Incidence of dysphagia after odontoid screw fixation of type II odontoid fracture in the elderly
Date of publication: 16-Apr-2018
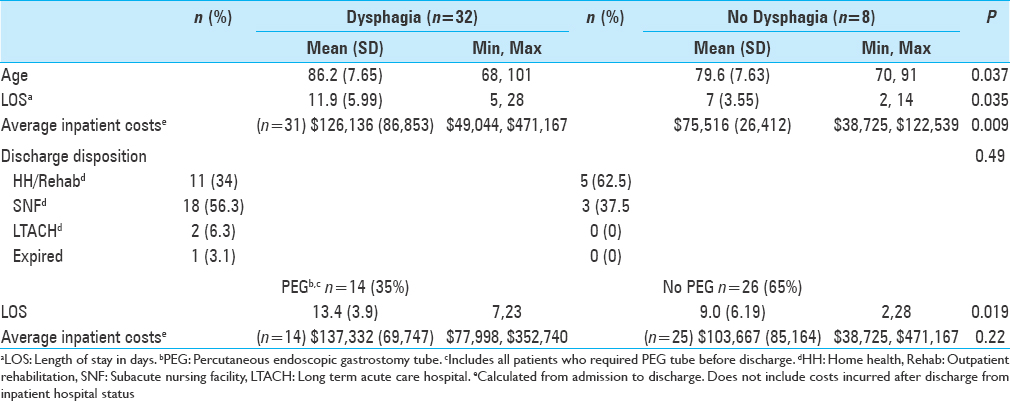
Background:Although surgery may reduce mortality rates from type II odontoid fractures in the elderly population, post-operative dysphagia resulting from screw fixation remains a serious complication.
Acute cauda equina syndrome following orthopedic procedures as a result of epidural anesthesia
Date of publication: 10-Apr-2018
Background:Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a rare complication of spinal or epidural anesthesia. It is attributed to direct mechanical injury to the spinal roots of the cauda equina that may result in saddle anesthesia and paraplegia with bowel and bladder dysfunction.
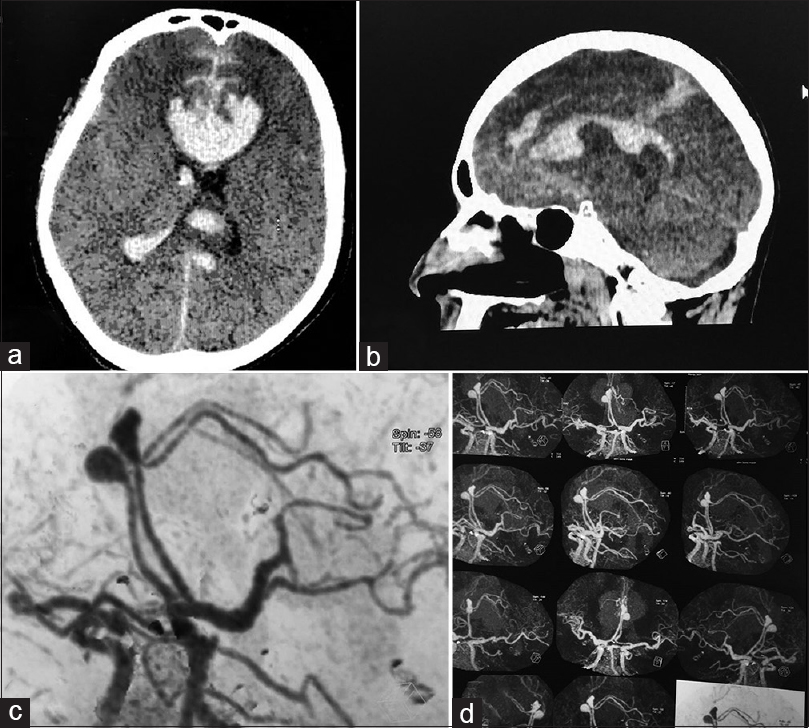
Mirror image of bilateral DACA aneurysm with its successful surgical management
Date of publication: 10-Apr-2018
Background:Among various locations of intracranial aneurysms reported in the literature, two different aneurysms situated symmetrically opposite on bilateral distal anterior cerebral arteries (DACA) are very rare.
