Co-existence of multiple sclerosis and germinoma in an adult male: Case report
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2021
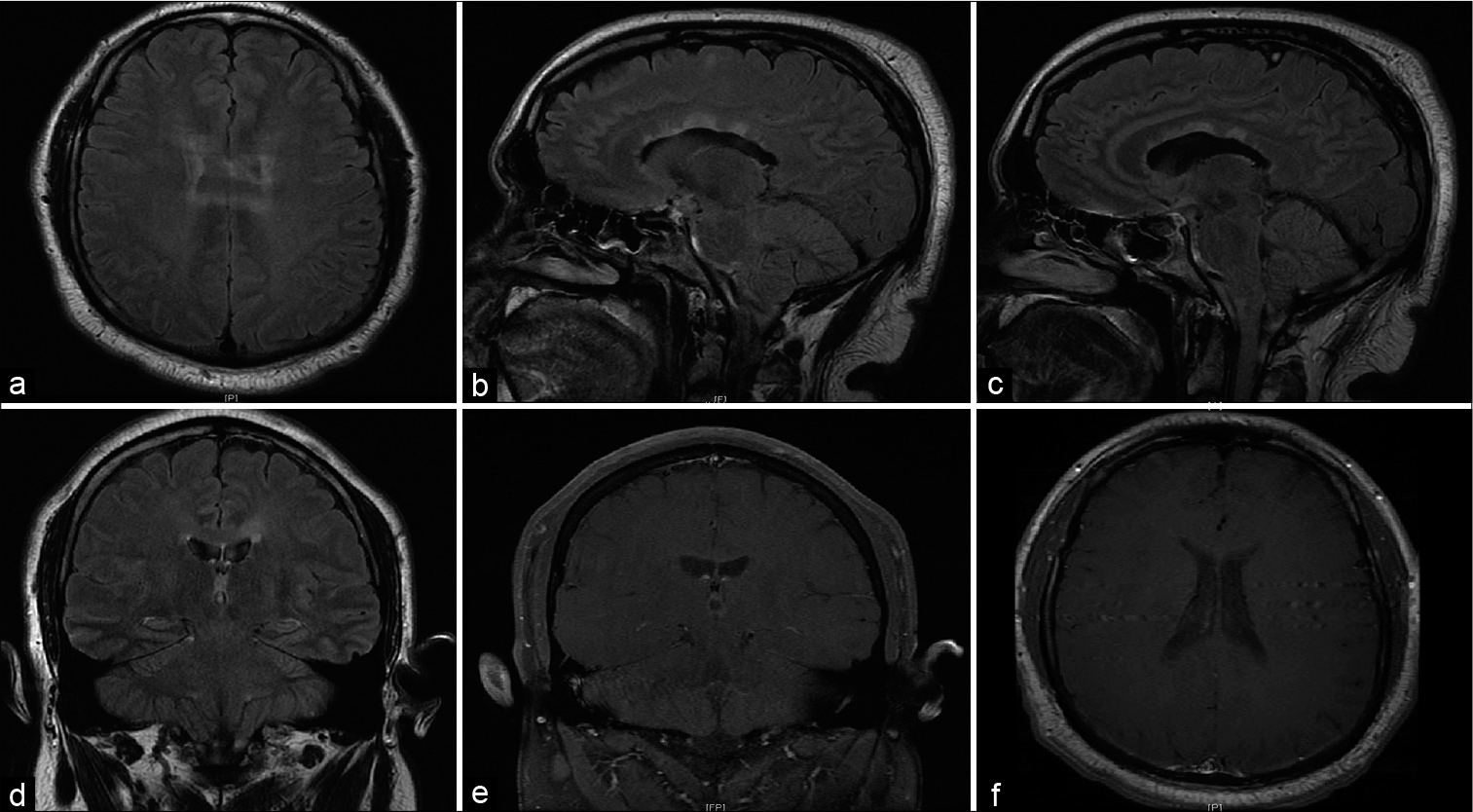
Background: Concurrent diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS) and the central nervous system (CNS) germinoma is rare. The diagnostic criteria for MS rely primarily on clinical presentation, and CNS germinoma can present as an MS mimic. These factors contribute to the rarity of dual diagnosis.
