Intramedullary spinal cord abscess as postoperative complication: A case report
Date of publication: 03-May-2024
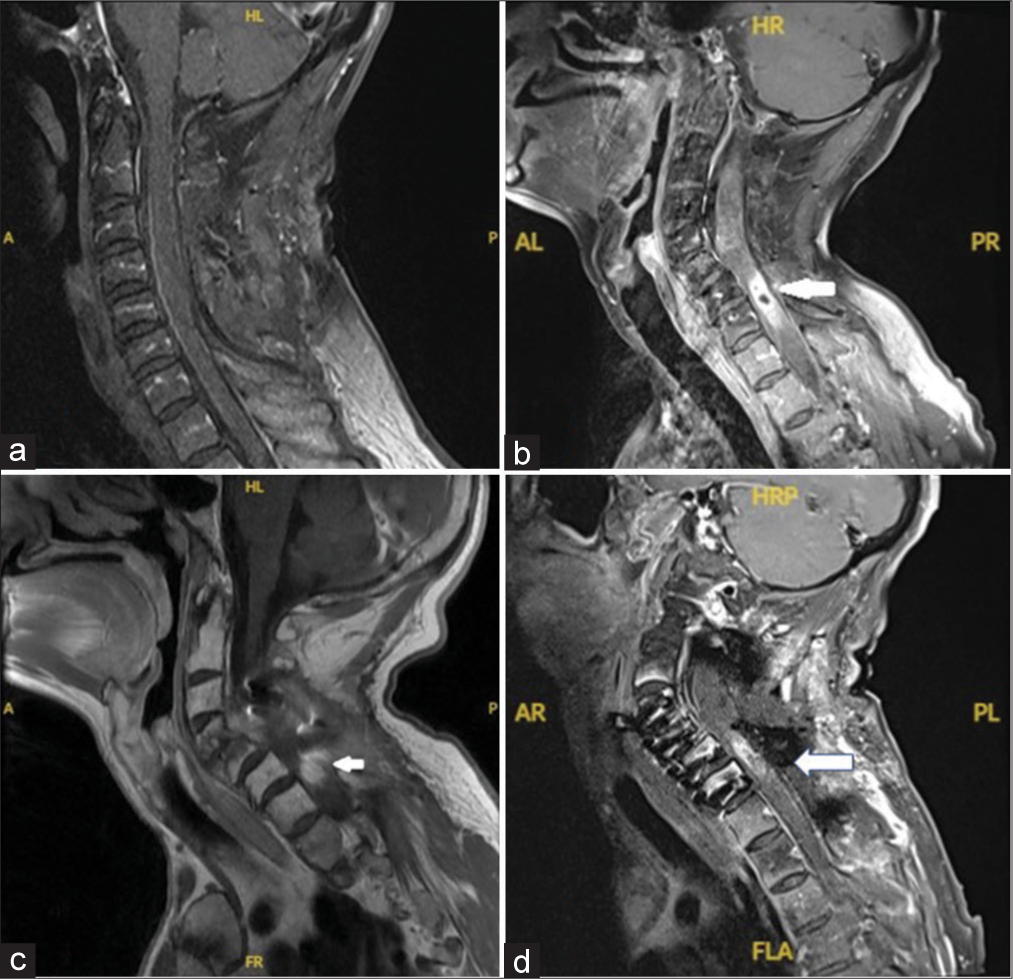
Background: Intramedullary spinal cord abscesses (ISCA) can result in high morbidity and mortality if not treated in a timely manner. The incidence and outcomes of postsurgical ISCA are unknown. We present a case of a 52-year-old male patient with neurofibromatosis type 1 who developed an intramedullary spinal cord abscess after a previous resection of a cervical intradural, extramedullary neurofibroma.
