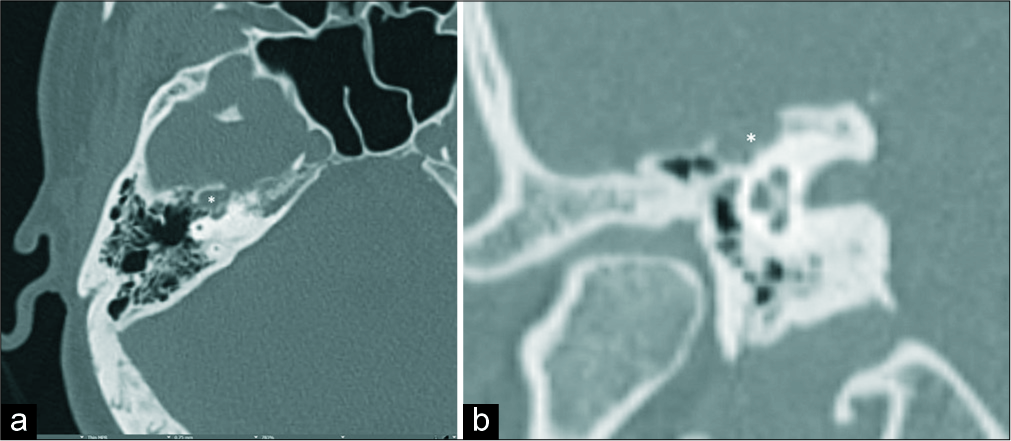
A case of a facial nerve venous malformation presenting with crocodile tear syndrome
Date of publication: 03-Jan-2020
Background: Crocodile tears syndrome, also known as Bogorad syndrome, is characterized by lacrimation secondary to olfactory and gustatory stimuli and mastication. Crocodile tear syndrome is typically encountered as an uncommon complication of Bell’s palsy and usually occurs during the recovery phase of the disease course.
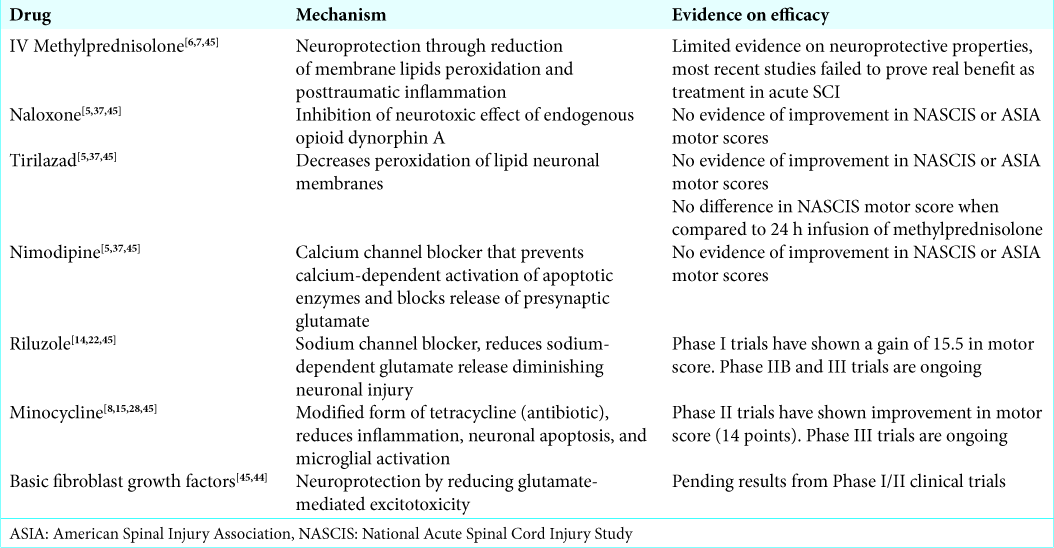
Current advancements in the management of spinal cord injury: A comprehensive review of literature
Date of publication: 03-Jan-2020
Background: Spinal cord injury (SCI) carries debilitating lifelong consequences and, therefore, requires careful review of different treatment strategies.