Percutaneous vertebroplasty for symptomatic osteoporotic compression fractures: A single–center prospective study
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2021
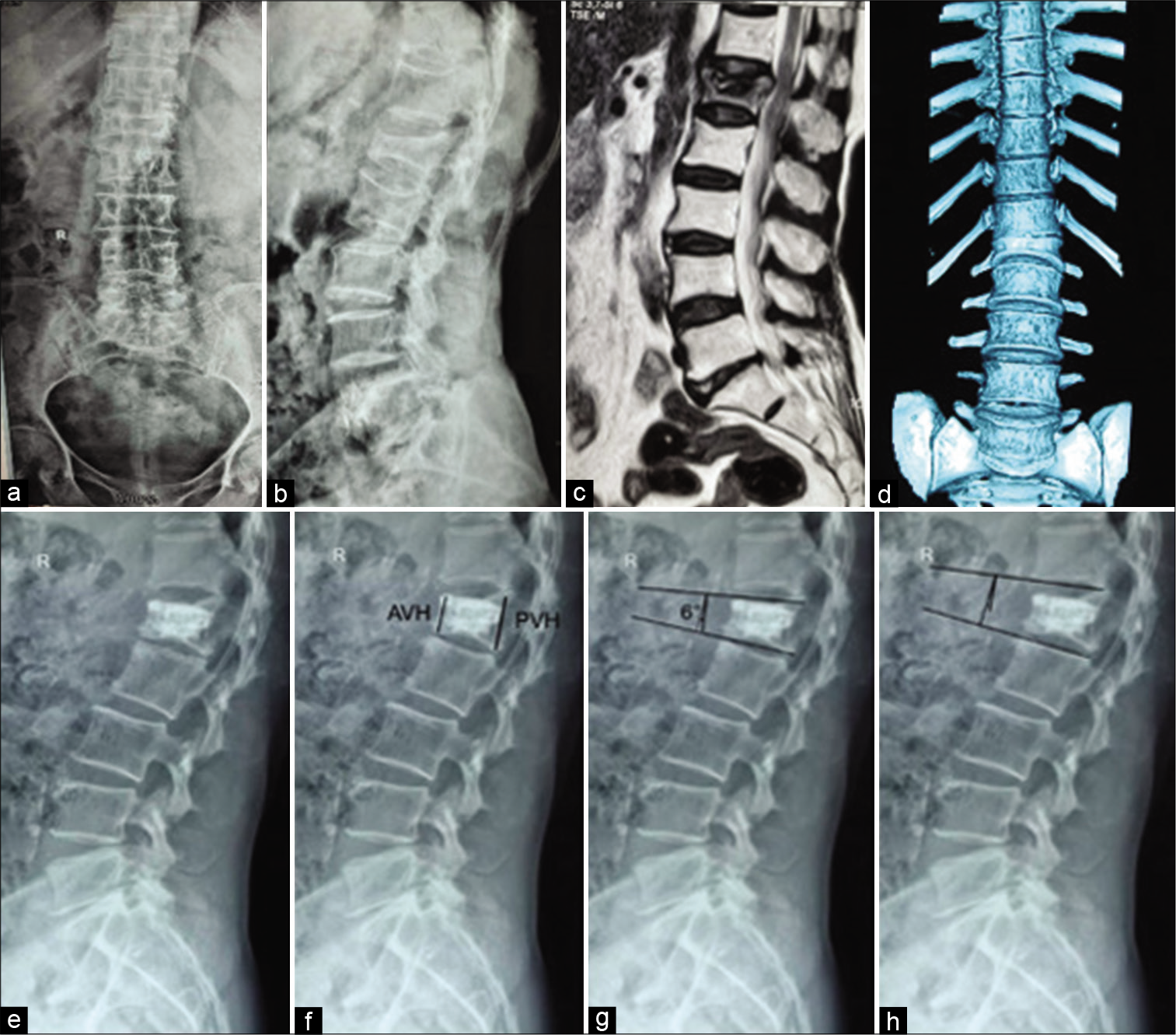
Background: Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) increasingly occur with advancing age, and are associated with significant morbidity, mortality, and cost. We assessed the clinical efficacy, radiological, and functional outcomes for patients undergoing percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP) due to OVCFs, with a special focus on the frequency of new vertebral compression fractures (VCFs).
