Right radial nerve decompression for refractory radial tunnel syndrome
Date of publication: 11-Oct-2021
Background: Radial tunnel syndrome arises due to compression of the radial nerve through the radial tunnel.[
Definitions of intracranial aneurysm size and morphology: A call for standardization
Date of publication: 06-Oct-2021
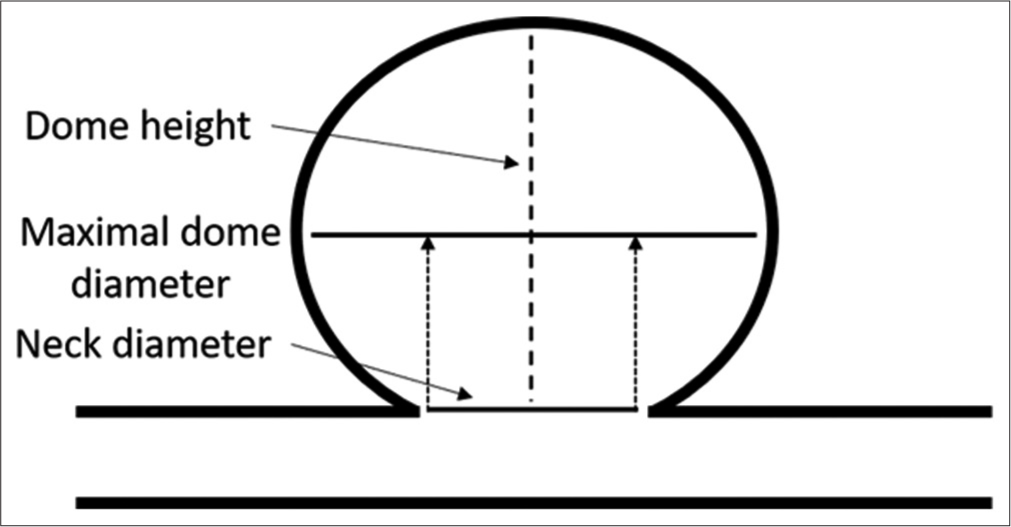
Background: Intracranial aneurysms (IAs) are classified based on size (maximal dome diameter) as well as additional parameters such as neck diameter and dome-to-neck ratio (DNR). The neurosurgical literature