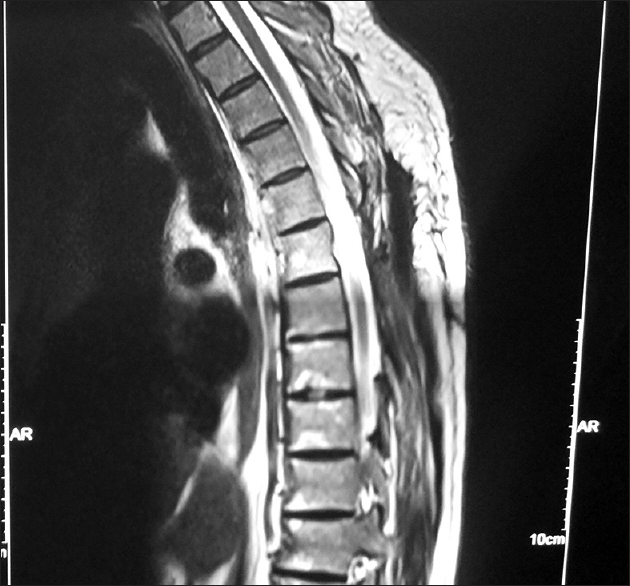
Spinal angiolipoma mimicking a schwannoma: A case report
Date of publication: 10-Apr-2018
Background:Angiolipomas rarely involve the spinal canal/foramina, and may prove difficult to differentiate from schwannomas.
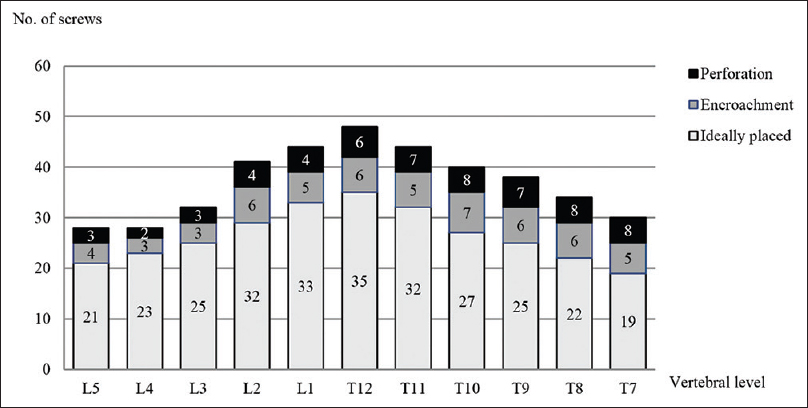
Accuracy of percutaneous pedicle screw insertion in spinal fixation of traumatic thoracic and lumbar spine fractures
Date of publication: 10-Apr-2018
Background:Percutaneous insertion of pedicle screws was developed as a minimally invasive alternative to the different open spinal procedures. Here, we determined the accuracy of percutaneous pedicle screw insertion.
Erratum: Engraftment, neuroglial transdifferentiation and behavioral recovery after complete spinal cord transection in rats
Date of publication: 09-Apr-2018
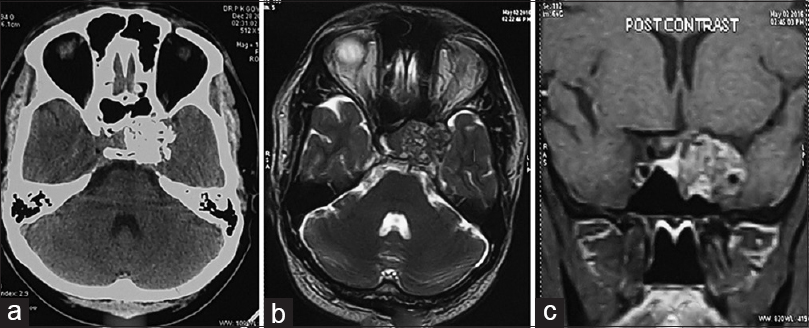
Pituitary fossa chondrosarcoma: An unusual cause of a sellar suprasellar mass masquerading as pituitary adenoma
Date of publication: 09-Apr-2018
Background:Chondrosarcoma is a mesenchymal malignant tumor composed of tumor cells producing cartilage. It is more commonly found in older age group and usually affects the axial skeleton. Intracranial chondrosarcoma is extremely rare, and chondrosarcoma arising from the sellar region are even rarer with only a few cases described in the literature. We report a case of chondrosarcoma mimicking a sellar suprasellar mass with parasellar extension.
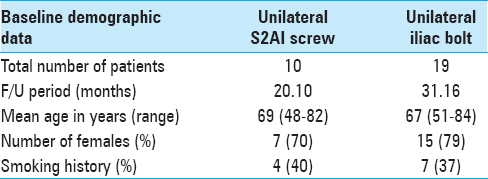
Unilateral S2 alar-iliac screws for spinopelvic fixation
Date of publication: 09-Apr-2018
Background:This study compared the clinical complications, radiographic measurements of deformity, and quality of life outcomes for patients with de novo scoliosis undergoing thoracolumbar fusions for spinopelvic fixation (SPF) utilizing unilateral S2 alar-iliac (S2AI) screw or unilateral iliac bolt fixation.