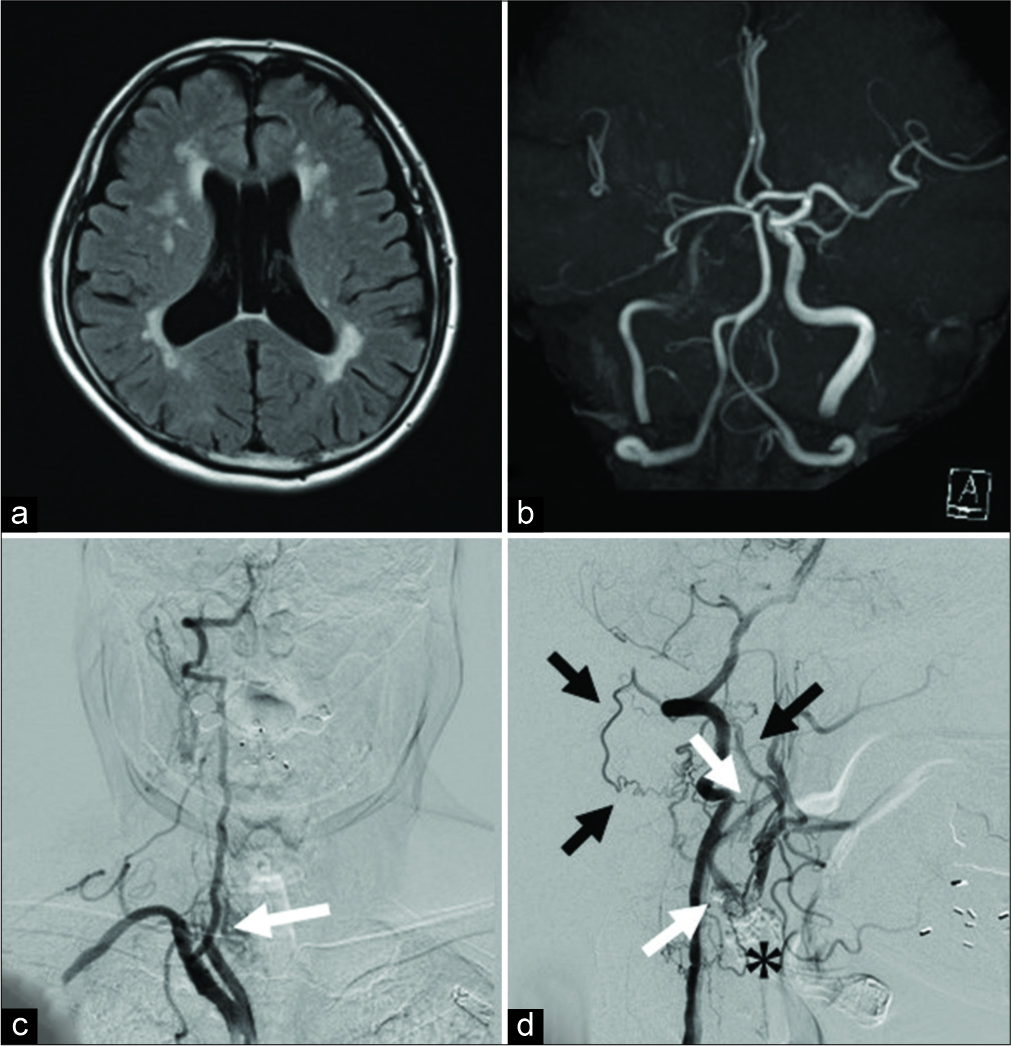
Two cases of symptomatic common carotid artery occlusion treated by carotid endarterectomy with L-shaped ministernotomy
Date of publication: 03-Jan-2020
Background: Common carotid artery occlusion (CCAO) is rare. Symptomatic lesions are resistant to medical treatment and revascularization are often required, but there is no consensus on the treatment of CCAO. In this paper, two cases of symptomatic CCAO treated by carotid endarterectomy (CEA) with L-shaped ministernotomy, in which the lesions extended to the beginning part of the CCA, are reported.