includes a wide variety of definitions for both IA size and neck classifications. Standardizing the definitions of IA size and wide-neck classifications would help eliminate inconsistencies and potential misunderstandings of aneurysm morphology and rupture risk.
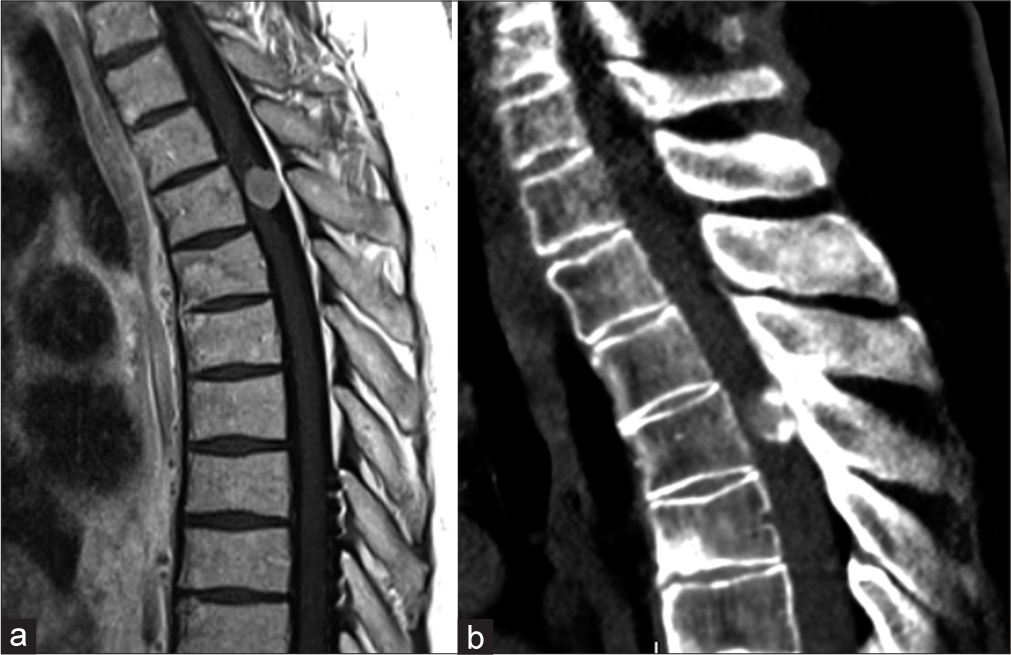
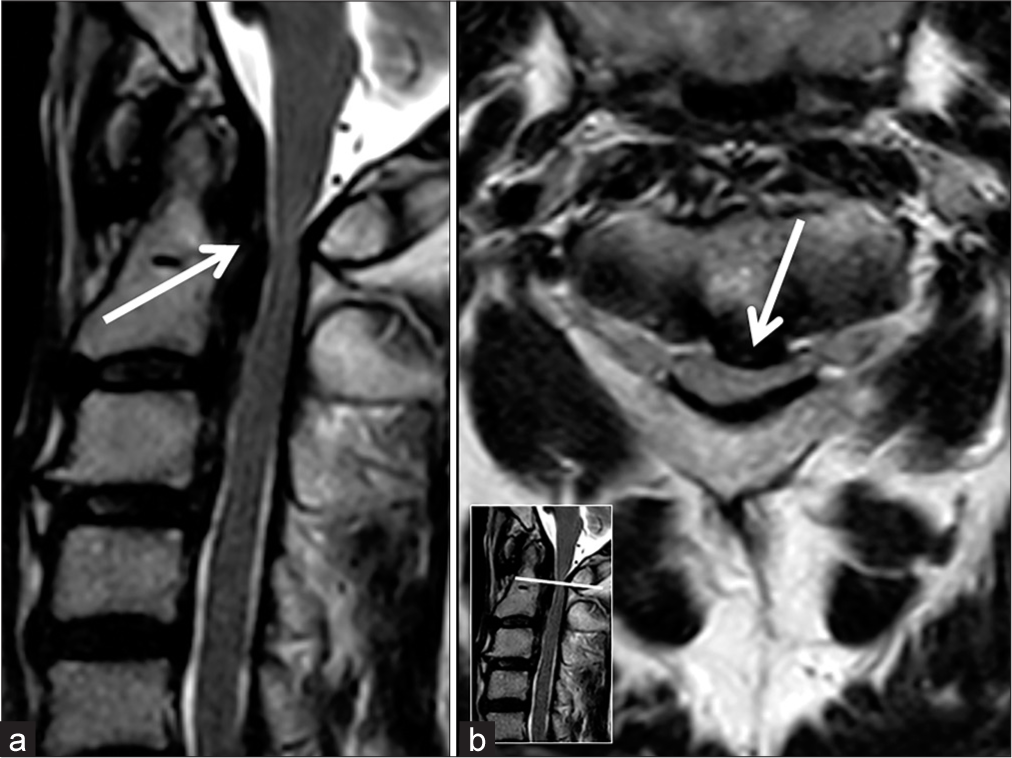
Thoracic meningioma with ossification: Case report
Date of publication: 06-Oct-2021
Background: The incidence of spinal meningiomas is 0.33/100000 population, and ossified spinal meningiomas are even less commonly encountered.
