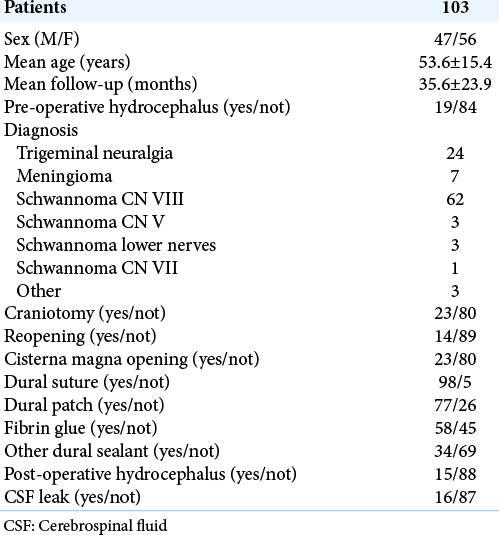
Factors associated with cerebrospinal fluid leak after a retrosigmoid approach for cerebellopontine angle surgery
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: The retrosigmoid approach represents a crucial surgical route to address different lesions in the cerebellopontine angle but cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak still remains the most frequent complication after this approach. Here, we analyzed the impact of different factors in CSF leak development after a retrosigmoid approach. Identifying risk factors related to a specific approach may help the surgeon to tailor the perioperative management and to appropriately counsel patients regarding their risk profile.
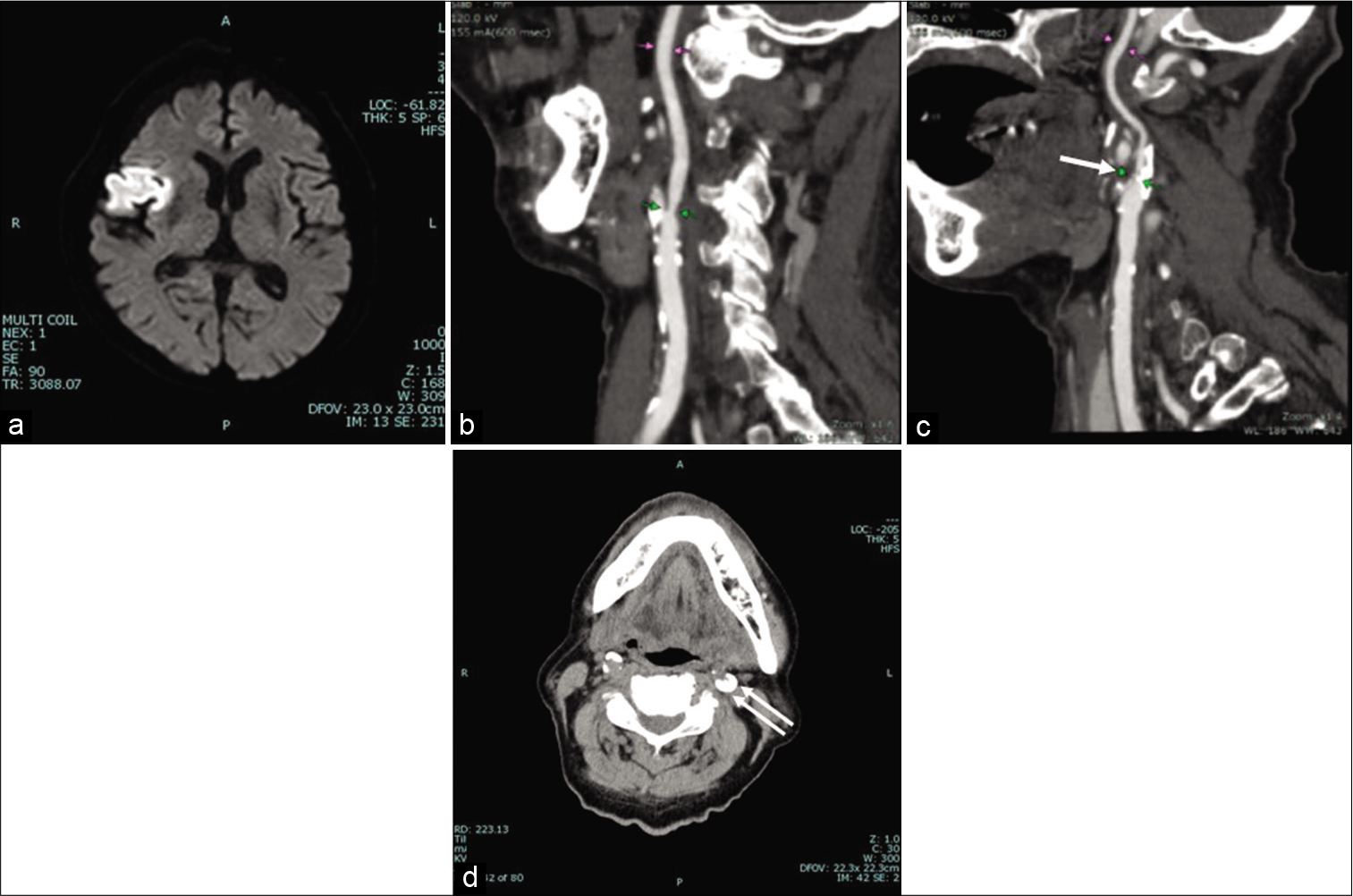
Eagle syndrome presenting as a neurological emergency: A case report
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Eagle syndrome, due to the elongation of the styloid process as well as the calcification of the stylohyoid ligament, rarely presents itself with a major neurological disorder such as a brain infarct.
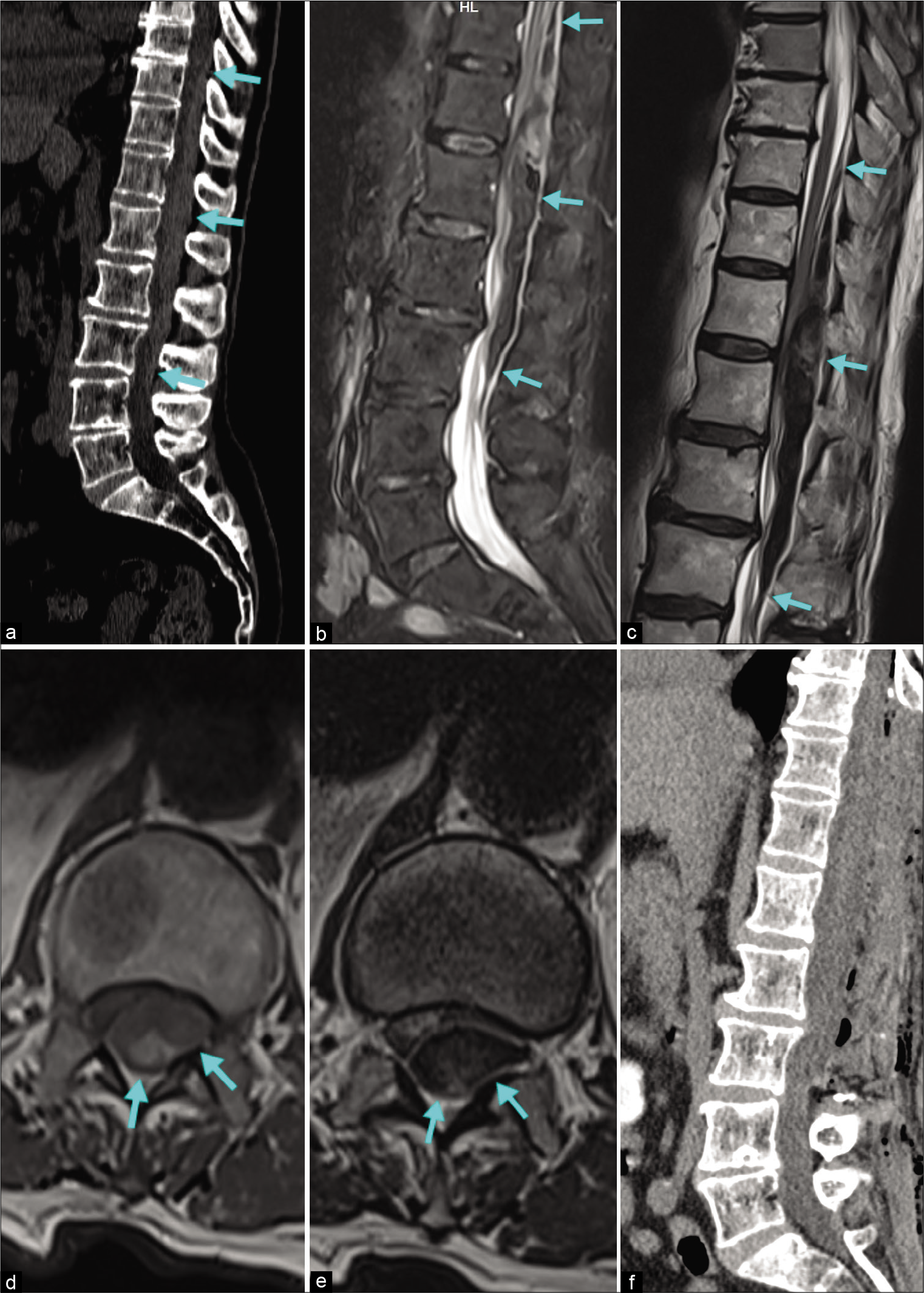
Spontaneous thoracolumbar epidural hematoma in an apixaban anticoagulated patient