Surgical excision of trigeminal (V3) schwannoma through endoscopic transpterygoid approach
Date of publication: 27-Dec-2019
Background: Endoscopic endonasal transpterygoid (EET) approach is well suited for trigeminal schwannomas.
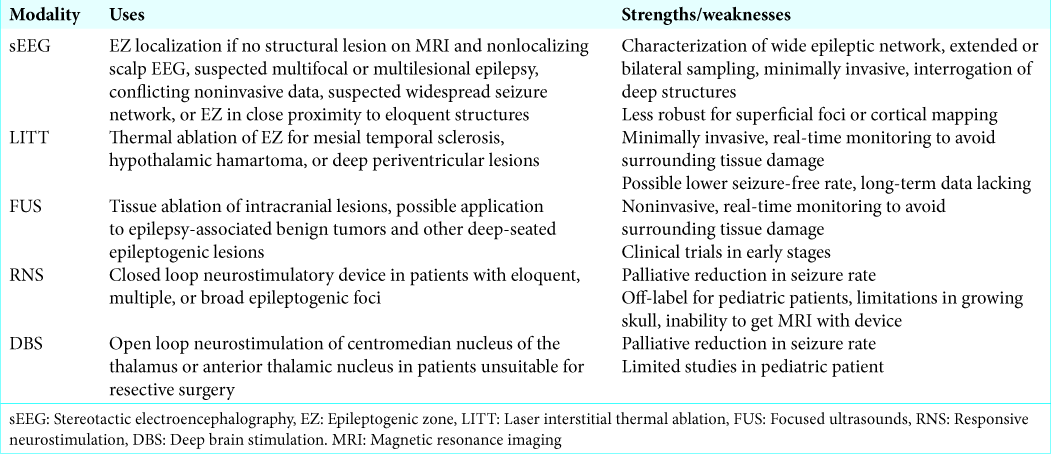
An update on pediatric surgical epilepsy: Part II
Date of publication: 27-Dec-2019
Background: Recent advances may allow surgical options for pediatric patients with refractory epilepsy not previously deemed surgical candidates. This review outlines major technological developments in the field of pediatric surgical epilepsy.
An update on pediatric surgical epilepsy: Part I
Date of publication: 27-Dec-2019
Abstract
Epilepsy affects many children worldwide, with drug-resistant epilepsy affecting 20–40% of all children with epilepsy. This carries a significant burden for patients and their families and is strongly correlated with poor cognitive outcomes, depression, anxiety, developmental delay, and impaired activities of daily living. For this reason, we sought to explore the role of pediatric epilepsy surgery and provide an overview of the factors contributing to epilepsy surgery planning and execution. We review the necessary preoperative evaluations, surgical indications, planning considerations, and surgical options to provide a clear pathway in the evaluation and planning of pediatric epilepsy surgery.