Transport of patients with giant disfiguring cranial tumors from Africa to the US for collaborative multidisciplinary treatment
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2021
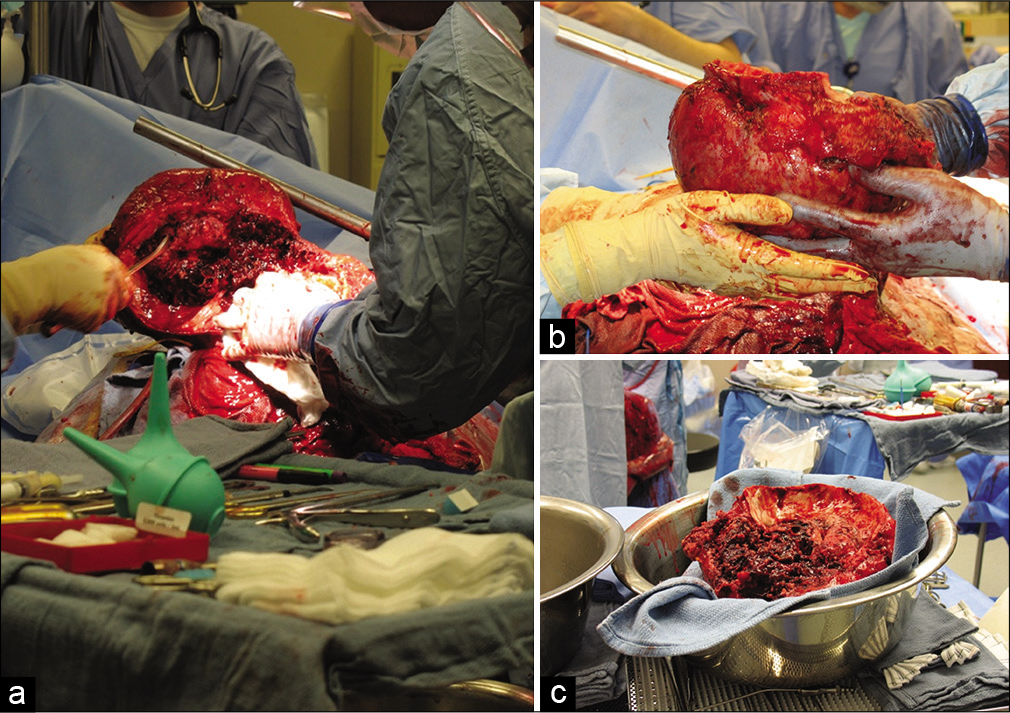
Background: Giant disfiguring cranial tumors are exceptionally rare and develop over the course of many years, typically in patients who lack access to medical care. Here, we describe four patients who were flown to our center for treatment by a multidisciplinary surgical team, who had previously been turned down for treatment at multiple international centers in Africa, Europe, and the United States (US) due to complexity and financial concerns. The case series describes socioeconomic implications and the feasibility of offering such care to patients from outside the US.
Perioperative cardiovascular changes in patients with traumatic brain injury: A prospective observational study
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2021
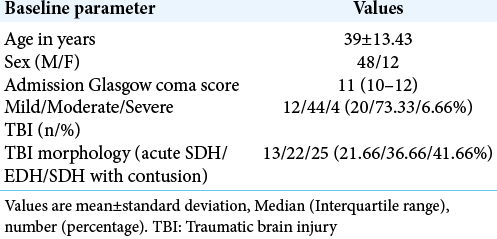
Background: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an acutely stressful condition. Stress and conglomeration of various factors predispose to the involvement of other organ systems. The stress response from TBI has been associated with cardiovascular complications reflecting as repolarization abnormalities on electrocardiogram (ECG) to systolic dysfunction on echocardiography. However, the perioperative cardiac functions in patients with TBI have not been evaluated.