Morphometric analysis of the foramen ovale in the Mexican population using computed tomography scan
Date of publication: 03-May-2024
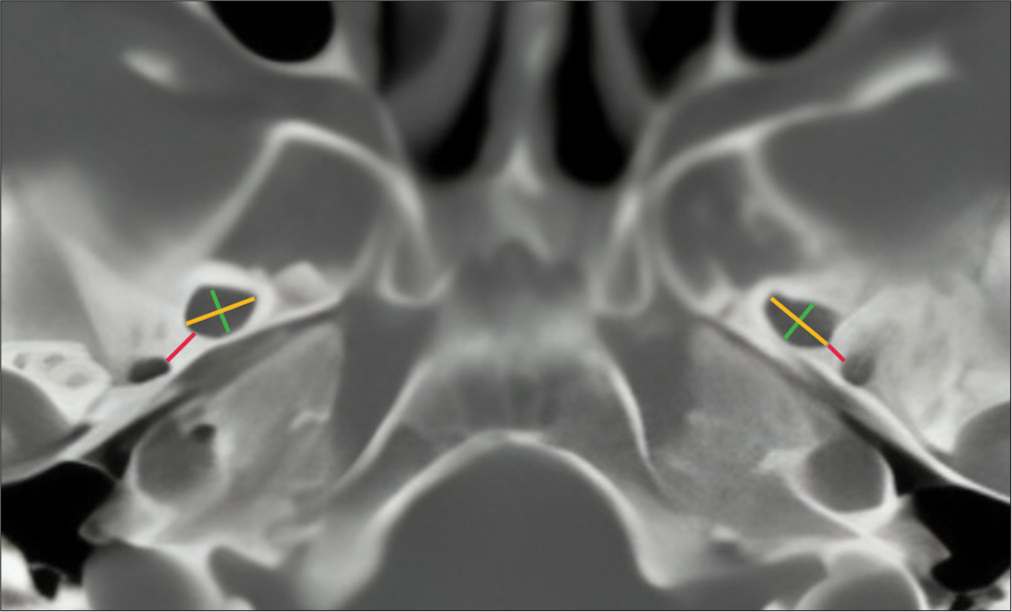
Background: The assessment of cranial foramina is an important part of the objective diagnostic and therapeutic study relevant to pathologies involving structures of the skull base. The study of the foramen ovale not only holds significance for anatomical development but also bears profound surgical importance, such as in trigeminal neuralgia, and diagnostic importance in tumors and various types of epilepsy. It becomes relevant in fine-needle aspiration techniques in perineural tumor procedures, for electroencephalographic analysis in seizures, and therapeutic procedures such as percutaneous trigeminal rhizotomy for trigeminal neuralgia.
