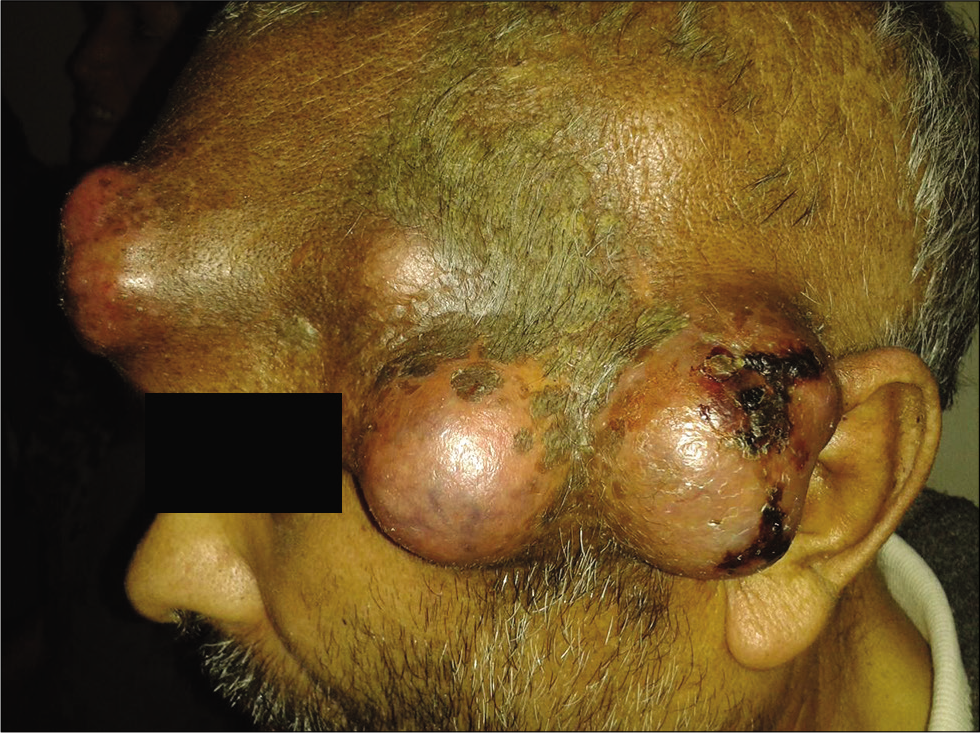
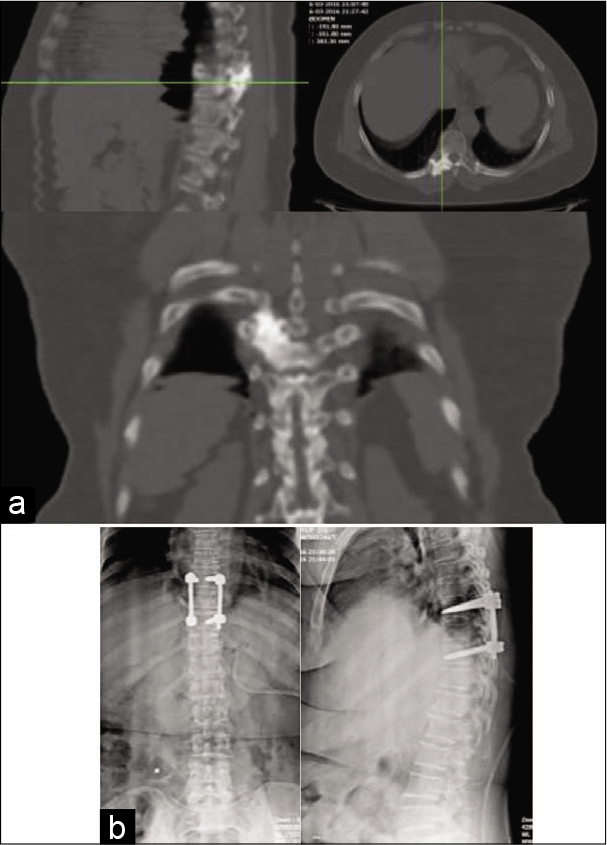
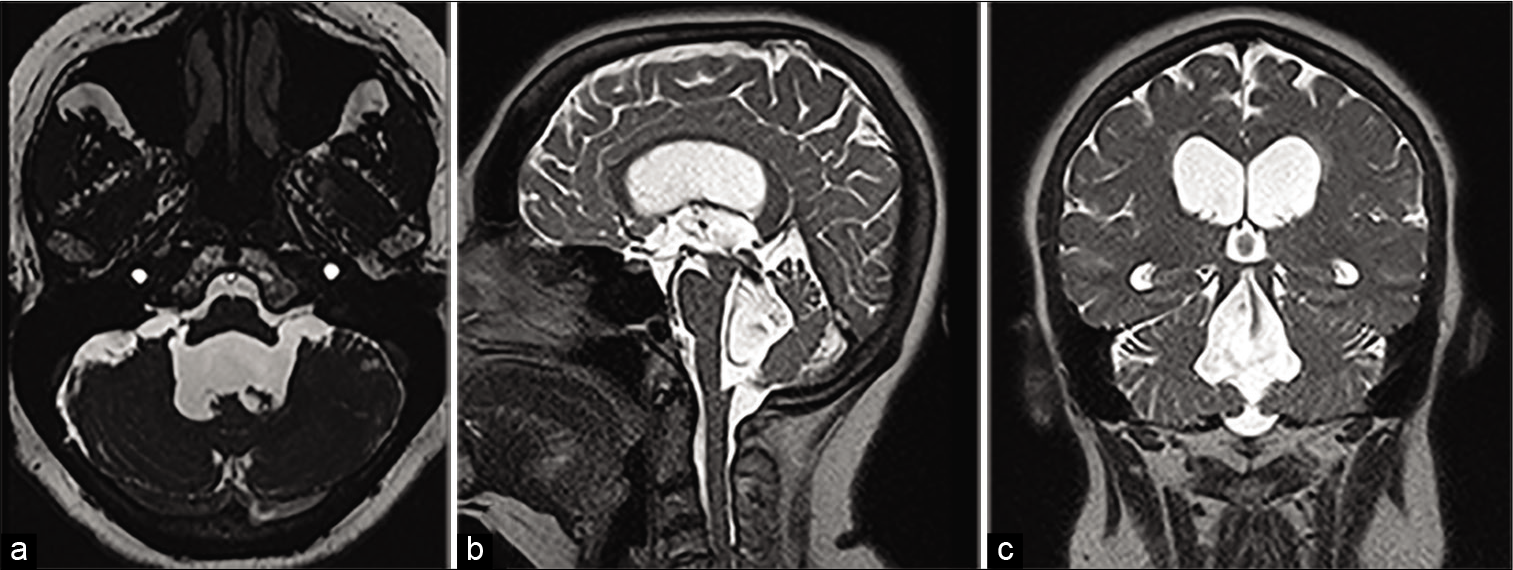
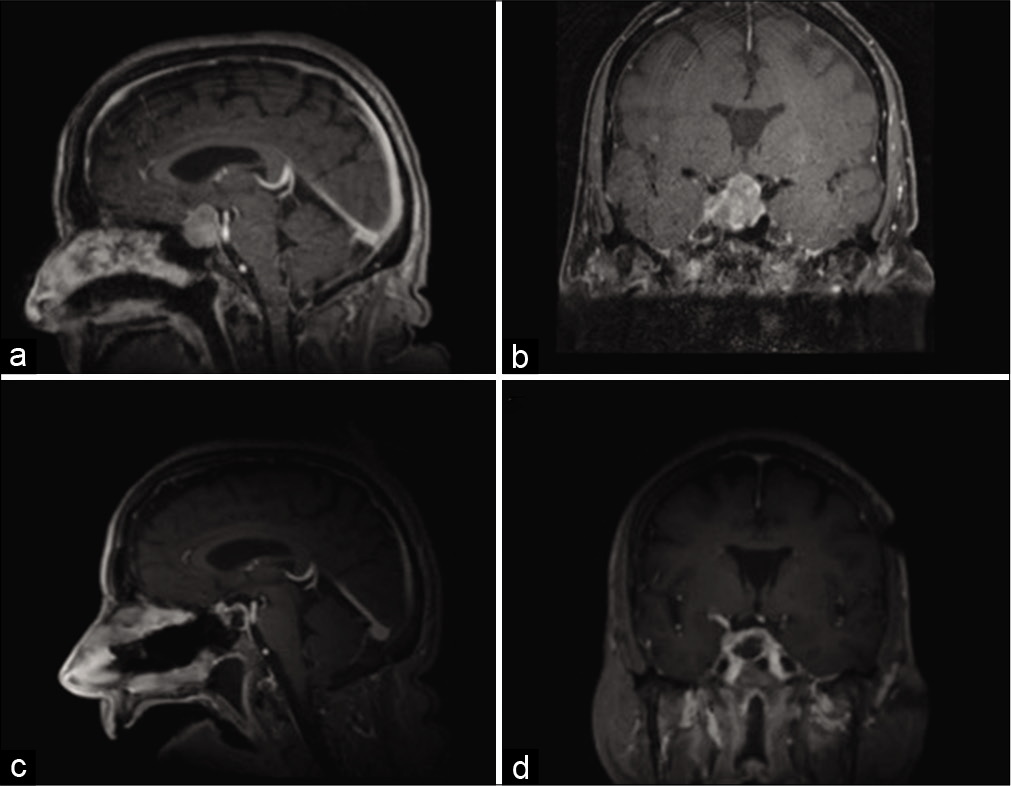
Bumpy head, unusual gliosarcoma metastasis
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic: A developing country perspective
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: Although primarily a respiratory disorder, the coronavirus pandemic has paralyzed almost all aspects of health-care delivery. Emergency procedures are likely continuing in most countries, however, some of them raises certain concerns to the surgeons such as the endoscopic endonasal skull base surgeries. The aim of this study is to present the current situation from a developing country perspective in dealing with such cases at the time of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Relationship of superior sagittal sinus with sagittal midline: A surgical application
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: Interhemispheric approach is widely used to surgical management of midline tumors and vascular lesion in and around the third ventricle. Complete exposure of the superior sagittal sinus to obtain adequate working space of midline lesion is difficult, because of the risk to inadvertent injury to the sinus and bridging veins, which may cause several neurological deficits. Understanding the SSS neuroanatomy and its relationships with external surgical landmarks avoid such complications. The objective of this study is to accurately describe the position of SSS and its displacement in relation with sagittal midline by magnetic resonance imaging.
Spinal osteoid osteoma: Surgical resection and review of literature
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: Osteoid osteoma (OO) is a rare benign tumor of the spine that involves the posterior elements with 75% tumors involving the neural arch. The common presenting symptoms include back pain, deformity like scoliosis, and rarely radiculopathy.