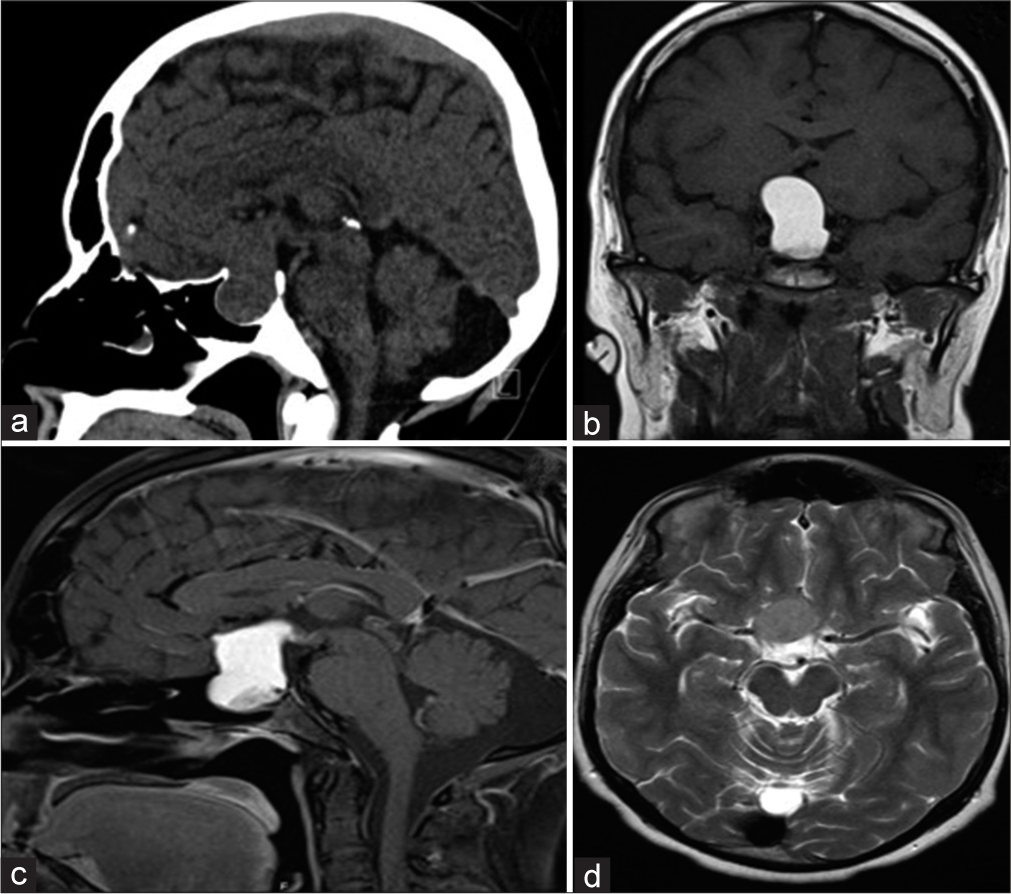
Rathke cleft cyst apoplexy: Hormonal and clinical presentation
Date of publication: 06-Oct-2021
Background: Rathke cleft cyst (RCC) apoplexy is an uncommon type of lesion that is challenging to diagnose without histopathological samples. Very few articles have been published describing the details of RCC apoplexy. We studied a good number of published articles to analyze its demographics, clinical and hormonal presentations, and outcomes.
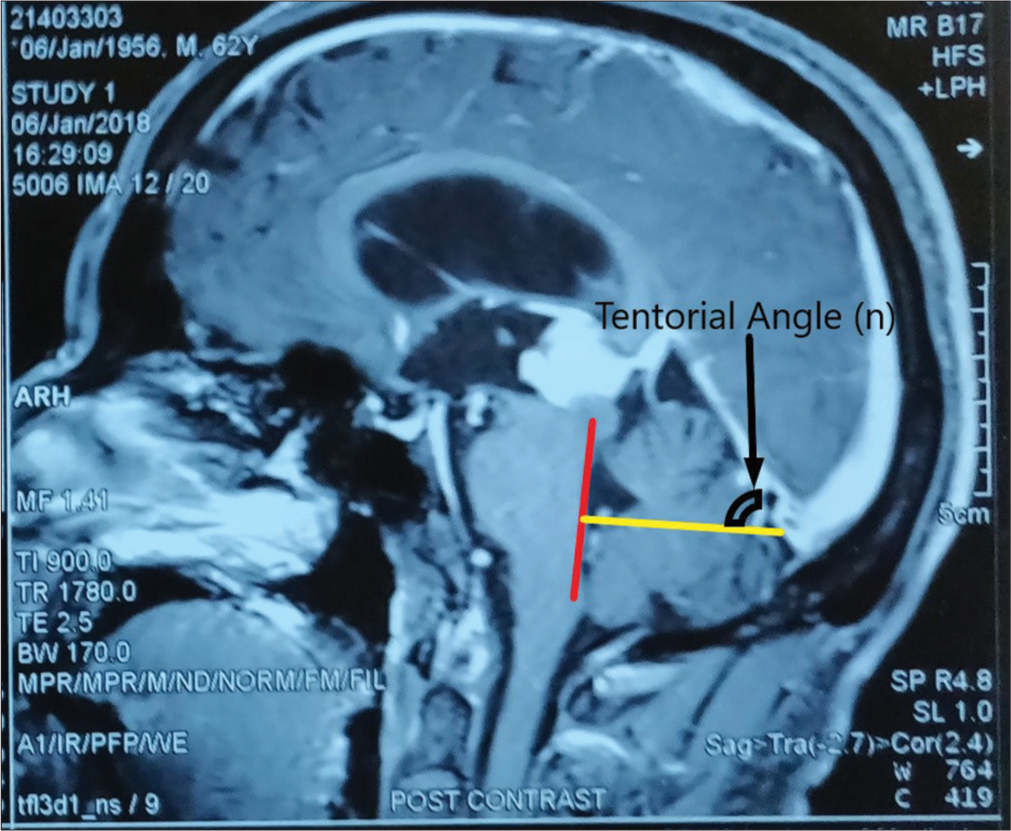
Occipital transtentorial approach for pineal region lesions: Addressing the controversies in conventional teaching
Date of publication: 06-Oct-2021
Background: The occipital transtentorial (OT) approach is well-established approach for pineal region tumors and can be of choice for the lesions located around the suboccipital part of tentorium such as the quadrigeminal plate, posterior part of thalamus, tentorial surface of cerebellum, splenial region, posterior falx, and lesions around the tentorial incisura. However, it is not very much extensively used in the above-mentioned locations other than the pineal region.