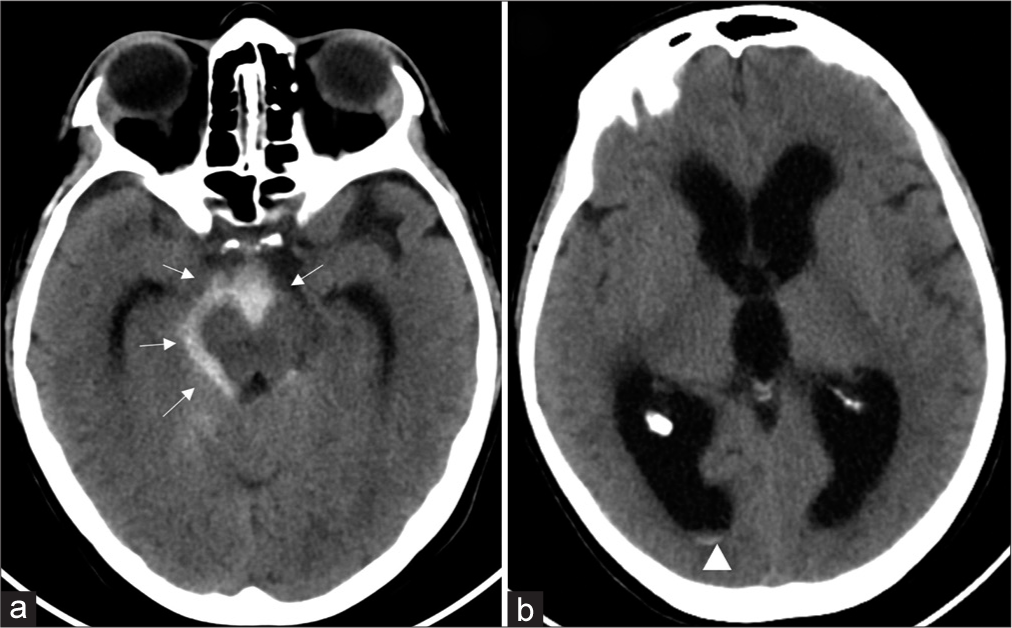
Estimation of the rupture point of the craniovertebral junction intradural arteriovenous fistula with vessel wall magnetic resonance image and its pathological findings: A case report
Date of publication: 03-May-2024
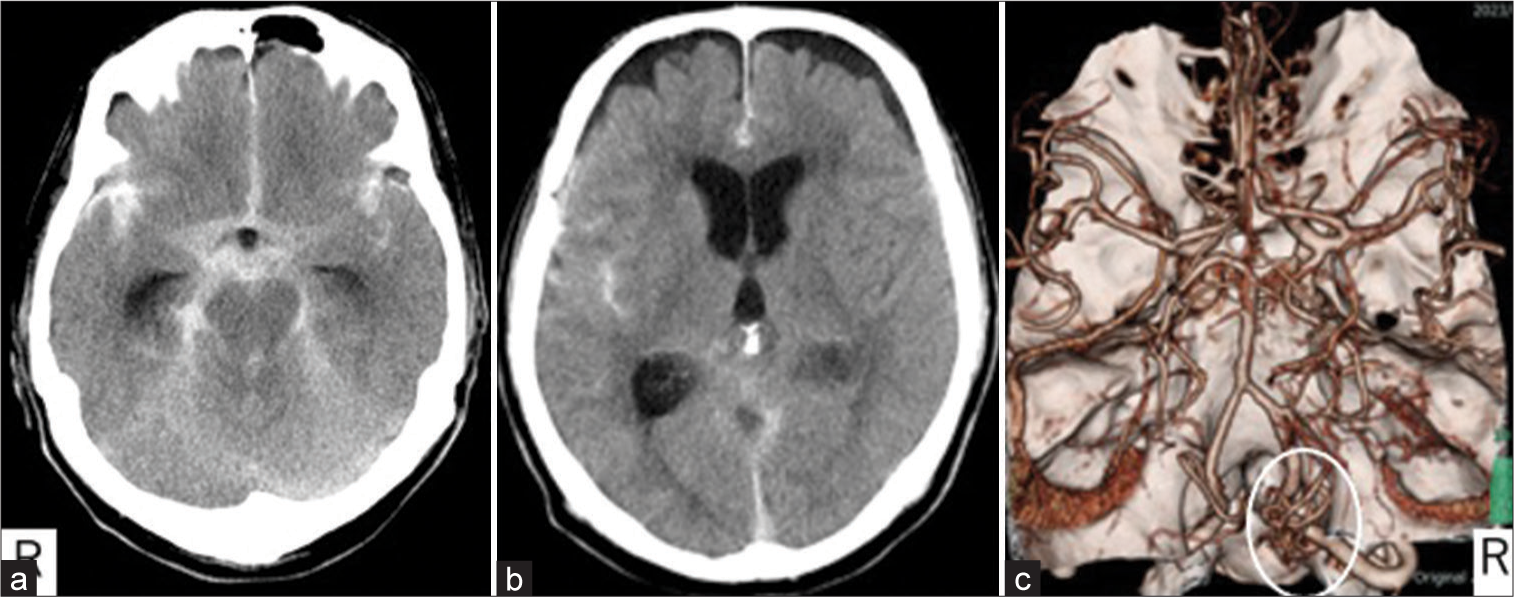
Background: Arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) of the craniocervical junction (CCJ) and intradural AVFs are often associated with aneurysms and varics, and it is sometimes difficult to identify the ruptured point on radiological images. We report a case in which vessel wall magnetic resonance image (VW-MRI) was useful for identifying the ruptured point at the CCJ AVF.