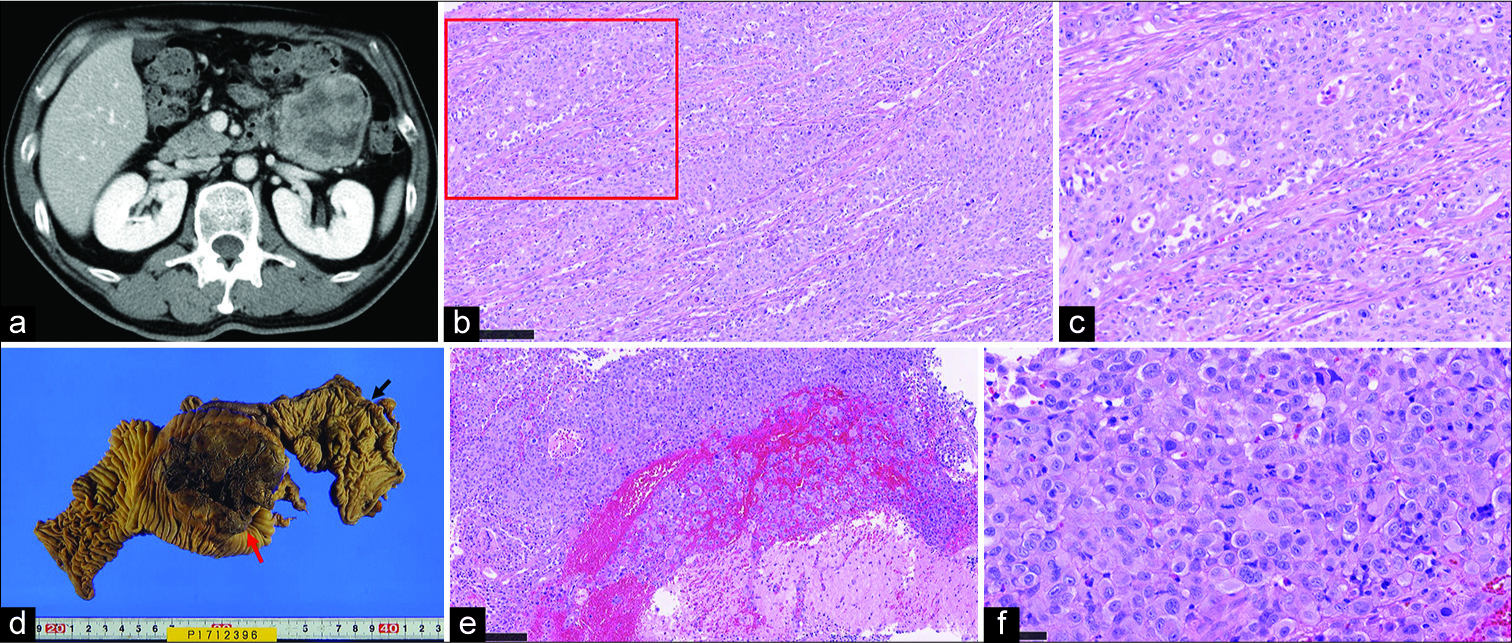
A rare case of brain metastasis from poorly differentiated small bowel adenocarcinoma
Date of publication: 27-Dec-2019
Background: Small bowel adenocarcinoma (SBA) accounts for <2% of all gastrointestinal malignancies. The most common organs of SBA metastases are the abdominal lymph node, liver, and peritoneum. There have been almost no reports of brain metastases of SBA. Dabaja et al. reported 1 case of brain metastasis out of 217 SBA cases, but details of the clinical course of the case were unclear. Our case might be the first report covering the full clinical course, pathological findings, and genetic data. Here, we report a very rare case of brain metastasis from poorly differentiated SBA.