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Spontaneous spinal epidural hematomas (SSEHs) are often attributed to anticoagulation. Although they are rare, they may contribute to significant morbidity and mortality.
Severe hemodynamic depression after carotid artery stenting: The problem overcome with a transvenous temporary cardiac pacemaker
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Carotid angioplasty stenting (CAS) may have adverse events including perioperative hemodynamic depression. A transvenous temporary cardiac pacemaker (TTCP) is an option for preventing devastating sequelae due to circulatory failure. An exploration of the predictors of hemodynamic depression following CAS is valuable for selecting candidates for preoperative TTCP implantation before CAS.
Intraoperative epileptogenic network visualization using gamma oscillation regularity correlation analysis in epilepsy surgery
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: We have recently demonstrated that gamma oscillation (30–70 Hz) regularity (GOR) analysis accurately localized epileptogenic focus using intraoperative electrocorticographic data. In this report, we assessed whether GOR correlation analysis could depict epileptogenic networks intraoperatively. Dual foci in temporal lobe epilepsy without hippocampal structural abnormalities are difficult to diagnose. Using our GOR correlation analysis, we aimed to intraoperatively visualize such dual foci and epileptogenic networks.
Cerebral cavernous malformation in a child leading to a fatal subarachnoid hemorrhage – “silent but sinister:” A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), otherwise known as cavernous hemangiomas/ cavernomas, are a type of vascular malformation. It is the third most common cerebral vascular malformation, histologically characterized by ectatic, fibrous, blood filled “caverns” with thin-walled vasculature without intervening normal brain parenchyma.
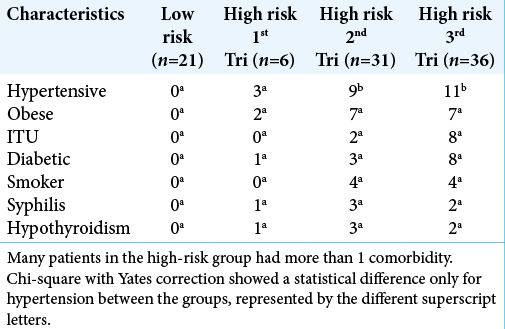
Intracranial pressure and laboratory parameters in high- and low-risk pregnant women
Date of publication: 31-May-2021
Background: Pregnancy can trigger several pathological changes, thus representing a great challenge for gynecology and obstetrics. The objective is to evaluate high- and low-risk pregnant women through Intracranial pressure (ICP) and laboratory parameters.