Akinetic mutism following bilateral parasagittal meningioma occupied supplementary motor area removal and the spontaneous recovery of symptoms
Date of publication: 03-May-2024
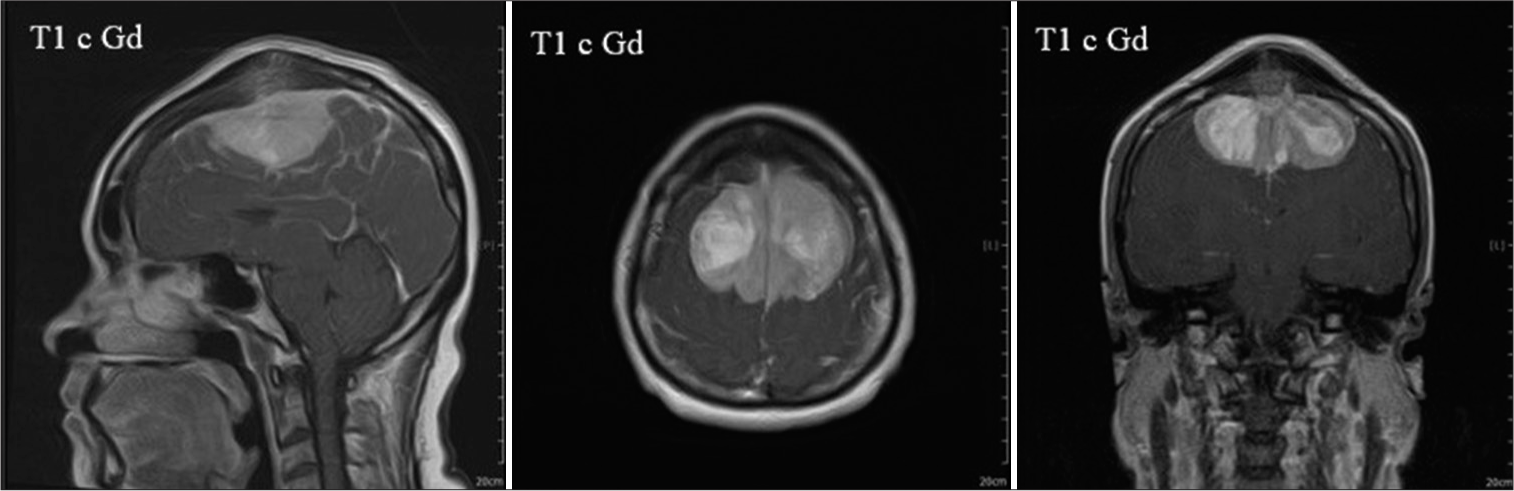
Background: Resection of bilateral parasagittal meningiomas of the dominant cortex is challenging. Some postoperative consequences are difficult to predict due to their low incidence. However, it is essential to recognize reversible symptoms. Akinetic mutism is a devastating but reversible symptom that occurs after supplementary motor area (SMA) injury. This report aims to provide more information to support the clinical progression of this syndrome.
Association of limited dorsal myeloschizis and corpus callosum lipoma: A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 03-May-2024
Background: Intracranial lipomas are a rare clinical entity. These lesions are frequently asymptomatic and originate in the pericallosal area. As they are fat-containing lesions which are intimately attached to the surrounding structures, surgery is not recommended. In some individual reports, subtotal resection is recommended to lessen complications. There have been no previous reports of corpus callosum lipoma (CCL) associated with limited dorsal myeloschizis (LDM).
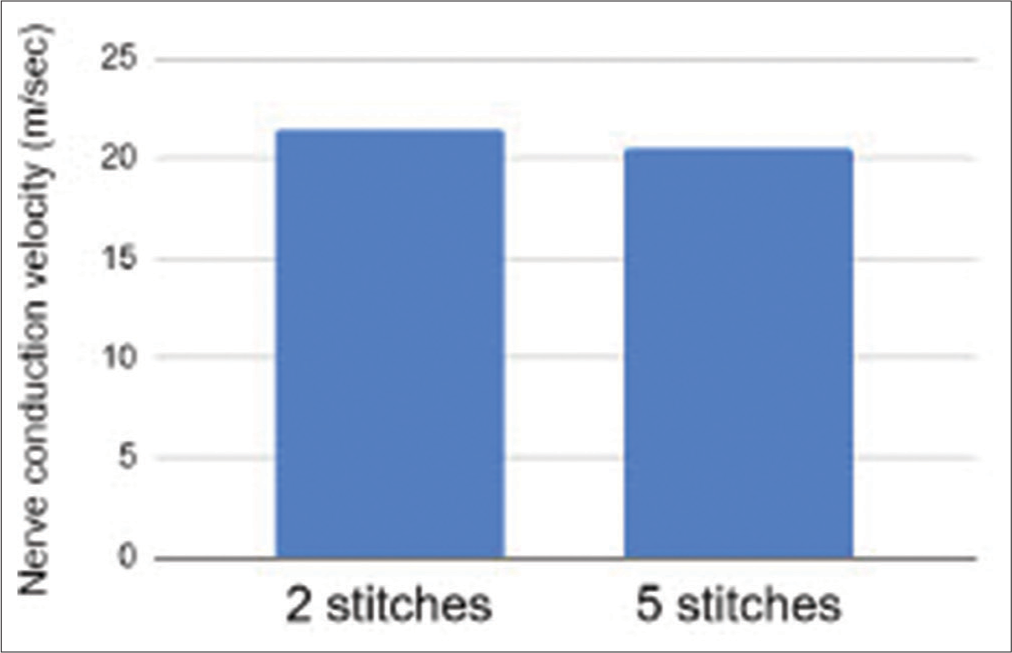
A comparison of two versus five epineural sutures to achieve successful polyethylene glycol (PEG) nerve fusion in a rat sciatic nerve repair model
Date of publication: 03-May-2024
Background: We compared rates of successful polyethylene glycol (PEG) nerve fusion between two epineural suture repairs (2SR) and five epineural suture repairs (5SR) in a rat sciatic nerve transection neurorrhaphy model. We hypothesise that the two and five epineural neural suture repair groups will achieve a similar rate of PEG fusion.