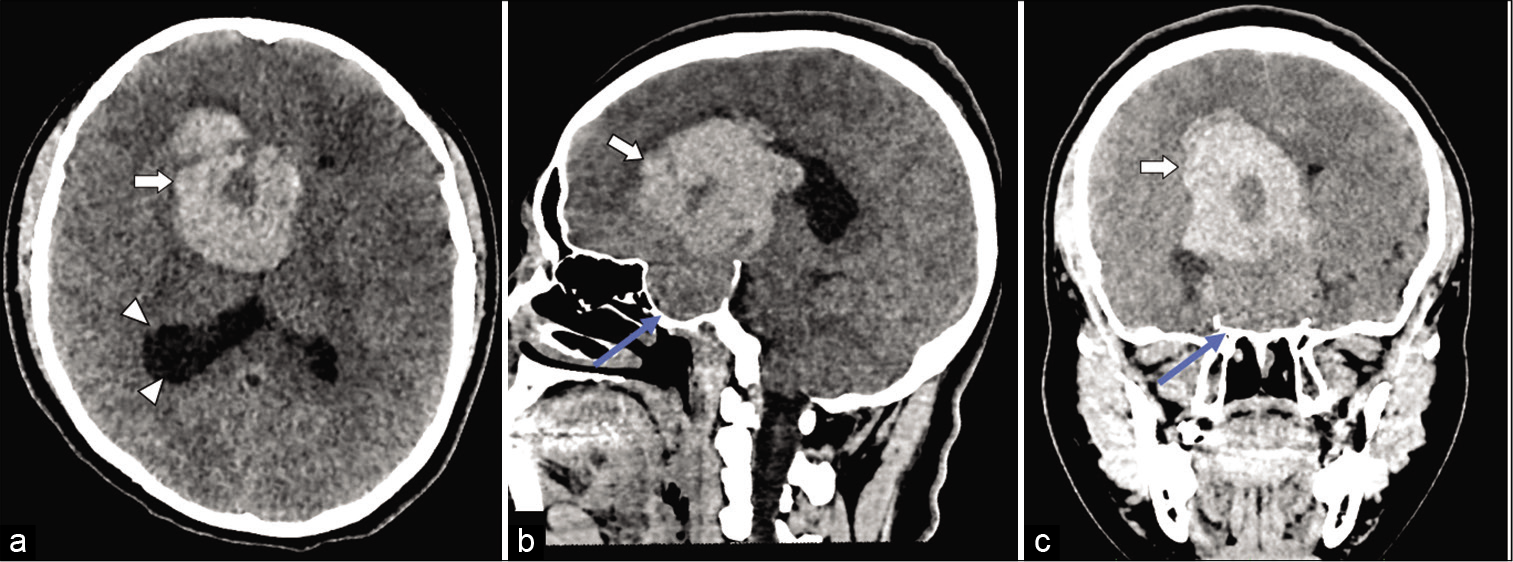
Bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most cited articles on the basilar artery
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: The basilar artery (BA) is one of the most critical vessels that supply blood to the brain stem, cerebellum, and parts of the cerebral hemispheres. Many studies on the BA from neurobiological, clinical, and experimental perspectives exist. This bibliometric study was aimed at identifying the most-cited articles related to the BA in different disciplines.
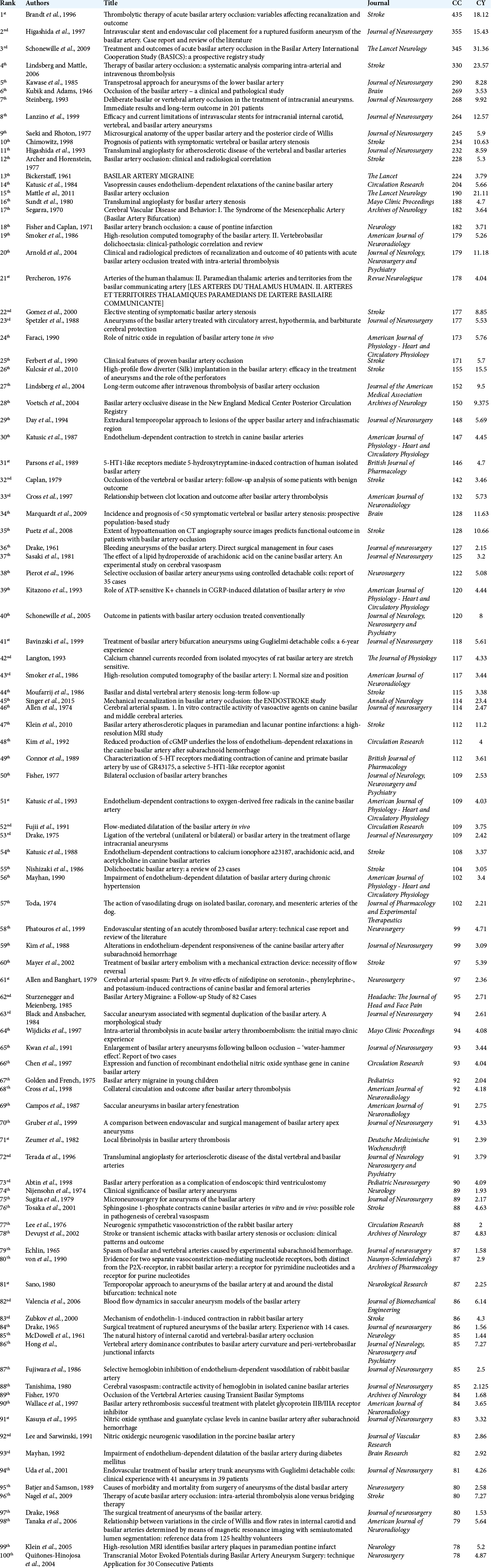
Spinal extradural arachnoid cyst: Rare cases from Indian Institutes
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: Spinal extradural arachnoid cyst (SEDAC), accounting for approximately 1% of all spinal lesions, rarely