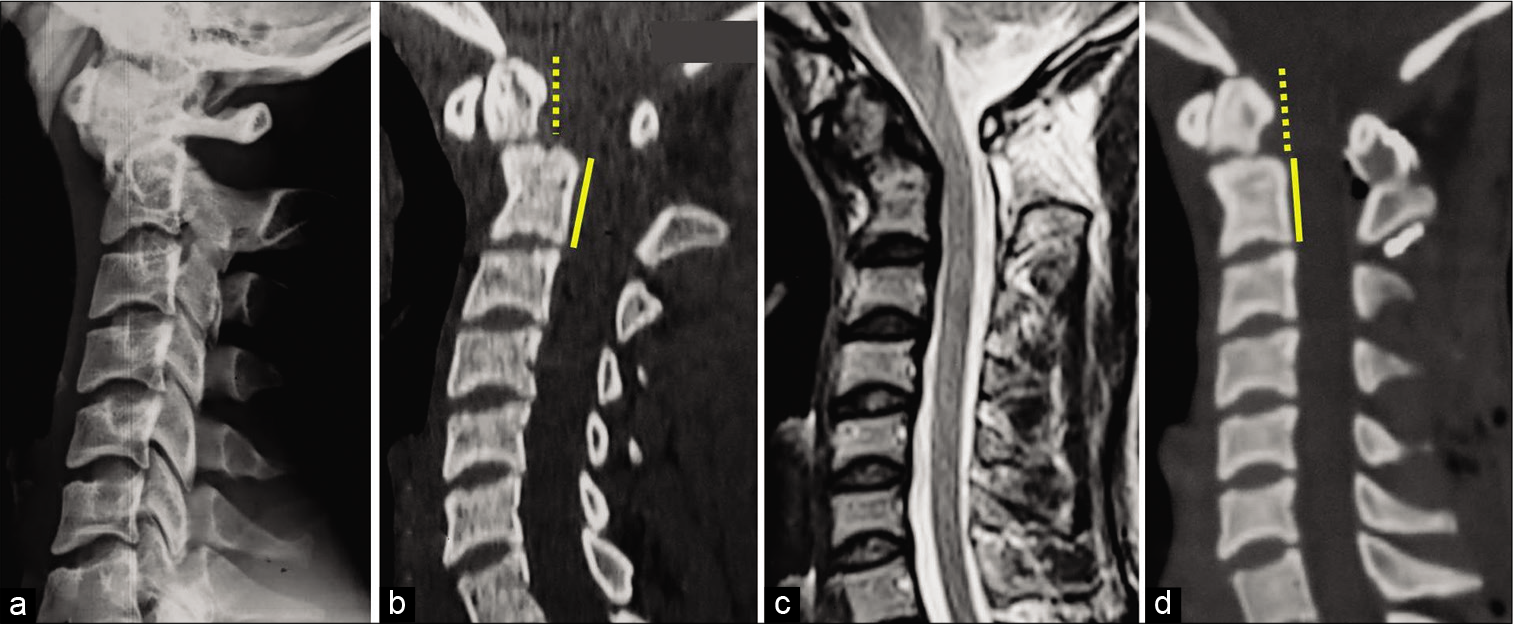
One-year follow-up for type II odontoid process fractures in octogenarians: Is there a place for surgical management?
Date of publication: 12-Sep-2020
Background: Type II odontoid fractures are becoming one of the most common injuries among elderly patients and are associated with increased morbidity rates. Here, we compared the safety/efficacy of conservative versus surgical treatment for type II C2 fractures and, in particular, evaluated the complications, hospital lengths of stay, and mortality rates for patients over 80 years of age.