C6 nerve root palsy after double-door cervical laminoplasty
Date of publication: 06-Oct-2021
Background: This study correlated the relationship between postoperative C6 nerve root palsies and various patient-related clinical, radiographic, and surgical parameters.
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament at the craniocervical junction presenting with Brown-Séquard syndrome: A case report
Date of publication: 06-Oct-2021
Background: Several case reports about spinal cord compression due to hyperostosis at the craniocervical junction are available. However, compression at C1-C2 solely due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) is rare.
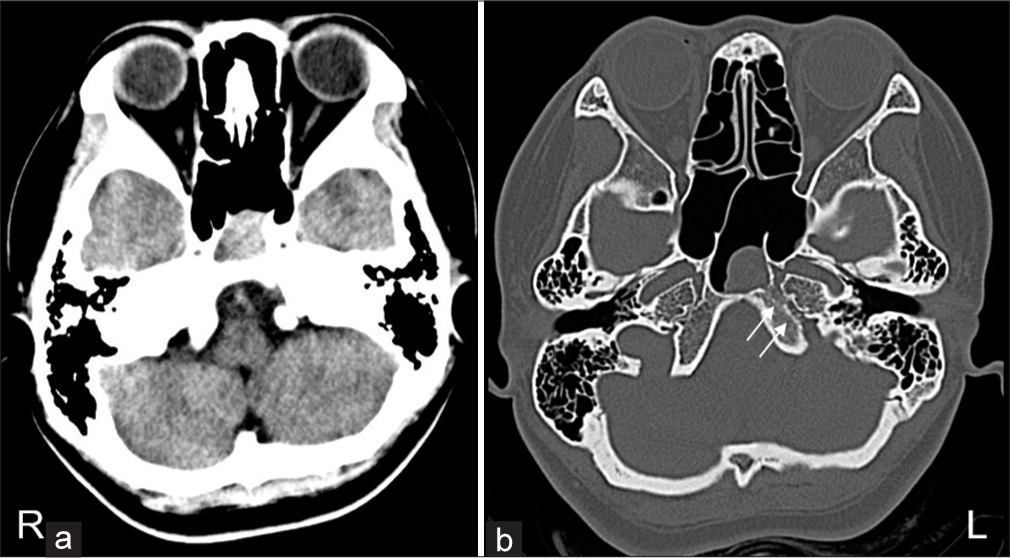
Surgical management of primary Ewing’s sarcoma of the petroclival bone extend into the sphenoid sinus: A case report and review of literatures
Date of publication: 06-Oct-2021
Background: Ewing’s sarcoma (ES) is a malignancy that arises from bones or soft tissue, characterized by primitive small and round blue cells. Primary ES typically occurs in the long bones, vertebrae, or pelvis, and is extremely rare in the skull base.
