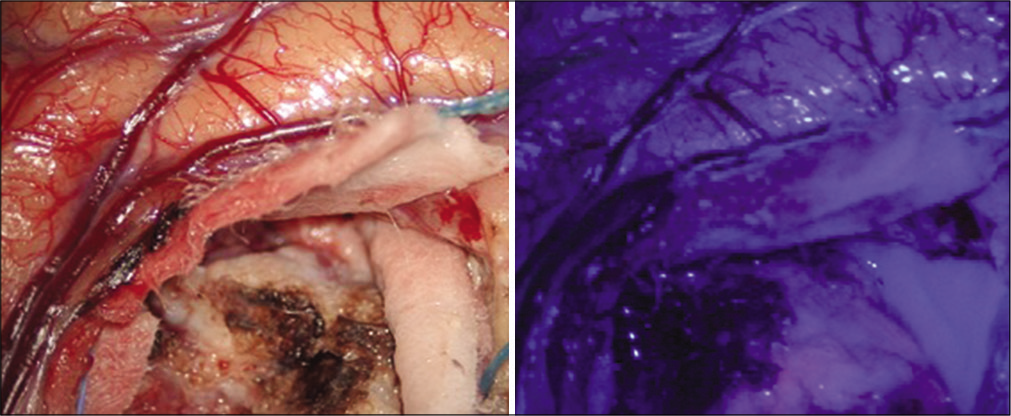
Background: Glioblastoma with primitive neuronal components (GB/PNC) is an extremely rare type of glioblastoma characterized by presenting histological and cytogenetic features of both entities. The mixed nature of these tumors limits the imaging diagnosis and supposes a therapeutic dilemma.
High flow bypass for right giant cavernous internal carotid artery aneurysm with fibromuscular dysplasia of cervical internal carotid artery: microsurgical 2-D video
Date of publication: 04-Jul-2020
Background: It is well known that intracranial aneurysms can be associated to fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD). Nevertheless, it is not clear the best treatment strategy when there is an association of giant symptomatic cavernous carotid aneurysm with extensive cervical internal carotid artery (ICA) FMD.
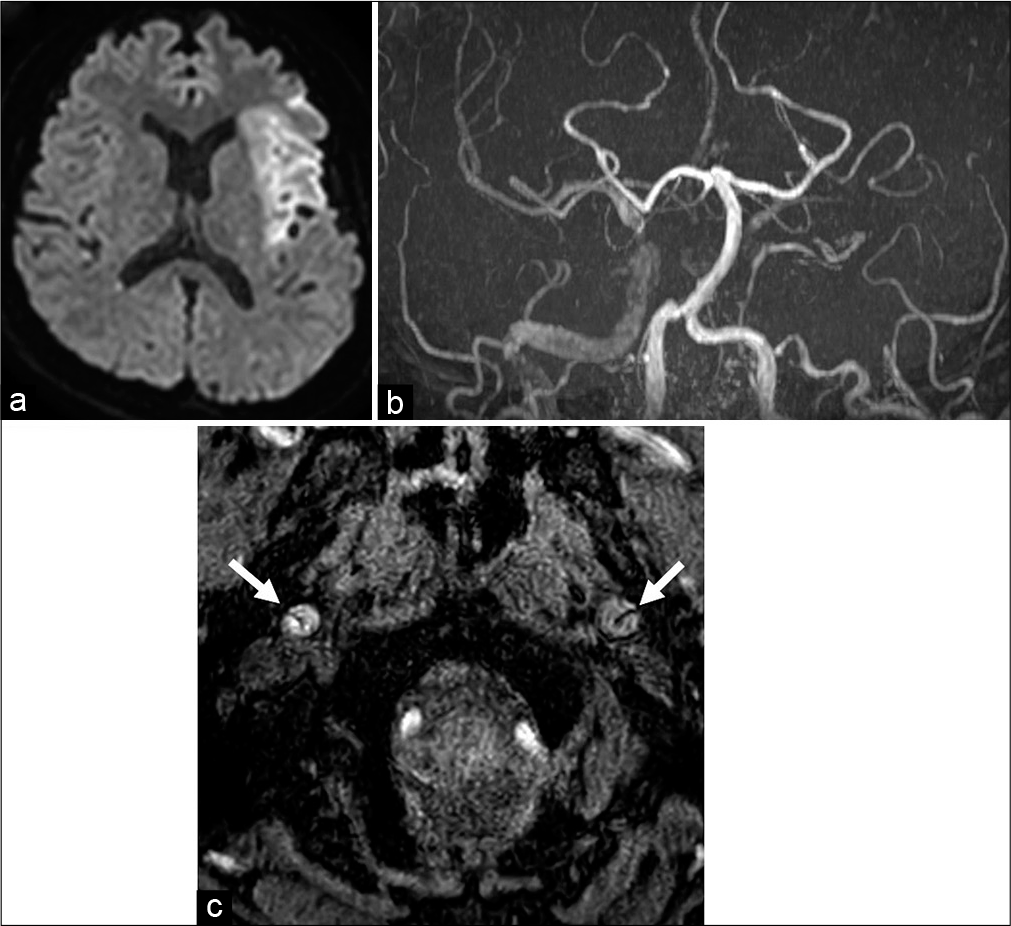
Dynamic assessment of internal carotid artery and elongated styloid process in a case of bilateral carotid artery dissection
Date of publication: 27-Jun-2020
Background: Vascular Eagle syndrome is that an elongated styloid process causes ischemic stroke due to internal carotid artery (ICA) dissection. Dynamic assessment using radiological imaging has not been well investigated. We assessed the change in the relative positional relationship between the elongated styloid process and the ICA using a cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
A sellar neuroblastoma showing rapid growth and causing syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone: A case report
Date of publication: 27-Jun-2020
Background: Sellar neuroblastoma is a very rare entity. We report a rare case of arginine vasopressin (AVP)- producing sellar neuroblastoma presumed to have originated from the lower part of sellar turcica, which grew very rapidly.