Letter to the Editor: Transneural transmission in COVID-19 without a positive nasopharyngeal swab
Date of publication: 12-Sep-2020
Efficacy of translamina terminalis ventriculostomy tube in prevention of chronic hydrocephalus after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
Date of publication: 12-Sep-2020
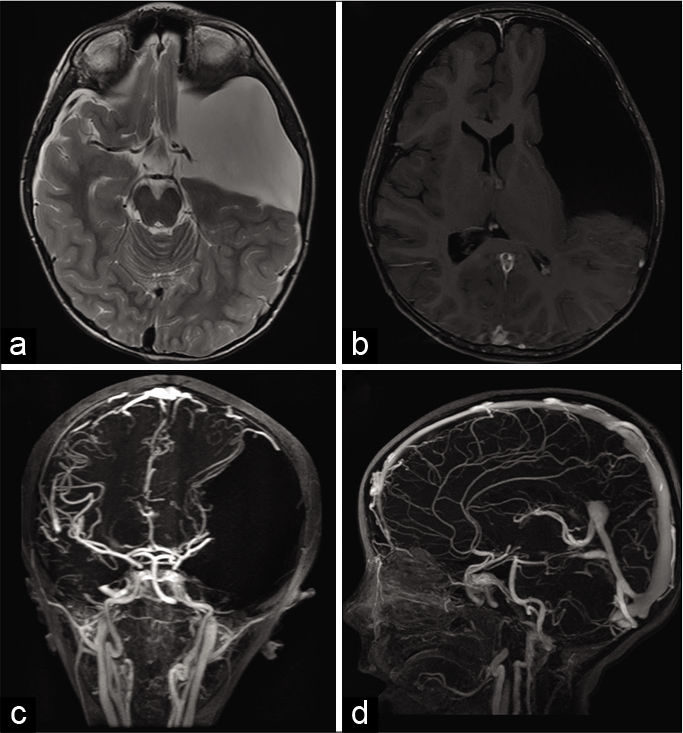
Background: Chronic shunt-dependent hydrocephalus is still a common complication after aneurysmal SAH (aSAH) and is associated with increased morbidity. Pathology of chronic shunt-dependent hydrocephalus after aSAH is complex and multifactorial which makes its prevention challenging. We thought to evaluate whether external ventricular drainage (EVD) through fenestrated lamina terminalis would decrease the rate of chronic shunt-dependent hydrocephalus after aSAH.
Spontaneous improvement of secondary empty sella syndrome due to re-expansion of an intrasellar cyst: A case report
Date of publication: 12-Sep-2020
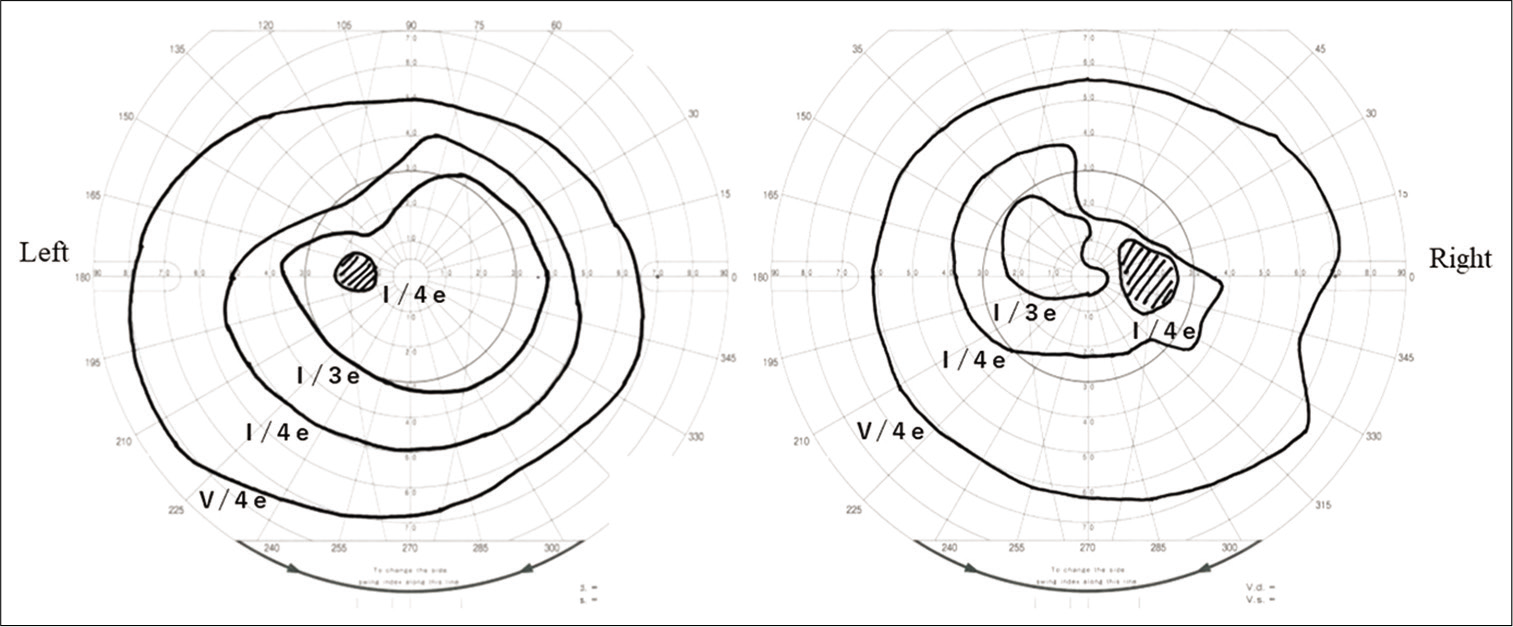
Background: In patients with secondary empty sella syndrome (ESS), optic nerve herniation into the sella turcica is caused by shrinkage of the mass lesion at the sella turcica, resulting in visual disturbance. ESS is often surgically treated using chiasmapexy. Here, we report the first case of spontaneous improvement in a patient with ESS.