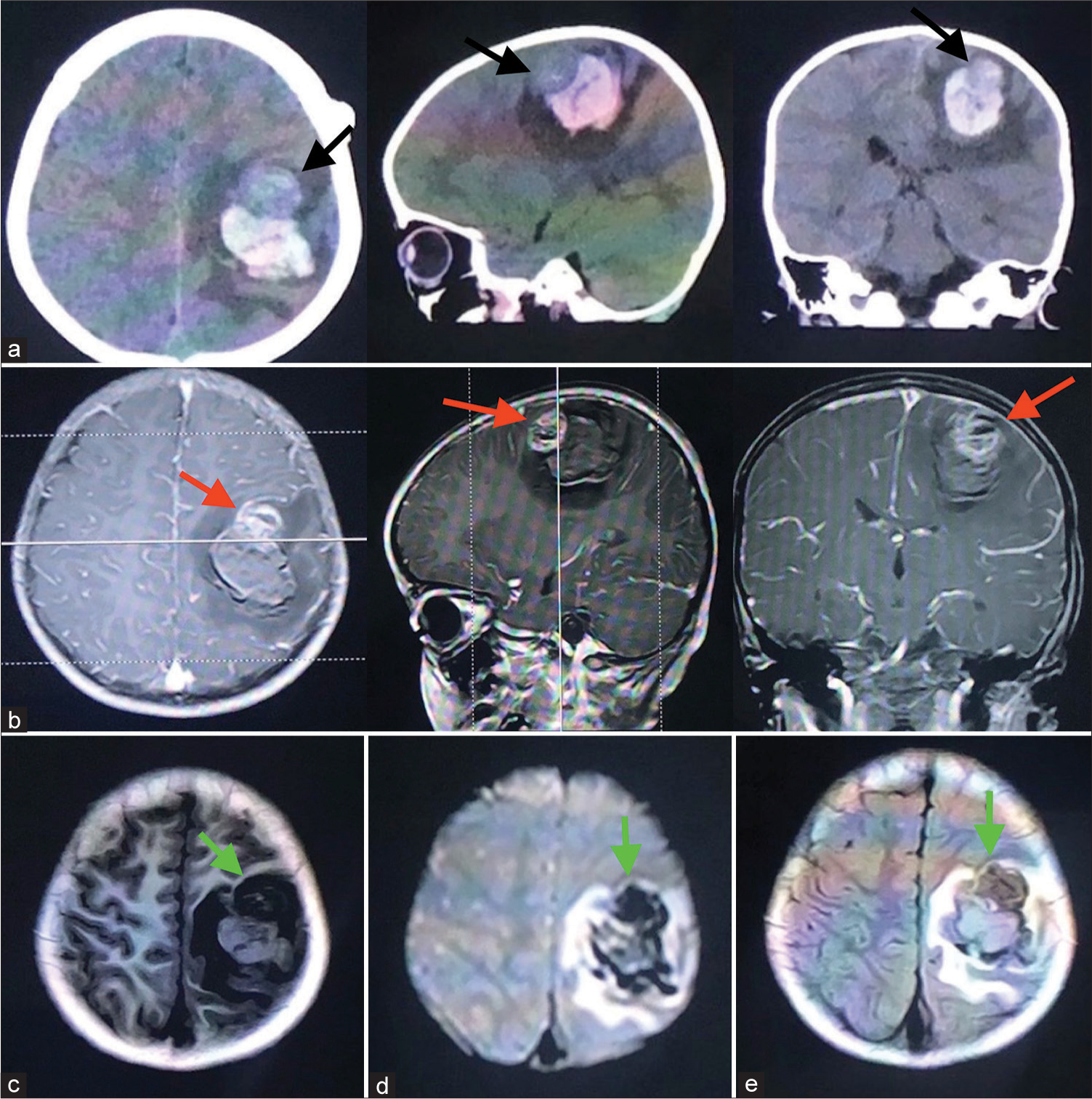
Pediatric angiocentric glioma with acute intracerebral hemorrhage: A case report with 36 months follow-up
Date of publication: 06-Oct-2021
Background: Angiocentric glioma (AG) is an extremely rare intracranial tumor that was first described in 2005 and identified as a special type of intracranial tumor in 2007 by the WHO, which mainly affects children and young adolescents. Epilepsy is the main presentation; therefore, it was recognized as a seizure-related tumor in the past. Here, we report a case of AG with acute intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) as the first symptom who never had a seizure onset.