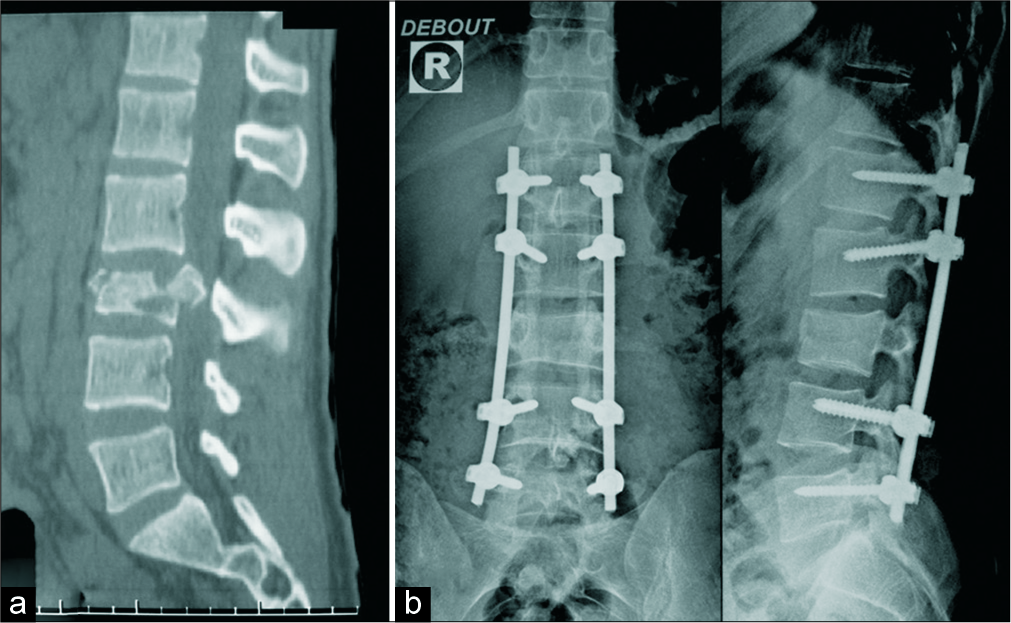
Polyaxial pedicle screw dislocation during screw tightening for posterior spinal lumbar stabilization
Date of publication: 27-Dec-2019
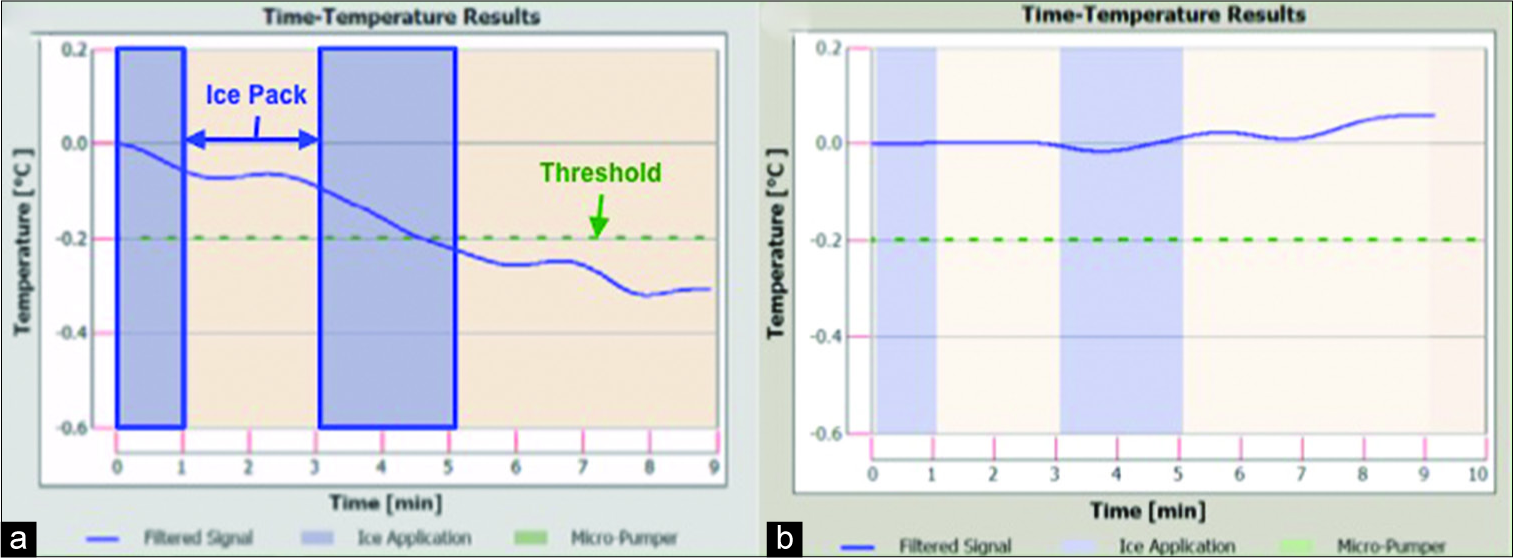
Noninvasive thermal evaluation for shunt failure in the emergency room
Date of publication: 27-Dec-2019
Background: Ventriculoperitoneal shunts (VPSs) have been the mainstay of treating hydrocephalus since the 1950s. However, shunts have a reported complication rate reaching nearly 50%. Devices have been developed that utilize noninvasive thermal transcutaneous diffusion technology. These shunt evaluation devices measure temperature gradients to detect shunt cerebrospinal fluid flow. We assessed the utility using a thermal diffusion technique to work up shunt failure in the emergency room (ER).
