Causes of hospital readmissions within 7 days from the neurosurgical service of a quaternary referral hospital
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: Evaluation of readmission rates as a proxy metric of health-care quality in neurological surgery has grown to become a prevalent area of investigation in the last several years. Significant attention has been paid to 30-day readmission rates due to the financial incentive to health-care providers following the enforcement of the penalties created by the Affordable Care Act. However, relatively little attention has been paid to patients readmitted within 7 days of discharge to large quaternary neurological surgery services. This study was conducted to examine the causes and unique characteristics of 7-day readmission rates from a neurosurgical service at a large quaternary referral hospital.
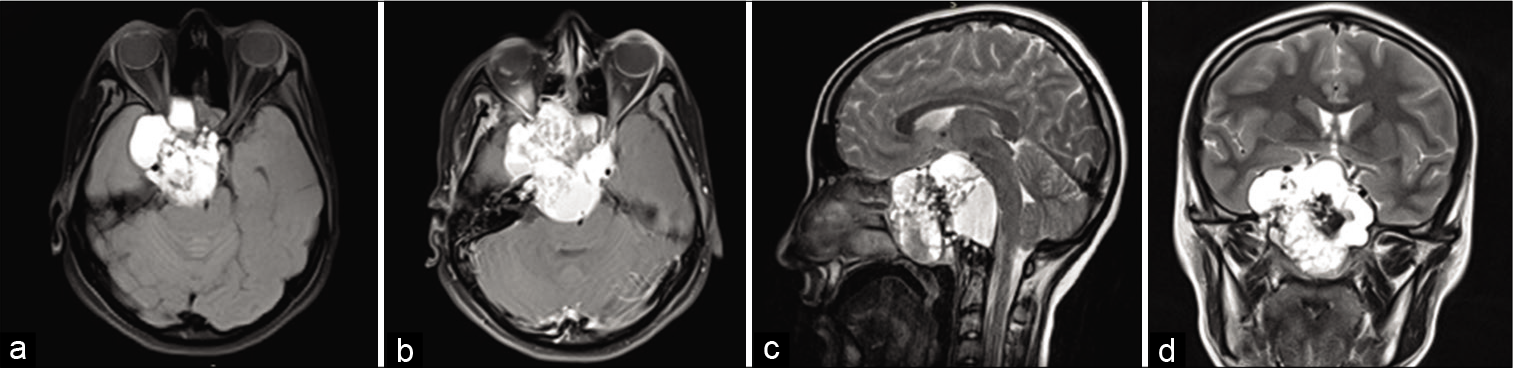
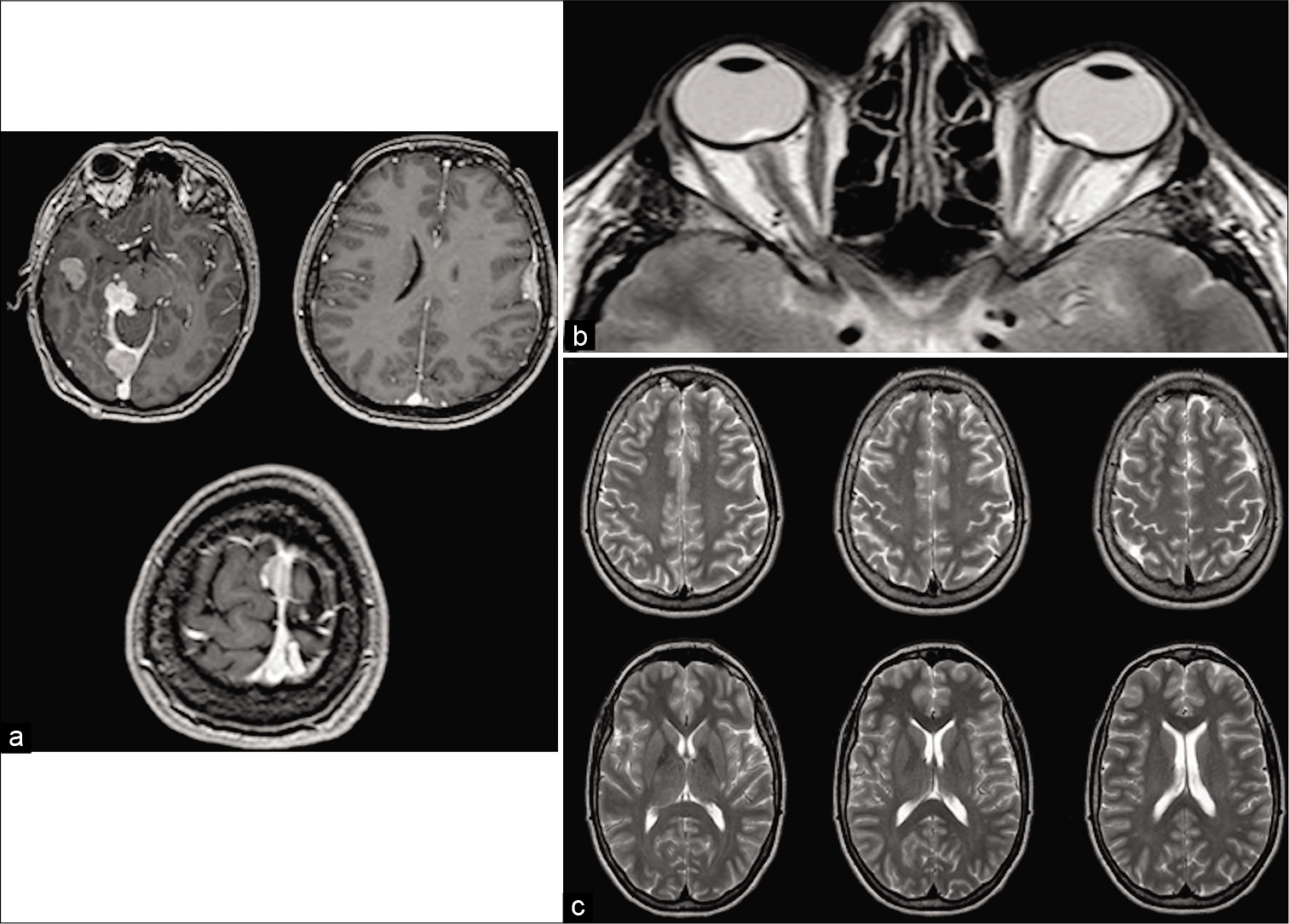
Pure endoscopic transsphenoidal treatment of skull base ameloblastoma with intracranial extension: Case report and literature review
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: Ameloblastoma is a benign locally invasive lesion that represents 1% of all oral tumors. Epidemiological characteristics are variable in the literature. The most common origin sites are mandible and maxilla. Rarely presents metastasis, but the skull base, lymph nodes, and the lung are described as metastatic sites. Low recurrence rates were reported by the authors when surgical treatment achieved complete resection.
Double neurophysiological certification of the filum terminale during sectioning surgery in pediatric population
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: Surgery of thickened-fibrolipoma filum terminale (FT) is performed routinely and without conflict but is not a risk-free surgical procedure. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring with mapping techniques can help to certify the FT before sectioning. However, a tailored surgical approach to cauda equina and a low threshold of surrounding nerve roots can confuse the final surgical decision. The aim is to demonstrate the usefulness of this double methodology for FT certification.