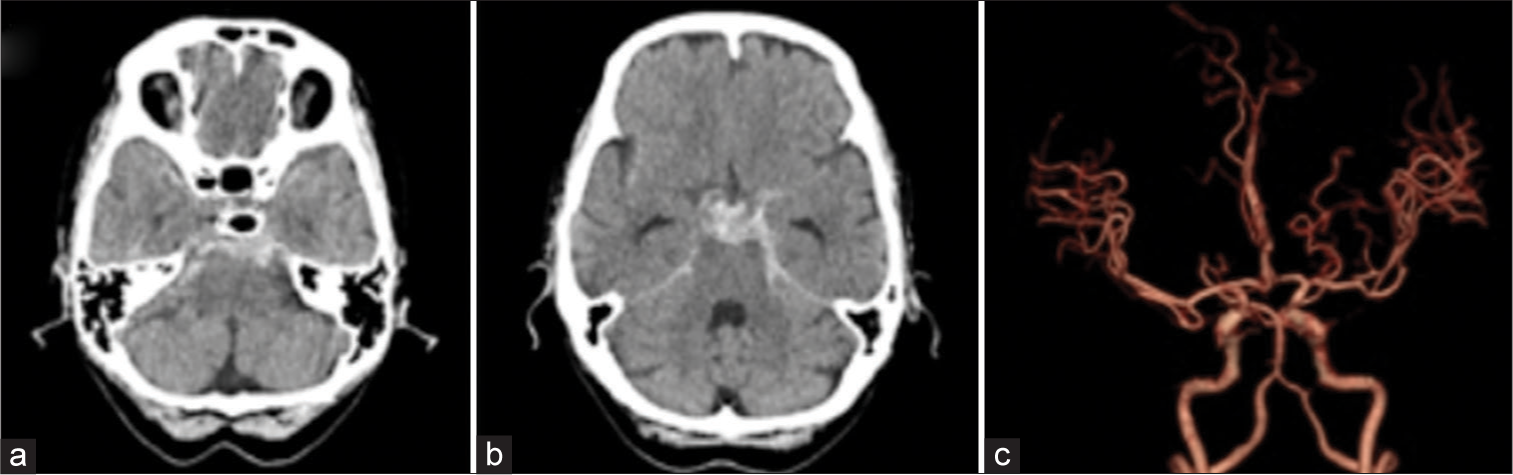
Contrast extravasation from basilar artery without aneurysm formation on digital subtraction angiography in computed tomography angiogram-negative subarachnoid hemorrhage: A case report
Date of publication: 06-Oct-2021
Background: The causes of angiogram-negative subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) on initial angiography, which accounts for 10–30% of spontaneous SAH, are heterogeneous and still unclear. We report a case of nonaneurysmal SAH, in which initial computed tomographic angiography (CTA) showed no source of bleeding, but the subsequent digital subtraction angiography (DSA) revealed contrast extravasation from the basilar artery without aneurysms.