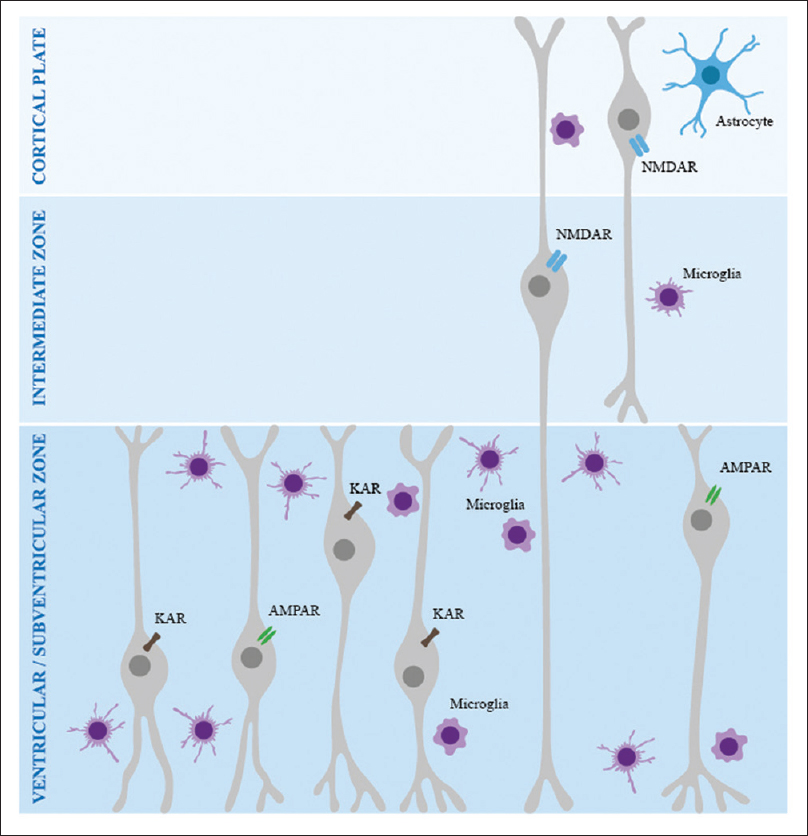
Immunoexcitotoxicity as the central mechanism of etiopathology and treatment of autism spectrum disorders: A possible role of fluoride and aluminum
Date of publication: 09-Apr-2018
Abstract
Our review suggests that most autism spectrum disorder (ASD) risk factors are connected, either directly or indirectly, to immunoexcitotoxicity. Chronic brain inflammation is known to enhance the sensitivity of glutamate receptors and interfere with glutamate removal from the extraneuronal space, where it can trigger excitotoxicity over a prolonged period. Neuroscience studies have clearly shown that sequential systemic immune stimulation can activate the brain's immune system, microglia, and astrocytes, and that with initial immune stimulation, there occurs CNS microglial priming. Children are exposed to such sequential immune stimulation via a growing number of environmental excitotoxins, vaccines, and persistent viral infections. We demonstrate that fluoride and aluminum (Al3+) can exacerbate the pathological problems by worsening excitotoxicity and inflammation. While Al3+ appears among the key suspicious factors of ASD, fluoride is rarely recognized as a causative culprit. A long-term burden of these ubiquitous toxins has several health effects with a striking resemblance to the symptoms of ASD. In addition, their synergistic action in molecules of aluminofluoride complexes can affect cell signaling, neurodevelopment, and CNS functions at several times lower concentrations than either Al3+ or fluoride acting alone. Our review opens the door to a number of new treatment modes that naturally reduce excitotoxicity and microglial priming.
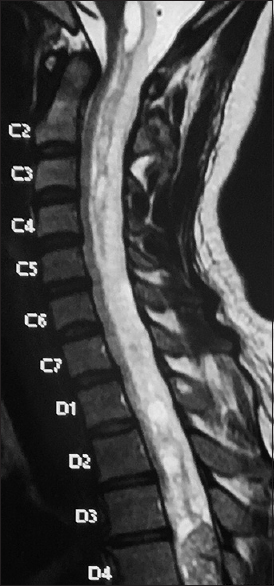
Dorsal hemangioblastoma manifesting as holocord syringomyelia
Date of publication: 05-Apr-2018
Background:Intramedullary spinal hemangioblastomas are known to be accompanied by syringomyelia.