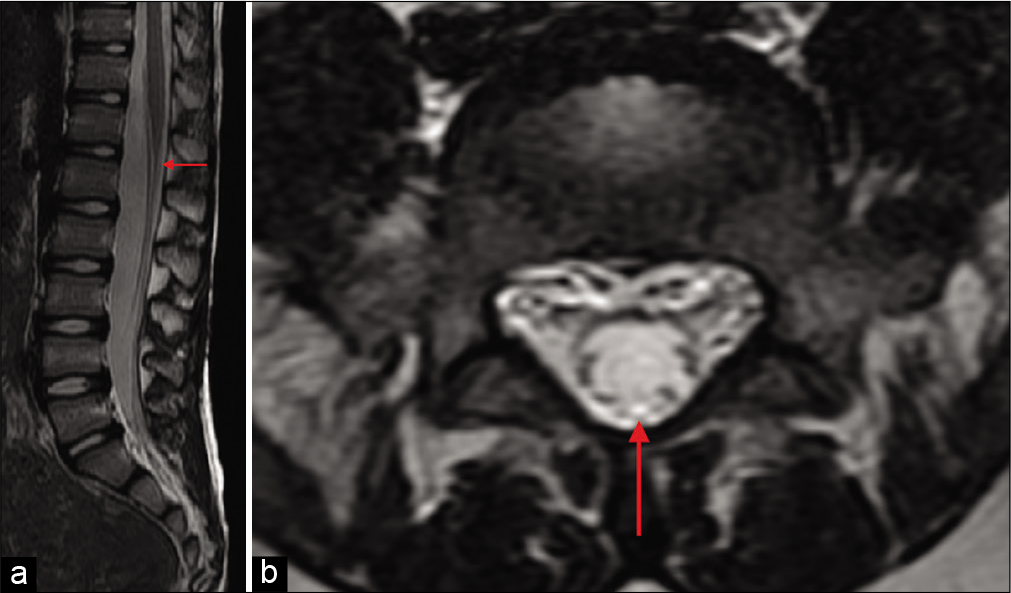
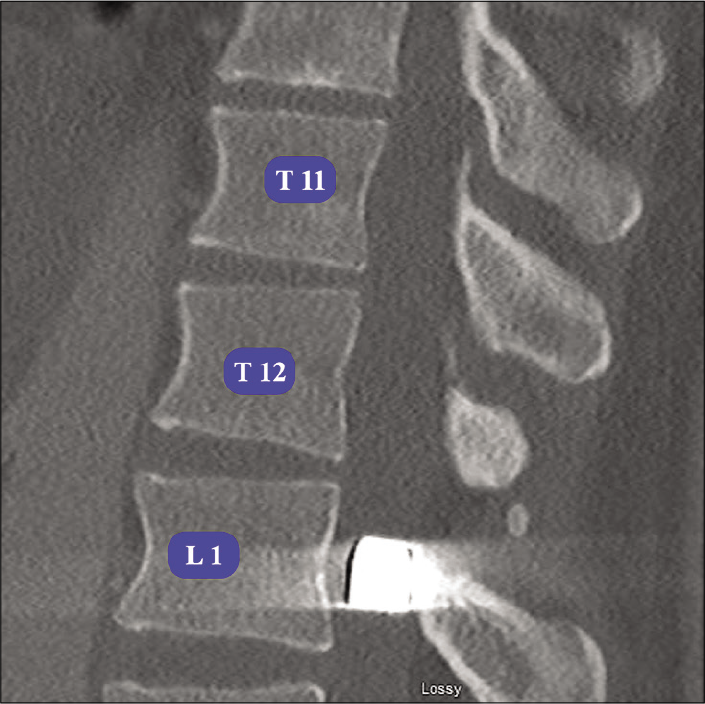
Surgical removal of a spinal intrathecal projectile led to a significant improvement of cauda equina syndrome
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: Penetrating gunshot wounds of the spine are common and can cause severe neurological deficits. However, there are no guidelines as to their optimal treatment. Here, we present a penetrating injury to the lower thoracic spine at the T12 level that lodged within the canal at L1, resulting in a cauda equina syndrome. Notably, the patient’s deficit resolved following bullet removal.
Elective inferior temporal lobe resection as an adjunct to subtemporal approach for a case of tentorial meningioma arising from the middle part of the free edge of the tentorium: A case report
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: Tentorial meningiomas attached to the inner edge of the tentorium are difficult to excise due to their deep location. Sufficient space may not be always available through a subtemporal approach. Thus, the aim of not retracting the brain is not fulfilled.
Subdural empyema caused by Morganella morganii
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: Morganella morganii is a species of Gram-negative enteric rod found in normal human gut flora. Pathologically, this most often presents as urinary tract infections, wound infections, and bacteremia. It is highly uncommon for M. morganii to be implicated in a central nervous system infection, with only 12 reported cases of parenchymal abscesses or meningitis.