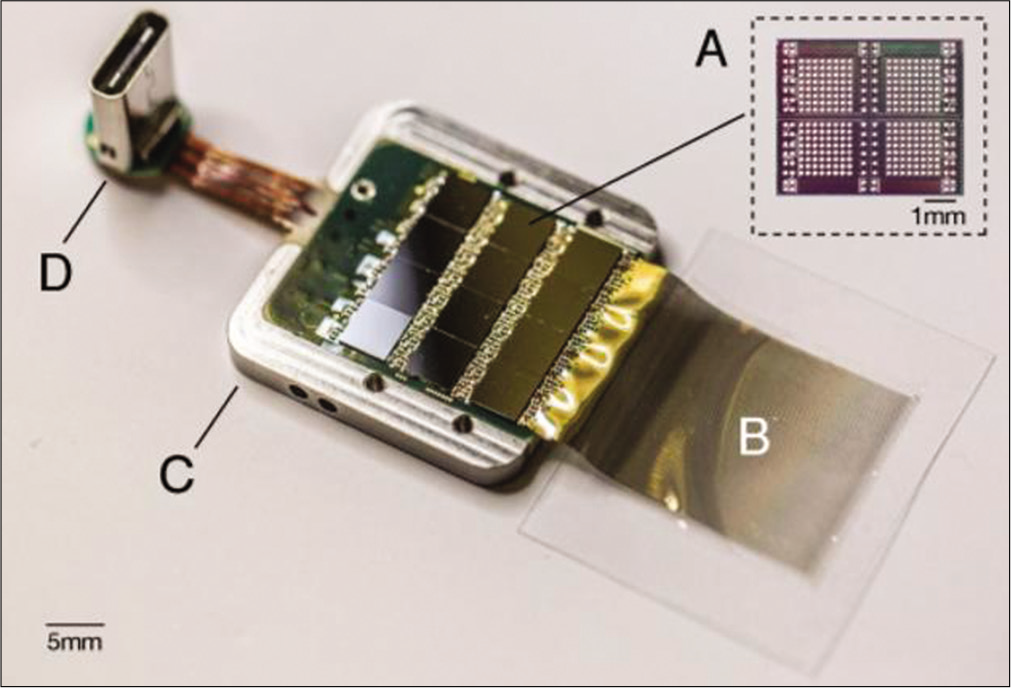
Neurochips: Considerations from a neurosurgeon’s standpoint
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2021
Abstract
A neurochip comprises a small device based on the brain-machine interfaces that emulate the functioning synapses. Its implant in the human body allows the interaction of the brain with a computer. Although the data-processing speed is still slower than that of the human brain, they are being developed. There is no ethical conflict as long as it is used for neural rehabilitation or to supply impaired or missing neurological functions. However, other applications emerge as controversial.
To the best of our knowledge, there have no been publications about the neurosurgical role in the application of this neurotechnological advance. Deliberation on neurochips is primarily limited to a small circle of scholars such as neurotechnological engineers, artists, philosophers, and bioethicists. Why do we address neurosurgeons? They will be directly involved as they could be required to perform invasive procedures.
Future neurosurgeons will have to be a different type of neurosurgeon. They will be part of interdisciplinary teams interacting with computer engineers, neurobiologist, and ethicists. Although a neurosurgeon is not expected to be an expert in all areas, they have to be familiar with them; they have to be prepared to determine indications, contraindications and risks of the procedures, participating in the decision-making processes, and even collaborating in the design of devices to preserve anatomic structures. Social, economic, and legal aspects are also inherent to the neurosurgical activity; therefore, these aspects should also be considered.