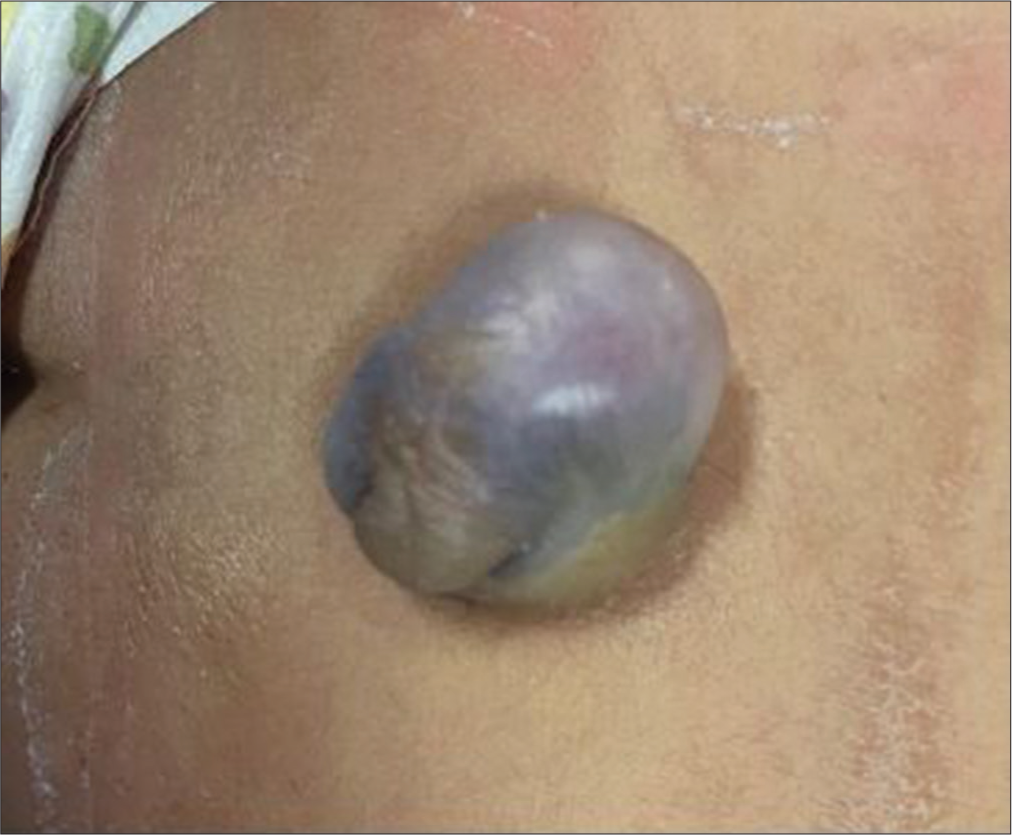
Multiple Abdominal abscesses following ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement in an immunosuppressed patient: An illustrative case
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2024
Background: Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt placement is one of the most performed procedures in neurosurgery to treat various types of hydrocephalus (HC). Immediate or late postoperative complications may quite commonly occur, especially in immunosuppressed patients, who are predisposed to develop rare and difficult-to-treat conditions.