A case of cerebral infarction due to pleomorphic carcinoma of the lung
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: With the increase in endovascular treatment, reports of embolism other than thrombus are scattered, but intracranial tumorigenic embolism is rare and difficult to diagnose. Here, we describe a case of a tumorigenic embolism in a patient with lung cancer whose invasion into the vascular system was not detected on preoperative whole-body imaging.
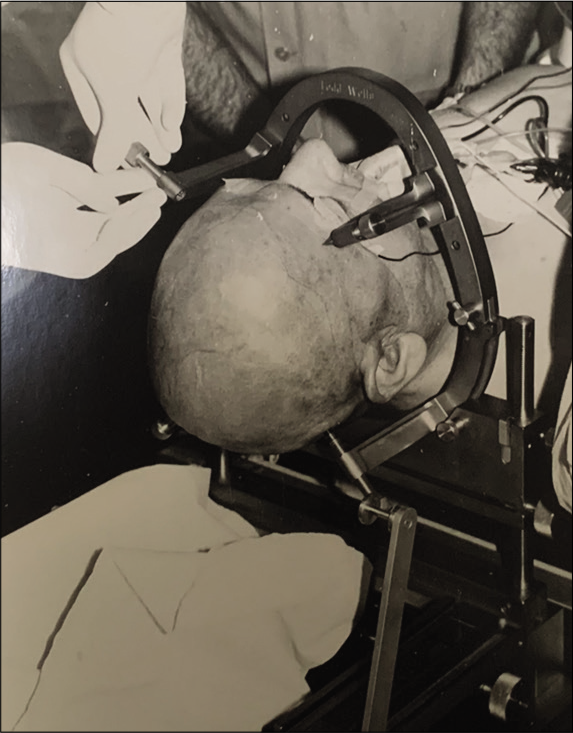
Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhages and frame-based stereotactic brain biopsy
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: Stereotactic biopsy is a well-established procedure in neurosurgery. Our objective is to define the clinical, radiological, and technical factors that can condition the emergence of postbiopsy symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage. Based on our findings, we suggest recommendations to improve its usual clinical practice.