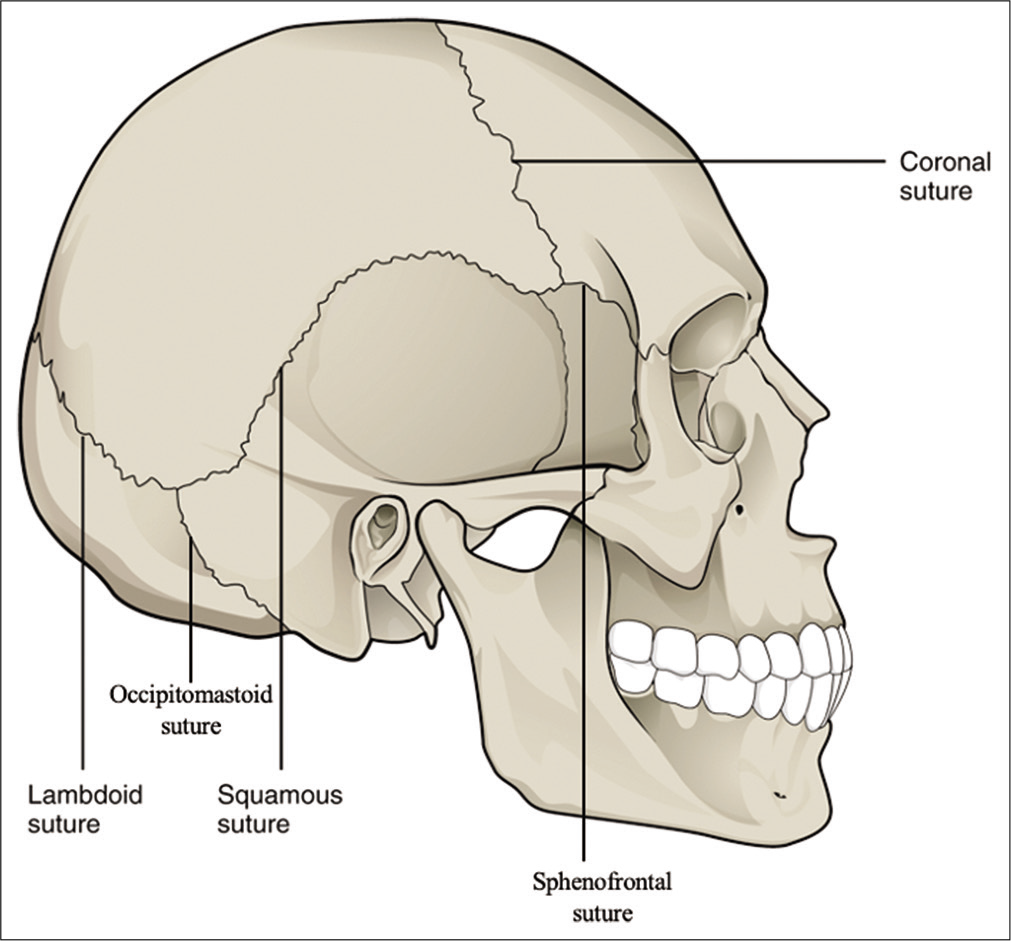
Magnetic resonance imaging analysis of human skull diploic venous anatomy
Date of publication: 31-May-2021
Background: The skull diploic venous space (DVS) represents a potential route for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) diversion and absorption in the treatment of hydrocephalus. The goal of this study was to carry out a detailed characterization of the drainage pattern of the DVS of the skull using high-resolution MRI, especially the diploic veins draining to the lacunae laterales (LLs) since the LLs constitute an important channel for the CSF to access the superior sagittal sinus and subsequently the systemic circulation. The objective was to identify those skull regions optimally suited for an intraosseous CSF diversion system.