Reproducibility of a new classification of the anterior clinoid process of the sphenoid bone
Date of publication: 12-Sep-2020
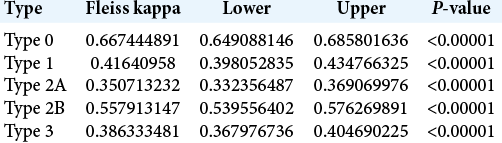
Background: Pneumatization of the anterior clinoid process (ACP) affects paraclinoid region surgery, this anatomical variation occurs in 6.6–27.7% of individuals, making its preoperative recognition essential given the need for correction based on the anatomy of the pneumatized process. This study was conducted to evaluate the reproducibility of an optic strut-based ACP pneumatization classification by presenting radiological examinations to a group of surgeons.
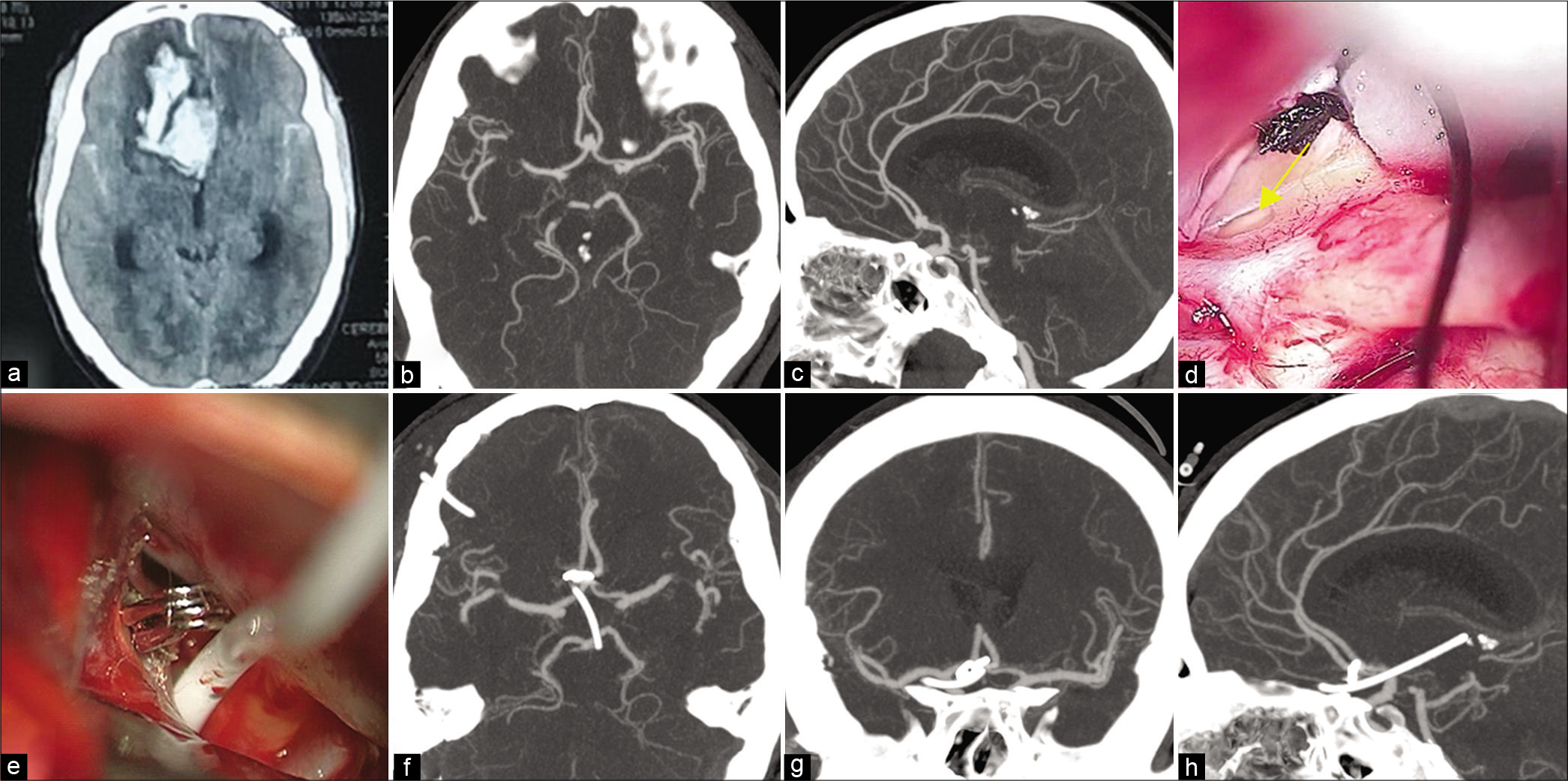
Coexisting arachnoid cyst and tentorial sinus: A therapeutic dilemma
Date of publication: 12-Sep-2020
Abstract