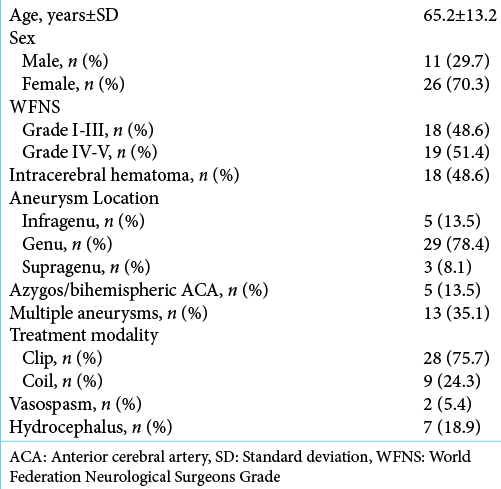
Current treatment options and prognostic factors for ruptured distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysms
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2021
Background: Distal anterior cerebral artery (ACA) aneurysms are rare, representing 1–9% of all intracranial aneurysms. The best treatment strategy for these aneurysms continues to be debated. We clarified the clinical features and treatment outcomes of patients with ruptured distal ACA aneurysms according to the treatment options at our institute.
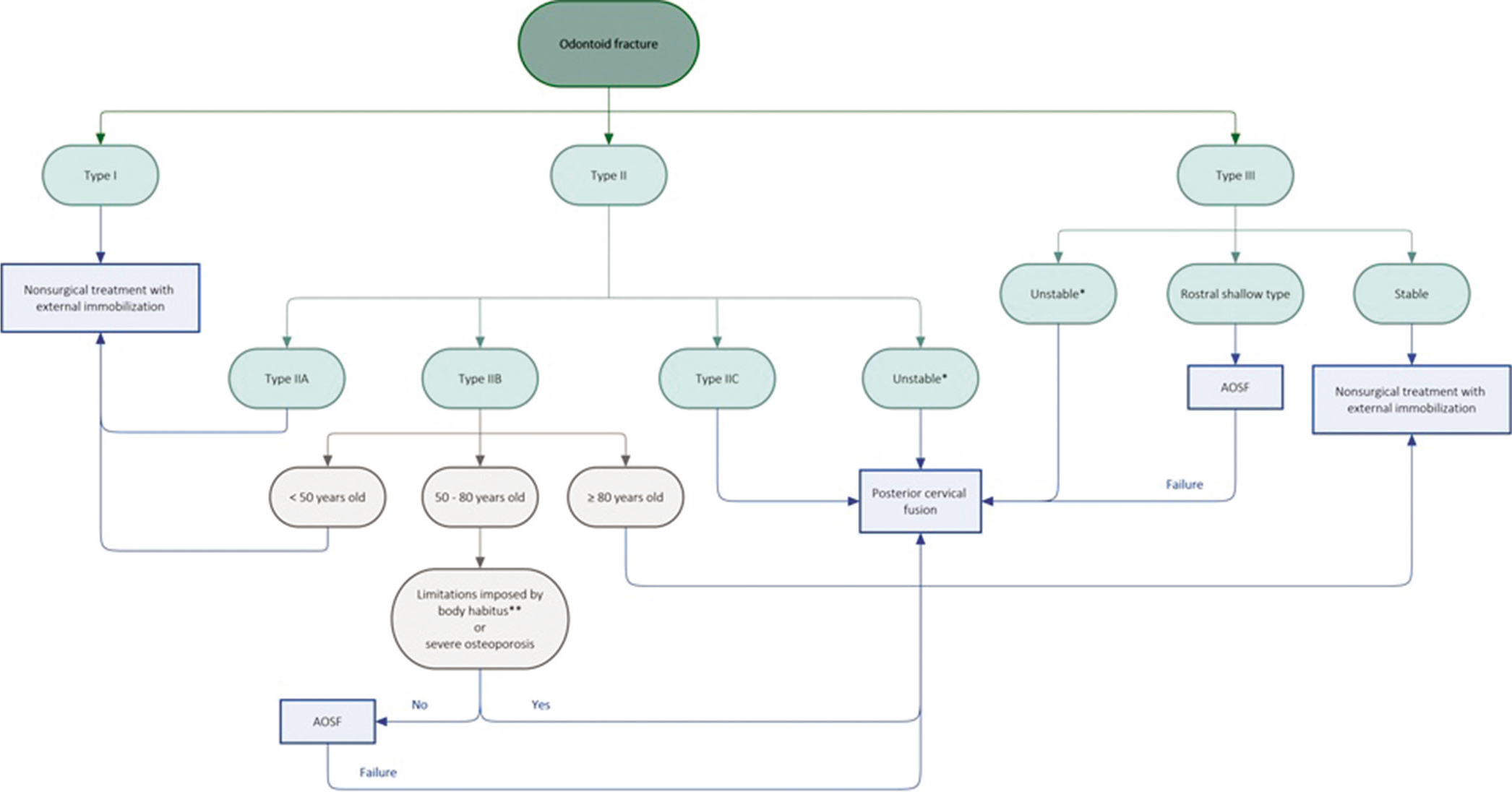
Determination and optimization of ideal patient candidacy for anterior odontoid screw fixation
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2021
Background: Odontoid process fractures are one of the most common spine fractures, especially in patients over age 70. There is still much controversy over the ideal candidate for anterior odontoid screw fixation (AOSF), with outcomes affected by