Primary myxoid temporal bone tumor: A rare neurosurgical manifestation of Carney complex?
Date of publication: 27-Jun-2020
Background: Carney complex (CNC) is a rare autosomal dominant syndrome, manifesting mainly with cardiac, cutaneous, and mucosal myxomas. Osteochondromyxoma is known as an extremely rare bone lesion of CNC which usually appears early in life; however, there were no reports of primary bone myxoma of the skull in the patients with CNC. We present the first case of primary myxoid skull tumor in the patient with CNC.
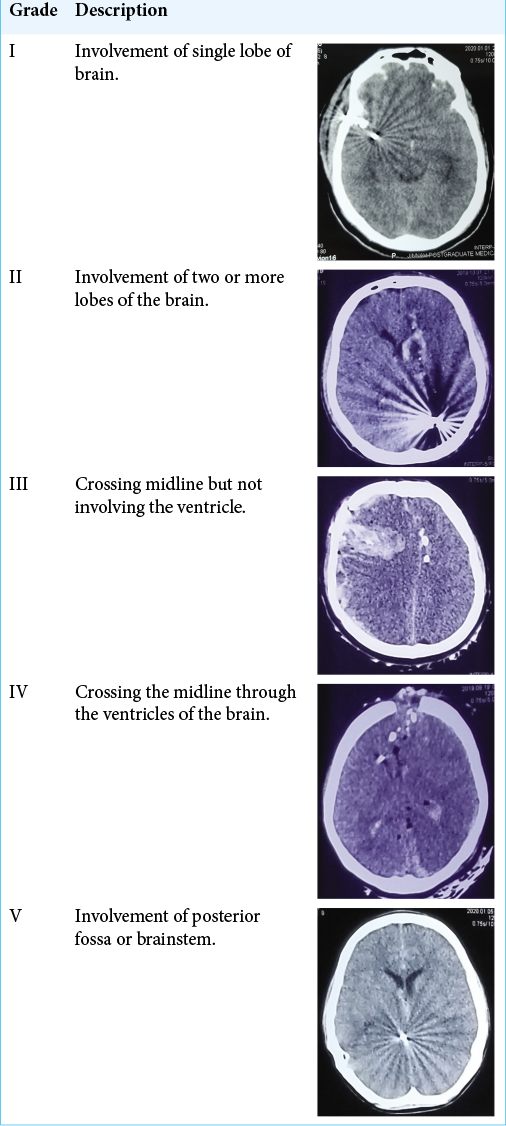
Outcome of cranial firearm injuries in civilian population based on a novel classification system
Date of publication: 27-Jun-2020
Background: Cranial firearm injuries (CFAIs) are expected to be frequent during warfare; however, it is becoming increasingly common among civilian population in our part of the world. These injuries are associated with significant morbidity and mortality in addition to financial loss. The objective of our study is to evaluate the pattern of gunshot injuries to cranium and their outcome.
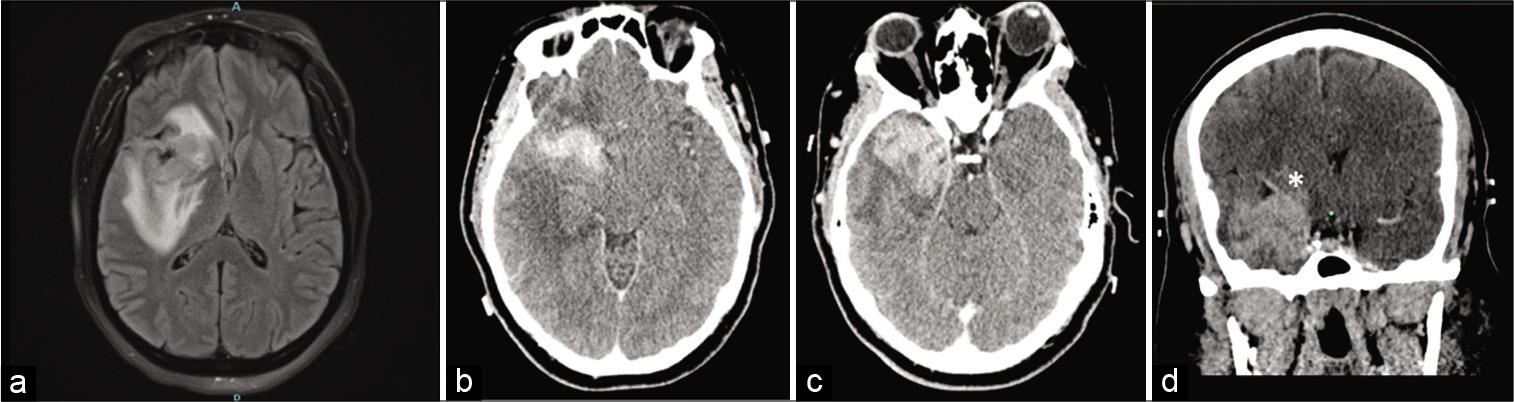
Symptomatic cerebral vasospasm in the setting of carmustine wafer placement for glioblastoma: A case presentation and review of literature
Date of publication: 27-Jun-2020
Background: Gliadel placement in glioblastoma resection, particularly with concurrent chemoradiation, has demonstrated an improvement in survival. There have been several reported adverse effects, some of which lend to significantly increased morbidity and mortality. With only two other cases described in literature, cerebral vasospasm secondary to carmustine-impregnated wafers is an extremely rare side effect.