causes compressive myelopathy. It is usually found at lower thoracic or upper lumbar levels in males in their forties to sixties. The standard surgical procedures include direct dural repair.
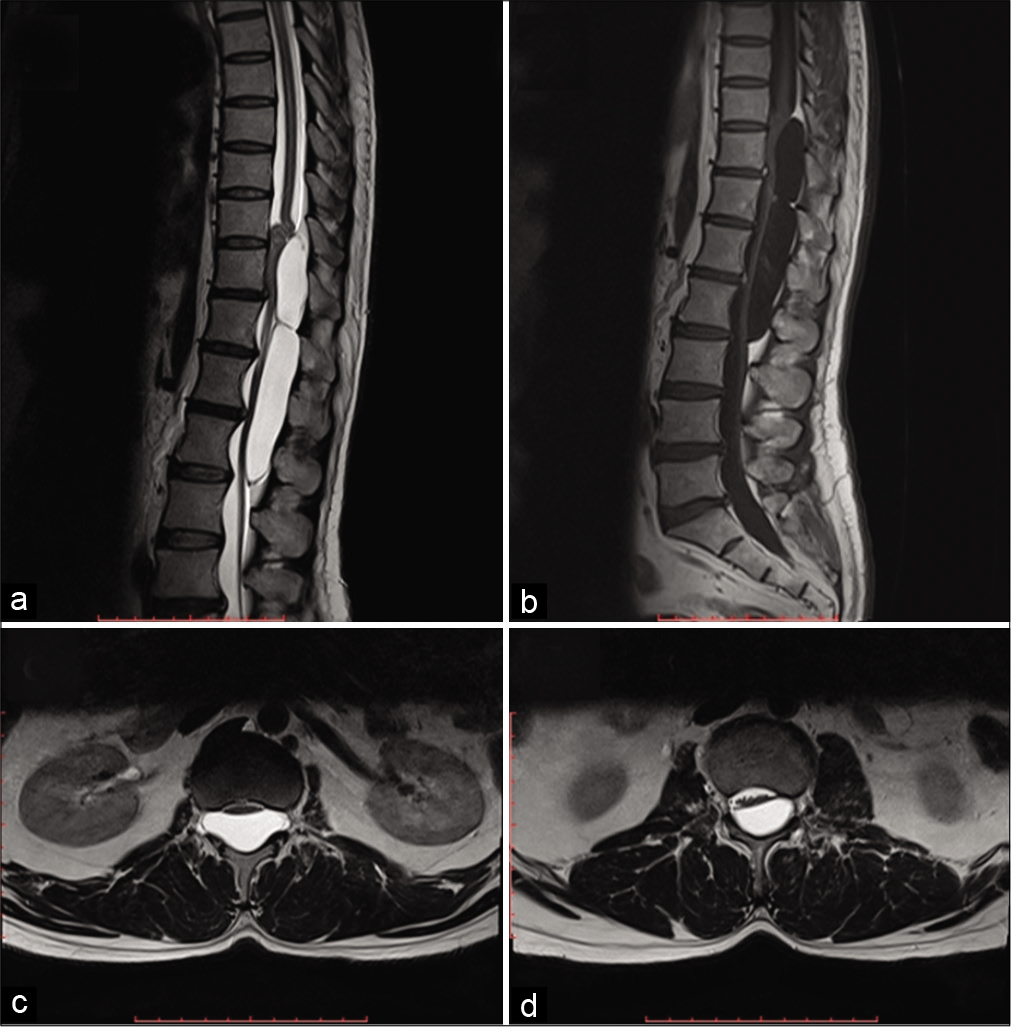
Idiopathic fourth ventricular outlet obstruction misdiagnosed as normal pressure hydrocephalus: A cautionary case
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: Fourth ventricular outlet obstruction is an infrequent but well-established cause of tetraventricular hydrocephalus characterized by marked dilatation of the ventricular system with ballooning of the foramina of Monro, Magendie, and Luschka. Multiple processes including inflammation, infection, hemorrhage, neoplasms, or congenital malformations are known to cause this pathological obstruction. However, true