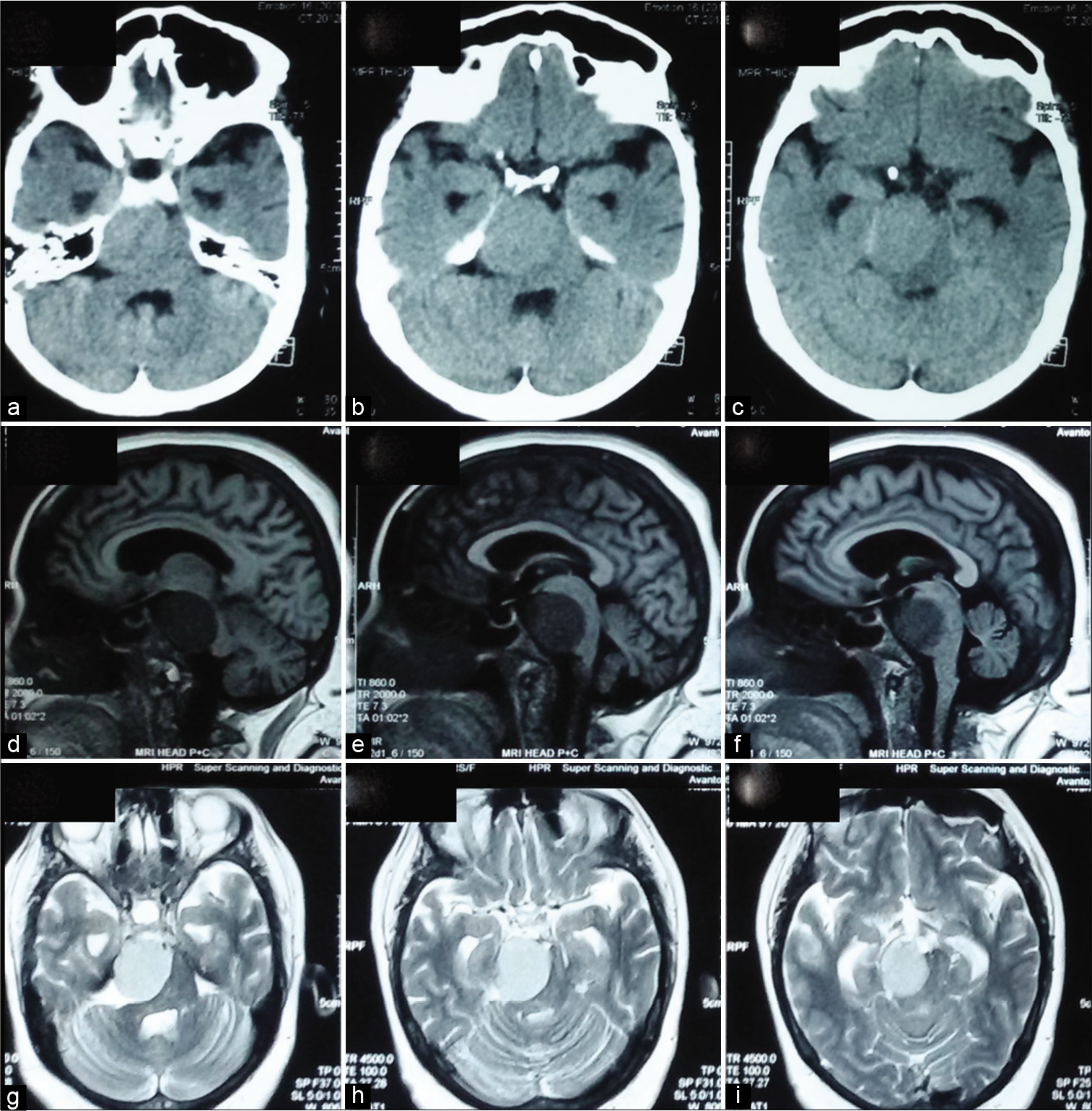
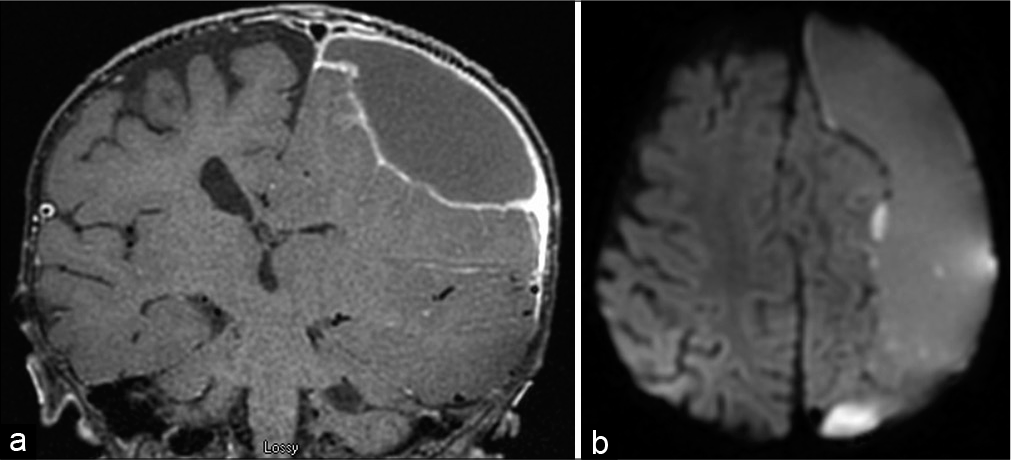
Slit-like hypertensive hydrocephalus: Report of a late, complex, and multifactorial complication in an oncologic patient
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: Several sophisticated techniques and many chemotherapy drugs have improved life expectancy of oncologic patients allowing us to observe late complications which present many years after the initial treatment.
Resolution of cauda equina syndrome after surgical extraction of lumbar intrathecal bullet
Date of publication: 25-Jul-2020
Background: Gunshot wound (GSW) injuries to the spinal column are correlated with potentially severe neurological damage. Here, we describe a GSW to the thoracolumbar junction (e.g., T12/L1 level) which resulted in a cauda equina syndrome that resolved once the bullet was removed.