characteristics such as fracture morphology, nonideal body habitus, and osteoporosis. Therefore, this systematic review seeks to discuss the optimal criteria, indications, and adverse postoperative considerations when deciding to pursue AOSF.
The utility of deep brain stimulation surgery for treating eating disorders: A systematic review
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2021
Background: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has demonstrated preliminary success as a treatment for neuropsychological disorders including obsessive-compulsive disorder and substance use disorder. This systematic review aims to assess the use of DBS in treating eating disorders (EDs) to determine its utility and the extent of adverse effects.
Spontaneous epidural hematoma of the cervical spine in two patients with sarcoidosis
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2021
Background: Sarcoidosis is correlated with hematological abnormalities that can result in spontaneous spinal epidural hematomas (EDH). As there is significant risk for permanent neurologic sequelae due to acute cord compression, these lesions often warrant emergent surgical intervention.
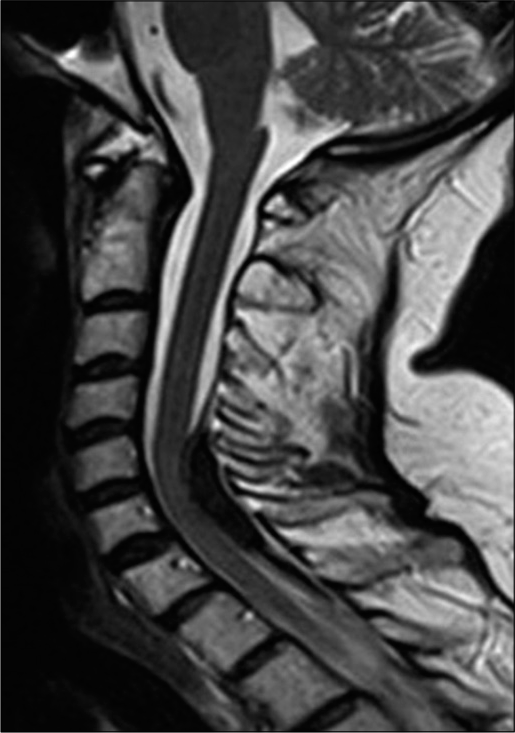
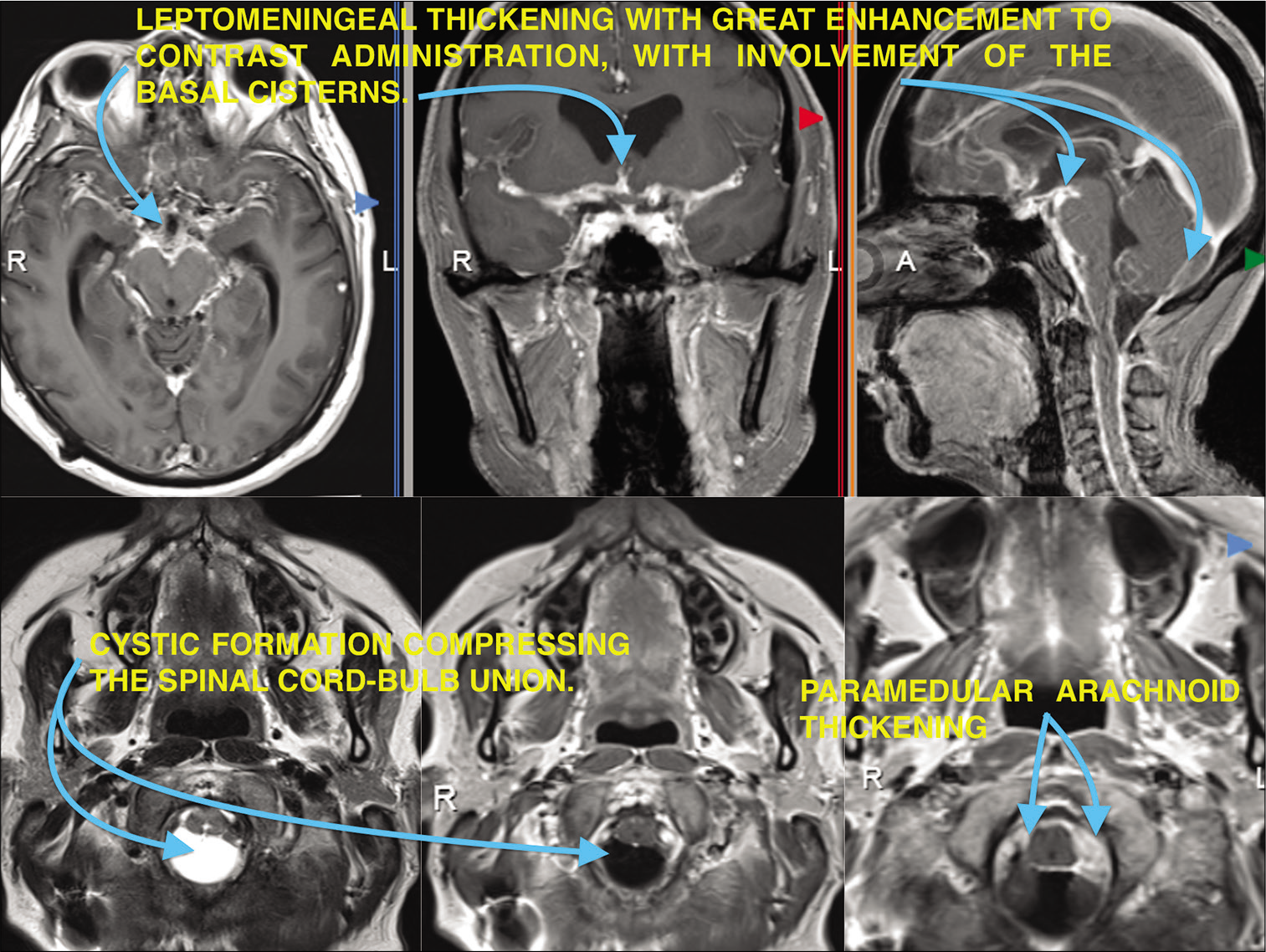
Cryptococcal meningitis presenting as anterior spinal cord syndrome with accessory nerve palsy in immunocompetent patient: A case report
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2021
Background: Cryptococcus has a tropism for the nervous system with a higher prevalence of infection in immunosuppressed patients; it remains a major cause of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-related mortality worldwide. Neurological compromise caused by this microorganism mainly debuts as a meningeal syndrome, spinal involvement has been reported in literature, neuropathological assessments have found Cryptococci in spinal roots and meninges, with perineuritic adhesions probably explaining compromise lower cranial nerves and even spinal nerve roots.