idiopathic fourth ventricular outlet obstruction is a rare phenomenon with only a limited number of cases reported in the literature.
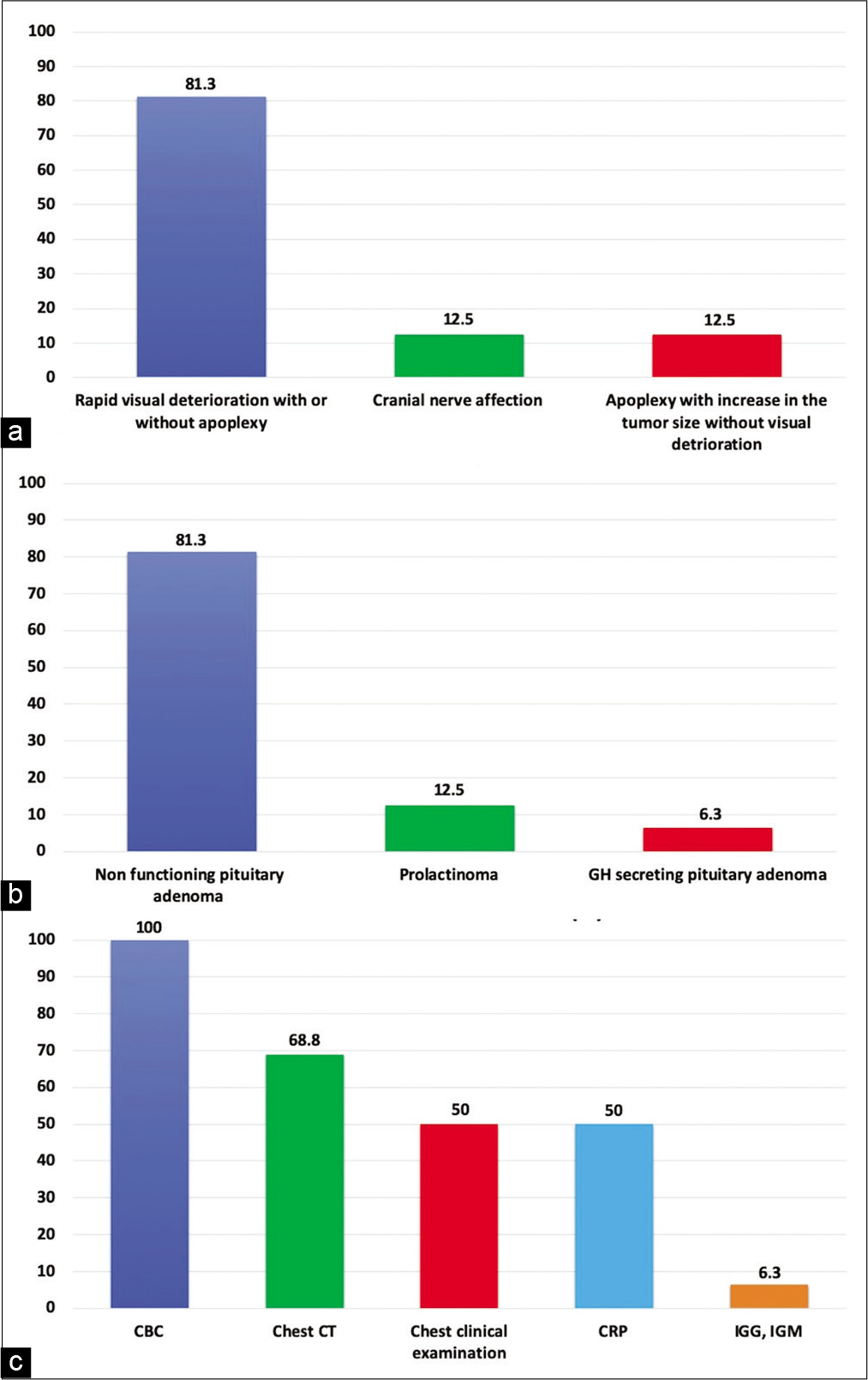
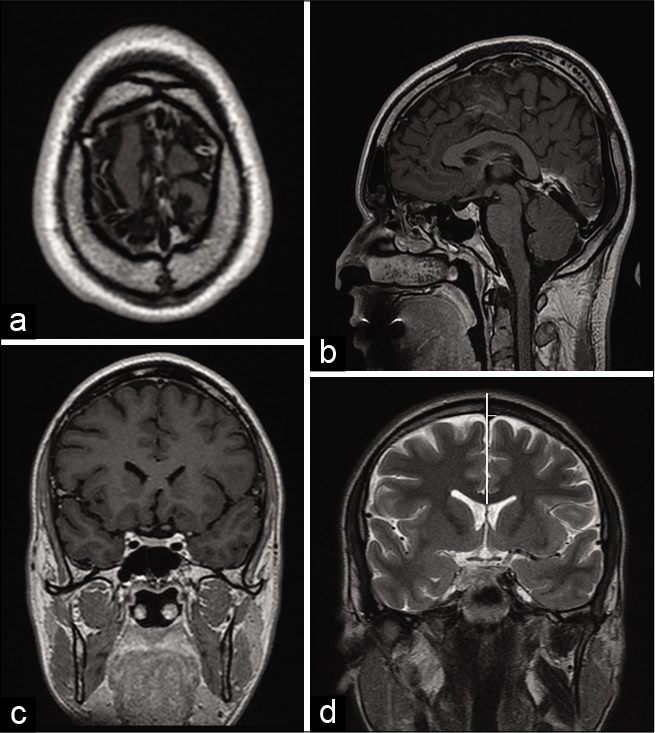
Pituitary macroadenoma apoplexy in a severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2-positive testing: Causal or casual?
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: In December 2019, in Wuhan, a new virus emerged, causing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) secondary to infection by a type of coronavirus, causing coronavirus disease (COVID-19). The pandemic caused by the new coronavirus has had implications in the central nervous system. COVID-19 is known to be characterized by coagulation activation and endothelial dysfunction, causing ischemic and hemorrhagic vascular syndromes.
Genetic characterization of a case of sellar metastasis from bronchial carcinoid neuroendocrine tumor
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: Metastasis to the pituitary gland from neuroendocrine tumors is a rare occurrence that may originate from primary tumors the lung, gastrointestinal tract, thyroid, and pancreas, among others. Patients may present with signs of endocrine dysfunction secondary to pituitary involvement, as well as mass effect-related symptoms including headaches and visual deficits. Despite a small but accumulating body of literature describing the clinical and histopathological correlates for pituitary metastases from neuroendocrine tumors, the genetic basis underlying this presentation remains poorly characterized.