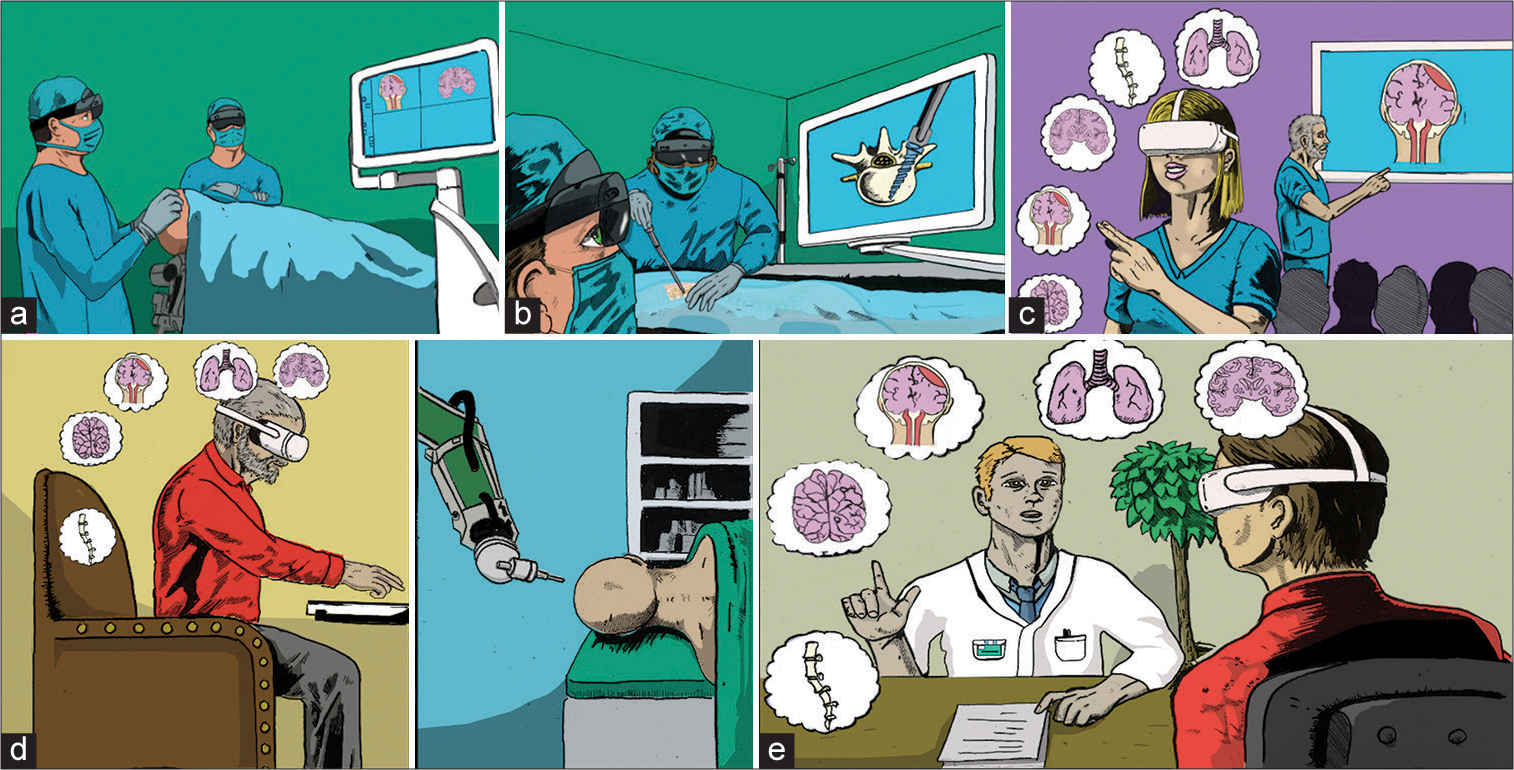
Evolution of the meta-neurosurgeon: A systematic review of the current technical capabilities, limitations, and applications of augmented reality in neurosurgery
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2024
Background: Augmented reality (AR) applications in neurosurgery have expanded over the past decade with the introduction of headset-based platforms. Many studies have focused on either preoperative planning to tailor the approach to the patient’s anatomy and pathology or intraoperative surgical navigation, primarily realized as AR navigation through microscope oculars. Additional efforts have been made to validate AR in trainee and patient education and to investigate novel surgical approaches. Our objective was to provide a systematic overview of AR in neurosurgery, provide current limitations of this technology, as well as highlight several applications of AR in neurosurgery.