A 4-year-old male presented with a large arachnoid cyst over the left temporal region causing displacement of adjacent structures. Cerebral angiography showed dilatation of the tentorial sinus without other apparent vascular alterations. The association of these two anomalies raises a therapeutic dilemma as no information is available about how the variants of the venous system can modify cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics and thus affect arachnoid cyst’s prognosis. In this case, the patient was treated conservatively and has remained stable for 2 years.
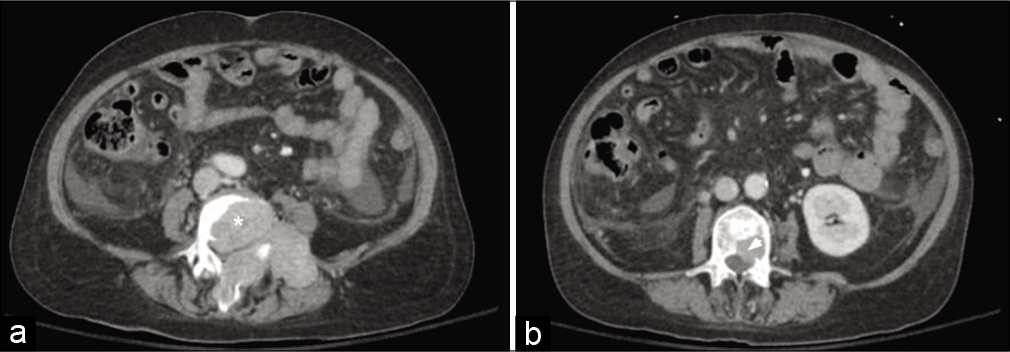
Metastatic epidural spinal column compression due to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma causing subacute Cauda equina syndrome: A case report
Date of publication: 05-Sep-2020
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common pancreatic malignancy, which rarely metastasizes to the spine.