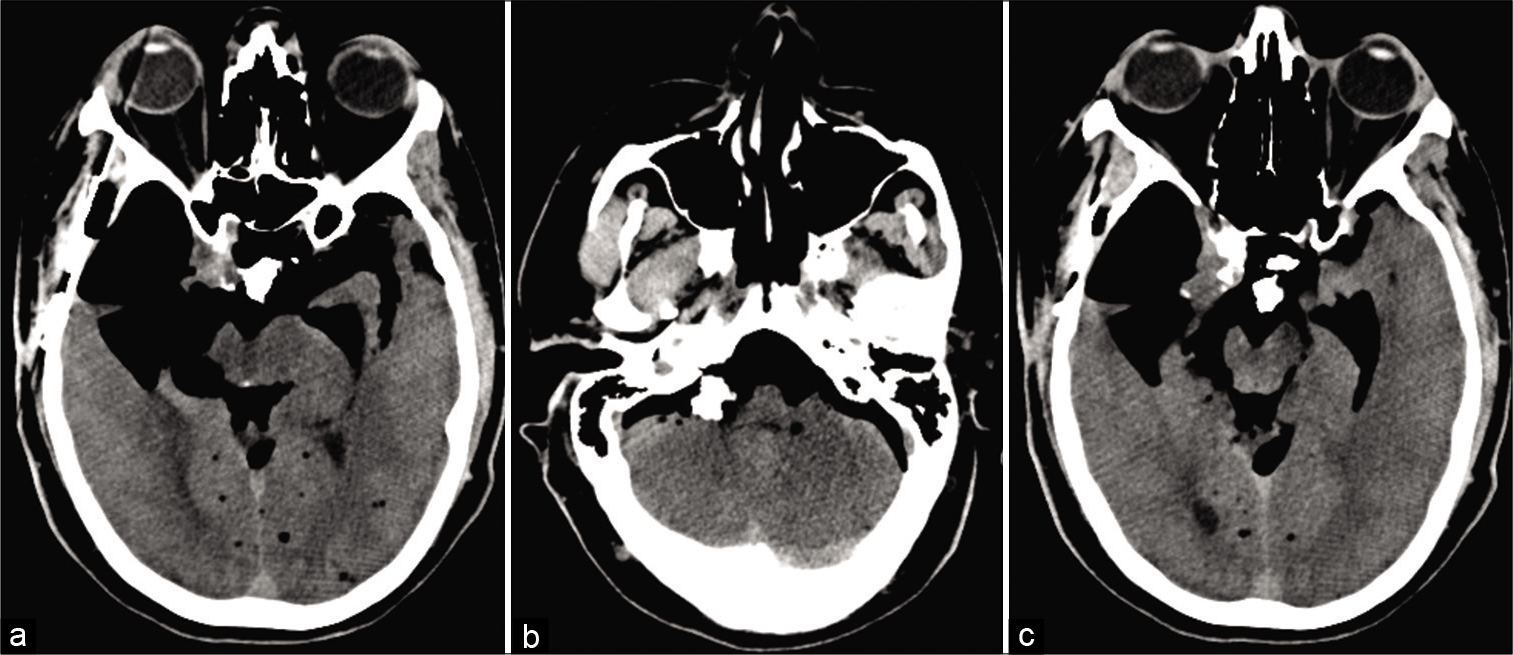
Pneumocephalus causing oculomotor nerve palsy: A case report
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: Pneumocephalus, the presence of gas or air within the intracranial cavity, is a common finding after cranial procedures, though patients often remain asymptomatic. Rare cases of cranial nerve palsies in patients with pneumocephalus have been previously reported. However, only two prior reports document direct unilateral compression of the third cranial nerve secondary to pneumocephalus, resulting in an isolated deficit.