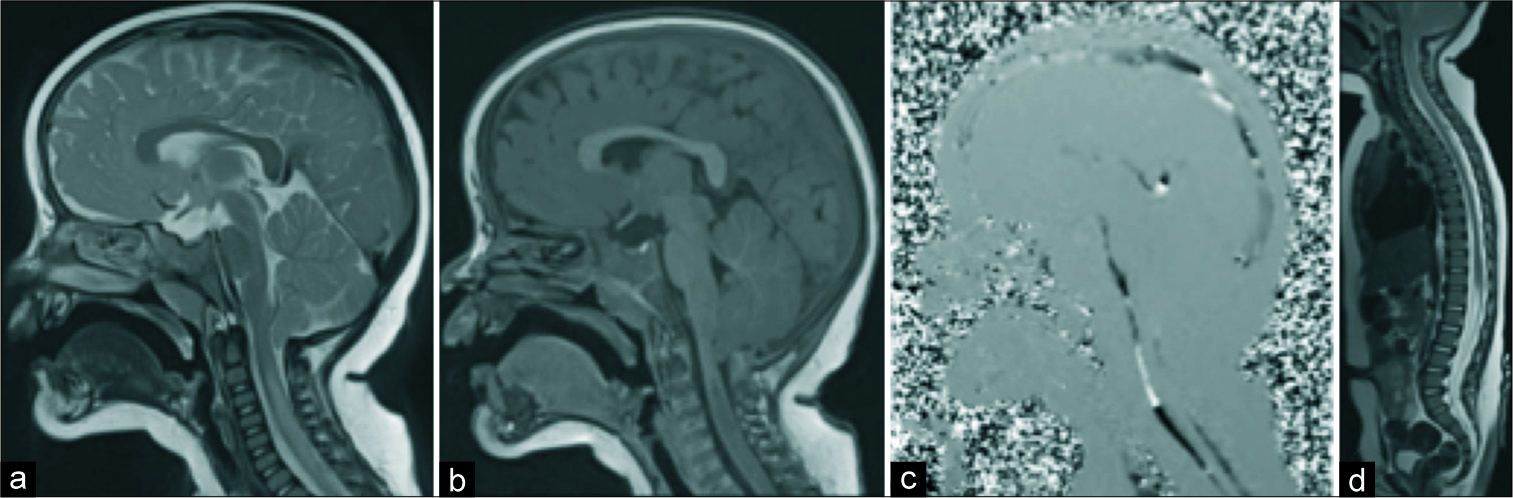
Acute traumatic presentation of Chiari I malformation with central cord syndrome and presyrinx in an infant
Date of publication: 27-Dec-2019
Background: Chiari I malformation (CM-I) typically presents in late childhood and early adulthood. Often these lesions are asymptomatic and discovered incidentally. Patients typically present with tussive headaches and focal neurological findings, especially when associated with syringomyelia. Here, an 11-month-old child with a severely symptomatic CM-I required surgery (e.g., suboccipital craniectomy and C1/2 laminectomy) within the 1st year of life.