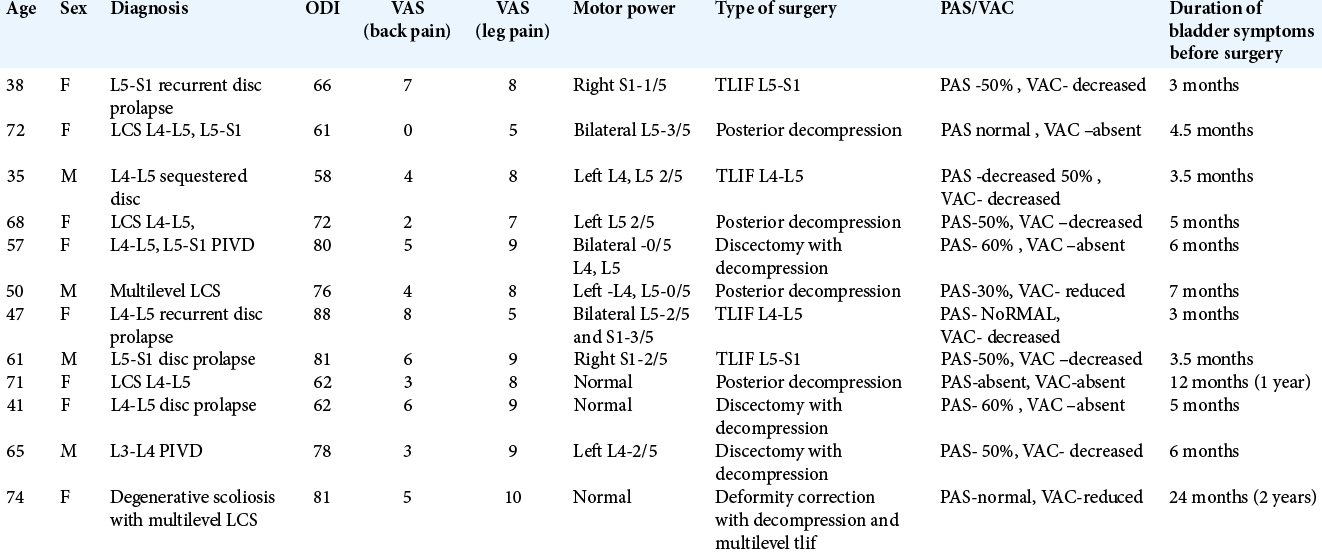
Does surgical decompression alleviate neglected cauda equina syndromes attributed to lumbar disc herniation and/or degenerative canal stenosis?
Date of publication: 05-Sep-2020
Background: Most studies recommend urgent decompression (e.g., within 48–72 h) of the symptomatic onset of a cauda equina syndrome. As patients in our area typically underwent >3 months delayed surgery for cauda equina syndromes due to disc disease/stenosis, we asked whether surgery was still worthwhile.
Unilateral blindness following superior laryngeal nerve block for awake tracheal intubation in a case of posterior cervical spine surgery
Date of publication: 05-Sep-2020
Background: Superior laryngeal nerve block (SUPLANEB) is a popular airway anesthesia technique utilized for successful awake endotracheal intubation in patients with significant cervical spine instability. If not performed by an expert, it carries the risk of general/neurologic complications that are typically minimal/transient. However, permanent blindness and/or upper cranial nerve neuropathies may occur. Here, we describe a case in which a young patient underwent an atlantoaxial fusion for a C2 nonunion (e.g., following a fracture) complicated by unilateral blindness due to a SUPLANEB.
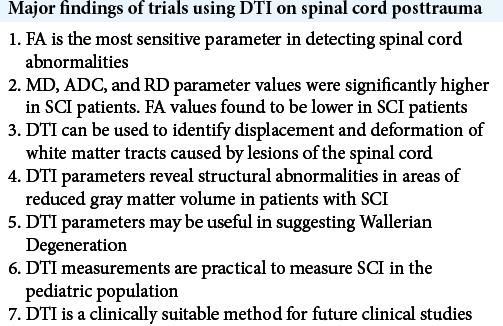
Diffusion tensor imaging of the spinal cord status post trauma
Date of publication: 05-Sep-2020
Background: Since its development in 1994, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has been successfully used to assess structural and functional changes to neurological tissue within the central nervous system. Namely, DTI is a noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based technique that uses anisotropic diffusion to visualize and estimate the organization of white matter in neuronal tissue. It has been used to study various spinal pathologies including neoplastic diseases, degenerative myelopathy, demyelinating diseases, and infections involving the spinal cord. However, due to technical uncertainties and experimental limitations, DTI has rarely been clinically applied to assess trauma-related spinal pathologies.