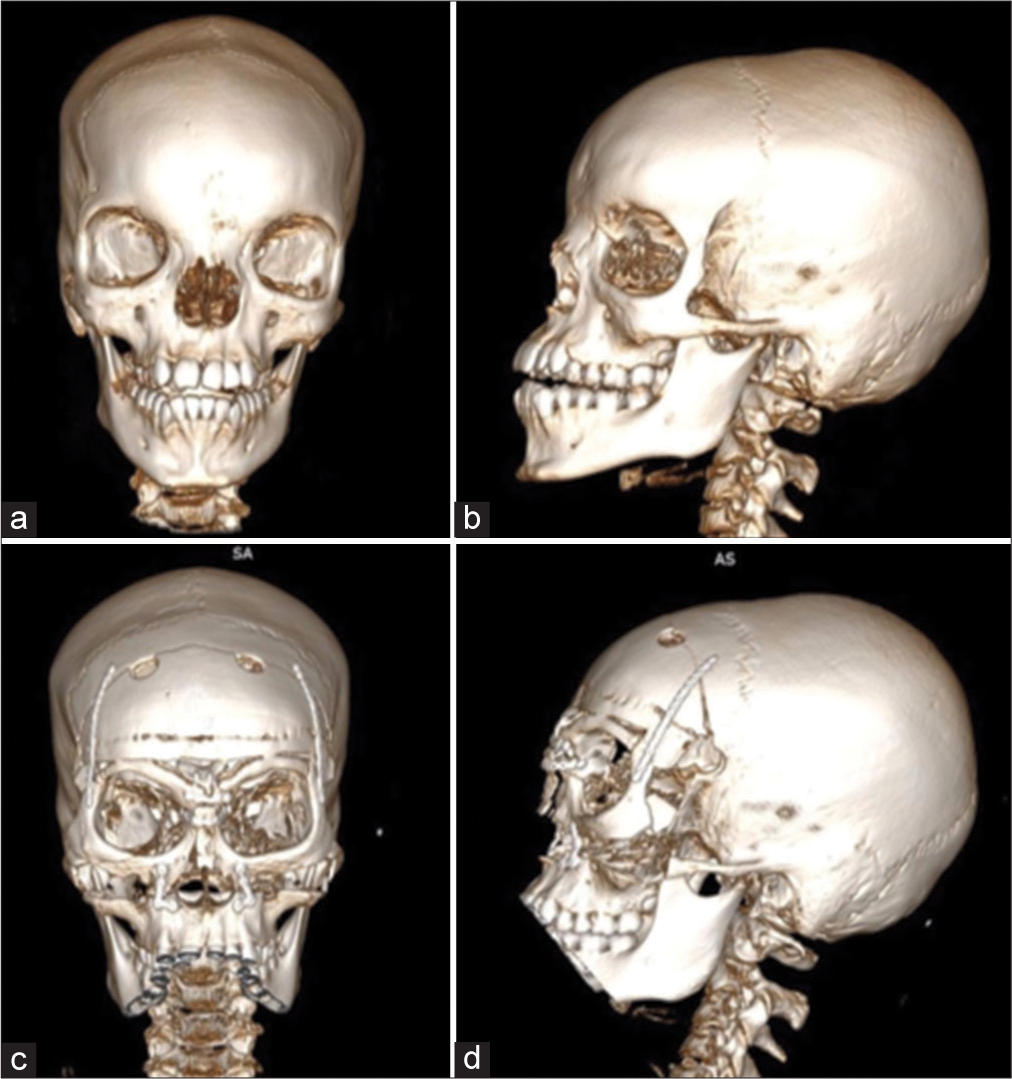
Isolated hypertelorism: Late surgical correction using the box osteotomy technique
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2024
Background: Orbital hypertelorism is a rare congenital condition caused by craniofacial malformations. It consists of complete orbital lateralization, characterized by an increase in distance (above the 95th percentile) of the inner canthal (ICD), outer canthal, and interpupillary distances. It can be approached surgically, and the main techniques are box osteotomy and facial bipartition. The surgical procedure is usually performed before the age of 8. We describe here two patients who underwent late surgical correction using the box osteotomy technique.