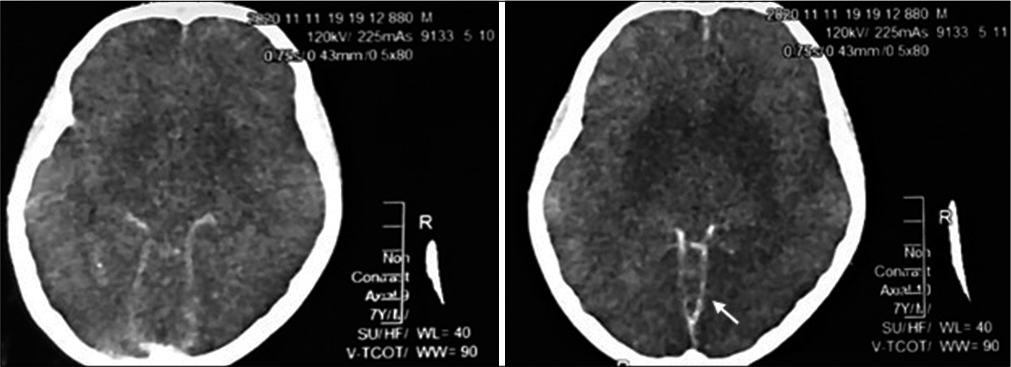
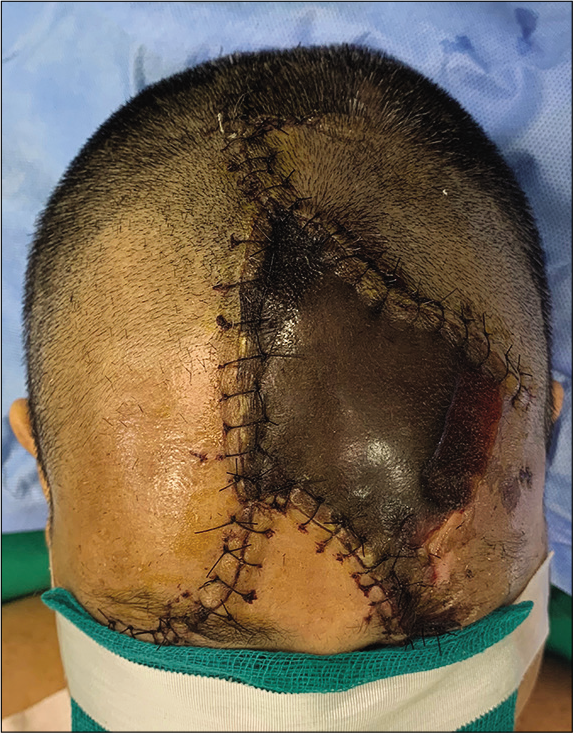
Minimalistic reconstruction of exposed skull in a complex craniovertebral polytrauma
Date of publication: 31-May-2021
Background:
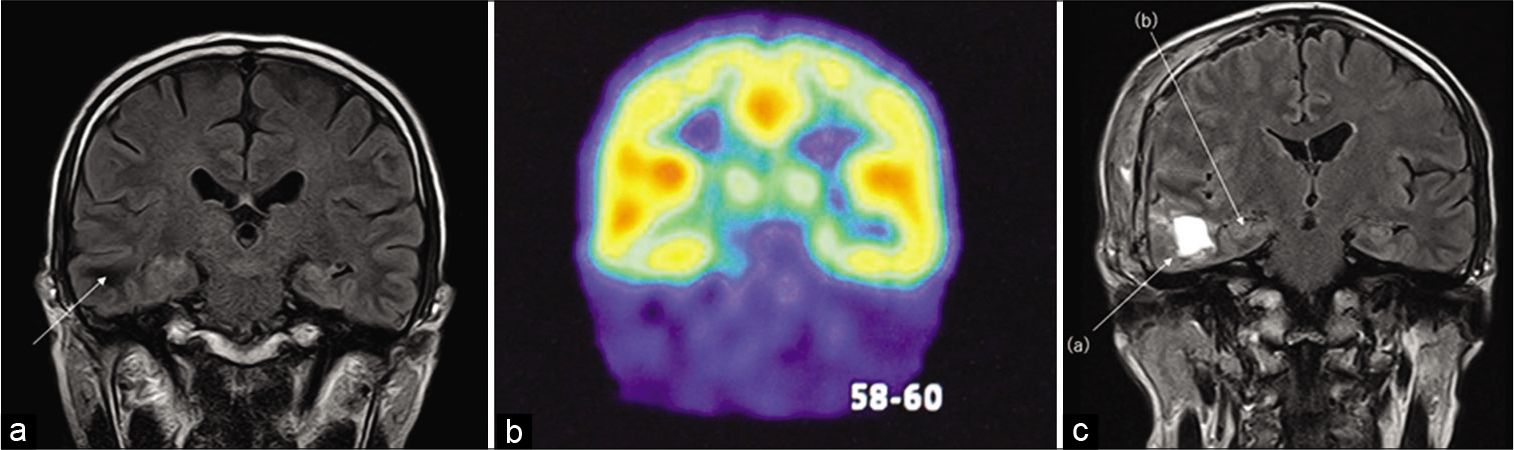
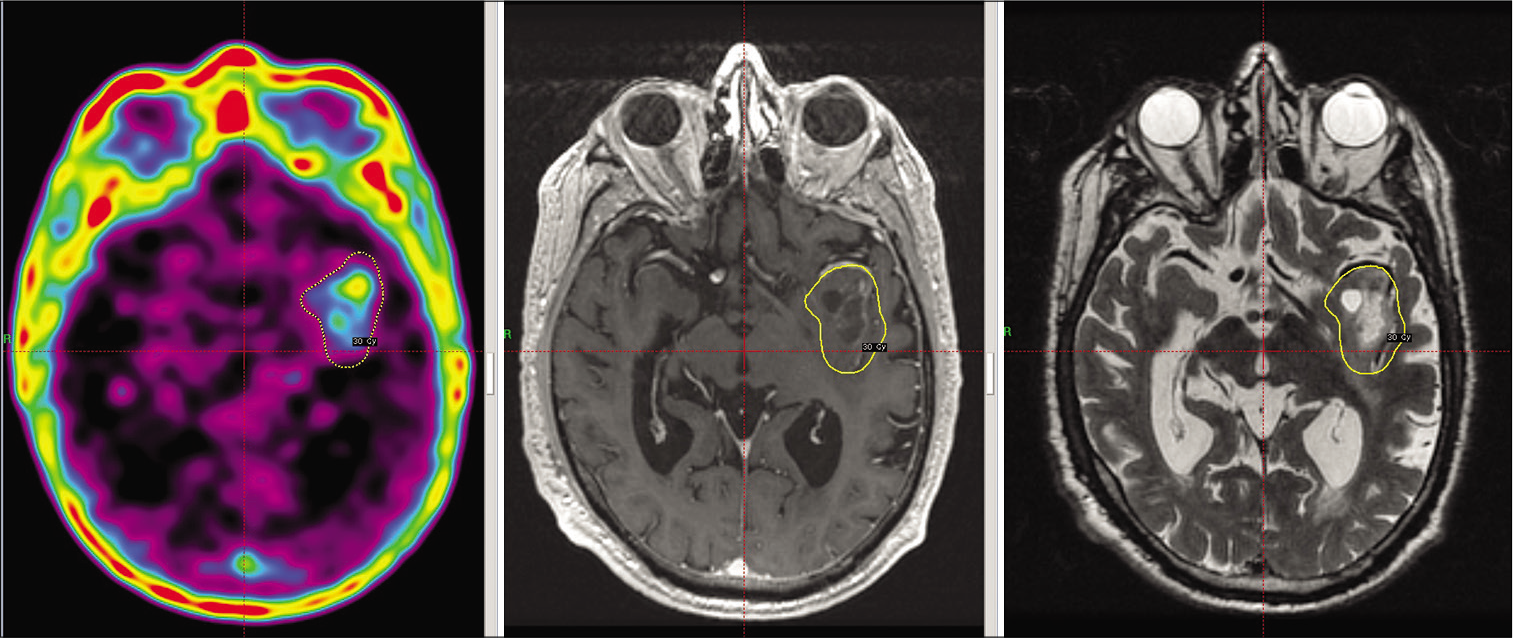
C-methionine-PET-guided Gamma Knife radiosurgery boost as adjuvant treatment for newly diagnosed glioblastomas
Date of publication: 31-May-2021
Background: The most common glial tumor is the glioblastoma, and the prognosis remains dismal despite a multimodal therapeutic approach. The role of radiosurgery for the treatment of glioblastomas has been evaluated in several studies with some benefit at the recurrent stage. We evaluate the results of the protocol administered at the Gamma Knife unit administering radiosurgery as a boost to metabolic active parts of the tumor after the patient had completed traditional external beam radiotherapy (XBRT) as part of the Stupp protocol for high-grade gliomas.