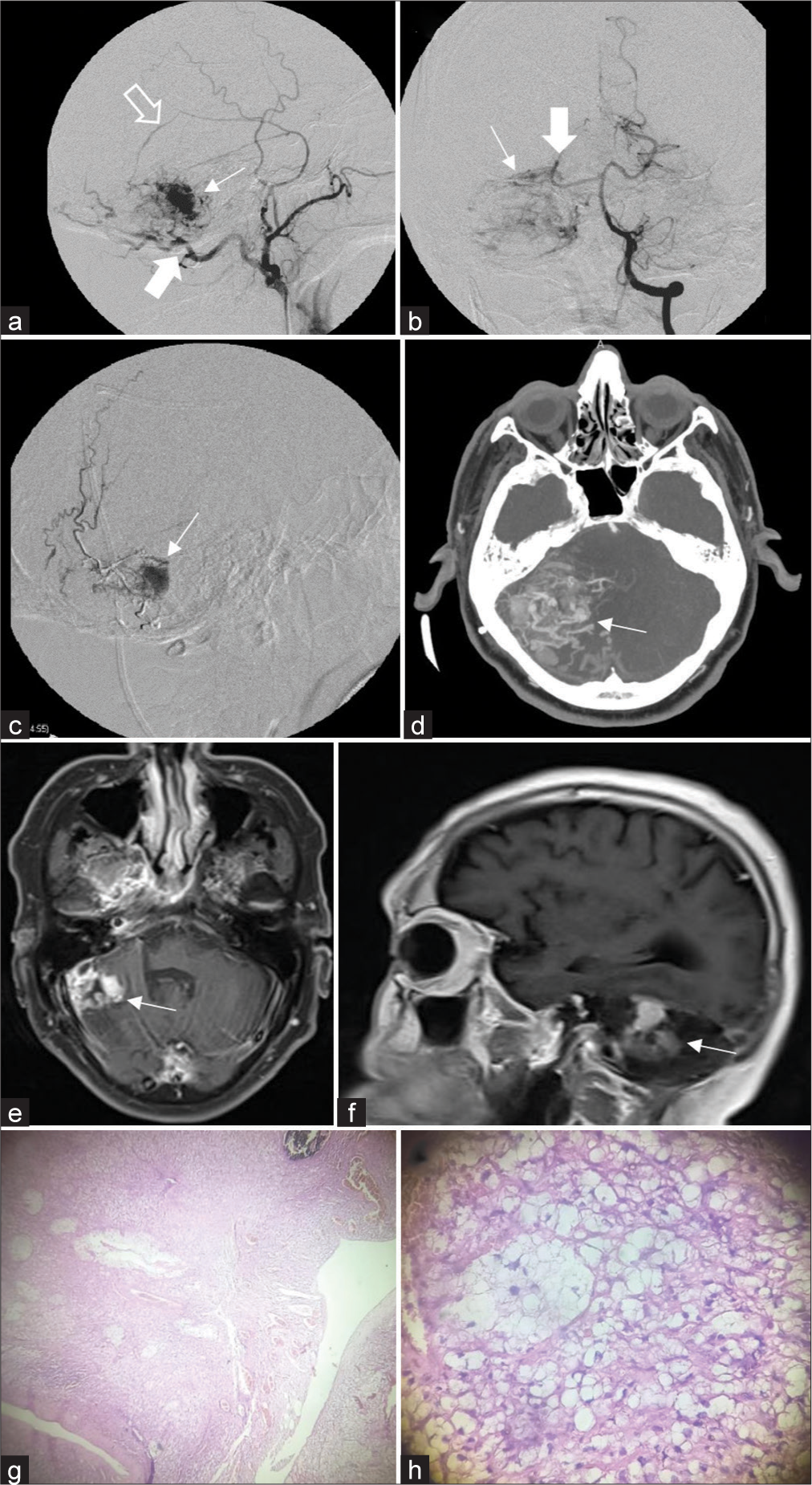
Multimodal management of giant solid hemangioblastomas in two patients with preoperative embolization
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2024
Background: Hemangioblastomas are benign vascular neoplasms, World Health Organization grade I, with the most frequent location in the cerebellum. Complete microsurgical resection can be a challenge due to excessive bleeding, which is why preoperative embolization takes importance.